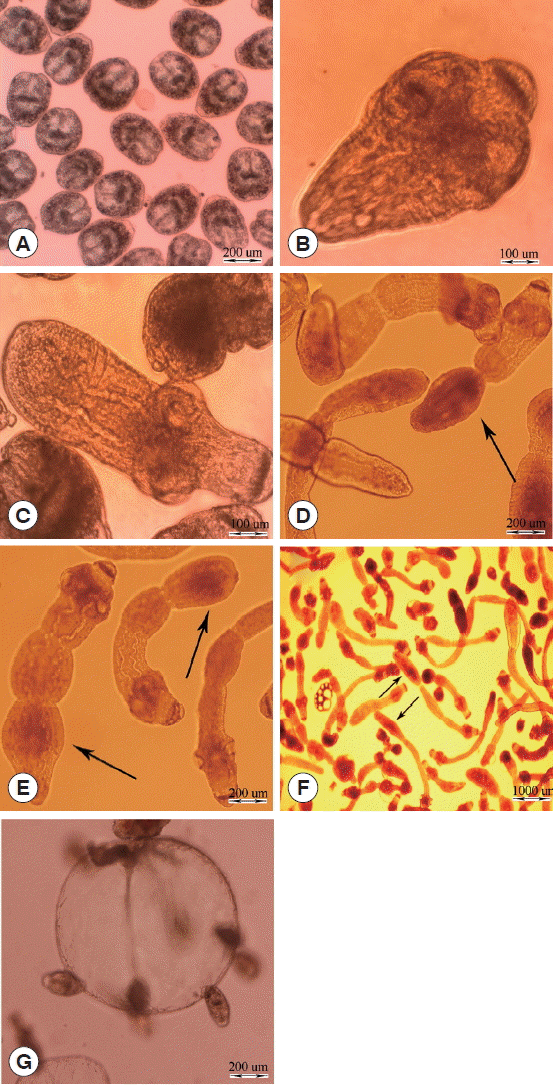
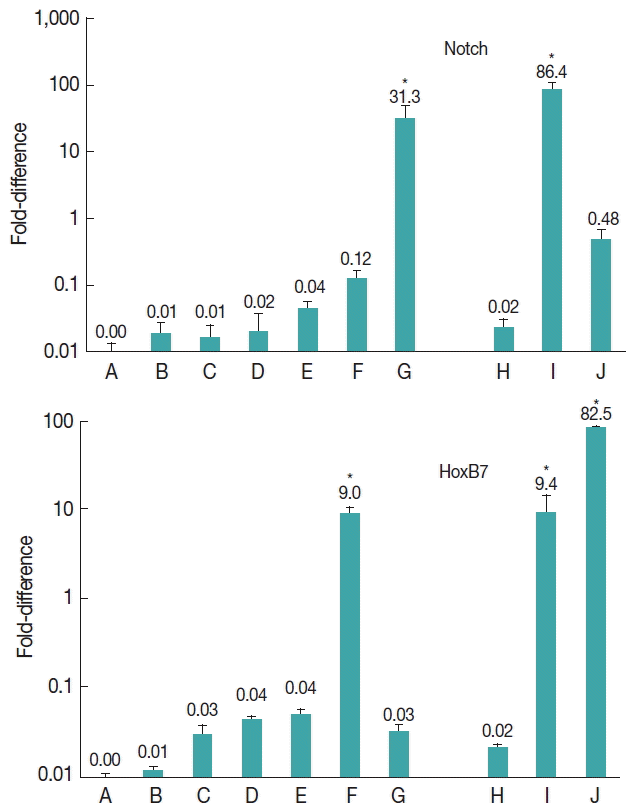
1. da Silva AM. Human echinococcosis: a neglected disease.
Gastroenterol Res Pract 2010;2010:1-9.

2. Moro P, Schantz PM. Echinococcosis: a review.
Int J Infect Dis 2009;13:125-133.


3. Smyth JD, Miller HJ, Howkins AB. Further analysis of the factors controlling strobilization, differentiation, and maturation of
Echinococcus granulosus in vitro.
Exp Parasitol 1967;21:31-41.


4. Smyth JD. Studies on tapeworm physiology.
Parasitology 1962;52:441-457.

5. Smyth JD, Howkins AB, Barton M. Factors controlling the differentiation of the hydatid organism,
Echinococcus granulosus, into cystic or strobilar stages
in vitro.
Nature 1966;211:1374-1377.


6. Zheng H, Zhang W, Zhang L, Zhang Z, Li J, Lu G, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Huang Y, Liu J, Kang H, Chen J, Wang L, Chen A, Yu Sh, Gao Z, Jin L, Gu W, Wang Z, Zhao L, Shi B, Wen H, Lin R, Jones KM, Brejova B, Vinar T, Zhao G, McManus DP, Chen Z, Zhou Y, Wang S. The genome of the hydatid tapeworm
Echinococcus granulosus.
Nat Genet 2013;45:1168-1175.


7. Thompson RC, Jenkins DJ.
Echinococcus as a model system: biology and epidemiology.
Int J Parasitol 2014;44:865-877.


8. Monteiro KM, de Carvalho MO, Zaha A, Ferreira HB. Proteomic analysis of the
Echinococcus granulosus metacestode during infection of its intermediate host.
Proteomics 2010;10:1985-1999.


9. Lappin TRJ, Grier DG, Thompson A, Halliday HL. HOX genes: seductive science, mysterious mechanisms.
Ulster Med J 2006;75:23-31.

10. Ladam F, Sagerström CG. Hox regulation of transcription: more complex(es).
Dev Dyn 2014;243:4-15.


11. Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Matsuno K, Fortini M.
Notch signaling.
Science 1995;268:225-232.


12. Priess JR. Notch signaling in the C. elegans embryo. WormBook: The Online Review of C. elegans Biology 2005;1-16.
13. Brehm K, Spiliotis M. Recent advances in the
in vitro cultivation and genetic manipulation of
Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes and germinal cells.
Exp Parasitol 2008;119:506-515.


14. Smyth JD. Development of monozoic forms of
Echinococcus granulosus during
in vitro culture.
Int J Parasitol 1971;1:121-124.


15. Hajialilo E, Harandi MF, Sharbatkhori M, Mirhendi H, Rostami S. Genetic characterization of
Echinococcus granulosus in camels, cattle and sheep from the south-east of Iran indicates the presence of the G3 genotype.
J Helminthol 2012;86:263-270.


16. Smyth JD, Davies Z.
In vitro culture of the strobilar stage of
Echinococcus granulosus (sheep strain): a review of basic problems and results.
Int J Parasitol 1974;4:631-644.


17. Smyth JD, Howkins AB. An
in vitro technique for the production of eggs of
Echinococcus granulosus by maturation of partly developed strobila.
Parasitology 1966;56:763-766.


18. Hemphill A, Stettler M, Walker M, Siles-Lucas M, Fink R, Gottstein B. Culture of
Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes: an alternative to animal use.
Trends Parasitol 2002;18:445-451.


19. Rossi A, Marqués JM, Gavidia CM, Gonzalez AE, García HH, Chabalgoity JA. Echinococcus granulosus: different cytokine profiles are induced by single versus multiple experimental infections in dogs. Exp. Parasitol 2012;130:110-115.
20. Jenkins DJ, Fraser A, Bradshaw H, Craig PS. Detection of
Echinococcus granulosus coproantigens in Australian canids with natural or experimental infection.
J Parasitol 2000;86:140-145.


21. Espínola SM, Ferreira HB, Zaha A. Validation of suitable reference genes for expression normalization in
Echinococcus spp. larval stages.
PLoS One 2014;9:e102228.



22. Liao WT, Jiang D, Yuan J, Cui YM, Shi XW, Chen CM, Biam XW, Deng YJ, Ding YQ.
HOXB7 as a prognostic factor and mediator of colorectal cancer progression.
Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:3569-3578.


23. Ishii M, Mitsunaga-Nakatsubo K, Kitajima T, Kusunoki S, Shimada H, Akasaka K. Hbox1 and Hbox7 are involved in pattern formation in sea urchin embryos.
Dev Growth Differ 1999;41:241-252.


24. Carè A, Valtieri M, Mattia G, Meccia E, Masella B, Luchetti L, Felicetti F, Colombo MP, Peschle C. Enforced expression of
HOXB7 promotes hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and myeloid-restricted progenitor differentiation.
Oncogene 1999;18:1993-2001.


25. Lewis EB. A gene complex controlling segmentation in
Drosophila.
Nature 1978;276:565-570.


26. Wellik DM. Hox genes and vertebrate axial pattern.
Curr Top Dev Biol 2009;88:257-278.


27. Kim KH, Lee YS, Jeon HK, Park JK, Kim CB, Eom KS. Hox genes from the tapeworm
Taenia asiatica (Platyhelminthes: Cestoda).
Biochem Genet 2007;45:335-343.


28. Sánchez Alvarado A, Newmark PA, Robb SM, Juste R. The
Schmidtea mediterranea database as a molecular resource for studying platyhelminthes, stem cells and regeneration.
Development 2002;129:5659-5665.


29. Olson PD. Hox genes and the parasitic flatworms: new opportunities, challenges and lessons from the free-living.
Parasitol Int 2008;57:8-17.


30. Koziol U, Lalanne AI, Castillo E. Hox genes in the parasitic platyhelminthes
Mesocestoides corti, Echinococcus multilocularis, and
Schistosoma mansoni: evidence for a reduced Hox complement.
Biochem Genet 2009;47:100-116.


31. Roma J, Almazán-Moga A, Sánchez de Toledo J, Gallego S.
Notch, wnt, and hedgehog pathways in rhabdomyosarcoma: from single pathways to an integrated network.
Sarcoma 2012;2012:695603.



32. Liu J, Sato C, Cerletti M, Wagers A.
Notch signaling in the regulation of stem cell self-renewal and differentiation.
Curr Top Dev Biol 2010;92:367-409.


33. Deng WM, Althauser C, Ruohola-Baker H. Notch-Delta signaling induces a transition from mitotic cell cycle to endocycle in
Drosophila follicle cells.
Development 2001;128:4737-4746.