Members of the family Echinostomatidae are zoonotic flukes, which infect birds and mammals including humans. Human infections by the echinostomatid flukes, i.e. Echinostoma hortense, E. cinetorchis, Echinochasmus japonicus, and Acanthoparyphium tyosenense, have been reported in Korea (Seo et al., 1983; Ryang et al., 1986; Ahn and Ryang, 1986). Of the four species, E. hortense is the most frequently reported to be a causative fluke (Chai and Lee, 2002). Endemic foci of E. hortense have been previously reported in Umsong-gun, Chungchongbuk-do (We, 1987) and Chongsong-gun, Kyongsangbuk-do (Lee et al., 1988).
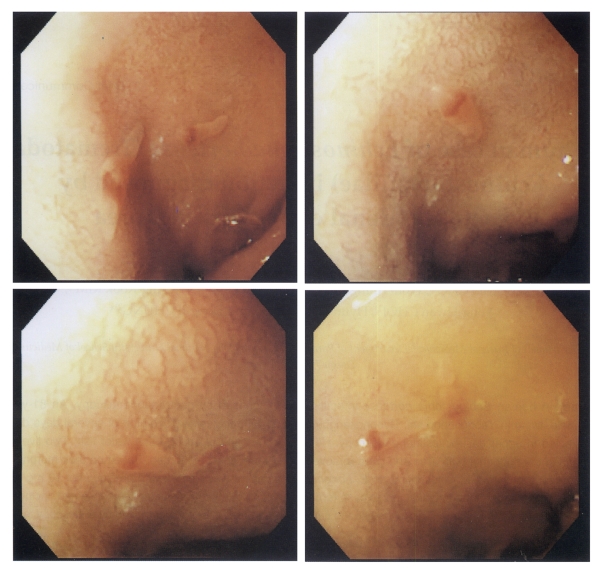
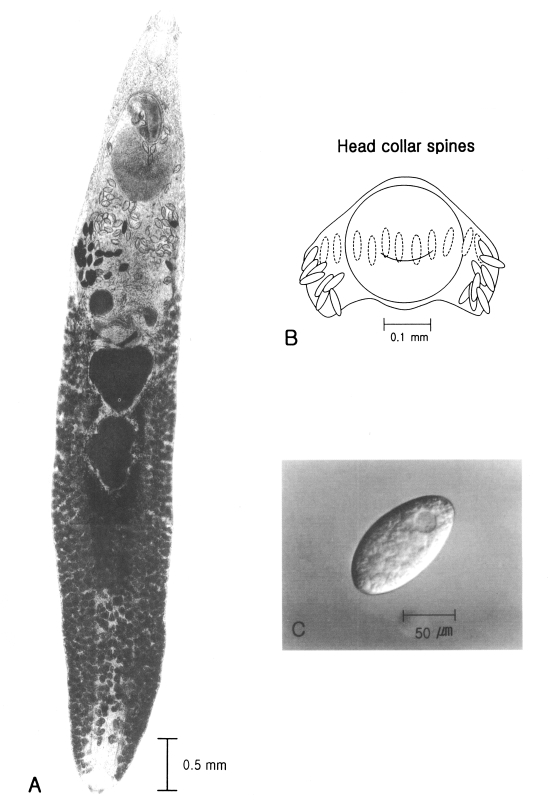
An 81-year-old Korean male, living in Yeongcheon-shi, Gyeongsangbuk-do, was admitted to the outpatient's department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital. The patient complained of epigastric discomfort of several days duration. No significant abnormality was detected by laboratory findings. He was in the habit of eating raw fresh water fish. Gastroduodenal endoscopy revealed two live worms in the duodenal bulb area; the mucosa of which showed mild erosion (Fig. 1). The worms were picked out with an endoscopic biopsy forcep and transported to the Department of Parasitology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, where they were fixed in 70% ethanol and stained with Semichon's acetocarmine. They were very slender (7.92 × 1.33 mm), and had a characteristic head crown equipped with 27 collar spines around the subterminal oral sucker (Fig. 2A and B). The ventral sucker (0.68 × 0.77 mm) was positioned at the anterior 1/3 of the body and was much larger than the oral sucker (0.25 × 0.26 mm). The uterus was distended and contained thin-shelled elliptical eggs. A spontaneously discharged egg (124.3 × 68.6 µm) had an operculum at the narrower end and a well-defined germ ball (Fig. 2C). Two testes were distinct, slightly lobulated, and located in tandem at the equatorial portion. The worms were identified as E. hortense by morphological characteristics and measurements.
The symptoms of echinostomiasis vary from none to abdominal pain, although a case in Korea showed duodenal ulceration (Chai et al., 1994). Because of high incidence of stomach cancer and ulcer in Korea, many senior citizens with gastrointestinal symptoms are subjected to endoscopic examinations. Echinostoma hortense can be easily demonstrated by gastroduodenoscopy due to its habitat in the upper small intestine and its relatively large size. The present case is the second Korean case of E. hortense infection, which was diagnosed by gastroduodenoscopy (Chai et al., 1994). Four cases diagnosed by endoscopy have been reported in Japan (Hamamoto et al., 1997).
The source of the infection in this case is unclear. Many senior residents of inland areas of Gyeongsangbuk-do eat raw fresh water fish, including loaches, a known source of human infection. An epizootiological survey in the Yeongcheon area should be performed to determine the sources of human infection. The residence of this patient was Yeongcheon-shi neighboring Cheongsong-gun, which has been reported to be one of the endemic foci of E. hortense. Yeongcheon-shi and Cheongsong-gun are inlands of Gyeongsangbuk-do and contain upper reaches of the Nakdong-gang (river). The geographic characteristics of both localities coincide well with the indications of Chai and Lee (2002), namely, that E. hortense is distributed inland along the upper reaches of large rivers. Therefore, to confirm Yeongcheon-shi as an endemic area of E. hortense, an epidemiological survey of this fluke should be undertaken.