Abstract
A survey of mosquitoes, including the vector status of Brugia malayi filariasis and their relative larval density, was conducted from 2002 to 2005 at several southern remote islands of Jeollanam-do (province), Gyeongsangnam-do, and Jeju-do, Korea, where filariasis was previously endemic. Overall, a total of 9 species belonging to 7 genera were collected. Ochlerotatus togoi (formerly known as Aedes togoi), Anopheles (Hyrcanus) group, and Culex pipiens were the predominant species captured at all areas. Oc. togoi larvae were most frequently collected at salinity levels <0.5% during June and July, with densities decreasing sharply during the rainy season in August. The most likely explanation for the eradication of filariasis in these areas is suggested to be an aggressive treatment program executed during the 1970s and the 1990s. However, high prevalence of the vector mosquitoes may constitute a potential risk for reemerging of brugian filariasis in these areas.
-
Key words: Ochlerotatus togoi (=Aedes togoi), Anopheles (Hyrcanus) group, vector, brugian filariasis, southern islands
INTRODUCTION
The identification of vector species and their relative population densities is important for a better understanding of the transmission of zoonotic and human pathogens and the epidemiology of emerging and reemerging diseases. In the Republic of Korea, lymphatic filariasis was prevalent in the inland areas of Gyeongsangbuk-do (do=province) and coastal and southern areas of Jeollanam-do and Jeju-do. However, the prevalence of filariasis has decreased sharply due to medical treatments of microfilaria-positive patients and increased use of mosquito nets [
1-
5]. The islands of Heuksan, Sinan-gun (county), Jeollanam-do, were identified as endemic foci of fila-riasis in the mid-1980s (mean microfilaria positive rate: 12.5%). However, the positive rate in endemic regions dropped to 0%, and it was finally reported that filariasis had been eradicated from Korea [
6].
Ochlerotatus togoi (formerly known as
Aedes togoi) is the primary vector of lymphatic filariasis along the coastal areas of Jeju-do and other southern islands, whereas
Anopheles sinensis sensu stricto, associated with rice paddies, is found in inland areas [
3,
7]. In these regions, however, vector mosquitoes and their larval densities have not been fully studied. There is also little information on their distribution and relative population densities of filariasis vectors and other mosquitoes in previous endemic areas. In the present study, mosquito surveillance was conducted to identify relative distributions and population den-sities of filariasis vectors in previous endemic areas in Korea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Survey areas
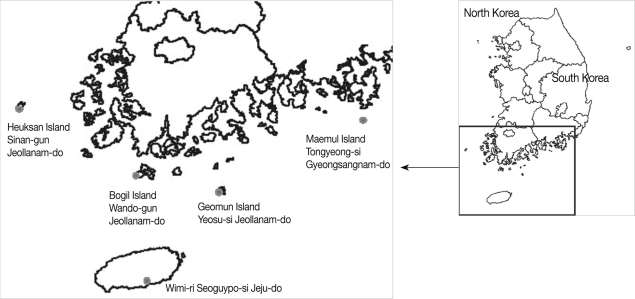
The southern islands of Jeollanam-do (Sa-ri [ri=village] and Sim-ri, Heuksan Islands in Sinan-gun, 2002; Baekdo-ri, Bogil Island in Wando-gun, 2003; Geomun-ri, Geomun Island in Yeosu-si [si=district], 2004), Gyeongsangnam-do (Maejuk-ri, Maemul Island in Tongyoung-si, 2004), and Jeju-do (Island) (Wimi-ri, Seoguipo-si, 2005) were surveyed (
Fig. 1).
Adult mosquitoes were collected twice weekly using the commercial Black Hole® mosquito black light trap (Model: Black Hole, Bio-trap Inc., Seoul, Korea). The traps were placed under the eaves of houses from 19:00 to 06:00 hr the following morning. All mosquitoes were identified to the genus or species level under a dissecting microscope using standard morphological keys [
8,
9].
The meshed sinking quadrat method [
3,
7] was used to estimate the relative larval density of
Oc. togoi. Briefly, 5 quadrats (size: 100 cm
2) were placed in each rock pool for 5 min and then removed simultaneously. Salinity was measured at the surface with a salinometer (SINAR NS-3P, Merbabu Trading Co., LTD, Tokyo, Japan). Larvae in each quadrat were counted, number recorded, and then identified under a dissecting microscope using standard morphological keys [
8,
9].
RESULTS
Sa-ri and Sim-ri, Heuksan Island, Sinan-gun
There were a mean of 347.0 mosquitoes collected from each trap at Sa-ri village on Heuksan Island (
Table 1). Among the 4 genera and 5 species collected,
Culex pipiens (45.8%) was the most frequently collected, followed by
Oc. togoi (41.2%),
An. (
Hyrcanus) Group (6.3%),
Culex tritaeniorhynchus (5.8%), and
Armigeres subalbatus (0.9%). The number of
Oc. togoi peaked in August, then decreased markedly thereafter. There were a trap mean of 359.0 mosquitoes from 5 genera and 7 species collected from Sim-ri (
Table 2). The collection rates were as follows:
Cx. pipiens, 56.3%;
Oc. togoi, 31.2%;
Cx. tritaeniorhynchus, 8.9%;
An. (
Hyrcanus) Group, 1.7%;
Ar. subalbatus, 1.4%;
Culex bitaeniorhynchus, 0.3%; and
Tripteroides bambusa, 0.3%. The density of mosquitoes and their seasonal prevalence were similar to those of Sa-ri on Heuksan Island.
A trap mean of 876.0 mosquitoes, comprising 4 genera and 8 species were collected from Baekdo-ri on Bogil Island (
Table 3).
Oc. togoi (41.2%), a vector of filariasis in shoreline areas, was the most frequently collected, followed by
An. (
Hyrcanus) group (26.5%),
Cx. tritaeniohynchus (16.6%),
Cx. pipiens (7.8%),
Ar. subalbatus (7.6%),
Aedes dorsalis (0.2%),
Aedes albopictus (0.1%), and
Cx. bitaeniorhynchus (0.1%).
O. togoi increased sharply during the rainy season from June through July, followed by a marked decline in numbers through October. The number of
An. (
Hyrcanus) group was very low in June, which rapidly increased in July and August, and decreased in October.
A trap mean of 56.2 mosquitoes belonging to 3 genera and 5 species were collected (
Table 4). While
Oc. togoi comprised of 85.4% of all mosquitoes, relatively low numbers of other mosquitoes were collected.
A total of 98.7 mosquitoes belong to 3 genera and 4 species were collected (
Table 5).
Oc. togoi comprised of 98.6% with the highest numbers collected from May to July (range 17.9-25.8) and October (15.7).
A total of 76 mosquitoes belong to 3 genera and 4 species were collected (
Table 6).
Cu. pipiens (53.9%) comprised the largest proportion of all mosquitoes, followed by
Oc. togoi (40.1%),
Cx. tritaeniohynchus (5.3%), and
An. (
Hyrcanus) group (0.7%).
The
Oc. togoi larval population was investigated at Geomun-ri and Maejuk-ri from rock pools using a meshed sinking quadrat from March through October (
Tables 7-
9), and Wimi-ri on Namwon-eup in Seoguypo-si from April though July (
Table 10). The number of larvae for each quadrat at Geomun-ri was 65.3 in March, peaked in June (93.5), and then gradually declined. While 3rd and 4th instars comprised the greatest proportion during the entire period at Geomun-ri, 1st and 2nd instars comprised the greatest proportion collected at Maejuk-ri (
Table 10). The salinity of the rock pools varied from 0.2% to 4.1% at both sites (
Tables 7,
8), while most of the larvae (68.6% and 78.1%) were collected in water with <0.5% salinity (
Table 10).
At Maejuk-ri, the number of mosquitoes in each quadrat was 24.9 in March, peaked in June (72.9), and decreased gradually after August (
Table 8).
At Wimi-ri, the number of Oc. togoi (14.7) was the highest in April. Unlike the previous 2 sites, larvae were comprised mostly of 1st and 2nd instars (70.7%). The sampling schedule was disrupted at times due to frequent periods of drought, which resulted in some of the rock pools drying.
DISCUSSION
Oc. togoi and
Cx. pipiens were the most frequently collected mosquitoes captured by black-light traps in southern islands of Korea during this survey.
An. (
Hyrcanus) group was collected at high densities only in the Baekdo-ri village, suggesting that it is a potential important vector of filariasis in this area. The mosquito population on Geomun-ri was the highest during the early rainy season and peaked a month earlier than the population on Maejuk-ri, due presumably to differences in climate (e.g., temperature and rainfall) between the 2 areas. However, both areas had a lower population after July because of frequent typhoons during the summer season (data not shown). The larval densities were the highest in June, when the average rainfall and temperature in these areas were 195-210 mm (data not shown) and 20-27℃ (
Tables 7,
8), respectively. The appearance of
Oc. togoi larvae coincided with decreases in the salinity of rock pools due to frequent rains (
Table 10). Thus, lower salinity during this period may be a reason for increased population densities as observed in previous reports [
10,
11]. Larval
Oc. togoi densities decreased during the drier summer due to strong direct sunlight and high water temperature [
12]. In a previous study, increase in salinity played a role in reducing the susceptibility of
Oc. togoi larvae [
4,
13]. The presence of <0.5% salt concentrations during the summer and the rainfall amount influenced the number of larval survival [
7,
14].
The number of
Oc. togoi collected in our study was greater than a previous survey collection by Lee et al. [
15] at the same location on Heuksan Island. This difference may have been due to differences in collection methods between the CDC miniature type (American Biophysics Co., East Greenwich, Rhode Island, USA) used in the Lee et al. study [
15] and black-light traps used in our study. However, the proportion of
Oc. togoi in the collected mosquitoes in this study was also lower than that reported by Kim et al. [
1] and Lee [
16]. These previous studies reported that collection of
Oc. togoi and
Cx. pipiens ranged 70-90% and 5-26%, respectively, in Jeju-do.
As both vector species are present in Korea, the most likely explanation for the eradication of filariasis is suggested to be an aggressive treatment program executed during the 1970s and 1990s [
2,
3,
17,
18], with the consequent benefit that there were fewer vector mosquitoes that have contracted the disease from human carriers. Furthermore, transmission of mosquito-borne diseases has been greatly reduced by the ommercialization of mosquito repellents and insecticides, as well as the use of bed nets and screened windows, all of which decrease human-vector contact [
19]. However, a steadily high prevalence of the vector mosquitoes may constitute a potential risk for reemergence of brugian filariasis in these areas.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank our colleagues at the Province and City Bureau of Health Center and the Research Institute of Health and Environment for their devoted support and efforts. This work was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Health (NIH-091-4800-4845-300), National Research and Development Program, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea.
References
- 1. Kim JS, Lee WY, Chun SL. Ecology of filariasis on Cheju Island. Korean J Parasitol 1973;11:33-53.
- 2. Lee OY, Lee JS, Yong TS, Kim TS, Lee IS, Kim SS, Seo BJ, Kim DC. Epidemiological studies of filariasis malayi on the southern islands Korea. Report of NIH Korea 1988;25:411-425.
- 3. Lee JS, Kim TS, Lee WJ, In TS, Kim H, Lee OY, Kim DC. Epidemiological studies of filariasis malayi on the southern islands in Korea (III). Report of NIH Korea 1992;29:114-122.
- 4. Kim DC, Lee OY, Lee KW. Epidemiology of malayan filariasis of inland Korea. II. Vector finding and transmission of Brugia malayi in Yongju area. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1977;8:23-32.
- 5. Chai JY, Lee SH, Choi SY, Lee JS, Yong TS, Park KJ, Yang KA, Lee KH, Park MJ, Park HR, Kim MJ, Rim HJ. A survey of Brugia malayi infection on the Heuksan islands, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2003;41:69-73.
- 6. Cheun HI, Lee JS, Cho SH, Kong Y, Kim TS. Elimination of lymphatic filariasis in the Republic of Korea: an epidemiological survey of formerly endemic areas, 2002-2006. Trop Med Int Health 2009;14:445-449.
- 7. Lee JS, Hong HK. Seasonal prevalence and behavior of Aedes togoi. Korean J Parasitol 1995;33:19-26.
- 8. Tanaka K, Mizusawa K, Saugstad ES. Mosquitoes of Japan and Korea. Contribution of the American Entomology Institute 1979;16:148-152.
- 9. Lee KW. A revision of the illustrated taxonomic keys to genera and species of female mosquitoes of Korea. Department of the Army, 5th Medical Detachment, 168th Medical Battalion, 18th Medical Command. 1998.
- 10. Lee JS, Hong HK. Effects of nutrient and salinity in egg and larval development of Aedes togoi. Korean J Parasitol 1995;33:9-18.
- 11. Shoji S. On the synecological observation of micro-organism communities in some tidewater rock-pool with special reference to the morphological variation of the larvae of mosquito, Aedes togoi Theobald. Ecol Rev 1955;14:91-98.
- 12. Nakamura S, Miyagi I, Toma T. Seasonal appearance of immature population of Aedes (finlaya) togoi (Theobald) in Okinawa. Japan J Sanit Zool 1988;39:91-96.
- 13. Sucharit S, Vutikes S, Leemingswasdi S, Kerdpibul V, Chomcharn Y. The effects of common salt on Aedes togoi and filarial infection. Korean J Parasitol 1982;20:21-27.
- 14. Hong HK, Kim CM, Lee JS. An improved device of effective sampling method for larval collection of Aedes togoi. Korean J Entomol 1995;25:181-183.
- 15. Lee OY, Lee JS, Kim TS, Son SC, Yong TS, Kim DC, Kim JB, Lee SS. Epidemiological studies on filariasis malayi on Cheju Do and the southern islands. Report of NIH Korea 1986;23:407-422.
- 16. Lee WY. A study on Aedes togoi as vector of filariasis in Cheju island. Korean J Parasitol 1969;7:153-159.
- 17. Soh CT, Kim DC. Efficacy of diethylcarbamazine citrate against filariasis malayi in modified low dosage schedule. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1977;8:51-56.
- 18. Seo BS, Lee WJ. Effectiveness of diethylcarbamazine in the mass treatment of Malayan filariasis with low dosage schedule. Korean J Parasitol 1973;11:61-69.
- 19. Lee OY, Lee JS, Kim TS, Son SC, Yong TS, Lee IS, Kim SS, Kim DC, Seo BJ, Lee HG. Epidemiological studies on filariasis malayi on the southern islands and inland Korea. Report of NIH Korea 1987;24:519-538. (Korean).
Fig. 1Areas surveyed for adult and immature mosquitoes during 2002-2005.
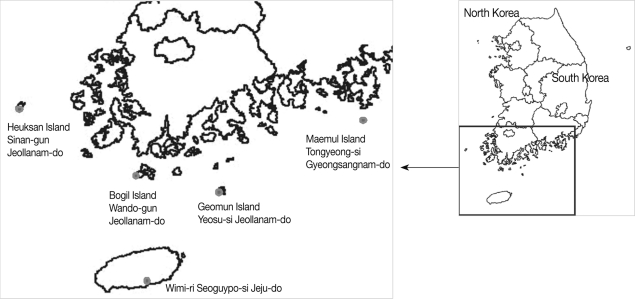
Table 1.Seasonal variations of mosquitoes collected in mosquito traps in Sa-ri, Heuksan Island (latitude 34˚39´N, longitude 125˚25´E), Sinan-gun, Jeollanam-do in 2002
Table 1.
|
Month |
Ochlerotatus togoi
|
Anopheles (Hyrcanus) group |
Culex pipiens
|
Culex tritaeniorhynchus
|
Armigeres subalbatus
|
Mean No./trap |
|
Jul. |
45 |
17 |
20 |
3 |
0 |
85 |
|
Aug. |
73 |
2 |
52 |
13 |
2 |
142 |
|
Sep. |
19 |
2 |
59 |
4 |
0 |
84 |
|
Oct. |
6 |
1 |
28 |
0 |
1 |
36 |
|
Total (%) |
143 (41.2) |
22 (6.3) |
159 (45.8) |
20 (5.8) |
3 (0.9) |
347 |
Table 2.Seasonal prevalence of mosquitoes collected in mosquito traps in Sim-ri in Heuksan Island (latitude 34˚39´N, longitude 125˚25´E), Sinan-gun, Jeollanam-do in 2002
Table 2.
|
Month |
Ochlerotatus togoi
|
Anopheles (Hyrcanus) Group |
Culex pipiens
|
Culex tritaeniohynchus
|
Culex bitaenirohynchus
|
Armigeres subalbatus
|
Tripteroides bambusa
|
Mean No./trap |
|
Jul. |
47 |
4 |
19 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
73 |
|
Aug. |
36 |
1 |
44 |
11 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
93 |
|
Sep. |
21 |
0 |
88 |
12 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
124 |
|
Oct. |
8 |
1 |
51 |
6 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
69 |
|
Total (%) |
112 (31.2) |
6 (1.7) |
202 (56.3) |
32 (8.9) |
1 (0.3) |
5 (1.4) |
1 (0.3) |
359 |
Table 3.Seasonal variation of adult mosquitoes collected in mosquito traps in Baekdo-ri, Bogil Island (latitude 34˚08´N, longitude 126˚32´E), Wando-gun, Jeollanam-do in 2003
Table 3.
|
Month |
Ochlerotatus togoi
|
Anopheles (Hyrcanus) Group |
Culex pipiens
|
Culex tritaeniorhynchus
|
Armigeres subalbatus
|
Aedes albopicthus
|
Ochlerotatus dorsalis
|
Culex bitaeniorhynchus
|
Mean No./trap |
|
May |
46.5 |
0.0 |
0.5 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
47.0 |
|
Jun. |
81.5 |
7.0 |
1.0 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.0 |
0.5 |
0.0 |
91.0 |
|
Jul. |
108.5 |
53.5 |
19.0 |
6.0 |
7.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
194.0 |
|
Aug. |
67.0 |
114.0 |
40.5 |
44.0 |
17.5 |
0.5 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
283.5 |
|
Sep. |
31.0 |
57.5 |
6.5 |
88.5 |
34.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
219.5 |
|
Oct. |
26.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
6.5 |
6.5 |
0.0 |
0.5 |
0.0 |
41.0 |
|
Total (%) |
361.0 (41.2) |
232.5 (26.5) |
68.0 (7.8) |
145.0 (16.6) |
66.5 (7.6) |
1.0 (0.1) |
1.5 (0.2) |
0.5 (0.1) |
876.0 |
Table 4.Seasonal variation in mosquitoes collected by black light trap in Geomun-ri (latitude 34˚17´N, longitude 127˚23´E), Geomun Island, Yeosu-si, Jeollanam-do in 2004
Table 4.
|
Month |
Ochlerotatus togoi
|
Culex pipiens
|
Culex tritaeniorhychus
|
Armigeres subalbatus
|
Aedes albopictus
|
Mean No./trap |
|
Mar. |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
|
Apr. |
0.5 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.5 |
|
May |
2.8 |
0.5 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
3.3 |
|
Jun. |
15.6 |
0.1 |
0.0 |
0.3 |
0.0 |
16.0 |
|
Jul. |
14.3 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.3 |
0.0 |
14.6 |
|
Aug. |
4.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
4.0 |
|
Sep. |
3.4 |
0.8 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
4.2 |
|
Oct. |
7.4 |
4.0 |
1.1 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
13.6 |
|
Total (%) |
48.0 (85.4) |
5.4 (9.6) |
1.1 (2.0) |
1.6 (2.8) |
0.1 (0.2) |
56.2 |
Table 5.Seasonal variation in mosquitoes collected by black light trap in Maejuk-ri (latitude 38˚38´N, longitude 128˚34´E), Maemul Island, Tongyeong-si, Gyeongsangnam-do in 2004
Table 5.
|
Month |
Ochlerotatus togoi
|
Culex pipiens
|
Culex tritaeniorhychus
|
Armigeres subalbatus
|
Mean No./trap |
|
Mar. |
1.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
Apr. |
3.8 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
3.8 |
|
May |
17.9 |
0.3 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
18.2 |
|
Jun. |
25.8 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.1 |
25.9 |
|
Jul. |
21.1 |
0.3 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
21.4 |
|
Aug. |
9.3 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
9.3 |
|
Sep. |
2.7 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
2.7 |
|
Oct. |
15.7 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.1 |
16.4 |
|
Total (%) |
97.3 (98.6) |
0.9 (0.9) |
0.3 (0.3) |
0.2 (0.2) |
98.7 |
Table 6.Seasonal variation in mosquitoes collected by black light trap in Wimi-ri (latitude 33˚16´N, longitude 126˚39´E), Seoguypo-si, Jeju-do in 2005
Table 6.
|
Month |
Ochlerotatus togoi
|
Anopheles (Hyrcanus) Group |
Culex pipiens
|
Culex tritaeniorhynchus
|
Mean No./trap |
|
Apr. |
2.0 |
0.0 |
4.5 |
0.0 |
6.5 |
|
May |
3.0 |
0.0 |
4.5 |
0.0 |
7.5 |
|
Jun. |
8.0 |
0.0 |
8.0 |
0.0 |
16.0 |
|
Jul. |
4.0 |
0.5 |
8.5 |
1.0 |
14.0 |
|
Aug. |
9.0 |
0.0 |
9.5 |
1.5 |
20.0 |
|
Sep. |
4.5 |
0.0 |
6.0 |
1.5 |
12.0 |
|
Total (%) |
30.5 (40.1) |
0.5 (0.7) |
41.0 (53.9) |
4.0 (5.3) |
76.0 |
Table 7.Larval density of Ochlerotatus togoi in rock pools using the meshed-sinking quadrat (100 cm2) collection method at Geomun-ri (latitude 34˚17´N, longitude 127˚23´E), Geomun Island, Yeosu-si, Jeollanam-do in 2004
Table 7.
|
Month |
Number of rock pools examined |
No. of dips |
1st-2nd
|
3rd
|
4th
|
Pupa
|
Mean |
Salinity (%) |
Water temperature (°C) |
|
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
|
Mar. |
7 |
31 |
10.4 |
15.9 |
32.4 |
49.6 |
22.4 |
34.3 |
0.1 |
0.2 |
65.3 |
0.2 |
5.8 |
|
Apr. |
7 |
30 |
1.4 |
4.3 |
5.8 |
17.9 |
10.7 |
33.0 |
14.5 |
44.8 |
32.4 |
0.1 |
22.5 |
|
May |
7 |
33 |
11.2 |
42.6 |
3.9 |
14.8 |
4.2 |
16.0 |
7.0 |
26.6 |
26.3 |
0.2 |
24.1 |
|
Jun. |
7 |
34 |
34.1 |
36.5 |
52.5 |
56.1 |
5.8 |
6.2 |
1.1 |
1.2 |
93.5 |
0.8 |
26.8 |
|
Jul. |
7 |
35 |
13.2 |
33.8 |
13.4 |
34.3 |
6.3 |
16.1 |
6.2 |
15.9 |
39.1 |
2.6 |
32.8 |
|
Aug. |
7 |
35 |
1.8 |
24.3 |
1.9 |
25.7 |
3.1 |
41.9 |
0.6 |
8.1 |
7.4 |
2.6 |
24.3 |
|
Sep. |
7 |
33 |
6.2 |
27.8 |
9.7 |
43.5 |
4.3 |
19.3 |
2.1 |
9.4 |
22.3 |
0.6 |
24.7 |
|
Oct. |
7 |
33 |
0.9 |
9.2 |
2.6 |
26.5 |
3.5 |
35.7 |
2.8 |
28.6 |
9.8 |
1.8 |
18.8 |
Table 8.Larval density of Ochlerotatus togoi in rock pools using the meshed-sinking quadrat (100 cm2) collection method at Maejuk-ri (latitude 34˚38´N, longitude 128˚34´E), Maemul Island, Tongyeong-si, Gyeongsangnam-do in 2004
Table 8.
|
Month |
Number of rock pools examined |
No. of dips |
1st-2nd
|
3rd
|
4th
|
Pupae
|
Mean |
Salinity (%) |
Water temperature (°C) |
|
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
|
Mar. |
7 |
23 |
2.1 |
8.4 |
19.1 |
76.7 |
3.0 |
12.1 |
0.7 |
2.8 |
24.9 |
0.6 |
16.1 |
|
Apr. |
7 |
28 |
2.8 |
9.9 |
5.8 |
20.5 |
12.9 |
45.6 |
6.8 |
24.0 |
28.3 |
0.3 |
18.9 |
|
May |
7 |
34 |
23.1 |
48.1 |
14.1 |
29.4 |
4.9 |
10.2 |
5.9 |
12.3 |
48.0 |
0.1 |
19.5 |
|
Jun. |
7 |
32 |
46.2 |
63.4 |
10.3 |
14.1 |
10.1 |
13.9 |
6.3 |
8.6 |
72.9 |
0.1 |
20.2 |
|
Jul. |
7 |
30 |
40.2 |
58.4 |
15.6 |
22.7 |
11.5 |
16.7 |
1.5 |
2.2 |
68.8 |
0.3 |
29.7 |
|
Aug. |
7 |
30 |
5.0 |
39.4 |
2.3 |
18.1 |
5.3 |
41.7 |
0.1 |
0.8 |
12.7 |
3.7 |
24.0 |
|
Sep. |
7 |
33 |
3.5 |
76.1 |
0.6 |
13.0 |
0.3 |
6.5 |
0.2 |
4.4 |
4.6 |
4.1 |
21.2 |
|
Oct. |
7 |
32 |
0.3 |
16.7 |
1.3 |
72.2 |
0.1 |
5.6 |
0.1 |
5.6 |
1.8 |
3.8 |
19.3 |
Table 9.Larval density of Ochlerotatus togoi in rock pools using the meshed-sinking quadrat (100 cm2) collection method at Namwon-eup (latitude 33˚16´N, longitude 126˚39´E), Seoguypo-si, Jeju-do in 2005
Table 9.
|
Month |
Number of rock pools examined |
No. of dips |
1st-2nd
|
3rd
|
4th
|
Pupae
|
Mean |
|
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
|
Apr. |
5 |
23 |
6.5 |
70.7 |
1.0 |
10.9 |
0.9 |
9.8 |
0.8 |
8.7 |
9.2 |
|
May |
5 |
25 |
2.8 |
68.3 |
0.6 |
14.6 |
0.5 |
12.2 |
0.2 |
4.9 |
4.1 |
|
Jun. |
3 |
15 |
14.6 |
99.3 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.1 |
0.7 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
14.7 |
|
Jul. |
5 |
25 |
6.0 |
100.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
6.0 |
Table 10.Frequency distribution of salinity of Ochlerotatus togoi larvae and pupae at Geomun-ri (latitude 34˚17´N, longitude 127˚23´E), Geomun Island, Yeosu-si, Jeollanam-do, and Maejuk-ri (latitude 34˚38´N, longitude 128˚34´E), Maemul Island, Tongyeong-si, Gyeongsangnam-do in 2004
Table 10.
Location
|
Geomun-ri
|
Maejuk-ri
|
Mean |
% |
|
Salinity (%) |
Number of rock pools |
Mean No. of larvae & pupae |
% |
Mean No. of rock pools |
Mean No. of larvae & pupae |
% |
|
0.0-0.4 |
27 |
1,373.9 |
68.6 |
13.0 |
1,126.5 |
78.1 |
2,500.4 |
72.5 |
|
0.5-0.9 |
6 |
257.5 |
12.8 |
5.0 |
182.2 |
12.6 |
439.7 |
12.8 |
|
1.0-1.9 |
3 |
93.2 |
4.7 |
2.0 |
11.2 |
0.8 |
104.4 |
3.0 |
|
2.0-2.9 |
8 |
200.0 |
10.0 |
3.0 |
7.6 |
0.5 |
207.6 |
6.0 |
|
3.0-3.9 |
5 |
79.4 |
4.0 |
2.0 |
16.4 |
1.1 |
95.8 |
2.8 |
|
4.0-4.9 |
0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
9.0 |
89.1 |
6.2 |
89.1 |
2.6 |
|
5.0-5.9 |
0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
2.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
|
6.0-6.9 |
0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
2.0 |
10.0 |
0.7 |
10.0 |
0.3 |
|
Total |
49 |
2,004.0 |
100.0 |
38.0 |
1,443.0 |
100.0 |
3,447.0 |
|