Abstract
Acanthamoeba spp. are single-celled protozoan organisms that are widely distributed in the environment. In this study, to understand functional roles of a mannose-binding protein (MBP), Acanthamoeba castellanii was treated with methyl-alpha-D-mannopyranoside (mannose), and adhesion and cytotoxicity of the amoeba were analyzed. In addition, to understand the association of MBP for amoeba phagocytosis, phagocytosis assay was analyzed using non-pathogenic bacterium, Escherichia coli K12. Amoebae treated with mannose for 20 cycles exhibited larger vacuoles occupying the most area of the amoebic cytoplasm in comparison with the control group amoebae and glucose-treated amoebae. Mannose-selected amoebae exhibited lower levels of binding to Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. Exogenous mannose inhibited >50% inhibition of amoebae (control group) binding to CHO cells. Moreover, exogenous mannose inhibited amoebae (i.e., man-treated) binding to CHO cells by <15%. Mannose-selected amoebae exhibited significantly decreased cytotoxicity to CHO cells compared with the control group amoebae, 25.1% vs 92.1%. In phagocytic assay, mannose-selected amoebae exhibited significant decreases in bacterial uptake in comparison with the control group, 0.019% vs 0.03% (P<0.05). Taken together, it is suggested that mannose-selected A. castellanii trophozoites should be severely damaged and do not well interact with a target cell via a lectin of MBP.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba castellanii, mannose-binding protein, adhesion, cytotoxicity, Escherichia coli K12
Acanthamoeba spp. are single-celled protozoan organisms that are widely distributed in the environment [
1-
3]. They cause cutaneous lesions and sinus infections, vision-threatening keratitis and chronic granulomatous encephalitis [
1,
4]. In particular,
A. castellanii is an agent of human keratitis caused mainly by exogenous trauma and contaminated cleaning solutions. According to Khan [
1], significant interest in this organism has risen over the years due to the ability of
Acanthamoeba to i) produce serious human infections associated with a rise in the number of immunocompromised patients and contact lense wearers, ii) its potential role in ecosystems, iii) its ability to act as a host/reservoir for microbial pathogens, and iv) its role as a model organism for motility studies. Regarding potential roles of
Acanthamoeba pathogenicity and pathophysiology in a manner of contact-dependent mechanism, lectins have been well known to be important to induce cytotoxicity to target cells. Among them, a mannose-binding protein (MBP) showed a strong pathogenic potential of
A. castellanii correlated with major virulence proteins [
5]. These extracellular matrices consisting of MBP may be essential for invasion. In this study, to understand functional roles of a MBP,
A. castellanii was treated with methyl-alpha-D-mannopyranoside (mannose) for 24 hr, resulting in 1 cycle, and then were morphogically analyzed using 20-cycled-amoebae. Furthermore, adhesion and cytotoxicity of the amoeba were studied and phagocytosis assay was analyzed using non-invasive bacterium,
Escherichia coli K12.
All chemicals were purchased from Sigma Laboratories (Poole, Dorset, England), unless otherwise stated. A clinical isolate of
A. castellanii belonging to T4 genotype, isolated from a keratitis patient (American Type Culture Collection, ATCC 50492, Manassas, Virginia, USA) was used in the present study.
A. castellanii was grown without shaking in 15-ml of PYG medium (proteose peptone 0.75% [w/v], yeast extract 0.75% [w/v] and glucose 1.5% [w/v]) in T-75 tissue culture flasks at 30℃ and the media was refreshed 17-20 hr prior to experiments as previously described [
6]. This resulted in more than 99% amoebae in the trophozoite form, which were subsequently used for carbohydrate selections.
A laboratory non-invasive
Escherichia coli strain, HB101 (K12) was used in phagocytosis assays. Bacteria were routinely cultured in Luria-Bertini (LB) medium at 37℃ overnight as previously described [
7]. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells were used for
A. castellanii adhesion and in vitro cytotoxicity assay [
8]. Briefly, CHO cells were cultured as a monolayer in Earle's minimal essential medium (EMEM; Gibco BRL, Grand Island, New York, USA) at 37℃. This experiment, in 24-well cell culture plates, was performed using 2×10
5 CHO cells either alone or co-cultured with i) amoeba or ii) amoeba pre-incubated with methyl-alpha-D-mannopyranoside (mannose), that is, mannose-selected amoeba, for the subsequent analysis mentioned above.
Adhesion assays were performed as previously described [
9]. Briefly, CHO cells were grown to confluency in 24-well plates.
Acanthamoeba trophozoites (2×10
5 amoebae/0.5 ml/well) were incubated with CHO cell monolayers in EMEM. The plates were incubated at 37℃ in a 5% CO
2 incubator. After 60 min incubations, the percentage of bound amoebae was calculated as follows: No. of unbound amoebae/total number of amoebae×100=% unbound amoebae. The numbers of bound amoebae were deduced as follows: 100%-unbound amoebae=% bound amoebae. To determine the effects of exogenous saccharides on amoebae binding to the host cells, adhesion assays were performed in the presence of mannose (100 mM final conc.). Briefly, amoebae were pre-incubated with the saccharides for 1 hr at room temperature. Following this incubation, amoebae plus saccharides were transferred to CHO cell monolayers and adhesion assays performed as described above.
To determine the ability of
Acanthamoeba to produce host cell death, cytotoxicity assay was performed as previously described [
9]. Adhesion assay was done, and the plates were observed periodically for monolayer disruptions under a phase contrast microscope for up to 24 hr. Following this incubation, the supernatants were collected and examined for host cell cytotoxicity by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release (cytotoxicity detection kit, Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA). Briefly, the supernatants of co-cultures of
Acanthamoeba and the host cells were assessed for the presence of LDH, the release of which is considered as an estimate of cell death. The percentage of LDH release was calculated as follows: (LDH activity in experimental sample [measured by optical density at 492 nm]-LDH activity in control samples/total LDH activity release-LDH activity in control samples×100=% cytotoxicity). Control samples were obtained from host cells or
Acanthamoeba incubated alone. Total LDH activity release was determined by total host cell lysis with 1% Triton X-100 for 30 min at 37℃.
To study the phagocytic ability of
Acanthamoeba and mannose-selected amoeba, phagocytosis assays were performed using
E. coli K12 as previously described [
10]. Briefly,
Acanthamoeba was grown to confluency in 24-well plates. Next, plates were washed with PBS for 3 times to remove unbound amoebae, and live
E. coli K12 (2×10
6/well) were added. The plates were incubated for 60 min to allow phagocytic uptake. Following this incubation, the supernatants were removed and gentamicin was added (final conc. 100 µg/ml for 45 min) to kill any remaining extracellular
E. coli. This allowed the determination of any intracellular
E. coli. The percent phagocytosis was calculated as follows: recovered
E. coli (cfu)/total
E. coli (cfu)×100=%
E. coli intracellular of
Acanthamoeba. In addition, the ratio of bacteria to amoebae was calculated as follows: recovered
E. coli (cfu)/number of
Acanthamoeba=
E. coli/
Acanthamoeba ratio.
To understand the functional roles of
A. castellanii mannose-binding protein (MBP) by saturating mannose saccharide, mannose selection was employed and was treated to
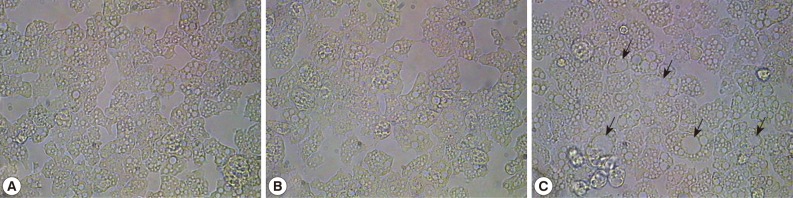
A. castellanii trophozoite forms for 24 hr, resulting in 1 cycle. For controls, A castellanii was treated with glucose. At the end of 20 cycles, the following resultant amoebae were obtained: i) control group amoebae, ii) glucose-treated amoebae, and iii) mannose-treated amoebae. Interestingly, mannose-treated amoebae exhibited large vacuoles compared with the control group amoebae and glucose-treated amoebae (
Fig. 1). For example, the vacuole size in control group amoebae and glucose-treated amoebae was up to 7 µm, while the mannose-treated amoebae exhibited vacuoles of up to 14 µm. The amoeba cytoplasm was occupied with 1 or 2 larger vacuoles, which made small organelles unclear to be observed.
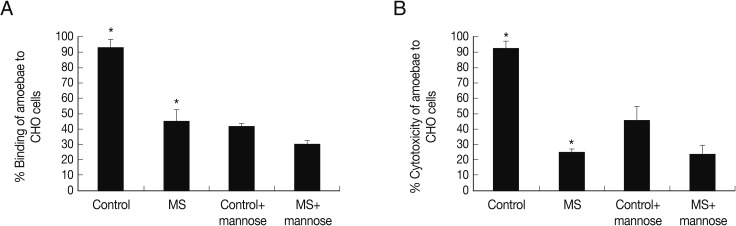
To determine whether mannose-selected amoebae exhibit binding to the host cells, adhesion assays were performed using CHO cells. The findings revealed that mannose-selected amoebae exhibited lower levels of binding to CHO cells (
Fig. 2A). Furthermore, to determine whether these interactions are mediated via mannose-dependent or mannose-independent manner, adhesion assays were performed in the presence of exogenous mannose. Interestingly, exogenous mannose inhibited >50% inhibition of amoebae (control group) binding to CHO cells. Moreover, exogenous mannose inhibited amoebae (i.e., man-treated) binding to CHO cells by <15% (
Fig. 2A).
Next, to determine the ability of control group and mannose-selected amoebae to produce host cell death, cytotoxicity assays were performed. As described in
Fig. 3, mannose-selected amoebae exhibited significantly decreased cytotoxicity to CHO cells compared with the control group amoebae, 25.1% vs 92.1% (
Fig. 2B) (
P<0.05; using the paired t-test, one-tail distribution). The cytotoxicity of control group and mannose-selected amoebae pre-incubated with mannose was 45.8% and 24.3%, respectively (
Fig. 2B). Overall, these findings showed that mannose-selected amoebae showed severely affected cytotoxic functions.
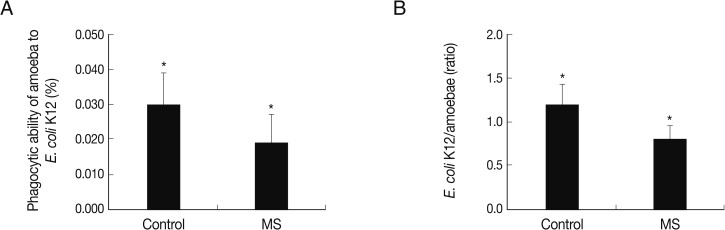
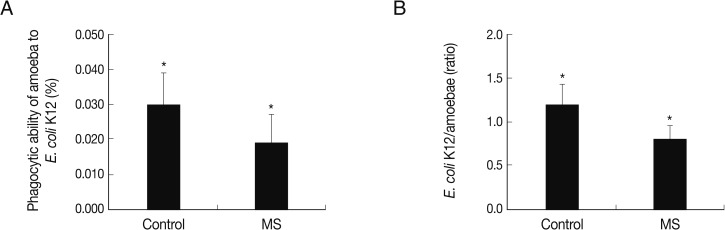
To determine the phagocytic ability of the control group and mannose-selected amoebae, phagocytosis assays were performed using live
E. coli K12. The experiment demonstrated that mannose-selected amoebae exhibited significant decreases in bacterial uptake compared to control group, 0.019% vs 0.03% (
P<0.05) (
Fig. 3A). Interestingly, bacteria and amoebae ratio also decreased in mannose-selected amoebae compared with the control group amoebae (
Fig. 3B).
The MBP of
A. castellanii is thought to play a key role in the pathogenesis of the infection by mediating the adhesion of parasites to the host cells. The isolation by chromatography on mannose affinity gel and molecular cloning revealed that about 400 kDa proteins constituted multiple 130 kDa subunits. In addition, they also composed of 3.6 kb of the amoeba genome, and therefore, included the coding for a precursor protein of 833 amino acids [
11]. Other MBP cloning was reported sequenced with 1,081 nucleotides coding for 194 amino acids from Iranian clinical isolate of
A. castellanii [
12]. Through gas chromatography combined with mass spectrometry, the carbohydrate composition of cyst walls of
Acanthamoeba revealed a high percentage of galactose and glucose and small amounts of mannose and xylose [
13].
In this present study, we demonstrated that the pathogenic potential of A. castellanii is severely damaged by saturating MBP with mannose. Interestingly, a long time treatment of mannose to A. castellanii trophozoite forms induced larger vacuoles than control group and glucose-treated amoebae. It implies that exogenous mannose would change the composition of amoeba cytoplasm or act as a nutrient. MBP is located on extracellular matrices of A. castellanii and may play a role in contact as a manner of extracellular protein interactions. Thus, we employed adhesion and cytotoxicity assays to elucidate functional roles of MBP. Mannose-selected amoeba exhibited lower adhesion and cytotoxicity than the control group. Moreover, exogenous mannose was pre-incubated with amoeba for 1 hr and then added to CHO target cells. The results showed that the adhesion and cytotoxicity of control group and mannose-selected amoebae pre-incubated with exogenous mannose were more decreased as amoebae were not added with exogenous mannose. Using the bacteria E. coli K12 as a nutrient or prey, the phagocytic activity of mannose-selected amoebae was severely damaged. The data demonstrating the pathogenic potential of A. castellanii trophozoites are associated with the mannose-binding protein and provide the candidate of pathogenic target to further target-based therapy.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Funding for this paper was provided by Namseoul University.
References
- 1. Khan NA. Acanthamoeba: biology and increasing importance in human health. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2006;30:564-595.
- 2. Marciano-Cabral F, Cabral G. Acanthamoeba spp. as agents of disease in humans. Clin Microbiol Rev 2003;16:273-307.
- 3. Siddiqui R, Khan NA. Biology and pathogenesis of Acanthamoeba. Parasit Vectors 2012;5:6.
- 4. Visvesvara GS, Moura H, Schuster FL. Pathogenic and opportunistic free-living amoebae: Acanthamoeba spp., Balamuthia mandrillaris, Naegleria fowleri, and Sappinia diploidea. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2007;50:1-26.
- 5. Garate M, Marchant J, Cubillos I, Cao Z, Khan NA, Panjwani N. In vitro pathogenicity of Acanthamoeba is associated with the expression of the mannose-binding protein. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2006;47:1056-1062.
- 6. Krishna-Prasad BN, Gupta SK. Preliminary report on engulfment and retention of Mycobacteria by trophozoites of axenically grown Acanthamoeba castellanii Douglas. Curr Sci 1978;47:245-247.
- 7. Alsam S, Sissons J, Dudley R, Khan NA. Mechanisms associated with Acanthamoeba castellanii (T4) phagocytosis. Parasitol Res 2005;96:402-409.
- 8. Jeong SR, Lee SC, Song KJ, Park S, Kim K, Kwon MH, Im KI, Shin HJ. Expression of the nfa1 gene cloned from pathogenic Naegleria fowleri in nonpathogenic N. gruberi enhances cytotoxicity against CHO target cells in vitro. Infect Immun 2005;73:4098-4105.
- 9. Sissons J, Kim KS, Stins M, Jayasekera S, Alsam S, Khan NA. Acanthamoeba castellanii induces host cell death via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent mechanism. Infect Immun 2005;73:2704-2708.
- 10. Alsam S, Jeong SR, Sissons J, Dudley R, Kim KS, Khan NA. Escherichia coli interactions with Acanthamoeba: a symbiosis with environmental and clinical implications. J Med Microbiol 2006;55:689-694.
- 11. Garate M, Cao Z, Bateman E, Panjwani N. Cloning and characterization of a novel mannose-binding protein of Acanthamoeba. J Biol Chem 2004;279:29849-29856.
- 12. Niyyati M, Rezaie S, Rahimi F, Mohebali M, Maghsood AH, Farnia SH, Rezaeian M. Molecular characterization and sequencing of a gene encoding mannose binding protein in an Iranian isolate of Acanthamoeba castellanii as a major agent of Acanthamoeba keratitis. Iranian J Publ Health 2008;37:9-14.
- 13. Dudley R, Jarroll EL, Khan NA. Carbohydrate analysis of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Exp Parasitol 2009;122:338-343.
Fig. 1Morphologic changes of A. castellanii trophozoites by adding mannose. Mannose was added to the amoebae for 24 hr, resulting in 1 cycle. At the end of 20 cycles, the following resultant amoebae were obtained. (A) control group, (B) glucose-treated amoebae, and (C) mannose-treated amoebae. Arrows indicates larger vacuoles in cytoplasm of mannose-selected amoebae. ×250.
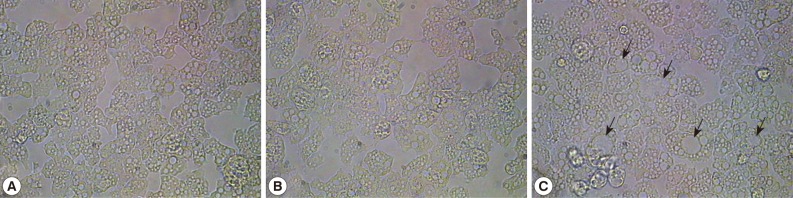
Fig. 2Adhesion and cytotoxicity assay of mannose-selected A. castellanii trophozoites to CHO cells. After mannose-selected amoebae (MS) were incubated with CHO cells for 1 hr at 37℃, adhesion assays were performed (A). Also, they were pre-incubated with exogenous saccharides for 1 hr and then added to CHO cells for 1 hr as mentioned in materials and methods. Cytotoxicity was measured post co-incubation of 24 hr (B). Results are representative of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. Asterisks indicate a significant difference, i.e., P<0.05, using the paired t-test, one-tail distribution.
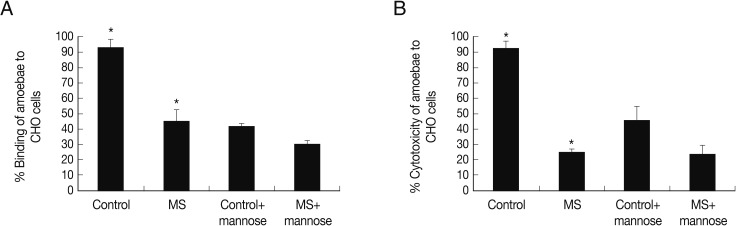
Fig. 3Phagocytosis of mannose-selected A. castellanii trophozoites using non-invasive E. coli K12. To determine the role of a mannose-binding protein in mannose-selected amoebae (MS), phagocytosis assays were performed. (A) represents bacterial association with amoebae and (B) represents ratio of bacteria per amoeba. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. Asterisks indicate a significant difference, i.e., P<0.05, using the paired t-test, one-tail distribution.