Abstract
Opisthorchis viverrini (O. viverrini) is a well-known causative agent of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) in humans. CCA is very resistant to chemotherapy and is frequently fatal. To understand the pathogenesis of CCA in humans, a rodent model was developed. However, the development of CCA in rodents is time-consuming and the xenograft-transplantation model of human CCA in immunodeficient mice is costly. Therefore, the establishment of an in vivo screening model for O. viverrini-associated CCA treatment was of interest. We developed a hamster CCA cell line, Ham-1, derived from the CCA tissue of O. viverrini-infected and N-nitrosodimethylamine-treated Syrian golden hamsters. Ham-1 has been maintained in Dulbecco's Modified Essential Medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum for more than 30 subcultures. These cells are mostly diploid (2n=44) with some being polyploid. Tumorigenic properties of Ham-1 were demonstrated by allograft transplantation in hamsters. The transplanted tissues were highly proliferative and exhibited a glandular-like structure retaining a bile duct marker, cytokeratin 19. The usefulness of this for in vivo model was demonstrated by berberine treatment, a traditional medicine that is active against various cancers. Growth inhibitory effects of berberine, mainly by an induction of G1 cell cycle arrest, were observed in vitro and in vivo. In summary, we developed the allo-transplantable hamster CCA cell line, which can be used for chemotherapeutic drug testing in vitro and in vivo.
-
Key words: Opisthorchis viverrini, cholangiocarcinoma, hamster model, allograft transplantation, anti-cancer effect, berberine
INTRODUCTION
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is the cancer of highest prevalence in northeastern Thailand [
1,
2]. High incidence in the area is strongly associated with consumption of raw fresh water fish containing infectious stages of the liver fluke,
Opisthorchis viverrini, a well-established risk factor of CCA [
2]. Diagnosis of early stage CCA is rather difficult, due to lack of specific symptoms and of specific tumor markers. Patients with an advanced stage of this disease are not candidates for curative surgical treatment [
3]. The results of adjunct therapies, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and chemoradiation, are still unclear. Currently, adjuvant chemotherapy is the treatment of choice for the advanced stage of CCA [
4]. No standard chemotherapeutic regimen for advanced CCA, however, is currently available. Hence, searching for an effective treatment for CCA is urgent.
To evaluate anti-cancer activity of a candidate substance preclinically, cell lines are valuable resources but limited information are yielded from in vitro experiments. Hence, in vivo models are required to demonstrate the physiological effects of the agents. A hamster carcinogenesis model of
O. viverrini-associated CCA was developed previously [
5-
7]. This model has been used extensively since the pathology is comparable to human
O. viverrini-associated CCA [
8-
12]. It is very useful for the comparative study of CCA initiation-promotion [
13], but due to its chronic inflammation-related nature, this model is rather time-consuming and may not be suitable for anti-cancer agent screening. On the other hand, the xenograft transplantation model of human CCA in immunodeficient mice is costly [
14]. Therefore, the development of an
O. viverrini-associated hamster CCA cell line is useful to develop an in vivo model for anti-CCA agent screening.
Berberine (BBR) is an isoquinoline alkaloid isolated from roots and stem barks of the
Berberis species that has been conventionally used in Chinese traditional medicine and Ayurveda medicine. Recently, various pharmacological properties of BBR have been reported including anti-parasitic, anti-hyperlipidemic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer activities [
15-
19]. Several anti-tumor activities of BBR have been reported including anti-proliferation, inhibition of the G1 cell cycle progression, and induction of apoptosis [
17-
19]. Nevertheless, the information regarding BBR effects on CCA is limited [
20]. Searching published literature, it seems that the effect of BBR on CCA has never been demonstrated in vivo. Thus, the effects of BBR on CCA in vivo were evaluated using this newly developed hamster model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Establishment of an O. viverrini-associated hamster CCA cell line
Hamsters were housed and monitored in the animal research facility according to the National Committee of Animal Ethics guidelines. All experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Thailand (ethical clearance no. AEKKU 08/2554 and AEKKU 34/2555). All cell culture reagents were purchased
from Gibco (Grand Island, New York, USA)
CCA was induced in hamsters using
O. viverrini-infection and N-nitrosodimethylamine as previously described [
5-
7]. Briefly, 4-5 week old male Syrian golden hamsters were given 50 metacercariae of
O. viverrini by gastric intubation and also were given 12.5 ppm N-nitrosodimethylamine in drinking water ad libitum. Hamsters were euthanized 6 months after induction of CCA and the livers were collected. Hamster CCA tissues were isolated, washed twice with PBS and minced into small pieces in Dulbecco's Modified Essential Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 µg/mL streptomycin. Then, the tissues were digested with 1,000 U/ml collagenase (Calbiochem, Billerica, Massachusetts, USA) and 0.1 mg/ml DNase I (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) for 3 hr, and the digested tissues were filtered through 100 µm and 70 µm nylon meshes. The cell suspensions were plated onto rat tail collagen-coated plates (5 µg collagen/cm
2, Gibco) containing DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 µg/ml streptomycin, and the plates were cultured at 37℃ in a humidified 5% CO
2 atmosphere. Tumor cells were separated from fibroblasts by partial trypsinization until tumor cells became homogenous. Tumor tissue from each hamster was separately prepared for a cell line. A hamster CCA cell line established was designated as Ham-1.
Ham-1 was subjected to chromosomal analysis as described earlier [
21]. Chromosomes were examined under a light microscope using an oil immersion objective lens (×1,000). The modal chromosome number was determined from more than 20 chromosome areas.
To demonstrate the tumorigenic property of Ham-1 cells, 4-5 week old male Syrian golden hamsters (n=10) were divided into 2 groups (5/group) and injected intradermally with 2×105 or 5×105 cells of Ham-1 (2 sites/hamster). Tumors were checked twice a week. At 3 weeks after transplantation, hamsters were euthanized and tumor masses were collected, weighed, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight for immunohistochemical studies.
Then, to test the anti-tumor effects of BBR, 5×105 cells of Ham-1 were injected intradermally (2 sites/hamster) into 10 hamsters. Then, they were divided into 2 groups of 5 animals. BBR treatment was started on day 3 after tumor cell injections. BBR (10 mg/kg) (berberine chloride form, B3251, Sigma-Aldrich) in sterile water was given by oral gavage to 5 hamsters daily for 3 weeks. Another 5 tumor-bearing hamsters given sterile water by oral gavage served as controls. Hamsters were weighed twice a week. After 21 days of treatment, tumors were collected, weighed, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. Paraffin-embedded tissues were processed as per the standard protocol, and sections of 5-7 µm thickness were prepared. Some tumor tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and observed under a light microscope (×100).
Immunohistochemistry analysis
CCA marker (cytokeratin-19; CK19), proliferative index (proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PCNA) and cell cycle control proteins (cyclin D1 and cyclin E) in hamster CCA tissues were determined using standard immunohistochemistry procedures. Briefly, after de-waxing tissue sections, the antigens were retrieved using 10 mM citrate buffer pH 6.0. Then, endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked by incubating with 0.3% H2O2 solution in methanol for 30 min followed by blocking non-specific binding by incubation in 5% FBS for 20 min at room temperature. Tissue sections were incubated with primary antibodies in a moist chamber at room temperature overnight and then with corresponding secondary antibody for 1 hr at room temperature. Immunoreactivity was detected with diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich) and 0.1% H2O2 in 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.8. Immunostained tissues were blindly evaluated by 2 assessors. Semi-quantitative analysis of 4 randomly selected areas from each tissue was performed according to the frequency (%) of immuno-positive tumor cells. The results were expressed as an immunohistochemistry score (IHC score); 0=<10%; 1=10-25%; 2=26-50%; 3=51-75%; 4=>75%.
Sources of antibodies were as follows: anti-PCNA was obtained from Leica Biosystems (Newcastle, UK), anti-CK-19 and anti-α-smooth muscle actin were from Abcam (Cambridge, UK), anti-cyclin D1 and anti-cyclin E were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Heidelberg, Germany) and goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP was from Zymed Laboratories (South San Francisco, California, USA).
Tetrazolium dye methylthiotetrazole assay
Anti-proliferative effects of BBR were determined in vitro using 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazole]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA). In brief, 6.5×103 Ham-1 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate overnight. Various concentrations of BBR were then added (triplicate wells/concentration), and the plates were incubated for 24 or 48 hr. Later, MTT was added to obtain a final concentration of 0.5 mg/ml, and the plates were incubated for 3 hr at 37℃. To solubilize the formazan crystals, 0.04 N HCl in isopropanol was added. Absorption at 540 nm was determined using an ELISA reader (TECAN Sunrise, Mannedorf, Switzerland). OD540 of BBR-treated samples were normalized by those of samples without BBR and presented as percent (%) cell viability.
Cell cycle analysis
The inhibitory effects of BBR on cell cycle progression were assessed using flow cytometry. After incubation of the cells with 0, 2.5, 12.5, and 25 µM BBR (duplicate samples/concentration) for 24 hr or 48 hr, cells were detached and fixed in 70% cold ethanol in PBS at 4℃ overnight. After that, the pellets were washed with cold PBS and incubated with propidium iodide (10 µg/ml final concentration) in the dark, then filtered through 70 µm nylon meshes. The cell cycle distributions were determined using flow cytometry. DNA histograms were analyzed using FlowJo software (Tree Star, San Jose, California, USA).
Statistical analysis
The Student's t-test was used to analyze the statistical significance. P-values less than 0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
Ham-1 morphology and chromosome analyses
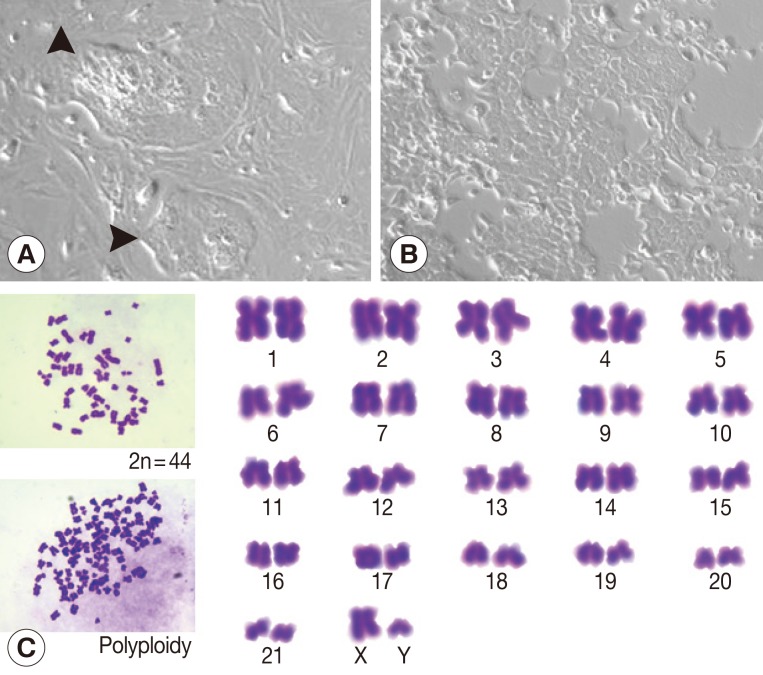
At week 1 after a primary culture, colonies of epithelial-like cells surrounded by spindle-shaped fibroblasts were observed (
Fig. 1A). Fibroblasts were removed by partial trypsinization. At the 15th passage, a homogenous culture cell line was established (
Fig. 1B). Ham-1 cells were successfully maintained under standard cell culture conditions for more than 30 passages over 6 months. Ham-1 cells exhibited a monotonous polygonal shape with a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio and high granularity in the nucleus and cytoplasm. The chromosome study revealed a modal chromosome number of 44 in the diploid mitotic metaphase (2n=44) with representative XY chromosomes. Fewer than 10% of cells were polyploid (
Fig. 1C).
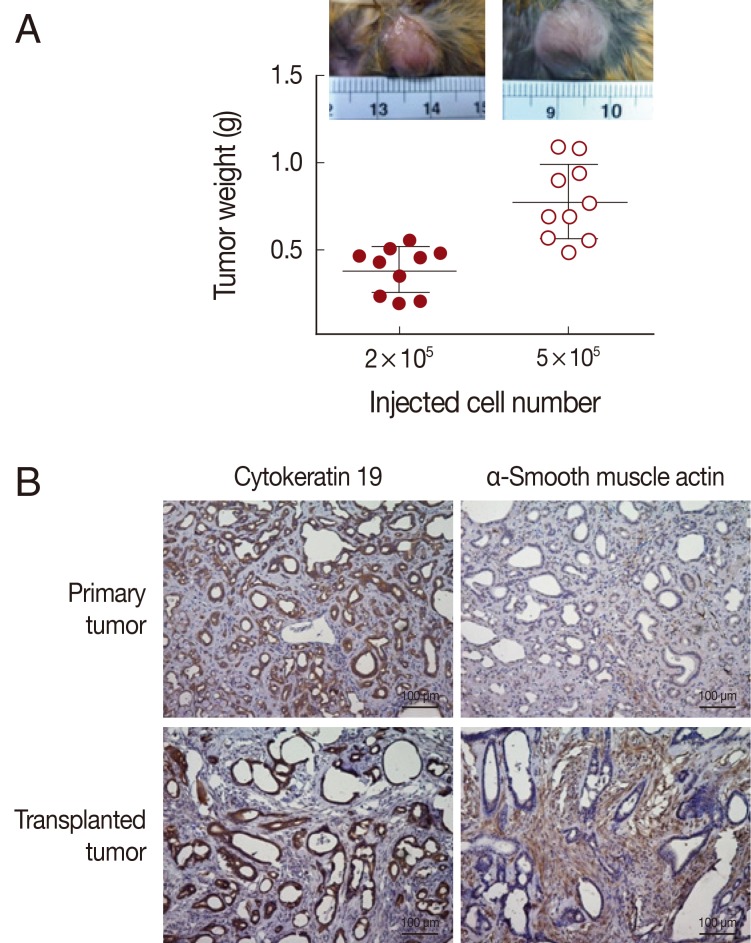
Tumorigenicity of the Ham-1 cell line was demonstrated by allograft transplantation in hamsters. Each hamster was intradermally injected either with 2×10
5 cells or 5×10
5 cells into the dorsal skin (5 animals for each dose, 2 sites/hamster). Tumor masses were observed in all injected sites at week 1 after transplantation. At week 3, the greatest diameters of 1.0 cm and 1.5 cm were observed in groups injected with 2×10
5 cells and 5×10
5 cells, respectively (
Fig. 2A, small insets). Tumors were weighed, and the tumor weights were correlated with the initial injected cell numbers (
Fig. 2A). Tumor masses were histologically assessed. Transplanted tumors exhibited well-differentiated glandular structure similar to the primary CCA in the hamster liver. The cholangiocyte origin of the Ham-1 allograft tumors was confirmed by CK-19-positive and α-smooth muscle actin-negative immunostaining patterns of tumor cells surrounded by strongly positive α-smooth muscle actin stromal cells, comparable to the original tumor (
Fig. 2B).
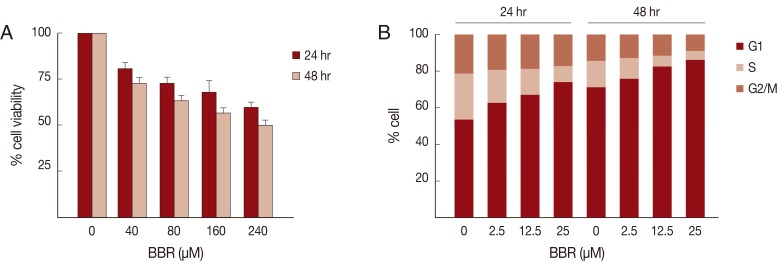
To evaluate the usefulness of the Ham-1 cell line and allograft transplantation model for the evaluation of anti-cancer treatment, an isoquinoline alkaloid; BBR, was selected as an anti-cancer agent in this study. Ham-1 cells were incubated with various concentrations (0-240 µM) of BBR for 24 and 48 hr, and Ham-1 proliferation was measured by the MTT assay. As shown in
Fig. 3A, BBR inhibited Ham-1 cell proliferation in a dose- and time-dependent manner; however, the IC50 of BBR on Ham-1 cell line was over 240 µM at 24 and 48 hr. Cell cycle distribution analyzed by flow cytometry indicated that the anti-proliferative effect of BBR on Ham-1 cells was mainly through an induction of cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase (
Fig. 3B).
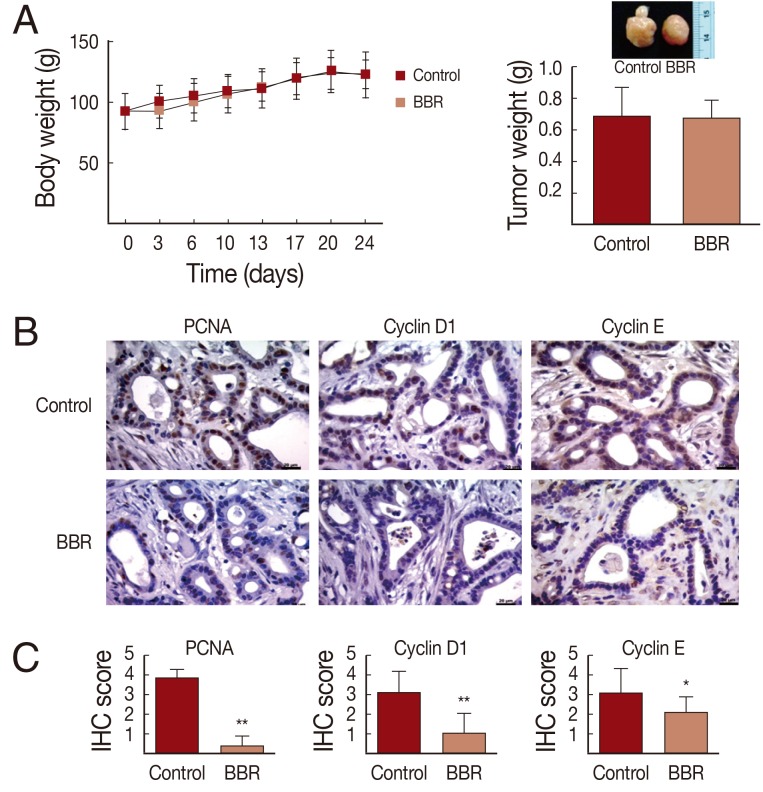
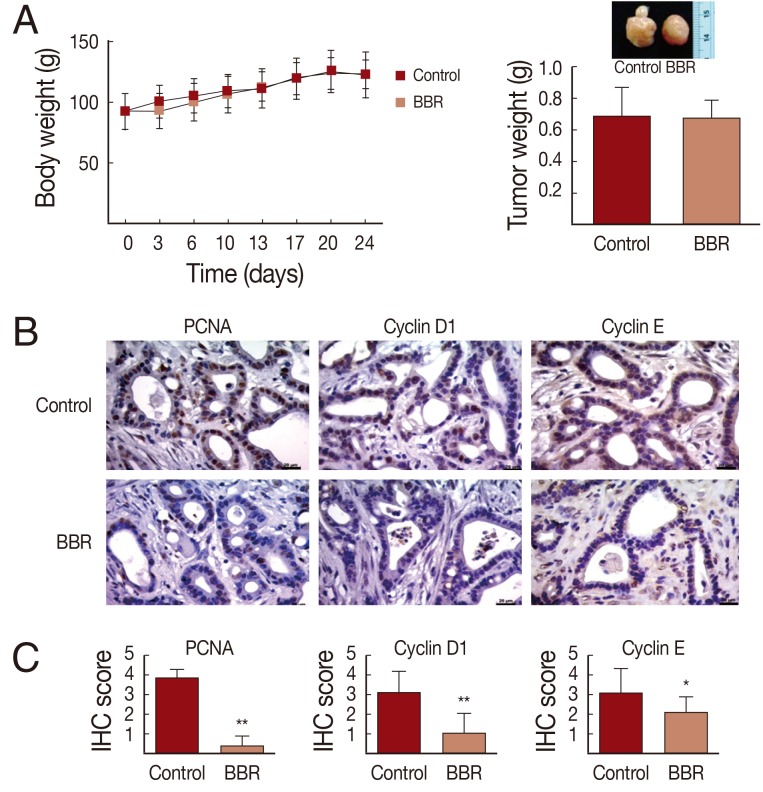
Anti-tumor effects of BBR were assessed in the hamster allograft model. Syrian golden hamsters were injected intradermally with Ham-1 and were divided into 2 groups (5/group). BBR at 10 mg/kg was given to the treatment groups by oral gavage daily for 3 weeks. Drinking water was administered in the same way to control hamsters. Based on the scheduled treatment, BBR had no effects on body weight as the BBR-treated hamsters were healthy and gained weight comparable to the control hamsters (
Fig. 4A). No side effects were observed during the course of treatment. As demonstrated in
Fig. 4B, tumor weights in BBR-treated groups were not different from those of the control group at the end of the experiment. However, the immunohistochemistry staining of proliferative index (PCNA) and the G1 to S cell cycle control proteins (cyclin D1 and cyclin E) showed BBR treatment suppressed the expression of all proteins when compared to the controls. Semi-quantitative analyses using the IHC scores of PCNA in BBR treated tumor tissues compared with controls were 0.38±0.50 vs 3.83±0.39 (
P<0.001); for cyclin D1, corresponding values were 1.06±1.00 vs 3.14±1.04 (
P<0.001) and cyclin E were 2.13±0.81 vs 3.11±1.23 (
P<0.05).
DISCUSSION
O. viverrini infection is a well-documented risk factor for CCA, especially in northeastern Thailand. Advanced stage CCA is relatively resistant to currently available adjunct treatments. Thus, searching for novel treatments is urgently needed. A hamster carcinogenesis model of CCA was previously developed and demonstrated molecular mimicry with the human CCA. In this study, we established a hamster O. viverrini-associated CCA cell line named Ham-1. The tumorigenicity of Ham-1 was validated by intradermal allograft transplantation. Transplanted tissues possessed well-formed gland-like structure with retained bile duct marker, CK-19. The advantage of the newly developed comparative CCA model was demonstrated by analysis of BBR treatment. Altogether, the allo-transplantable hamster CCA cell line for anti-cancer testing was developed in the current study. This O. viverrini-associated hamster cell line model might be useful for the complete evaluation of CCA treatment in vitro and in vivo.
The Ham-1 CCA cell line developed in the current study is similar to the previously described HaLCCA-1.1 cell line [
22,
23]. Ham-1 cells are polygonal in shape, similar to HaLCCA-1.1. The population doubling times of these cell lines are comparable (36 hr in Ham-1 vs 31 hr in HaLCCA-1.1, data not shown). The chromosome analysis of the hamster CCA cell line has never been reported. Ham-1 retains diploidy. The Ham-1 cell line is highly tumorigenic. With initial cell numbers of 2×10
5, it efficiently formed a tumor mass in the hamster skin and was detectable within a week. This model was superior to the previously reported model [
22,
23] since the current model requires injection of fewer cells (2-5×10
5 cells in the current model vs 5×10
6 cells in the other model) and shorter time (3 weeks in this model vs 4 weeks in the other model) but with comparable tumor sizes. This might be due to the use of the intradermal route in this study vs subcutaneous injections in others.
The benefit of the Ham-1 model on anti-tumor activity testing was demonstrated by analysis of BBR treatment. This compound has been previously reported to inhibit proliferation, inducing G1 arrest and promoting apoptosis of human CCA cells (QBC939 cell line) [
20]. The in vivo effect of BBR, however, has never been tested. In the present study, BBR could inhibit Ham-1 cell proliferation in vitro, but the effect was not impressive. The partial growth-inhibitory effect of BBR on Ham-1 was confirmed by the in vivo model. This ineffectiveness of BBR in the Ham-1 cell line compared to the QBC939 cell line might be due to the different etiologies of both cell lines [
20]. It was previously reported that
O. viverrini-associated CCA possessed a distinct gene expression profile when compared to non-
O. viverrini-associated CCA [
24]; genes involved in xenobiotic metabolism, such as
UGT2B11 and
UGT1A10, were substantially increased in
O. viverrini-associated CCA while increases of genes in growth factor signaling, such as
TGFBI,
PGF, and
IGFBP1, were observed in non-
O. viverrini-associated CCA. Even though the growth inhibitory effects of BBR on Ham-1 proliferation in vitro and in vivo were weak, BBR could effectively inhibit G1 to S phase cell cycle progression in Ham-1 cells, which is comparable to those in QBC939 [
20]. G1 phase cell cycle arrest is mainly due to the inhibition of nuclear cyclin D1 and cyclin E accumulations in tumor cells demonstrated by immunohistochemical staining. Similar results were reported in a prostate cancer and the human CCA cell line; QBC939 [
19,
20].
Taken together, the hamster CCA cell line and allograft transplantation model were established herein. This model is fast, efficient, and rather inexpensive when compared to the other in vivo CCA models. It might be a suitable system for anti-cancer agent screening.
National Research University1070
Office of the Higher Education CommissionKhon Kaen University540504
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by a grant from the National Research University (grant no. 1070), Office of the Higher Education Commission, through the Health Cluster (SHeP-GMS), Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen University research fund, 2553-2554 (grant no. 540504 to KV), and a grant for new researcher from Khon Kaen University, Thailand (to KV). NP was scholarship recipient from the National Research University Project, Khon Kaen University. We would like to thank Professor James A. Will, University of Wisconsin, Madison, USA, for the English presentation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Shin HR, Oh JK, Masuyer E, Curado MP, Bouvard V, Fang YY, Wiangnon S, Sripa B, Hong ST. Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma: an update focusing on risk factors. Cancer Sci 2010;101:579-585.
- 2. Sripa B, Pairojkul C. Cholangiocarcinoma: lessons from Thailand. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2008;24:349-356.
- 3. Khan SA, Davidson BR, Goldin R, Pereira SP, Rosenberg WM, Taylor-Robinson SD, Thillainayagam AV, Thomas HC, Thursz MR, Wasan H. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma: consensus document. Gut 2002;51(suppl 6):VI1-VI9.
- 4. Morise Z, Sugioka A, Tokoro T, Tanahashi Y, Okabe Y, Kagawa T, Takeura C. Surgery and chemotherapy for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Hepatol 2010;2:58-64.
- 5. Thamavit W, Bhamarapravati N, Sahaphong S, Vajrasthira S, Angsubhakorn S. Effects of dimethylnitrosamine on induction of cholangiocarcinoma in Opisthorchis viverrini-infected Syrian golden hamsters. Cancer Res 1978;38:4634-4639.
- 6. Boonjaraspinyo S, Wu Z, Boonmars T, Kaewkes S, Loilome W, Sithithaworn P, Nagano I, Takahashi Y, Yongvanit P, Bhudhisawasdi V. Overexpression of PDGFA and its receptor during carcinogenesis of Opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma. Parasitol Int 2012;61:145-150.
- 7. Prakobwong S, Khoontawad J, Yongvanit P, Pairojkul C, Hiraku Y, Sithithaworn P, Pinlaor P, Aggarwal BB, Pinlaor S. Curcumin decreases cholangiocarcinogenesis in hamsters by suppressing inflammation-mediated molecular events related to multistep carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer 2011;129:88-100.
- 8. Pinlaor S, Sripa B, Ma N, Hiraku Y, Yongvanit P, Wongkham S, Pairojkul C, Bhudhisawasdi V, Oikawa S, Murata M, Semba R, Kawanishi S. Nitrative and oxidative DNA damage in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients in relation to tumor invasion. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:4644-4649.
- 9. Thanan R, Murata M, Pinlaor S, Sithithaworn P, Khuntikeo N, Tangkanakul W, Hiraku Y, Oikawa S, Yongvanit P, Kawanishi S. Urinary 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine in patients with parasite infection and effect of antiparasitic drug in relation to cholangiocarcinogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2008;17:518-524.
- 10. Boonmars T, Wu Z, Boonjaruspinyo S, Pinlaor S, Nagano I, Takahashi Y, Kaewsamut B, Yongvanit P. Alterations of gene expression of RB pathway in Opisthorchis viverrini infection-induced cholangiocarcinoma. Parasitol Res 2009;105:1273-1281.
- 11. Sawanyawisuth K, Silsirivanit A, Kunlabut K, Tantapotinan N, Vaeteewoottacharn K, Wongkham S. A novel carbohydrate antigen expression during development of Opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma in golden hamster: a potential marker for early diagnosis. Parasitol Int 2012;61:151-154.
- 12. Silsirivanit A, Araki N, Wongkham C, Pairojkul C, Narimatsu Y, Kuwahara K, Narimatsu H, Wongkham S, Sakaguchi N. A novel serum carbohydrate marker on mucin 5AC: values for diagnostic and prognostic indicators for cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer 2011;117:3393-3403.
- 13. Flavell DJ, Lucas SB. Promotion of N-nitrosodimethylamine-initiated bile duct carcinogenesis in the hamster by the human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini. Carcinogenesis 1983;4:927-930.
- 14. Seubwai W, Vaeteewoottacharn K, Hiyoshi M, Suzu S, Puapairoj A, Wongkham C, Okada S, Wongkham S. Cepharanthine exerts antitumor activity on cholangiocarcinoma by inhibiting NF-κB. Cancer Sci 2010;101:1590-1595.
- 15. Imanshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H. Pharmacological and therapeutic effects of Berberis vulgaris and its active constituent, berberine. Phytother Res 2008;22:999-1012.
- 16. Tang J, Feng Y, Tsao S, Wang N, Curtain R, Wang Y. Berberine and Coptidis rhizoma as novel antineoplastic agents: a review of traditional use and biomedical investigations. J Ethnopharmacol 2009;126:5-17.
- 17. Letasiová S, Jantova S, Cipak L, Muckova M. Berberine-antiproliferative activity in vitro and induction of apoptosis/necrosis of the U937 and B16 cells. Cancer Lett 2006;239:254-262.
- 18. Hwang JM, Kuo HC, Tseng TH, Liu JY, Chu CY. Berberine induces apoptosis through a mitochondria/caspases pathway in human hepatoma cells. Arch Toxicol 2006;80:62-73.
- 19. Mantena SK, Sharma SD, Katiyar SK. Berberine, a natural product, induces G1-phase cell cycle arrest and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2006;5:296-308.
- 20. He W, Wang B, Zhuang Y, Shao D, Sun K, Chen J. Berberine inhibits growth and induces G1 arrest and apoptosis in human cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 cells. J Pharmacol Sci 2012;119:341-348.
- 21. Kaewkong W, Choochote W, Kanla P, Maleewong W, Intapan PM, Wongkham S, Wongkham C. Chromosomes and karyotype analysis of a liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini, by scanning electron microscopy. Parasitol Int 2012;61:504-507.
- 22. Tengchaisri T, Chawengkirttikul R, Rachaphaew N, Reutrakul V, Sangsuwan R, Sirisinha S. Antitumor activity of triptolide against cholangiocarcinoma growth in vitro and in hamsters. Cancer Lett 1998;133:169-175.
- 23. Tengchaisri T, Prempracha N, Thamavit W, Boonpucknavig S, Sriurairatana S, Sirisinha S. Establishment and characterization of cell lines from liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma induced in a hamster model. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 1995;26:231-239.
- 24. Jinawath N, Chamgramol Y, Furukawa Y, Obama K, Tsunoda T, Sripa B, Pairojkul C, Nakamura Y. Comparison of gene expression profiles between Opisthorchis viverrini and non-Opisthorchis viverrini associated human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2006;44:1025-1038.
Fig. 1Ham-1 cell line. (A) A mixture of CCA cells and stromal cells were isolated and cultured for a week. Arrowheads indicate CCA cell clusters surrounded by fibroblasts. (B) Ham-1 cells at the 15th passage. Ham-1 cells exhibited polygonal shapes. Pictures were taken under a phase contrast microscope at ×100 magnification. (C) Ham-1 chromosome. Ham-1 cells were prepared and stained as previously described [
21]. Pictures on the left represent diploid chromosomes (2n=44) (upper) and polyploid chromosomes (lower). Pictures were taken under a light microscope using an oil immersion lens (×1,000). A representative diploid karyotype is presented on the right.
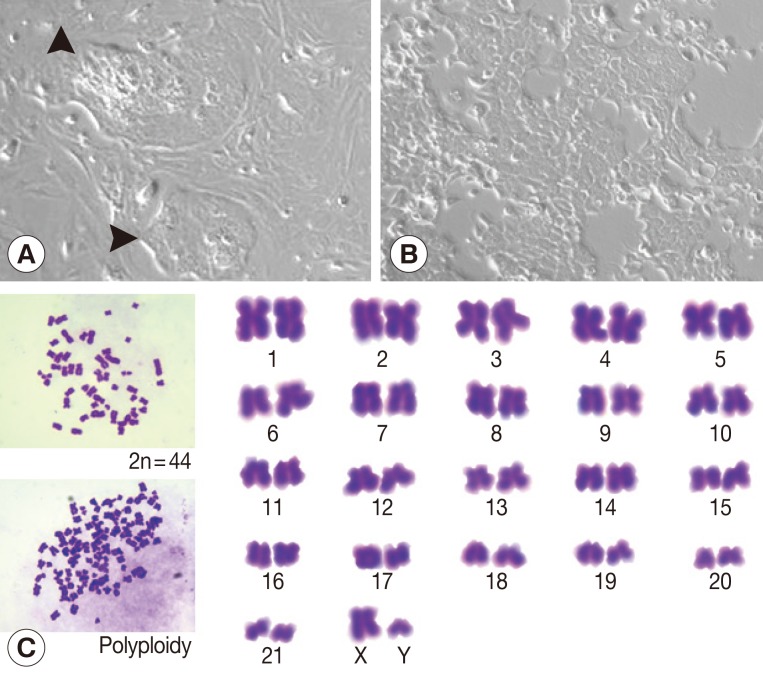
Fig. 2Ham-1 allograft tumors. (A) 2×105 or 5×105 Ham-1 cells were injected intradermally into the hamster skin (n=10/group). Tumors were successfully formed at all injected sites and were collected on day 24. The tumors were weighed. Tumor weights were correlated with the starting cell numbers. Tumors within the hamster skin were demonstrated in the small insets. (B) The allograft transplanted tumors exhibited similar histopathological properties as the primary tumor; strongly positive tumor cell cytoplasmic immunostaining for cytokeratin 19 and positive stromal staining for a myofibroblast marker (α-smooth muscle actin). Pictures were taken under light microscopy (×100). Bar=100 µm.
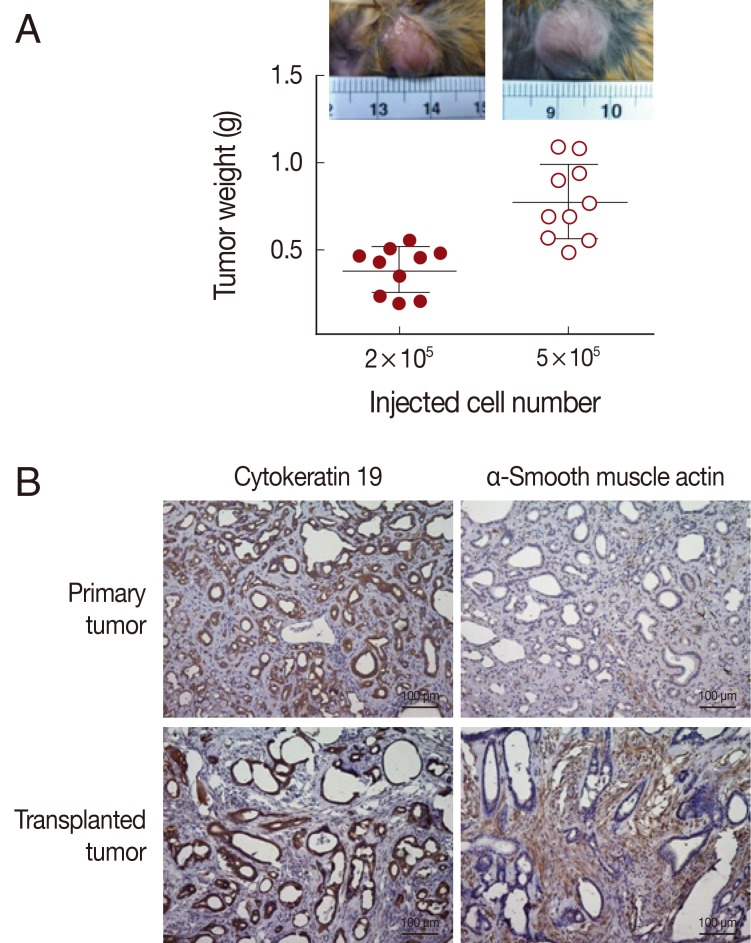
Fig. 3BBR inhibited Ham-1 proliferation and induced G1 cell cycle arrest in vitro. (A) Ham-1 cells were treated with various concentrations of BBR for 24 hr and 48 hr. The anti-proliferative effects were determined by the MTT assay. The percent cell numbers relative to untreated cells are presented as the mean±SD of 3 independent experiments. (B) Effects of BBR on cell cycle distribution were checked by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry analysis. The percentages of cells in each phase are indicated. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.
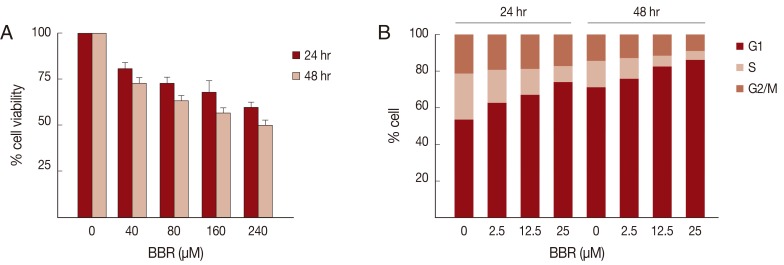
Fig. 4In vivo anti-tumor effects of BBR on the Ham-1 allograft hamster model. 5×105 cells of Ham-1 were injected intradermally into the dorsal skin of hamster (n=10/group). 10 mg/kg of BBR were given orally every day for 21 days. Equal volumes of drinking water were given to the control group. (A) Average weights of hamsters were compared. (B) Tumor weights were determined and representative tumors from control and BBR groups are shown (small inset). (C) The proliferative index (PCNA) and expressions of cell cycle control proteins (cyclin D1 and cyclin E) of Ham-1 cells in tumor tissues were assessed by immunohistochemistry. Pictures were taken under light microscope (×400). Bar=20 µm. (D) IHC scores were determined by 2 independent assessors and presented as mean±SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.001, vs the control group.