Abstract
To identify sequences of Entamoeba histolytica associated with the development of amebic liver abscess (ALA) in hamsters, subtractive hybridization of cDNA from E. histolytica HM-1:IMSS under 2 growth conditions was performed: 1) cultured in axenic medium and 2) isolated from experimental ALA in hamsters. For this procedure, 6 sequences were obtained. Of these sequences, the mak16 gene was selected for amplification in 29 cultures of E. histolytica isolated from the feces of 10 patients with intestinal symptoms and 19 asymptomatic patients. Only 5 of the 10 isolates obtained from symptomatic patients developed ALA and amplified the mak16 gene, whereas the 19 isolates from asymptomatic patients did not amplify the mak16 gene nor did they develop ALA. Based on the results of Fisher's exact test (P<0.001), an association was inferred between the presence of the mak16 gene of E. histolytica and the ability to develop ALA in hamsters and with the patient's symptoms (P=0.02). The amplification of the mak16 gene suggests that it is an important gene in E. histolytica because it was present in the isolates from hamsters that developed liver damage.
-
Key words: Entamoeba histolytica, subtraction hybridization, mak16 gene, amebic liver abscess
Amebiasis is a disease of global importance caused by the protozoan
Entamoeba histolytica. It is estimated that between 40,000 and 110,000 people die from this disease annually [
1]. The protozoan has 2 stages: the cyst, which is its infectious form, and the trophozoite, which is the invasive form. Transmission is achieved by the consumption of water and food contaminated with mature cysts. This protozoan can live as commensals in the large intestine or invade the intestinal mucosa, causing ulcerations and extraintestinal locations, predominantly in the liver [
2]. There are characteristic molecules involved in the virulence of the parasite, such as cysteine proteases, pore-forming proteins and lectins, which allow various activities, such as phagocytosis and tissue invasion [
3,
4]. It has been demonstrated that the inhibition of gene expression using antisense sequences blocks the production of molecules that can decrease virulence-altering cytopathic or cytotoxic events or phagocytosis [
5,
6,
7,
8]. However, blocking these cellular factors does not completely inhibit the pathogenicity of the protozoan.
It has been reported that transcriptomes from cell lines derived from the HM-1:IMSS strain have lost the ability to cause amebic liver abscesses (ALA) compared with virulent cell lines of the same strain, and several genes were identified, including ribosomal proteins, grainin-1, flavoproteins, GTP binding proteins, and GTPase, which confer resistance to bacterial infections, Ariel-1, and genes that encode proteins rich in lysine and glutamic acid [
9]. In addition, it has been shown that trophozoites of the
E. histolytica strain HM-1: IMSS can be cultured in TYI-S-33 medium for 1 or more years and demonstrate different levels of virulence with respect to trophozoites that have passed through the hamster liver due to the rapid response of the host's defense mechanisms [
10]. To determine which molecules enable the differentiation between strains that cause damage from strains that do not cause damage, we used in vivo models, such as the hamster, that develops ALA with similar characteristics to human abscesses [
11]. In addition, the molecules that are expressed in this process represent probable pathogenicity markers. Interestingly, the
mak16 gene was obtained by hybridization subtraction of an invasive amoeba from another amoeba that is not. In addition, it has been reported that this gene is involved in metabolic processes, such as the transport of molecules to the nucleolus and in ribosome biosynthesis. It has also been described that
mak16 mutants sensitive to temperature do not allow G1 phase cell cycle arrest to occur.
Trophozoites of
E. histolytica HM-1:IMSS were axenically cultured in TYI-S-33 medium (TAXE) [
12] and divided into 2 groups. One group consisted of 10
6 trophozoites that were intrahepatically inoculated into 2 male hamsters (
Mesocricetus auratus), 6-week-old, with an average weight of 50 g [
13]. Eight days post-inoculation, laparotomy was performed, and the trophozoites were isolated and cultured in TYI-S-33 media (TALA).
The RNA from a suspension of 103
E. histolytica TAXE trophozoites and an equal number of TALA trophozoites was extracted using an RNAqueous kit (Ambion, Austin, Texas, USA), and subtractive hybridization was performed using the PCR-Select™ cDNA subtraction kit (Clontech, Palo Alto, California, USA). The cDNAs (100 ng) from the amoebas that had passed through the hamster liver and did not hybridize with the culture amebas were cloned into the pCR® 2.1 TOPO vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA) and then transformed into E. coli TOP10 competent bacteria. Subsequently, the plasmid DNA was isolated with a Miniprep kit (Roche, Penzberg, Germany).
For the sequencing reaction, we used 200 ng of plasmid DNA, 10× enzyme buffer, 8 U of
Taq polymerase, 15 mM MgCl
2, and 200 µM nucleotides. The sequencing was performed as follows: 1 cycle of denaturation for 5 min, 25 cycles of 96℃ for 10 sec, 50℃ for 5 min, and 60℃ for 4 min and 1 cycle of 60℃ for 7 min. The ABIPRISM model 310, v.3.4 ABI-CE 1 v.3.2 software was used for sequencing. The obtained DNA sequences were compared to the TIGR
E. histolytica genome and to sequences in the GenBank, KEGG
E. histolytica and Pathema-Entamoeba databases [
14].
E. histolytica cysts were collected from the feces of 29 patients (aged 15-20 years). Ten of the patients had intestinal symptoms (constipation alternating with diarrhea or semiformed stools, abdominal cramps), and 19 patients were asymptomatic. The Faust method [
15] was used, and the cysts were cultured in Robinson medium [
16]. To identify
E. histolytica isolates, amplification was performed for the 530-bp
enhhic gene, which encodes the 30-kDa cysteine protease (data not shown) [
17].
Subsequently, each isolate (10
5 trophozoites) was inoculated intrahepatically in groups of 2 male hamsters (
M. auratus). Eight days later, the liver was removed, and the trophozoites of
E. histolytica were recovered in Robinson medium. Next, 10
4 trophozoites were harvested, and their DNA was extracted using the Wizard genomic kit (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA). Oligonucleotides were designed to amplify the
mak16 gene using the PRIMER3 program (
http://www-genome.wi.mit.edu/cgi-bin/primer/primer3_www.cgi): F, 5'-CGAATGGCCAAACTTGATTT-3'; R, 5'-CAAACGTT CTGCCCAATCTT-3'. Amplification was performed using PCR in a 25-µl reaction mixture containing the following components: 800 ng of amoeba DNA cultured in Robinson medium, 1× enzyme buffer, 1.5 mM MgCl
2, 200 µM of each dNTPs, 0.05 µM primers and 1.5 U of
Taq polymerase. The amplification program consisted of 1 cycle of 94℃ for 5 min, 30 cycles of 94℃ for 1 min and 30 sec, 55℃ for 1 min and 72℃ for 2 min, and 1 extension cycle of 72℃ for 15 min. Subsequently, the amplified product was separated on a 1.5% agarose gel, stained with ethidium bromide and visualized using a UV light transilluminator. The amplicons were sequenced according to the described procedure and compared with the
mak16 sequence reported in GenBank. The use of
E. histolytica cultures as well as the management of cysts obtained from the feces samples of patients was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez (HIMFG). All of the clinical investigations were performed according to the principles expressed in the Helsinki Declaration. Animals used in this experiment as well as the procedures for their sacrifice were performed according to the technical specifications delineated in the Mexican Official Standard (NOM-062-ZOO-1999) for the production, care and use of laboratory animals.
We performed Fisher's exact test with PASW statistics 18 to determine the association between the development of ALA in hamsters and the amplification of the mak16 gene and between the presence of intestinal symptoms and the amplification of the mak16 gene.
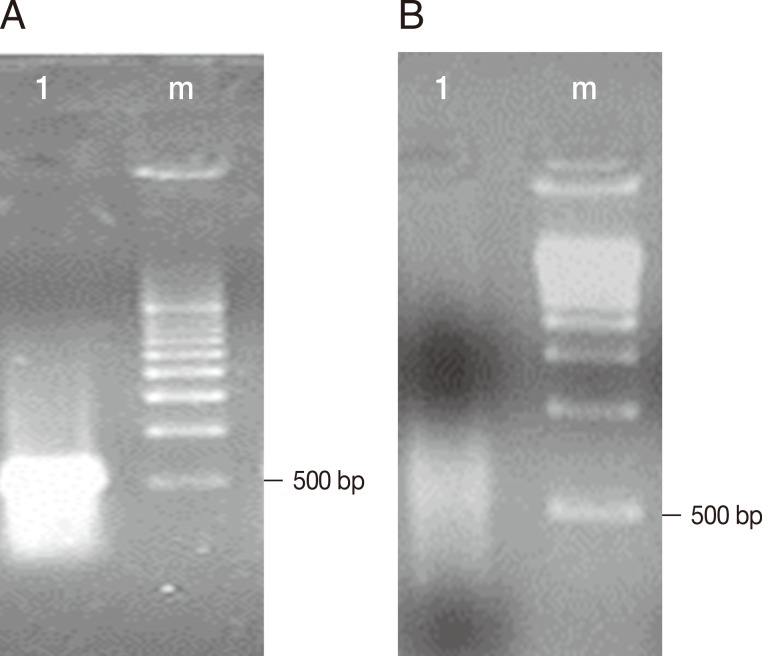
Fig. 1A shows the cDNA of trophozoites of
E. histolytica TALA obtained before subtractive hybridization with trophozoites of
E. histolytica TAXE, and an intense band with a molecular size between 500 and 1,000 bp was observed.
Fig. 1B shows the decrease in the concentration of cDNA from trophozoites of
E. histolytica TALA after subtractive hybridization.
Table 1 shows that the sequences analyzed, which corresponded to 6 sequences obtained by subtractive hybridization, demonstrated a similarity with proteins reported in the database of the Genomic Research Institute for
E. histolytica. These proteins were ribosomal protein L30 of the 60S subunit (XP_649197.1, 360 bp), nitrile hydratase alpha chain (CAC83631.1, 79 bp), MAK16 (XP_655185.1, 360 bp), cyclophilin (AF017993.1, 520 bp), hemolysins (HLY1, 5mc1, 5mcz y4, 475 bp), episomal rRNA (Z29969.1, 475 bp), and 40s ribosomal protein S3a (XM_647307.2, 257 bp).
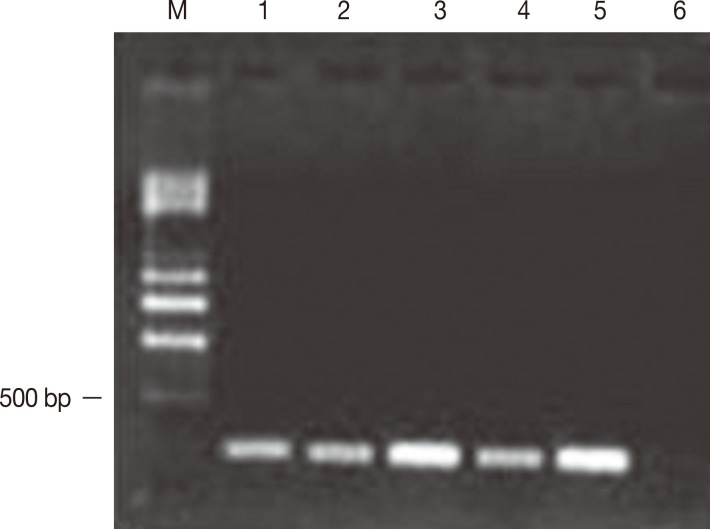
Five of the 10 isolates of
E. histolytica obtained from samples of the feces of symptomatic patients developed amebic abscesses in the hamsters' livers and reached 50% of the tissue, including the parenchyma and the internal region of the organ. In addition, these isolates amplified a 216-bp fragment corresponding to the
mak16 gene (
Fig. 2). Nineteen isolates from asymptomatic patients did not amplify the
mak16 gene and did not result in the development of ALA in hamsters. The protein sequence of
mak16 presented alignment with the reported sequence pfam04874 with an E value of 3.35e
-06.
Table 2 shows the comparison of a specific protein region of
mak16 of
E. histolytica vs the protein sequences reported for
mak16 in 3 parasites (the flatworm parasite
Schistosoma mansoni and the protozoans
Cryptosporidium muris and
Toxoplasma gondii), and the percentages obtained were less than 50%. With respect to the amplifications obtained from the isolates from patients who developed ALA, 3 of the 4 isolates of
E. histolytica exhibited an identity of >93%, whereas the other isolate presented an identity of 56%. The confidence index analyzed using the Fisher's exact test was
P<0.001 between ALA and the amplification of the
mak16 gene and
P=0.002 between the appearance of symptoms in patients and the amplification of the gene.
We identified the
mak16 gene when it was expressed in trophozoites from the axenic strain of
E. histolytica HM-1:IMSS, the virulence of which was stimulated by passage through the hamster liver. These virulent trophozoites were subjected to subtractive hybridization with trophozoites of the same strain that were not passaged through the hamster liver. However, this strain demonstrated attenuated virulence with longer culture time. These procedures occurred because the trophozoites in culture frequently changed their phenotypes and lost their virulence in axenic cultures, which was recovered by passage through the hamster liver [
18]. The hepatic abscess that developed with isolates obtained from patients' feces samples presented variability in size, i.e., from punctiform lesions to masses that encompassed 50% of the organ. This finding suggests that
E. histolytica exhibits different levels of pathogenicity. Thus, we may infer that the ability to cause biological damage is associated with different factors of the parasite [
19].
Alignment of the amino acid sequences of the mak16 obtained from the patients' samples showed identity greater than 93% with respect to E. histolytica HM-1:IMSS. Thus, we can infer that the trophozoites of E. histolytica present genetic diversity in the mak16 that could be correlated with different pathogenicity levels. The development of ALA as well as the host-parasite interaction has been reported; nevertheless, the mak16 gene has not been studied in E. histolytica.
The mak16 gene demonstrated its origin when were studied some strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (K1 killers), which secretes a protein toxin that kills other sensitive strains. The genes encoding toxin production and resistance are localized on a 1.5-megadalton linear double-stranded (ds) RNA molecule known as M1. There are at least 28 nuclear genes that are required for the replication or maintenance of M dsRNA or killer plasmid. To further study and control the interactions of mak genes and the killer plasmid, were isolated a series of temperature-sensitive (Ts) mak mutants. The mak16 is defined by the thermosensitive lethal mak16-1 mutation, which results in the loss of M1 double-stranded RNA virus-like particles and is an essential gene localized on chromosome no. I. The mak16 gene was sequenced, and an open reading frame of 306 amino acids encoding a predicted protein of 35 kDa was found. In the C-terminal third of the MAK16 open reading frame is an acidic region in which 25 of 41 residues are either glutamate or aspartate. This region contains potential phosphorylation sites that are specific for serine or threonine residues. In addition, MAK16 proteins display a similar degree of sequence homology to the predicted protein CeMAK16 in Caenorhabditis elegans, the SmMAK16 gene in S. mansoni and the putative MAK16 protein in E. histolytica HM-1: IMSS.
A high degree of sequence conservation combined with the ability to direct nucleolar protein transport supports the hypothesis that
MAK16 proteins play a key role in the biogenesis of 60S ribosomal subunits [
20,
21]. Ribosomal synthesis is a process that consumes a large amount of cell resources and is thus tightly regulated [
22]. A change in the secretory pathway caused by stress may be due to the environment, i.e., the environment in which
E. histolytica is grown affects its expression of the
mak16 gene and thus influences the gene transcription of ribosomal proteins and rRNA. However, if MAK proteins intervene in the phosphorylation of kinase protein molecules important for intra- and intercellular communication, they may also affect the signal transduction process, reorganization of the cytoskeleton, and migration [
23]. Importantly, kinase proteins have recently been considered attractive targets for treatments against cancer and inflammatory processes [
24], which are events that have been associated with the mechanisms of invasiveness of
E. histolytica [
25]. Thus, identification of the
mak16 gene in relationship to the development of ALA indicates that it is an important gene in these processes.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this study.
References
- 1. Walsh JA. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis 1986;8:228-238.
- 2. Espinosa-Cantellano M, Martínez-Palomo A. Pathogenesis of intestinal amebiasis: from molecules to disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 2000;13:318-331.
- 3. Santi-Rocca J, Rigothier MC, Guillén N. Host-microbe interactions and defense mechanisms in the development of amoebic liver abscesses. Clin Microbiol Rev 2009;22:65-75.
- 4. Weber C, Guigon G, Bouchier C, Frangeul L, Moreira S, Sismeiro O, Gouyette C, Mirelman D, Coppee JY, Guillén N. Stress by heat shock induces massive down regulation of genes and allows differential allelic expression of the Gal/GalNAc lectin in Entamoeba histolytica. Eukaryot Cell 2006;5:871-875.
- 5. Gilchrist CA, Petri WA Jr. Using differential gene expression to study Entamoeba histolytica pathogenesis. Trends Parasitol 2009;25:124-131.
- 6. MacFarlane RC, Singh U. Identification of differentially expressed genes in virulent and nonvirulent Entamoeba species: potential implications for amebic pathogenesis. Infect Immun 2006;74:340-351.
- 7. Biller L, Schmidt H, Krause E, Gelhaus C, Matthiesen J, Handal G, Lotter H, Janssen O, Tannich E, Bruchhaus I. Comparison of two genetically related Entamoeba histolytica cell lines derived from the same isolate with different pathogenic properties. Proteomics 2009;9:4107-4120.
- 8. Biller L, Davis PH, Tillack M, Matthiesen J, Lotter H, Stanley SL Jr, Tannich E, Bruchhaus I. Differences in the transcriptome signatures of two genetically related Entamoeba histolytica cell lines derived from the same isolate with different pathogenic properties. BMC Genomics 2010;11:63.
- 9. Faust DM, Guillen N. Virulence and virulence factors in Entamoeba histolytica, the agent of human amoebiasis. Microbes Infect 2012;14:1428-1441.
- 10. Tsutsumi V, Mena-Lopez R, Anaya-Velázquez F, Martínez-Palomo A. Cellular bases of experimental amebic liver abscess formation. Am J Pathol 1984;117:81-91.
- 11. Bruchhaus I, Roeder T, Lotter H, Schwerdtfeger M, Tannich E. Differential gene expression in Entamoeba histolytica isolated from amoebic liver abscess. Mol Microbiol 2002;44:1063-1072.
- 12. Diamond LS, Harlow DR, Cunnick CC. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1978;72:431-432.
- 13. Crisóstomo-Vázquez M del P, Jiménez-Cardoso E, Arroyave-Hernández C. Entamoeba histolytica sequences and their relationship with experimental liver abscess in hamsters. Parasitol Res 2006;98:94-98.
- 14. Brinkac LM, Davidsen T, Beck E, Ganapathy A, Caler E, Dodson RJ, Durkin AS, Harkins DM, Lorenzi H, Madupu R, Sebastian Y, Shrivastava S, Thiagarajan M, Orvis J, Sundaram JP, Crabtree J, Galens K, Zhao Y, Inman JM, Montgomery R, Schobel S, Galinsky K, Tanenbaum DM, Resnick A, Zafar N, White O, Sutton G. Pathema: a clade-specific bioinformatics resource center for pathogen research. Nucleic Acids Res 2010;38:D408-D414.
- 15. Faust EC, Sawitz W, Tobie J, Odom V, Peres C, Lincicome DR. Comparative efficiency of various techniques for the diagnosis of protozoa and helminth in feces. J Parasitol 1939;25:241-261.
- 16. Robinson GL. The laboratory diagnosis of human parasitic amoebae. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1968;62:285-294.
- 17. Crisóstomo Vázquez P, Jiménez-Cardoso E. Genetic differentiation with restriction patterns between pathogenic and non-pathogenic monoxenic Entamoeba histolytica. Rev Invest Clin 2000;52:255-260.
- 18. Cruz-Reyes JA, Ackers JP. A DNA probe specific to pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Arch Med Res 1992;23:271-275.
- 19. Campbell D, Chadee k. Survival strategies of Entamoeba histolytica: Modulation of cell-mediated immune responses. Parasitol Today 1997;13:184-190.
- 20. Wickner RB, Leibowitz MJ. Mak mutants of yeast: mapping and characterization. J Bacteriol 1979;140:154-160.
- 21. Guerry-Kopecko P, Wickner RB. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mak mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 1980;144:1113-1118.
- 22. Milhon JL, Albert TJ, Vande Waa EA, O'Leary KA, Jackson RN, Kessler MA, Schuler LA, Tracy JW. SmMAK16, the Schistosoma mansoni homologue of MAK16 from yeast, target protein transport to the nucleolus. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2000;108:225-236.
- 23. Cheetham GM. Novel protein kinases and molecular mechanisms of Autoinhibition. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2004;14:700-705.
- 24. Zhao Y, Sohn JH, Warner JR. Autoregulation in the biosynthesis of ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol 2003;23:699-707.
- 25. Wickner RB. Host function of Mak16: G1 arrest by a mak16 mutant of Shaccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988;85:6007-6011.
Fig. 1cDNAs obtained from the hybridization of E. histolytica HM-1:IMSS TAXE (trophozoites from culture) and TALA (trophozoites from amebic liver abscess). The electrophoretic separation was performed using a 1.5% agarose gel. (A) Lane 1, cDNAs of trophozoites of E. histolytica TALA; Lane m, molecular weight marker pBR322 cut with AvaII/EcoR1 (BioRad). (B) Lane 1, cDNAs obtained after subtractive hybridization between trophozoites of E. histolytica TAXE and TALA. Lane m, molecular weight marker pBR322 cut with AvaII/EcoR1 (BioRad).
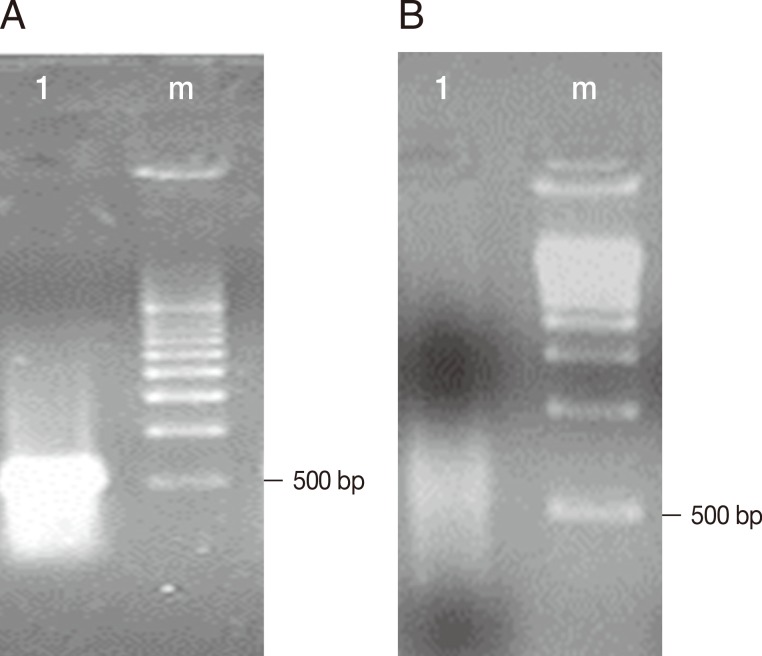
Fig. 2Amplification of mak16 of E. histolytica. Electrophoresis was performed using a 1.5% agarose gel. The amplification of mak16 was obtained from trophozoites without encystation that were obtained from patients with symptoms of amebiasis. The products were 216 bp in length. Lane m, molecular weight marker of 0.5-4.0 kb (BioRad). Five of the 10 isolates of E. histolytica that resulted in the development of liver abscesses amplified a 216-bp fragment corresponding to the mak16 gene; lanes 1-5, samples 1-5. Lane 6 is the reactive control.
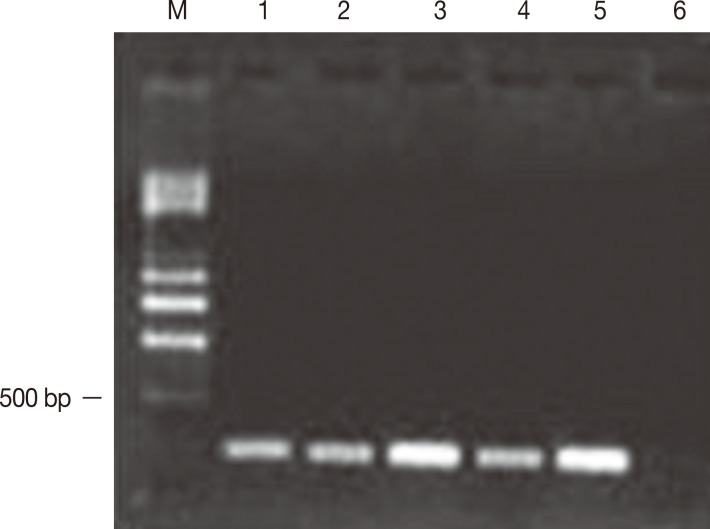
Table 1.DNA sequences of E. histolytica that were differentially expressed in the 2 culture conditions
Table 1.
|
Clone |
Size (bp) |
Identification |
GenBank accession no. |
|
1 |
360 |
Ribosomal protein L30 of the 60S subunit |
XP_649197.1 |
|
2 |
79 |
Nitrile hydratase alpha chain |
CAC83631.1 |
|
3 |
360 |
MAK16 |
XP_655185.1 |
|
4 |
520 |
Cyclophilin |
AF017993.1 |
|
5 |
475 |
Hemolysins (HLY1, 5mc1, 5mcz y4), episomal rRNA |
Z29969.1 |
|
6 |
257 |
40s ribosomal protein S3a |
XM_647307.2 |
Table 2.Comparison of a specific region of the MAK16 protein sequence from E. histolytica
Table 2.
|
gi |
Organism |
Protein region of MAK16 |
% identity |
|
256080140 |
Schistosoma mansoni
|
LRASTSSKEIYNI-DQsafEKALEAEE |
40 |
|
209878446 |
Cryptosporidium muris
|
LHEGAY-DGIYNY-PRgnfKKVDTEEV |
43 |
|
221484951 |
Toxoplasma gondii
|
LQQGVYGT-LYNFeSEktaEAEADQEE |
48 |
|
Strain |
E. histolytica HM-1:IMSS
|
MKDGVYDDLYENL-------QELEQNP |
100 |
|
Isolated 2 |
E. histolytica 2
|
MKDGVYDDLYENL-------QELEQNP |
93 |
|
Isolated 4 |
E. histolytica 4
|
MKDGVYDDLYENL-------QELEQNP |
94 |
|
Isolated 5 |
E. histolytica 5
|
MKDGVYDDLYENL-------QELEQTP |
95 |
|
Isolated 3 |
E. histolytica 3
|
MNDGVYDDLYENL-------QELEQTP |
56 |