Abstract
Wuchereria bancrofti, Dirofilaria immitis, and Dirofilaria repens are filarial nematodes transmitted by mosquitoes belonging to Culex, Aedes, and Anopheles genera. Screening by vector dissection is a tiresome technique. We aimed to screen filarial parasites in their vectors by single and multiplex PCR and evaluate the usefulness of multiplex PCR as a rapid xenomonitoring and simultaneous differentiation tool, in area where 3 filarial parasites are coexisting. Female mosquitoes were collected from 7 localities in Assiut Governorate, were microscopically identified and divided into pools according to their species and collection site. Detection of W. bancrofti, D. immitis, and D. repens using single PCR was reached followed by multiplex PCR. Usefulness of multiplex PCR was evaluated by testing mosquito pools to know which genera and species are used by filarial parasites as a vector. An overall estimated rate of infection (ERI) in mosquitoes was 0.6%; the highest was Culex spp. (0.47%). W. bancrofti, D. immitis, and D. repens could be simultaneously and differentially detected in infected vectors by using multiplex PCR. Out of 100 mosquito pools, 8 were positive for W. bancrofti (ERI of 0.33%) and 3 pools each were positive for D. immitis and D. repens (ERI 0.12%). The technique showed 100% sensitivity and 98% specificity. El-Nikhila, El-Matiaa villages, and Sahel Seleem district in Assiut Governorate, Egypt are still endemic foci for filarial parasites. Multiplex PCR offers a reliable procedure for molecular xenomonitoring of filariasis within their respective vectors in endemic areas. Therefore, it is recommended for evaluation of mosquito infection after lymphatic filariasis eradication programs.
-
Key words: Wuchereria bancrofti, Dirofilaria immitis, Dirofilaria repens, xenomonitoring, mosquito, multiplex PCR, Egypt
INTRODUCTION
Filariasis is one of the most common parasitic infections of the world. Approximately 106 million people are infected, with 1 billion people thought to be at risk of infection [
1]. Lymphatic filariasis caused by
Wuchereria bancrofti remains a public health problem in many tropical countries, including Nile delta and Assiut Governorate in Upper Egypt [
2,
3]. It is a serious tropical disease that can lead to chronic, disabling conditions such as lymphedema, elephantiasis, and genital deformities [
4].
Dirofilaria immitis and
D. repens are important filarioids of carnivores and are also accidental parasites of humans. An increase in annual numbers of reported cases in humans in areas previously recognized as non-endemic [
5], with 372 cases described between 1995 and 2000 [
6], has led to human dirofilariasis to be classified as an emerging zoonosis [
7]. Human dirofilariasis is manifested as subcutaneous or pulmonary nodules and in rare cases, eyes and periocular tissues can be involved, either caused by
D. immitis or
D. repens [
8]. Although these lesions are typically benign but they may be misdiagnosed as more important diseases, such as lung tumors, needing prompt unnecessary diagnostic procedures with attendant cost, discomfort, and morbidity [
9].
Xenomonitoring of
W. bancrofti,
D. immitis, and
D. repens when based on individual dissection of female mosquito vectors (
Culex,
Aedes, and
Anopheles sp.) [
10] is a time-consuming and barely applicable technique [
11]. Over the past decades, several PCR-based tools have been developed to detect filarial DNA in the definitive hosts and mosquito vectors [
12]. Multiplex PCR is a variant of PCR techniques in which 2 or more target sequences can be amplified by including more than 1 pair of primers in the same reaction [
13]. Multiplex PCR can offer scope for simultaneous detection of the tested filarial parasites for rapid surveillance and monitoring of mosquitoes [
14,
15].
The present study aimed to screen the presence of filarial parasites in mosquitoes in certain endemic localities in Assiut Governorate, Egypt by single and multiplex PCRs, and to compare the results of these 2 techniques in order to evaluate the usefulness of multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection and differentiation between the different filarial parasites in various mosquito species as a rapid tool for epidemiological surveillance.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sampling areas and mosquito collection
The study was done in Assiut Governorate, Egypt, located about 375 km to the south of Cairo. It was carried out in 7 districts; El-Nikhila, El-Matiaa and Mankabad villages, Sahel Seleem, El-Badary, Dairout, and Manfalout districts (
Fig. 1). A total of 2,500 adult female mosquitoes were collected (from March 2012 to December 2013) by using mechanical aspirators [
16]. The collected mosquitoes were microscopically identified according to a previously described method [
17]. Female mosquitoes were divided into 100 mosquito-pools according to species and collection site (each pool contained 25 mosquitoes). All pool specimens were labeled and maintained refrigerated until being used.
Two types of PCR assays were carried out for detection of filarial parasites (W. bancrofti, D. immitis, and D. repens) on all mosquito pools. Single PCR was firstly conducted followed by multiplex PCR. The same sets of primers used in single PCR were also applied in Multiplex PCR. The utility of Multiplex PCR in the simultaneous detection and differentiation of filarial parasites was evaluated by testing every pool of mosquito genera (Culex, Anopheles, and Aedes) to know which genera and species are used as a vector for filarial parasites in endemic localities, where they coexist.
Extraction of filarial DNA from mosquitoes
Genomic DNA was isolated from all mosquito pools using Qiagen tissue kit (QIAamp DNA Minikit, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Single PCR Assay
A Perkin Elmer 480 Thermal Cycler (Perkin Elmer Cetus, Norwalk, Connecticut, USA) was used for the PCR amplification process. A pair of forward and reverse PCR primers were used for each of the 3 filarial parasites. The oligonucleotide primers used for the PCR were obtained from (Metabion International AG, Martinsried, Germany). PCR procedure for detection of
W. bancrofti in mosquito vectors was executed according to Kithmini et al. [
18], using forward pWb12 F (5’-CTGAGTGAAATCAATGAACTGC-3’) and reverse pWb12 R (5’-GTCCATCCGATGAAGTTCCACC-3’) primers. Rishniw et al. [
19] described the PCR primers used for detection of
D. immitis and
D. repens in mosquito vectors, respectively. Forward DI COI-F1 (5’-AGTGTAGAGGGTCAGCCTGAGTTA-3’) and reverse DI COI-R1 (5’-ACAGGCACTGACAATACCAAT-3’) and
D. repens used forward primer Dr ITS2-F (5’-CATTGATAGTTTA-CATTCAAATAA-3’) and reverse Dr ITS2-R (5’-GATTCATTTATTGCATTA-AGCAAGC-3’). Each amplification reaction was done in a final volume of 50 μl containing 32.6 μl double-distilled water, 5 μl 10×Taq buffer, 3 μl MgCl
2 (25 mM), 2 μl dNTP (5 mM), 1 μl forward primer (10 pmol/μl), 1 μl reverse primer (10 pmol/μl), 0.4 μl Taq polymerase (5 U/μl), and 5 μl template (mosquito DNA extract). Total 35 amplification cycles with template denaturation at 94˚C (30 sec), primer annealing at 55˚C (30 sec), primer extension at 72˚C (30 sec), and an extra 30-sec extension as the final cycle were routinely used.
Multiplex PCR was done for all mosquito pools by using QIAamp DNA Minikit (Qiagen), following the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR products were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. DNA was visualized by an ultraviolet transilluminator following staining the gel with 2% ethidium bromide. A 100-bp ladder molecular weight marker (100 bp DNA ladder, Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA) and a negative control (non-blood fed mosquitoes, which were obtained from Research Institute of Medical Entomology, Dokki, Egypt) were used in each PCR reaction.
Statistical analysis
Data was collected and entered by using the Excel program, and the statistical analysis was done by using SPSS 20 program. The rate of infection in mosquitoes was adjusted for pooled samples, calculating the Estimated Rate of Infection (ERI) using the following formula: ERI = 1 - (1- x/m) 1/k [
20], where ‘x’ is the number of positive pools; ‘m’ is the number of examined pools, and ‘k’ the average number of specimens in each pool. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and the accuracy rate of multiplex PCR as compared to single PCR were calculated.
RESULTS
Mosquitoes collected from 7 localities in Assiut Governorate, Egypt were microscopically identified as Culex pipiens molestus (56%), C. antennatus (8%), C. pusillus (5%), Anopheles pharoensis (16%), and Aedes caspius (15%).
Preliminary, using single PCR technique could localize the presence of filarial nematodes only in 3 out of 7 localities. El-Nikhila was the only village where the 3 genera of filarial nematodes (
W. bancrofti, 4%;
D. immitis, 2%, and
D. repens, 2%) coexist. Sahel Seleem district was harboring
W. bancrofti (2%) and
D. immitis (1%), while El-Matiaa village was harboring
W. bancrofti (2%) and
D. repens (1%). We could say that
W. bancrofti is the most highly detected filarial nematode (
Table 1;
Fig. 2) with 0.33% ERI, while
D. immitis and
D. repens both had ERI of 0.12%. The overall estimated rate of infection of all collected mosquitoes with the 3 filarial parasites was 0.6%.
Afterwards, multiplex PCR had confirmed the single PCR results performed in the 3 localities (
Fig. 3A), in fact multiplex PCR was superior to single PCR as it positively detected
W. bancrofti in previously negative tested pool (
Fig. 3B). The sensitivity of multiplex PCR as compared to single PCR was 100%, and the specificity was 98%. The positive predictive value was 93%, the negative predictive value was 100%, and the accuracy rate was 99% (
Table 1).
Each pool of mosquito genera (
Culex,
Anopheles, and
Aedes) was tested by multiplex PCR to know which filarial nematode is the vector in the 3 localities (
Table 2;
Fig. 3C).
Culex spp. were found as the most common mosquito genus infected with filarial nematodes in all localities, especially in El-Nikhila village, with the highest ERI of 0.47% (
Table 2).
Since
Culex spp. had the highest ERI among the 3 mosquito genera, and El-Nikhila village harbored the 3 filarial nematodes, multiplex PCR was applied to determine the species of
Culex mosquitoes involved as the vector for these nematodes in El-Nikhila village.
C. pipiens was the vector for all 3 filarial nematodes (ERI, 3.6%);
C. antennatus was the vector for
D. repens (ERI, 0.89%), whereas
C. pusillus was the vector for
D. immitis (ERI, 0.89%) (
Table 3;
Fig. 3D).
DISCUSSION
Culex spp. were the most commonly collected mosquitoes (69%) throughout the period of the study. Southgate [
21] reported that
C. pipiens was widely distributed across Egypt; Khalil [
22] found it as the most predominant mosquito species in Upper Egypt. In Assiut Governorate, Abdel-Aal [
23], El-Nazer [
24], and Mahmoud [
25] found similar results.
El-Nikhila village had recorded the highest ERI (2%) with the 3 filarial parasites over El-Matiaa villages and Sahel Seleem district, and
Culex spp. was the predominant vector.
Culex pipiens molestus has the highest rate of infection (ERI, 2% and 0.89%) for
W. bancrofti and
D. immitis, respectively. Interestingly, the high
W. bancrofti infection rate in
C. pipiens molestus indicates the role of this species as a putative vector, as previously described [
24-
26]. Cancrini and Gabrielli [
10] and Capelli et al. [
27] added that
C. pipiens is not only the most efficient natural vector for
W. bancrofti, but also potential vectors of
D. immitis and
D. repens. It had to be in mind that Assiut Governorate villages had been enrolled as endemic foci in the international and national programs of elimination of lymphatic filariasis [
2]. Although efforts were done all over the last years, the mass drug administration (MDA) program and intensive use of residual insecticides for mosquito control [
28], vectors loaded with filarial parasites still exist. Abundance of vectors could be explained by environmental and biological features supporting vectors breeding in these localities. El-Nikhila, El-Matiaa villages, and Sahel Seleem district stretch along the banks of the Nile and have water canals traversing their agricultural lands boosting the presence of stagnant water. Besides, poor quality of sanitation accompanied by inadequate disposal of humans and water waste lead to an alteration in water quality parameters with low dissolved oxygen, favorable temperature, and pH which may be contributing to successful
C. pipiens mosquito breeding inside and/or near human habitations [
29]. Moreover, this provided favorable conditions for the bacteria, alga, and protozoa, which are chief food sources for mosquito larvae [
30]. In addition, dense vegetation covering throughout the periphery of water banks not only provides favorable oviposition sites but also protects mosquito larvae from predacious insects and fish [
31].
Bahgat et al. [
32] found
C. pipiens to be primarily anthropophagic (96% human feeding) and to be fairly endophagic as most of the collected engorged females were from indoors. Appearance of insecticides “Chlorpyrifos” resistant strain among Assiut
C. pipiens population might also decline the effort made in the elimination program and enhance the spread of vector-born disease [
33]. Previous documented factors in addition to earlier history of filariasis endemicity helped in making these localities foci for filarial parasites.
An overall ERI in mosquitoes was 0.6%, being higher in
Culex spp. and
Anopheles pharoensis (0.47% and 0.08%), respectively. Mosquito infection rate with filarial parasites in our study was higher than in previous studies performed in the same localities [
24-
26], as they were based on mosquito dissection only. Therefore, we used the multiplex PCR. Multiplex PCR confirmed the results given by single PCR done for each parasite. Moreover, multiplex PCR was more accurate than single PCR in detection of filarial infections in mosquitoes with 100% sensitivity and 98% specificity. This may be explained by the combined use of Hot Start Taq DNA polymerase with a unique PCR buffer specifically developed for multiplex PCR reactions. The newly developed reaction buffer containing factor MP and a special multiplex PCR-enhancing synthetic factor that provides an efficient primer annealing and extension. This synthetic factor increases the local concentration of primers at the template DNA and stabilizes specifically bound primers [
13]. This makes multiplex PCR as a good tool for simultaneous detection of
W. bancrofti,
D. immitis, and
D. repens in mosquitoes. Similar results were previously reported by Latrofa et al. [
15] in a study performed in Italy in which a duplex real-time PCR was used for the detection of and differentiation between
D. immitis and
D. repens in mosquitoes.
Data herein presented clearly indicate the usefulness of the molecular diagnosis assay for a broader field application in order to gain more information on the epidemiology of mosquitoes acting as vectors of filarial parasites. A continuous monitoring of infection rates for mosquito vector populations is pivotal to evaluate the success of an anti-filarial campaign in endemic areas. The advantages of using a highly sensitive molecular diagnostic tool for xenomonitoring was shown to be pivotal for assessing the efficacy and progress of eradication programs of human lymphatic filariasis based on MDA [
34].
In conclusion, results presented submit 100% sensitivity and 98% specificity of multiplex PCR herein used in field-collected samples, clearly representing an alternative to classic microscopic methods and to single PCR-based assay for xenomonitoring of W. bancrofti, D. immitis, and D. repens in mosquitoes, mainly in areas where these species are endemic and/or occur sympatrically. Multiplex PCR could differentiate between Dirofilaria species in the same reaction, in addition to being easier and time and effort saving, and was more sensitive than single PCR in detection of mosquito filarial infection. We have reached that El-Nikhila, El-Matiaa villages, and Sahel Seleem district in Assiut Governorate, Egypt are still endemic areas of filarial parasites. More attention of health workers is recommended for control and elimination of filarial diseases in these areas.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
Fig. 1.

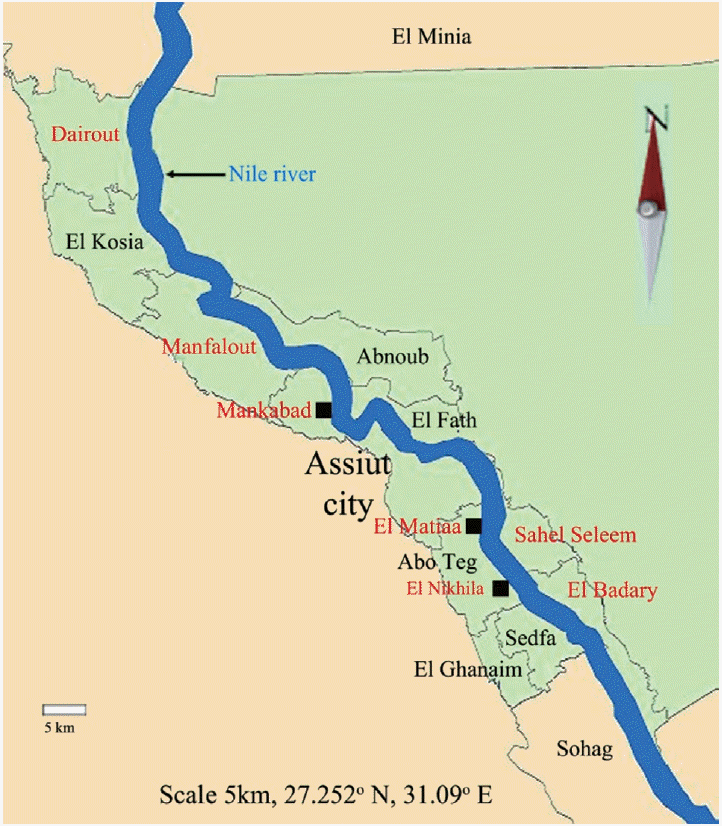
Fig. 2.Distribution of filarial parasites in different Assiut localities using single PCR pattern. M, 100 bp DNA marker; N, negative control (non-blood fed mosquitoes); lane1, El-Nikhila village; lane 2, El-Matiaa village; lane 3, Sahel Seleem district; lane 4, El-Badary district; lane 5,Mankabad village; lane 6, Dairout district; lane 7, Manfalout district. (A) W. bancrofti positive samples (lanes 1-3). (B) D. immitis positive samples (lanes 1, 3). (C) D. repens positive samples (lanes 1, 2).
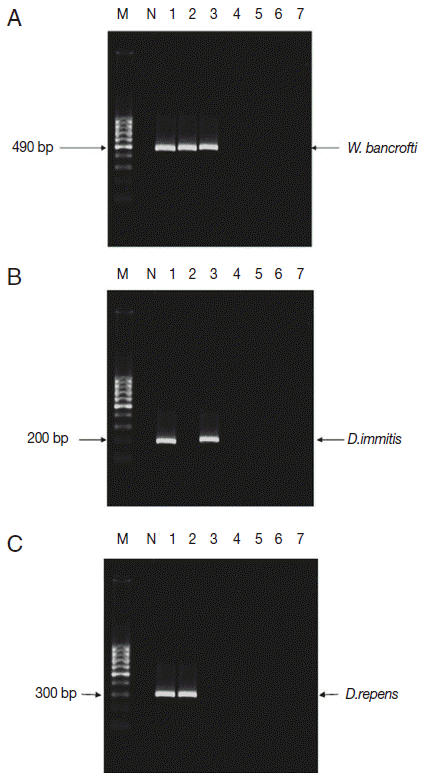
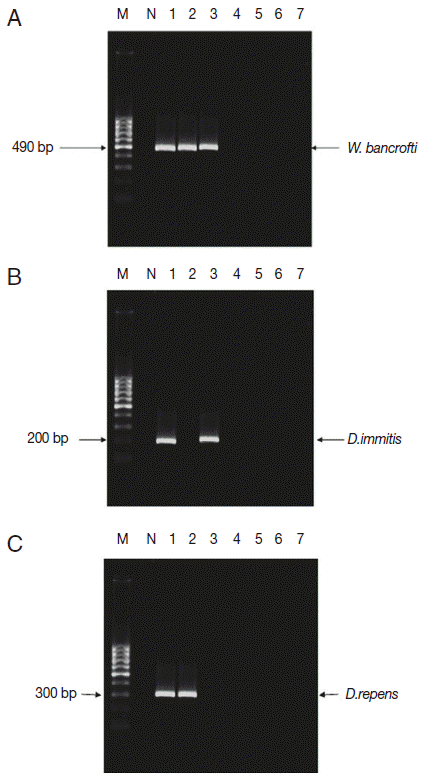
Fig. 3.Multiplex PCR pattern on 2% ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel. Lane 1, W. bancrofti; lane 2, D. immitis; lane 3, D. repens. (A) Multiplex PCR confirmed the results of single PCR in El-Nikhila, El-Matiaa villages and Sahel Seleem district. (B) Multiplex PCR detected a positive sample of W. bancrofti (lane 1) that could not be detected by single PCR in El-Nikhila village. (C) Distribution of filarial parasites among different mosquito genera using multiplex PCR. Lane 1, Culex spp.; lane 2, Anopheles spp.; lane 3, Aedes spp. (D) Distribution of filarial parasites among different Culex species in El-Nikhila village. Lane 1, Culex pipiens; lane 2, Culex antennatus; lane 3, Culex pusillus.
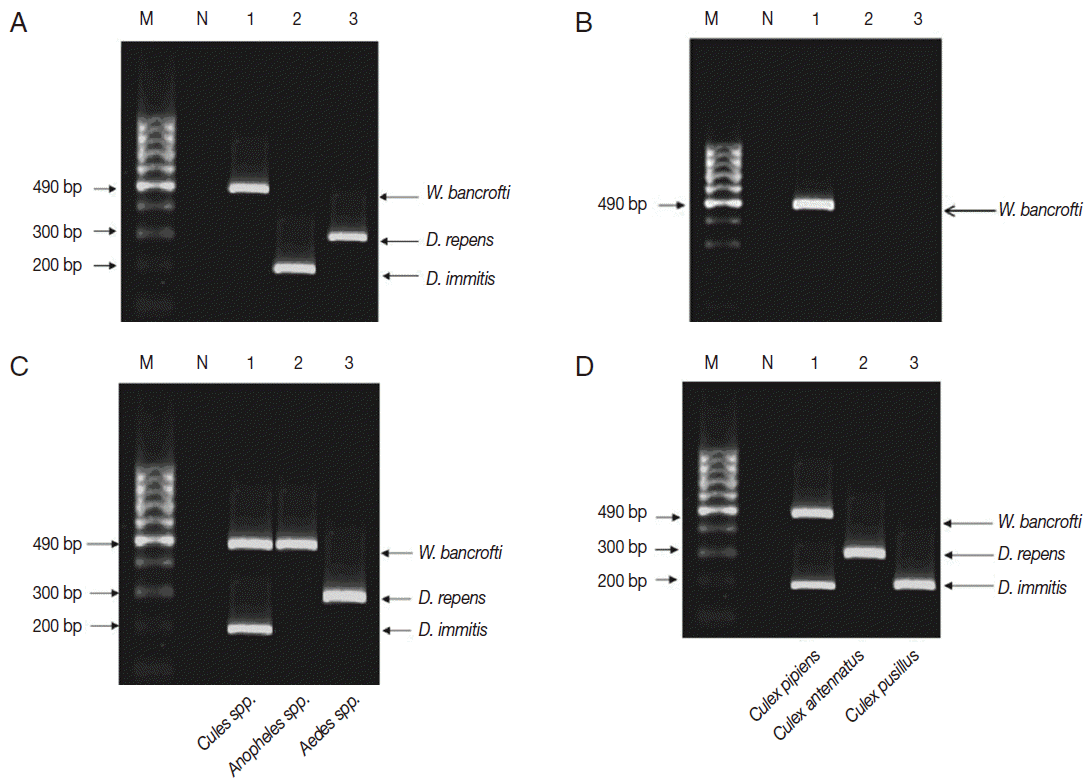
Table 1.Comparison between the results of positive pools for filarial parasites in 100 collected mosquito pools detected by single and multiplex PCR
Table 1.
|
Filarial parasites |
Locality |
No. of positive pools by single PCR |
No. of positive pools by multiplex PCR |
|
Wuchereria bancrofti
|
El-Nikhila |
3 |
4 |
|
El-Matiaa |
2 |
2 |
|
Sahel Seleem |
2 |
2 |
|
Dirofilaria immitis
|
El-Nikhila |
2 |
2 |
|
El-Matiaa |
0 |
0 |
|
Sahel Seleem |
1 |
1 |
|
Dirofilaria repens
|
El-Nikhila |
2 |
2 |
|
El-Matiaa |
1 |
1 |
|
Sahel Seleem |
0 |
0 |
|
Total |
|
13 |
14 |
Table 2.Distribution of filarial parasites among mosquito genera performed by multiplex PCR in different Assiut localities and estimated rate of infection (ERI)
Table 2.
|
Locality |
Mosquito vector |
No. of Pools |
W. Bancrofti
|
D. immitis
|
D. repens
|
|
No. of positive pools |
ERI (%) |
No. of positive pools |
ERI (%) |
No. of positive pools |
ERI (%) |
|
El Nikhila |
Culex sp. |
10 |
3 |
1.42 |
2 |
0.89 |
1 |
0.42 |
|
Anopheles sp. |
5 |
1 |
0.89 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
|
Aedes sp. |
5 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
1 |
0.89 |
|
El Matiaa |
Culex sp. |
10 |
2 |
0.89 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
|
Anopheles sp. |
5 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
1 |
0.89 |
|
Aedes sp. |
5 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
|
Sahel Seleem |
Culex sp. |
10 |
2 |
0.89 |
1 |
0.42 |
0 |
0.0 |
|
Anopheles sp. |
5 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
|
Aedes sp. |
5 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
Table 3.Distribution of filarial parasites among Culex spp. in El-Nikhila village performed by multiplex PCR and estimated rate of infection (ERI)
Table 3.
|
Culex spp. |
No. of Pools |
W. Bancrofti
|
D. immitis
|
D. repens
|
|
No. of positive pools |
ERI (%) |
No. of positive pools |
ERI (%) |
No. of positive pools |
ERI (%) |
|
Culex pipiens
|
5 |
2 |
2.0 |
1 |
0.89 |
0 |
0.0 |
|
Culex antennatus
|
5 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
1 |
0.89 |
|
Culex pusillus
|
5 |
0 |
0.0 |
1 |
0.89 |
0 |
0.0 |
References
- 1. Hopkins DR. Disease eradication. N Engl J Med 2013;368:54-63.
- 2. Ramzy RM, Goldman AS, Kamal HA. Defining the cost of the Egyptian lymphatic filariasis elimination programme. Filaria J 2005;4:7.
- 3. World Health Organization (WHO). Annual country reports, 2012. who.int/mapLibrary/Files/Maps/LF_2012.png
- 4. Addiss DG. Global elimination of lymphatic filariasis: origins, progress and challenges. Indian J Urol 2005;7:12-17.
- 5. Genchi C, Kramer LH, Rivasi F. Dirofilarial infections in Europe. Vector Borne Zoon Dis 2011;11:1307-1317.
- 6. Pampiglione S, Rivasi F. Human dirofilariasis due to Dirofilaria (Nochtiella) repens: an update of world literature from 1995 to 2000. Parassitologia 2000;42:231-254.
- 7. Abdel-Rahman SM, Mahmoud AE, Galal LA, Gustinelli A, Pampiglione S. Three new cases of human infection with Dirofilaria repens, one pulmonary and two subcutaneous, in the Egyptian governorate of Assiut. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 2008;102:499-507.
- 8. Orihel TC, Eberhard ML. Zoonotic filariasis. Clin Microbiol Rev 1998;11:366-381.
- 9. Athari A. Zoonotic subcutaneous dirofilariasis in Iran. Arch Iran Med 2003;65:63-65.
- 10. Cancrini G, Gabrielli S. Vectors of Dirofilaria nematodes. In Genchi C, Rinaldi L, Cringoli G eds, Biology, behavior and host/parasite relationships. In Dirofilaria immitis and D. repens in dog and cat and human infections. Napoli, Italy. Rolando; 2007, pp 49-58.
- 11. Bockarie MJ. Molecular xenomonitoring of lymphatic filariasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2007;77:591-592.
- 12. Thanchomnang T, Intapan PM, Lulitanond V, Sangmaneedet S, Chungpivat S, Taweethavonsawat P, Choochote W, Maleewong W. Rapid detection of Dirofilaria immitis in mosquito vectors and dogs using a real-time fluorescence resonance energy transfer PCR and melting curve analysis. Vet Parasitol 2010;168:255-260.
- 13. Toblas J, Vulukuru SR. Simple and rapid multiplex PCR for identification of the main human diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Microbiol Res 2012;167:564-570.
- 14. Mishra K, Raj DK, Hazra RK, Dash AP, Supakar PC. The development and evaluation of a single step multiplex PCR method for simultaneous detection of Brugia malayi and Wuchereria bancrofti. Mol Cell Probes 2007;21:355-362.
- 15. Latrofa MS, Montarsi F, Ciocchetta S, Annoscia G, Dantas-Torres F, Ravagnan S, Capelli G, Otranto D. Molecular xenomonitoring of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens in mosquitoes from north-eastern Italy by real-time PCR coupled with melting curve analysis. Parasit Vectors 2012;5:76.
- 16. Silver JB. Mosquito ecology: field sampling methods. 3rd ed. New York, USA. Springer; 2008.
- 17. Gad AM. Mosquitoes of the oasis of the Libyan Desert of Egypt. Bull Soc Entomol Egypt 1956;40:131-136.
- 18. Siridewa K, Karunanayake EH, Chandrasekharan NV. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)-based technique for the detection of Wuchereria bancrofti in human blood sample, hydrocele fluid and mosquito-vectors. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1996;54:72-76.
- 19. Rishniw M, Barr SC, Simpson KW, Frongillo MF, Franz M, Dominquez Alpizar JL. Discrimination between six species of canine microfilariae by a single polymerase chain reaction. Vet Parasitol 2006;135:303-314.
- 20. Cowling DW, Gardner IA, Johnson WO. Comparison of methods for estimation of individual-level prevalence based on pooled samples. Prev Vet Med 1999;39:211-225.
- 21. Southgate BA. Bancroftian filariasis in Egypt. Trop Dis Bull 1979;76:1045-1063.
- 22. Khalil GM. A preliminary survey of mosquitoes in Upper Egypt. J Egypt Public Health Assoc 1981;55:355-359.
- 23. Abdel-Aal AA. Survey and ecology of the mosquitoes with emphasis on the relationship between filariasis and culicids in Assiut Governorate. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Assiut University, Egypt. 1983.
- 24. El-Nazer MM. Parasitological and immunological studies on filarial worms in Assiut Governorate. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Medical Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, Egypt. 1990.
- 25. Mahmoud AE. Parasitological studies on filariasis in Assiut Governorate. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Medical Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, Egypt. 2004.
- 26. Hany AM, Hussein MS, Mandour AM. Complicated filariasis in rural Upper Egypt El-Nikhila, Assiut Governorate. Proceedings of 10th Annual Scientific Conference, April; 1992. 303:312.
- 27. Capelli G, Frangipande di Regalbono A, Simonato G, Cassini R, Cazzin S, Cancrini G, Otranto D, Pietrobelli M. Risk of canine and human exposure to Dirofilaria immitis infected mosquitoes in endemic areas of Italy. Parasit Vectors 2013;6:60.
- 28. Ramzy RM, El Setouhy M, Helmy H, Ahmad ES, Abd Elaziz KM, Farid HA, Shannon WD, Weil GJ. Effect of yearly mass drug administration with diethylcarbamazine and albendazole on bancroftian filariasis in Egypt: a comprehensive assessment. Lancet 2006;367:992-999.
- 29. Adebote DA, Oniye SJ, Muhammed YA. Studies on mosquitoes breeding in rock pools on inselbergs around Zaria, northern Nigeria. J Vector Borne Dis 2008;45:21-28.
- 30. Opoku AA, Ansa-Asare OD, Amoako J. The occurrences and habitat characteristics of mosquitoes in Accra, Ghana. West African J Appl Ecol 2007;11:99-107.
- 31. Keljo KS. Effects of hydrologic pulsing and vegetation on invertebrate communities in Wetlands. Electronic Thesis. Ohio State University; 2009. https://etd.ohiolink.edu/
- 32. Bahgat IM, El Kadi GA, Sowilem MM, El Sawaf BM. Host-feeding patterns of Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae) in a village in Qalubiya Governorate and in a new settlement in Ismailia Governorate. Bull Ent Soc Egypt 2004;81:77-84.
- 33. Emtithal AES, Thanaa AEB. Efficacy of some insecticides on field populations of Culex pipiens (Linnaeus) from Egypt. J Basic Appl Zool 2012;65:62-73.
- 34. Farid HA, Morsy ZS, Helmy H, Ramzy RM, El Setouhy M, Weil GJ. A critical appraisal of molecular xenomonitoring as a tool for assessing progress toward elimination of lymphatic filariasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2007;77:593-600.