Abstract
Leishmaniasis is a worldwide uncontrolled parasitic disease due to the lack of effective drug and vaccine. To speed up effective drug development, we need powerful methods to rapidly assess drug effectiveness against the intracellular form of Leishmania in high throughput assays. Reporter gene technology has proven to be an excellent tool for drug screening in vitro. The effects of reporter proteins on parasite infectivity should be identified both in vitro and in vivo. In this research, we initially compared the infectivity rate of recombinant Leishmania major expressing stably enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) alone or EGFP-luciferase (EGFP-LUC) with the wild-type strain. Next, we evaluated the sensitivity of these parasites to amphotericin B (AmB) as a standard drug in 2 parasitic phases, promastigote and amastigote. This comparison was made by MTT and nitric oxide (NO) assay and by quantifying the specific signals derived from reporter genes like EGFP intensity and luciferase activity. To study the amastigote form, both B10R and THP-1 macrophage cell lines were infected in the stationary phase and were exposed to AmB at different time points. Our results clearly revealed that the 3 parasite lines had similar in vitro infectivity rates with comparable parasite-induced levels of NO following interferon-γ/lipopolysaccharide induction. Based on our results we proposed the more reporter gene, the faster and more sensitive evaluation of the drug efficiency.
-
Key words: Leishmania major, EGFP, luciferase, amphotericin B, MTT, nitric oxide
INTRODUCTION
Leishmaniasis is an endemic disease in 98 countries and is caused by a protozoan parasite of the Trypanosomatidae family and
Leishmania genus. There are approximately 0.2-0.4 and 0.7-1.2 million annually new cases worldwide for visceral (VL) and cutaneous (CL) leishmaniasis, respectively [
1]. The known causative agents of CL include several species as
L. major,
L. tropica, and
L. mexicana [
2].
Leishmania are intracellular parasites with 2 principal forms including (i) an extracellular promastigote form in sandfly vectors and in vitro culture and (ii) an intracellular amastigote form in mammalian macrophages.
Macrophages are primary host cells that play a major role in antimicrobial host defence against
Leishmania [
3,
4]. Macrophages are activated by IFN-γ secreted from T-helper type 1 (Th1) cells to clear intracellular parasites by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) II mediated nitric oxide (NO) production from L-arginine [
5,
6]. Therefore, assays that use infected macrophages as a model to investigate these immune mechanisms provide an easy and reliable method of quantifying intracellular parasite survival [
7].
Despite many attempts, there is still no effective anti-leishmanial approach to control diseases, even in endemic areas. An increased rate of drug resistance and the high cost of therapy necessitate the continued effort to identify new drugs [
8]. There needs to be a simple, reliable, rapid, and valid drug screening system for the selection of efficient anti-leishmanial compounds that can be used for high throughput screening (HTS) with in vitro and in vivo assays [
8]. Currently, most laboratories assess drug effects using the classic microscopic method with Giemsa-staining and the counting of amastigotes in macrophages [
9]. Other methods, such as the MTT cell viability assay (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) [
10], the Almar blue assay [
11], and radiolabeled precursors [
12], are used to determine the inhibitory potential of drugs. However, there are various drawbacks such that these methods are not widely applicable for screening several drugs at the same time [
13]. Some problems that prevent their routine laboratory use include technical mistakes owing to lack of automation, steps that require high manipulation, their laborious nature, and potential health hazards from some reagents such as radioactive nucleotides [
14,
15].
Recently, reporter genes such as green fluorescent protein (GFP), luciferase (LUC), and other colorimetric enzymes like chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT), β-galactosidase, and secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) were used in different experiments as promising tools for monitoring disease progression and cell biological and antimicrobial activity against different pathogens [
16,
17]. Among the reporter genes, GFP and LUC are more attractive due to their benefits under different conditions; in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo [
18].
GFP is intrinsically fluorescent and can be detected easily and directly, without the need for any extra processing, by several instruments such as the fluorescent microscope, fluorimeter, and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Among different reporter genes, LUC has been introduced as a more efficient reporter in the HTS mode [
16,
19] for drug screening [
20] due to its high sensitivity and low background.
Despite many benefits, several limitations of EGFP (high background) [
8,
14] and LUC (high expense and cell lysis that makes it impossible to repeat the same experiment [
14] have restricted their usage [
14,
19]. Recently, scientists have been interested in transiently or stably manipulating many species and strains of
Leishmania to provide reporter parasites. Recombinant pathogens that express more than 1 reporter gene were generated to estimate the infection level with more accurate visibly and quantitatively through different signals derived from their expression by several instruments [
21]. Hence, a dual reporter gene was developed in several pathogens such as
Plasmodium [
22] and some types of viruses, including hepatitis [
21], to maximize the benefits of reporter genes.
Herein, we used a recombinant L. major that stably expresses 2 fused EGFP and LUC reporter genes. These exogenous genes were integrated into the 18S rRNA locus in the genome, and the host RNA polymerase I performed their cytosolic expression. The main purpose of this study was to evaluate the impact of reporter gene expression on the infectivity potential of recombinant parasites and NO production in infected cell lines. Also, we compared parasite sensitivity against amphotericin B (AmB) on different lines of parasites (wild-type and recombinant) and infected cell lines.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Parasite and cell culture
Wild-type (WT)
L. major parasite (strain MRHO/IR/75/ER) was grown at 26˚C in M199 medium (Sigma, Deisenhofen, Germany) supplemented with 5% hi-FCS (heat inactivated-fetal calf serum) (Gibco, Paisley, UK), 40 mM HEPES, 0.1 mM adenosine, 0.5 µg⁄ml hemin, 2 mM L-glutamine, and 50 µg⁄ml gentamycin (Sigma). Two recombinant lines,
L. majorEGFP [
19] and
L. majorEGFP-LUC [
23], encoding the EGFP and EGFP-LUC genes, respectively, were cultured under the same conditions after the integration of reporter genes into 18S rRNA locus. To maintain infectivity potential, 3 different lines of parasites were passaged in female BALB⁄c mice. Promastigotes in the stationary phase (at 5 days) were used to infect cells.
Two macrophage cell lines, B10R (an immortalized murine bone marrow-derived macrophage cell line, a gift from Prof. Martin Olivier, McGill University, Canada) and THP-1 (an immortalized human macrophage) were used. The B10R cells were cultured in phenol red-free DMEM media (Sigma) supplemented with 10% hi-FCS and incubated at 37˚C in humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Suspended THP-1 cells were stimulated and differentiated by 50 ng/ml of PMA (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, Sigma) in RPMI media (Sigma) with 10% hi-FCS to adhere overnight before use.
In vitro infectivity
The cells were harvested and seeded at a density of 3×105 cell/ml in 96-or 48-well flat bottom culture plates (Orange, California, USA) overnight. Then, all wells were washed to remove any unattached cells and were then separately infected with the stationary phase of 3 different parasite lines (L. majorWT, L. majorEGFP, and L. majorEGFP-LUC) and incubated at 37˚C with 5% CO2 overnight. After 4 hr, non-internalized parasites were removed by washing with culture media or PBS.
NO quantification by Griess reaction assay
Parasite-infected B10R cells were treated with various concentration (10, 50, 100, and 200 ng/ml) of recombinant murine interferon-γ (Gibco, Eggenstein, Germany) alone or in combination with 10 ng/ml LPS derived from
Salmonella abortusequi (Gibco) 24 hr post-infection and were further incubated at 37˚C for 6, 24, and 48 hr. Supernatants were collected at indicated time points to measure the produced NO using the Griess test [
7]. Briefly, the supernatants were mixed with Griess reagent (1% sulphanilamide, 0.1% naphthylethylendiamine dihydrochloride, 3% H
3PO
4 in H
2O) (all reagent from Sigma), incubated for 5 min at room temperature and the absorbance was measured at 570 nm. Non-infected/non-treated cells, non-treated/infected cells and non-infected/treated cells were used as controls. NO concentration was calculated using a standard curve obtained from a serial dilution of sodium nitrite.
AmB (Photericin B, Cipla, India) was reconstituted in culture medium as stock. Different concentrations of AmB (ranging from 0.03 to 2.7 µM) were prepared and added directly to promastigotes or infected cells after removing non-internalized parasites. Depending on experiment, cell viability was measured at different time points after drug exposure.
Parasite rescue and transformation assay
To survey the drug efficacy, the parasite rescue and transformation assay was used as described previously [
24]. Briefly, PMA-treated/infected THP-1 cells were incubated at 37˚C alone or in the presence of different concentrations of AmB for 24 and 48 hr. Then, cells were lysed by RPMI medium containing 0.05% SDS for 30 sec to release viable amastigotes. The lysis process was stopped using Schneider's insect medium (Sigma) containing 10% hi-FCS, and viability was determined by MTT assay after 3-4 days incubation at 26˚C and transformation into promastigotes.
L. majorWT, L. majorEGFP, and L. majorEGFP-LUC at 2×106 promastigote/ml in stationary growth phase were harvested, washed, and plated in 96-well flat-bottom tissue culture plates. Parasites were allowed to grow for 24 and 48 hr at 26˚C in medium alone or in the presence of various concentrations of AmB. To measure parasite viability by MTT assay, sterile MTT reagent at a final concentration of 5 mg/ml in PBS (Sigma) was added to each well and incubated at 37˚C for 4 hr to produce formazan crystals solubilized in DMSO (Sigma) for OD determination at 492 nm.
Also, B10R and THP-1 cell lines infected by the stationary phase of promastigotes were incubated alone or in the presence of various concentrations of AmB for 48 hr at 37˚C. The percentage of viable cells was determined by MTT as previously described. The parasite viability at amastigote or promastigote stage was calculated using following equation: % viability=(mean treated cells/mean untreated cells)×100.
Luciferase activity measurement
Live promastigotes of recombinant Leishmania expressing EGFP-LUC and/or cell lines infected with L. majorEGFP-LUC in the presence or absent of different concentrations of AmB were cultured in 96-well flat-bottom culture plates. At different time points (24 and 48 hr), 50 μl of lysis buffer (Glo Lysis Buffer, Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA) was added on promastigotes for 5 min. To avoid any background luminescence from adjacent wells, the cell lysates were transferred to 96-well white plates (Brands, Germany) and incubated with the same volume of luciferin substrate (Promega) at room temperature. The luminescence signal was quantified immediately set at 1s/well and sensitivity of 100 with top-reading mode using a luminometer/fluorimeter reader (Multimode Microplater Reader, Synergy, BioTek, Winooski, Vermont, USA). Relative infectivity was determined by comparing the relative luciferase unit (RLU) of the drug-treated cells using untreated cells as negative control. The percentage of infectivity was calculated using the following equation: % infectivity=(mean treated cells/mean untreated cells)×100.
EGFP signal detection by flow cytometry
The THP-1 or B10R cell lines infected with recombinant parasites were treated with serial dilutions of AmB for 24 and 48 hr. Then, adherent cells were detached by cold PBS and transferred to flow cytometry tubes. The infection rate was measured by comparing the EGFP signal between treated and untreated cells (Flow Cytometer, Partec, Münster, Germany). Fifty thousand events were detected and the frequency of infected macrophages was obtained on histograms using FlowJo software (TreeStar version 7.2, Ashland, Oregon, USA).
Data analysis
Data are presented as a mean±SD of duplicate to quaternary samples in at least 3 independent experiments. GraphPad Prism version 5 software was used to calculate CC50 (the concentration of drug necessary to prevent the growth of 50% of cells), IC50 (concentration of drug to kill 50% of parasites) and EC50 (concentration of drug necessary to remove 50% of infected cells). The student’s t-test was used for all statistical analyses. Statistical differences between samples were considered significant at P<0.05.
RESULTS
Comparison of viability and infectivity among 3 lines of parasites
The infectivity potential of the 3 different lines of parasites was compared in vitro with 2 current methods, the MTT (using human non-dividing THP-1) and NO measurement (using mouse dividing B10R cell line). The PMA-treated THP-1cells were infected with different multiplicity of infection (MOI) (1:10, 1:20, and 1:50 cell to parasite ratios) with 3 lines of parasites (2 recombinant and 1 wild-type strain). Then, the MTT was used to measure cell proliferation or survival (
Fig. 1). As shown in
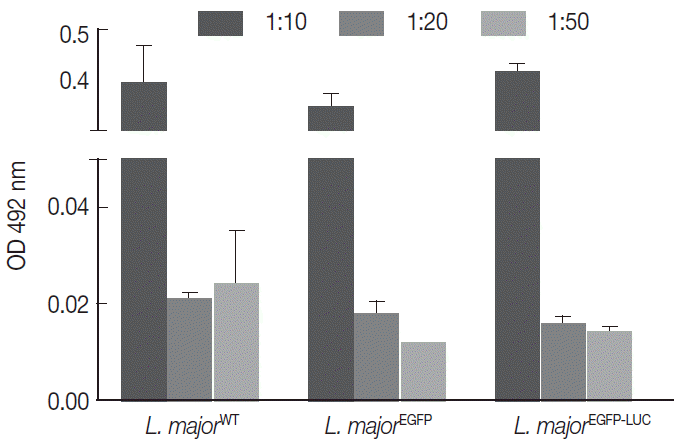
Fig. 1, the level of infectivity of THP-1 was similar for all recombinant
Leishmania compared with the wild-type line. Also, different MOIs showed different infectivity efficiency that was comparable between all lines. With different MOIs, 3 lines of parasites showed similar infectivity rates without significant difference (
Fig. 1).
To understand whether the expression of reporter genes could affect NO release from macrophages, endogenous NO levels were compared as important biomarkers of macrophages to combat
Leishmania infection. The B10R macrophage cell lines were separately infected with each recombinant (
L. majorEGFP and
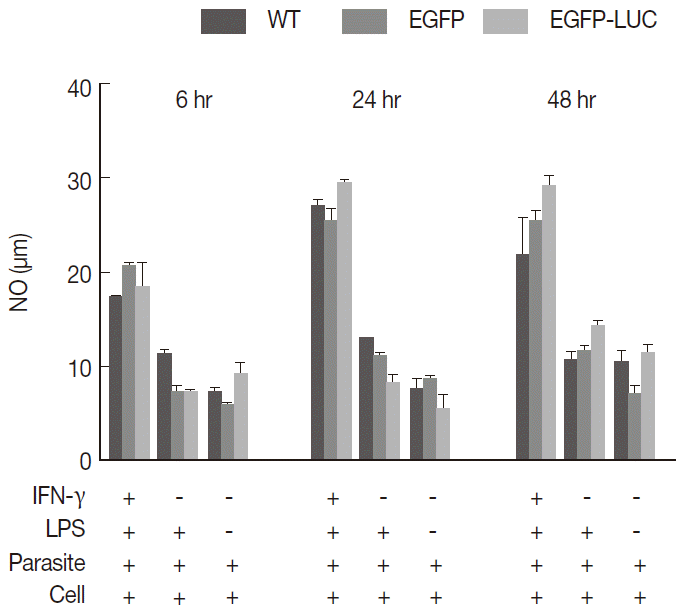
L. majorEGFP-LUC) and wild-type lines as the control. The combination of inducers (IFN-γ and LPS) caused stimulated cells to potentially secrete NO in comparison with unstimulated cells or individual inducers. Cells were induced before infection with a combination of IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) and LPS (10 ng/ml), and then the NO levels were measured at 3 different time points (6, 24, and 48 hr) post-infection. No significant difference was observed among wild-type
L. major and 2 recombinant lines (
Fig. 2) at any time point (11.59-20.29 after 6 hr, 24.77-29.74 after 24 hr, and 18.81-29.92 after 48 hr). There was less detectable production of NO in the early hours after infection (6 hr) compared with that produced at 24 or 48 hr (
P<0.05).
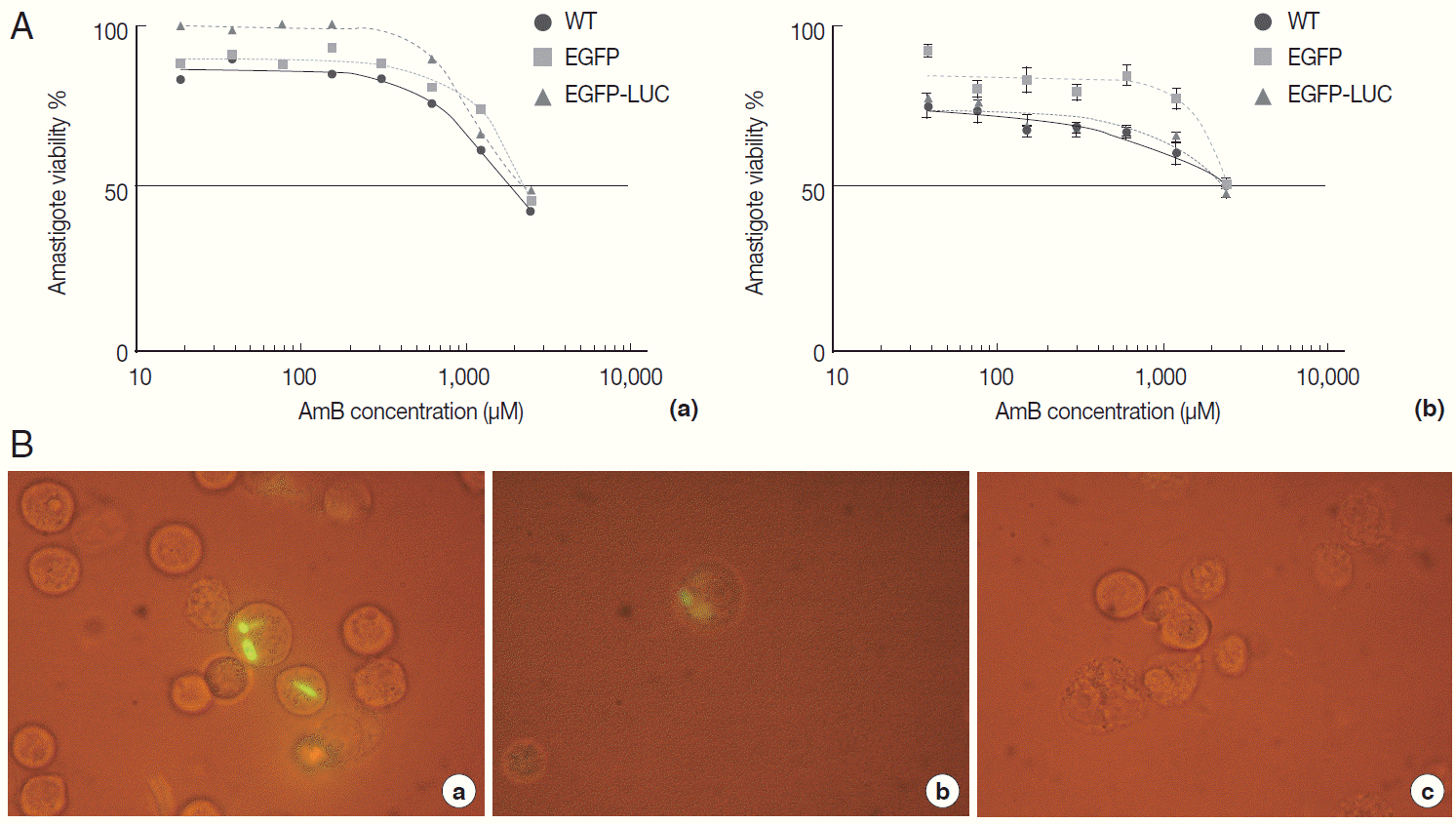
To evaluate the cross reaction between expression of reporter genes and resistance gene (neomycin) included in recombinant parasites, their drug susceptibility against AmB was studied and compared with the wild-type in both growth phase of parasites. Initially, promastigotes of all 3 lines were treated with different concentrations of AmB. The MTT test was used to observe the effect of AmB on parasite multiplication after 24 and 48 hr. All 3 lines produced formazan crystals comparable to viable promastigotes in the presence of various low AmB concentrations (0.0-2.7 µM). With increasing AmB concentration, parasite viability decreased at 24 hr (
Fig. 3A, a) and 48 hr (
Fig. 3A, b) after treatment. As shown in
Table 1, no significant difference was detected in IC50 between promastigotes of all 3 lines evaluated by MTT test (0.16-0.2 µM for
L. majorWT, 0.21-0.29 µM for
L. majorEGFP, and 0.17-0.21 µM for
L. majorEGFP-LUC). Luciferase activity of the recombinant
L. majorEGFP-LUC parasite was determined at 24 hr after AmB exposure as RLU (
Fig. 3B, a), and IC50 was evaluated accordingly (
Fig. 3B, b). The result was quite comparable to the MTT test (0.07-0.1 µM).
The AmB treatment of infected macrophages (THP-1 and B10R) with 3 lines of
L. major promastigote showed that AmB inhibited the growth of all 3 lines of parasites proportional to the drug concentration (
Fig. 4A). Using the MTT test, the EC50 value for THP-1 cell infected with 3 different lines of
Leishmania was similar (~2.7 µM) (
Table 1). Similar results were observed with infected B10R cells (2.16, 2.7, and 2.7 µM for
L. majorWT,
L. majorEGFP, and
L. majorEGFP-LUC, respectively) (
Table 1). Fluorescent microscopy also confirmed that EGFP was expressed in infected cells with both recombinant parasites (
Fig. 4B); however, with less intensity in
L. majorEGFP-LUC-infected than in
L. majorEGFP-infected cells.
The infectivity rate was also determined by EGFP intensity in infected/treated cells with recombinant parasites at 48 hr post-infection (or 24 hr after drug administration) by flow cytometry. As expected, in comparison to infected/untreated cells as a control (5.77%), the EGFP signal in infected/treated cells with L. majorEGFP decreased proportional to increasing concentration of AmB (at 24 hr: 0.44% in 0.07 µM to 0.61% in 1.35 µM for B10R cells).
In parallel, B10R cells were infected with
L. majorEGFP-LUC, and the infection rate was evaluated by flow cytometry. A decrease of EGFP intensity was observed using
L. majorEGFP-LUC, but EGFP signals were significantly lower than
L. majorEGFP (
Fig. 5). After 24 hr, the EGFP intensity decreased (from 0.06% in 1.35 to 0.04% in 0.07 µM). The EC50 values obtained by flow cytometry in each cell line are shown in
Table 1. The EGFP intensity was quantified with flow cytometry but its sensitivity was not enough to differentiate between different concentrations of AmB. The reduced EGFP intensity level almost removed application of EGFP in this issue.
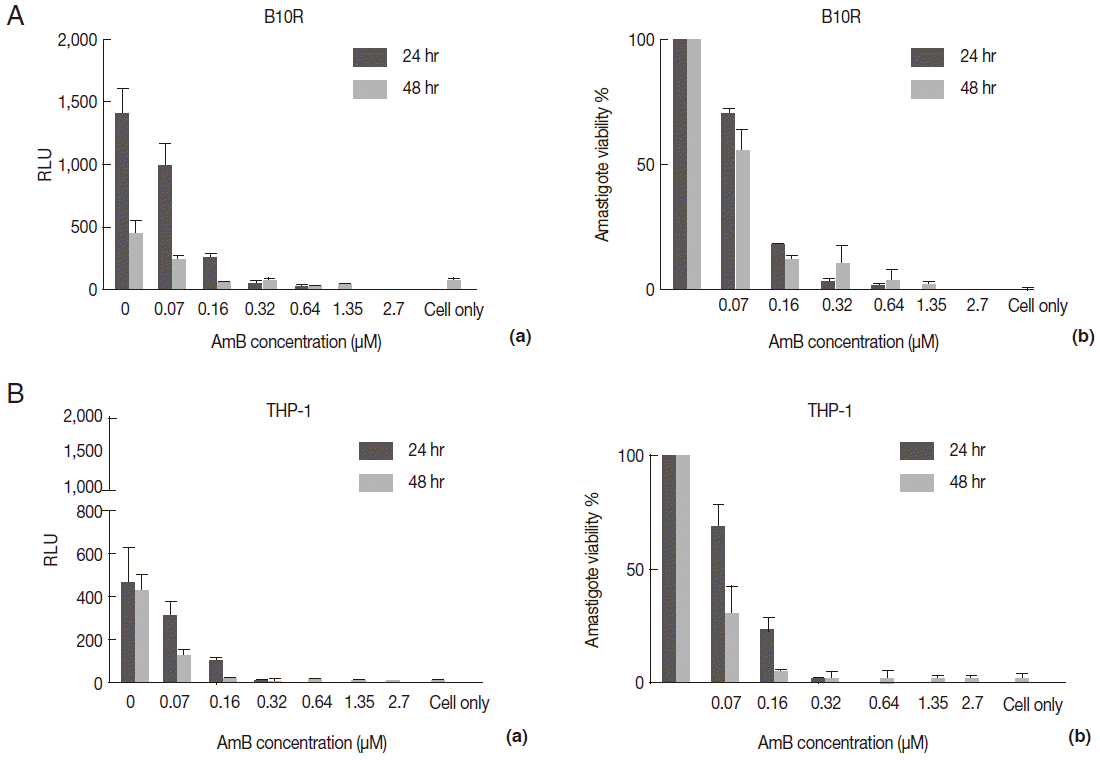
Furthermore, viability of
L. majorEGFP-LUC-infected cells was evaluated by measuring luciferase activity of drug-treated/infected cells and untreated/infected cells (as control) at 24 and 48 hr after treatment (
Fig. 6A, B10R and 6B THP-1 cells). The luciferase activity correlates with amastigote survival within phagosomes of macrophages. It was shown to decrease proportionally to increase of AmB concentrations and was weakly detected at 48 hr after treatment. This decline was due to the AmB during incubation.
Fig. 6A and
B present the luciferase activity in B10R and THP-1 cells. The IC50 for the amastigotes obtained from luciferase activity, flow cytometry, and MTT assay are summarized in
Table 1.
DISCUSSION
Several studies about intracellular pathogenic microorganisms like
Leishmania have indicated that independent reporter genes, such as GFP or luciferase, practically facilitate antimicrobial drug and cell biological activity research both in vitro and in vivo [
7,
8,
20,
25,
26]. Dual reporter gene-expressing pathogens were then generated to more benefit the reporter activity [
21,
22,
27]. The intensity of parasites expressing EGFP-LUC was much lower than those expressing EGFP alone due to a loss of folding of EGFP protein that has direct effects on intensity [
23]. However, EGFP-LUC expressing parasites maintain their ability to be detected in vitro and in vivo. However, there is a concern whether expression of heterologous reporter genes in pathogenic cells like
Leishmania could affect parasite infectivity potential. Herein, the main objective of this study was to compare the infectivity potential of 2 recombinant lines of
Leishmania (
L. majorEGFP and
L. majorEGFP-LUC stably expressing EGFP or EGFP-LUC reporters, respectively) with the wild-type line.
First, we evaluated the impact of stable reporter gene expression on NO as a critical macrophage product, because the production of NO metabolites by macrophages is pivotal in the elimination of parasites [
28]. Following infection, macrophages are activated by IFN-γ from Th1 cells to combat parasites via induction of NOS II and NO synthesis from L-arginine. NO is a cytotoxic metabolite towards a variety of pathogens such as
Leishmania [
5]. In contrast, suppression of NO synthesis helps
Leishmania to survival. Cytokines, such as IFN-γ alone or IFN-γ in combination with LPS stimulate the immune system to overcome parasite infections. Thus, the balance between Th1 and Th2 cytokines in directing immune responses is important for anti-leishmanial activities [
29].
NO production in B10R macrophages was evaluated at different time points after induction. Our data showed that NO production 6 hr after induction was at the lowest level and maximum levels were detected after 48 hr (
Fig. 1). Previously, Pearson et al. [
30] had reported that respiratory burst happened within the first hour after phagocytosis, whereas the maximum level of NO production was detectable later (48-72 hr after infection). This could be due to a requirement for transcription and translation of an inducible NOS enzyme [
3]. The NO level in cells infected with the 3 parasite lines was compared to accurately determine infectivity potential. No significant differences in NO production were detected at different times and with different inducer concentrations. Quite contrary to B10R cells, we could not detect NO production in THP-1 cell lines under the same condition (data not shown). This could be explained by low levels of NO production by human macrophage cells due to efficient intracellular scavenging by other molecules [
3].
Comparison between the 3 lines was also performed in the presence or absence of AmB as a standard drug against
L. major. We used reporter signals measurement to determine the optimum drug dose for both promastigote and amastigote growth inhibition. In addition to these modern techniques, the MTT assay was used for all lines of parasites as a standard available method. For the promastigote form, no significant difference was observed between IC50 values of different lines of parasites using the MTT test, and the IC50 values were very similar (~0.16-0.29 µM) (
Table 1). Measuring the luciferase activity, the sensitivity of EGFP-LUC-expressing promastigotes against the AmB was 0.07-0.1 µM. In both techniques (MTT and luciferase activity), an increase in drug concentration was associated with a decrease in parasite viability or LUC activity, both of which indicated cell death. The comparison of these 2 techniques showed higher sensitivity of LUC as compared with the MTT assay. These results were consistent with other reports, which have shown that the luciferase activity is a sensitive indicator to assess parasite viability and drug selection rather than classical methods such as the MTT assay [
8,
31,
32].
To validate recombinant parasites’ potential in drug assessments, dividing B10R was infected and treated with AmB. As shown in
Table 1, the EC50 value for AmB using MTT tests for all parasites ranging from 2.16 to 2.7 µM. We did not observe any difference between the 2 cell lines used. Recently, we experienced that fluorescent intensity in
L. majorEGFP-LUC was lower than in
L. majorEGFP. This could be due to the high sensitivity of EGFP protein folding. Therefore, it may not be possible to monitor comparable fluorescent intensity between these 2 parasites. Also, using luciferase measurement in cells infected with
L. majorEGFP-LUC, the EC50 of AmB was 0.07-0.1 µM for both cell lines.
Taken together, our results here showed that using a standard method (the MTT test), the IC50 values obtained in the promastigote form (~0.16-0.29 µM) and the EC50 obtained in the amastigote form of all 3 parasite strains (2.16-2.7 µM for both B10R and THP-1 cell) were very similar (
Table 1). However, high-throughput drug screening assays against
Leishmania demand more sensitive and rapid methods. Reporter genes alone or in combination with other genes could be good surrogates for conventional methods such as the MTT. Expression of 2 reporter genes spontaneously allows monitoring and the quantifying of live parasites by different systems, although the expression of 1 of the 2 genes might be slightly weaker. Thus, we suggest that
L. majorEGFP-LUC may be more appropriate for drug screening study than the wild-type strain or
L. majorEGFP.
Ashutosh et al. [
8] reported that
L. donovani episomally expressing LUC not only keeps the infectivity potential in macrophages but also presented higher sensitivity in comparison with conventional methods like the MTT test. Reimão et al. [
33] confirmed that the EC50 value of AmB against promastigotes and amastigotes of recombinant
L. amazonensis lines expressing the luciferase gene was in concordance with the values obtained for wild-type strain.
Here, we confirmed that there was no significant observable difference in infectivity rate and sensitivity against AmB and NO levels between the 3 lines of parasites. Of course, it remains to characterize the role of these reporter genes in animal models. Our results clearly revealed that stable expression of 1 or 2 reporter genes has no biological effects on the potential of Leishmania to infect and survive within macrophages. This suggests that these recombinant parasites could be used successfully in in vitro experiments especially for drug screening and vaccine studies in high throughput systems.
Notes
-
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest statement.
The authors are grateful to Dr. K. Azadmanesh (Department of Virology, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Tehran, Iran) for his advice. We also acknowledge Mr. Sh. Alizadeh (Department of Immunotherapy and Leishmania Vaccine Research, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Tehran, Iran) for his technical help. This project was supsupported by a grant from Pasteur Institute of Iran (grant no. 653).
Fig. 1.Comparison of infectivity potential of different lines of parasites in THP1 cells. The cells were infected with different lines of parasites separately. Results were depicted as mean±SD based on OD 492 nm.

Fig. 2.Measurement of released nitric oxide (NO) from infected cells. B10R cell lines were infected with 3 lines of parasites, and the level of NO production was estimated using Griess assay. The produced NO level was compared between infected cells with 2 recombinant parasites (L. majorEGFP and L. majorEGFP-LUC) and wild-type line at different time period of 6, 24, and 48 hr. In this experiment, all cells were infected after induction with both inducers (IFN-γ/LPS). No statistically significant difference was observed between 3 lines of parasites.
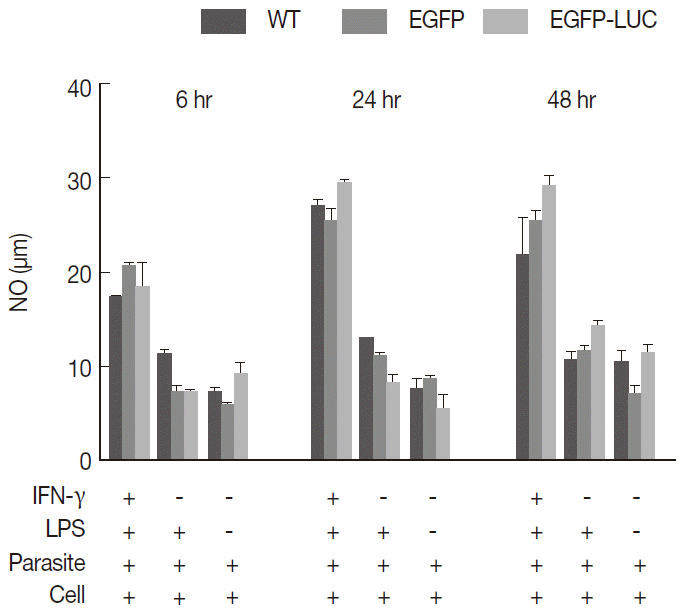
Fig. 3.Evaluation of AmB effect on promastigote form. (A) Anti-leishmanial activity of AmB against parasites using MTT assay. Promastigote form of 3 lines of parasite were incubated in presence of various AmB concentration and viability percentage measured at 24 hr (a) and 48 hr (b) post incubation by MTT test. (B) Luminescence assay. Susceptibility of parasite lines expressing EGFP-LUC to AmB was evaluated by luciferase activity measurement as relative ligwht unit (RLU) (a) and percentage viability (b) in presence of various dilutions of AmB. The results were obtained in duplicates as representatives of 2 independent experiments.
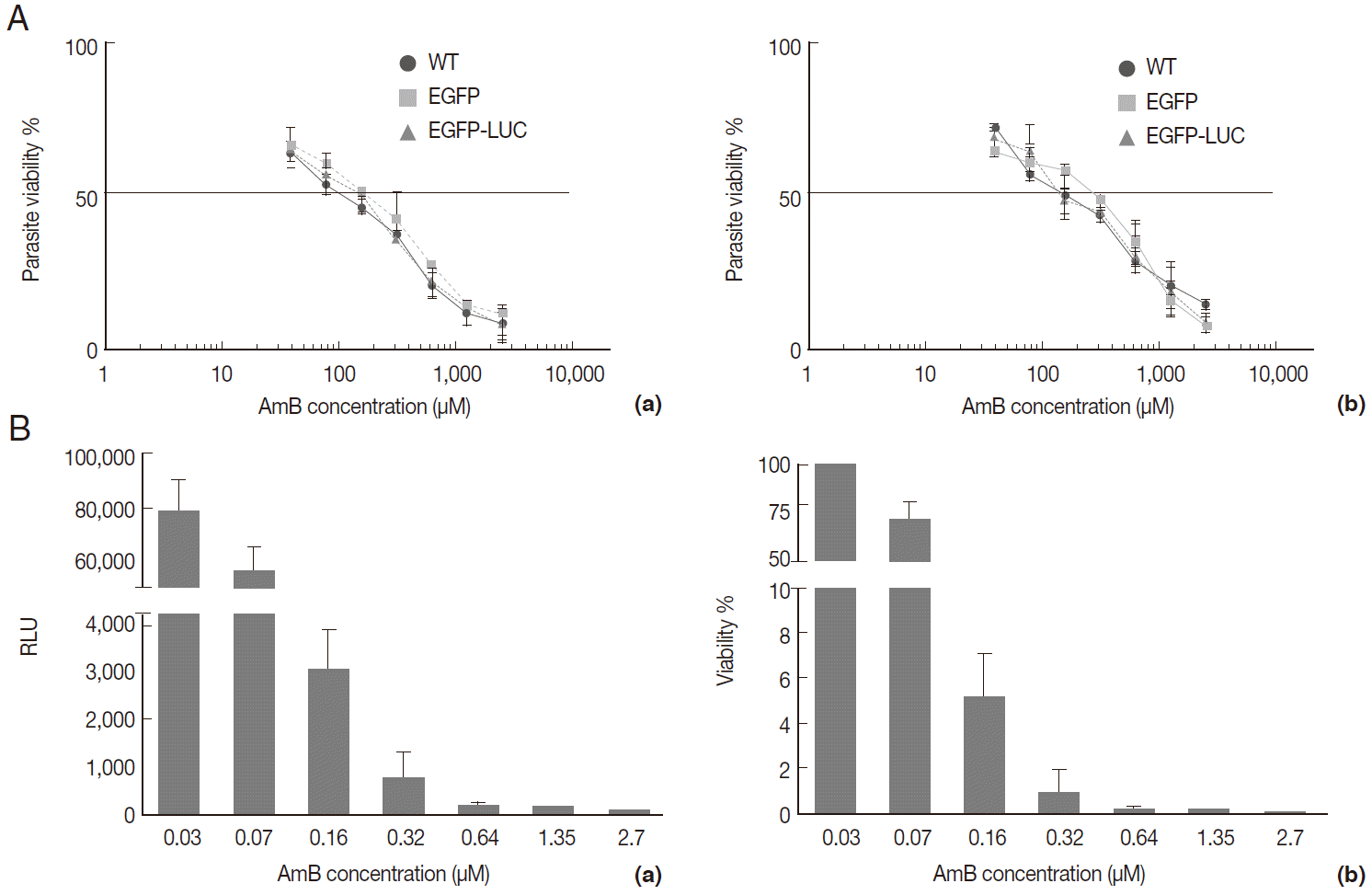
Fig. 4.Evaluation of AmB effects on amastigote forms by MTT and microscope. The B10R and PMA-treated THP-1 cell lines were infected with 3 lines of parasite. Then, infected cells were incubated with various concentrations of AmB at 37˚C for 48 hr. (A) Using MTT test infectivity rate for B10R (a) THP-1 (b) cell lines was calculated with the following equation: % viability (mean±SD treated cells/mean±SD control cells) ×100. (B) Fluorescent microscopic photos from infected cells with L. majorEGFP (a), L. majorEGFP-LUC (b), and L. major wild-type (c). Magnification ×1,000.
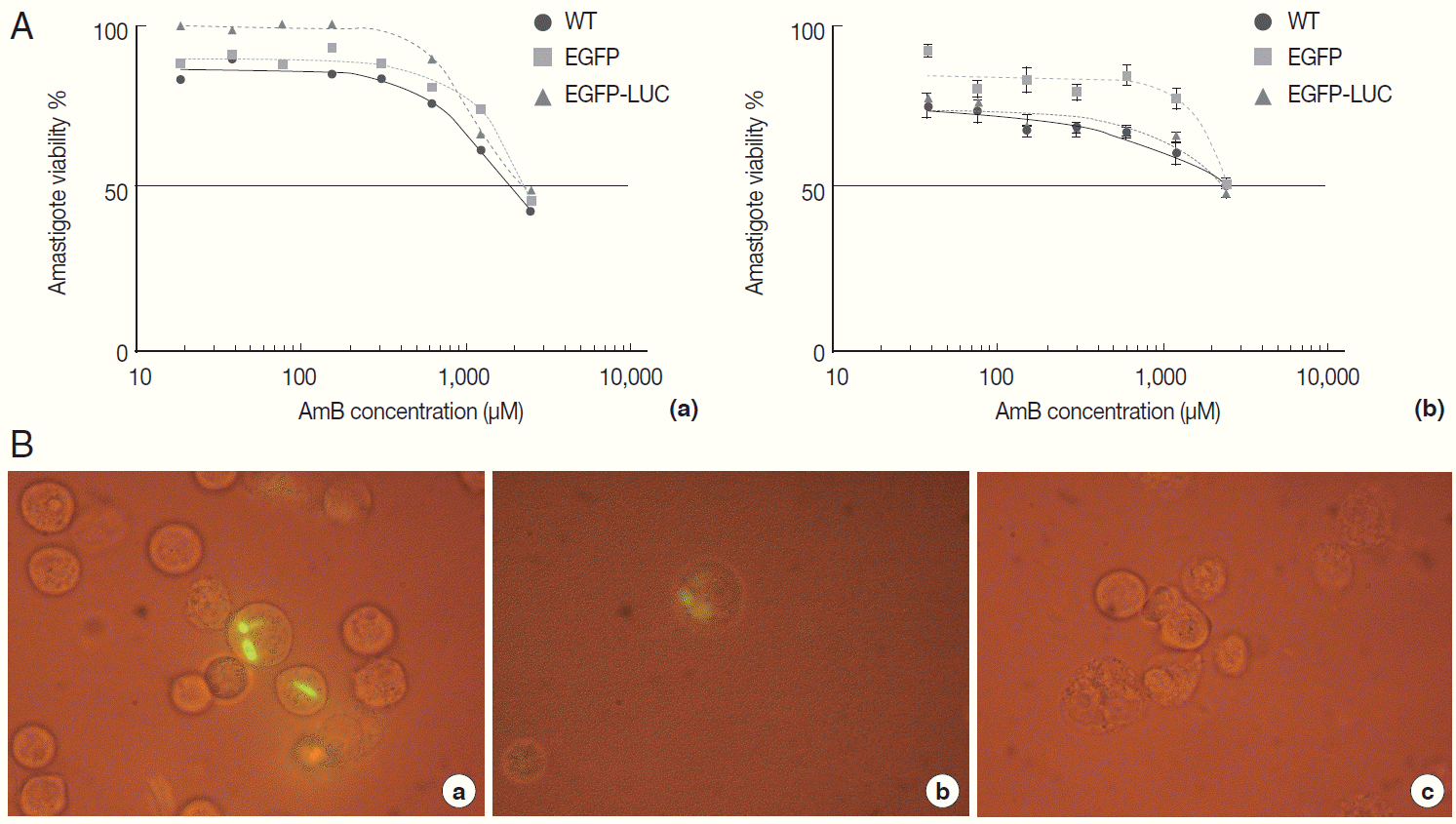
Fig. 5.Evaluation of AmB effects on amastigote forms by flow cytometry. The derived EGFP signal of amastigotes into infected B10R cell line with recombinant parasites after adding different concentrations of AmB (0.07, 0.32, and 1.35 μM) was evaluated using flow cytometry at 24 hr after adding the drug.
Fig. 6.Evaluation of AmB effects on amastigote forms by Luminescence assay. The effect was surveyed using luciferase activity in infected cell lines with L. majorEGFP-LUC, B10R (A, a and b), and THP-1 (B, a and b). Infection of cells was calculated following an equation: % viability: (mean±SD treated cells/mean±SD control cells) ×100. The results were obtained in duplicates as representative of 2 independent experiments.
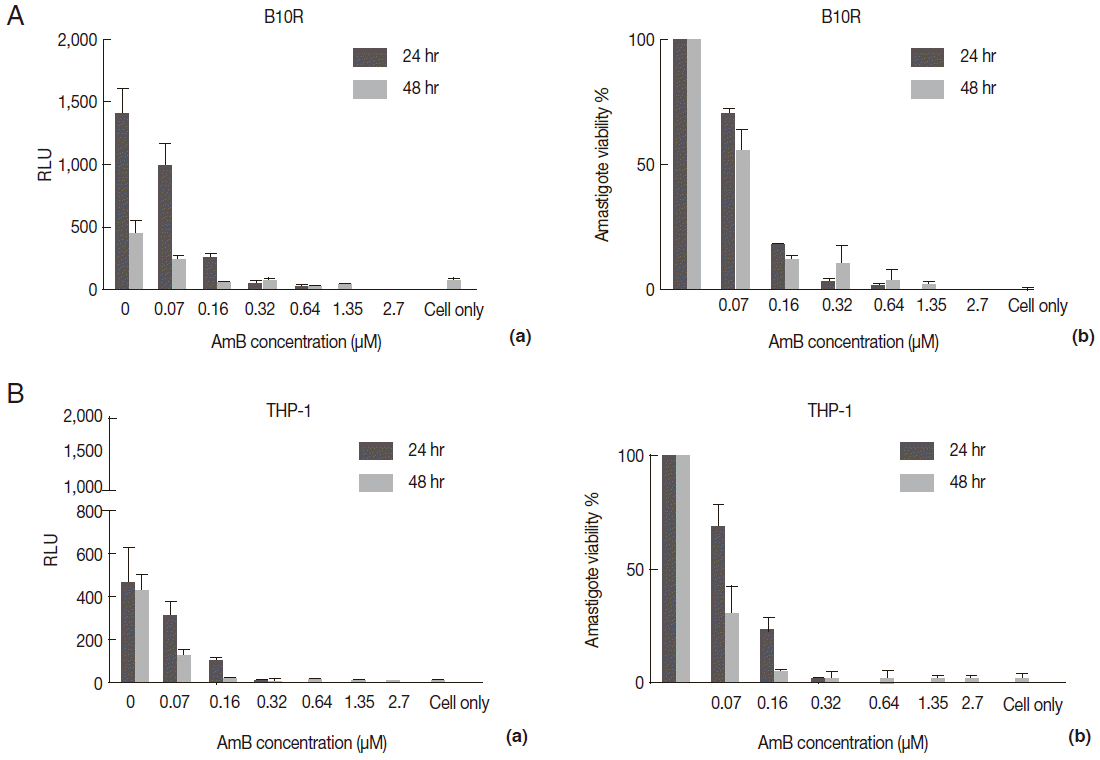
Table 1.The obtained IC50 and EC50 value from 3 lines of parasites in 2 forms, promastigote and amastigote, in presence of AmB by different techniques
Table 1.
|
Parasites (promastigote) |
IC50 (μM)
|
Parasites (amastigote) |
EC50 (μM)
|
|
MTT |
LUC assay |
B10R
|
THP1
|
|
MTT |
Flow cytometry |
LUC assay |
MTT |
LUC assay |
|
L. majorWT
|
0.16-0.2 |
- |
L. majorWT
|
2.16 |
- |
- |
2.7 |
- |
|
L. majorEGFP
|
0.21-0.29 |
- |
L. majorEGFP
|
2.7 |
< 0.03 |
- |
2.7 |
- |
|
L. majorEGFP-LUC
|
0.17-0.21 |
0.07-0.1 |
L. majorEGFP-LUC
|
2.7 |
- |
< 0.01-0.03 |
2.7 |
0.07-0.1 |
References
- 1. Alvar J, Velez ID, Bern C, Herrero M, Desjeux P, Cano J, Jannin J, den Boer M, Team WLC. Leishmaniasis worldwide and global estimates of its incidence. PLoS One 2012;7:e35671.
- 2. Papadopoulou B, Huang XF, Boucher N, McNicoll F. Stage-specific regulation of gene expression in Leishmania. ASM News, American Society for Microbiology 2003;69:282-288.
- 3. Gantt KR, Goldman TL, McCormick ML, Miller MA, Jeronimo SM, Nascimento ET, Britigan BE, Wilson ME. Oxidative responses of human and murine macrophages during phagocytosis of Leishmania chagasi. J Immunol 2001;167:893-901.
- 4. Garg R, Gupta S, Tripathi P, Naik S, Sundar S, Dube A. Immunostimulatory cellular responses of cured Leishmania-infected patients and hamsters against the integral membrane proteins and non-membranous soluble proteins of a recent clinical isolate of Leishmania donovani. Clin Exp Immunol 2005;140:149-156.
- 5. Holzmuller P, Sereno D, Cavaleyra M, Mangot I, Daulouede S, Vincendeau P, Lemesre JL. Nitric oxide-mediated proteasomedependent oligonucleosomal DNA fragmentation in Leishmania amazonensis amastigotes. Infect Immun 2002;70:3727-3735.
- 6. Sharma U, Singh S. Immunobiology of leishmaniasis. Indian J Exp Biol 2009;47:412.
- 7. Kram D, Thäle C, Kolodziej H, Kiderlen AF. Intracellular parasite kill: flow cytometry and NO detection for rapid discrimination between anti-leishmanial activity and macrophage activation. J Immunol Methods 2008;333:79-88.
- 8. Gupta S, Sundar S, Goyal N. Use of Leishmania donovani field isolates expressing the luciferase reporter gene in in vitro drug screening. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005;49:3776-3783.
- 9. Rocha MN, Corrêa CM, Melo MN, Beverley SM, Martins-Filho OA, Madureira AP, Soares RP. An alternative in vitro drug screening test using Leishmania amazonensis transfected with red fluorescent protein. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2013;75:282-291.
- 10. Avlonitis N, Lekka E, Detsi A, Koufaki M, Calogeropoulou T, Scoulica E, Siapi E, Kyrikou I, Mavromoustakos T, Tsotinis A. Antileishmanial ring-substituted ether phospholipids. J Med Chem 2003;46:755-767.
- 11. Mikus J, Steverding D. A simple colorimetric method to screen drug cytotoxicity against Leishmania using the dye Alamar Blue®. Parasitol Int 2000;48:265-269.
- 12. Bodley AL, McGarry MW, Shapiro TA. Drug cytotoxicity assay for African trypanosomes and Leishmania species. J Infect Dis 1995;172:1157-1159.
- 13. Croft S. In vitro screens in the experimental chemotherapy of leishmaniasis and trypanosomiasis. Parasitol Today 1986;2:64-69.
- 14. Gupta S. Visceral leishmaniasis: experimental models for drug discovery. Indian J Med Res 2011;133:27.
- 15. Lang T, Goyard S, Lebastard M, Milon G. Bioluminescent Leishmania expressing luciferase for rapid and high throughput screening of drugs acting on amastigote-harbouring macrophages and for quantitative real-time monitoring of parasitism features in living mice. Cell Microbiol 2005;7:383-392.
- 16. Dube A, Gupta R, Singh N. Reporter genes facilitating discovery of drugs targeting protozoan parasites. Trends Parasitol 2009;25:432-439.
- 17. Naylor LH. Reporter gene technology: the future looks bright. Biochem Pharmacol 1999;58:749-757.
- 18. Monzote L. Current treatment of leishmaniasis: a review. Open Antimicrob Agnts J 2009;1:9-19.
- 19. Bolhassani A, Taheri T, Taslimi Y, Zamanilui S, Zahedifard F, Seyed N, Torkashvand F, Vaziri B, Rafati S. Fluorescent Leishmania species: Development of stable GFP expression and its application for in vitro and in vivo studies. Exp Parasitol 2011;127:637-645.
- 20. Gangwar S, Goyal N. Development of luciferase expressing Leishmania donovani axenic amastigotes as primary model for in vitro screening of antileishmanial compounds. Curr Microbiol 2012;65:696-700.
- 21. Wu Y, Liao Q, Yang R, Chen X, Chen X. A novel luciferase and GFP dual reporter virus for rapid and convenient evaluation of hepatitis C virus replication. Virus Res 2011;155:406-414.
- 22. Vaughan AM, Mikolajczak SA, Camargo N, Lakshmanan V, Kennedy M, Lindner SE, Miller JL, Hume JC, Kappe SH. A transgenic Plasmodium falciparum NF54 strain that expresses GFP-luciferase throughout the parasite life cycle. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2012;186:143-147.
- 23. Taheri T, Saberi Nik H, Seyed N, Doustdari F, Etemadzadeh MH, Torkashvand F, Rafati S. Generation of stable L. major+EGFP-LUC and simultaneous comparison between EGFP and luciferase sensitivity. Exp Parasitol 2015;150:44-55.
- 24. Jain SK, Sahu R, Walker LA, Tekwani BL. A parasite rescue and transformation assay for antileishmanial screening against intracellular Leishmania donovani amastigotes in THP1 human acute monocytic leukemia cell line. J Vis Exp 2012;(70):e4054.
- 25. Michel G, Ferrua B, Lang T, Maddugoda MP, Munro P, Pomares C, Lemichez E, Marty P. Luciferase-expressing Leishmania infantum allows the monitoring of amastigote population size, in vivo, ex vivo and in vitro. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2011;5:e1323.
- 26. Mehta SR, Zhang X-Q, Badaro R, Spina C, Day J, Chang KP, Schooley RT. Flow cytometric screening for anti-leishmanials in a human macrophage cell line. Exp Parasitol 2010;126:617-620.
- 27. Ploemen IH, Prudêncio M, Douradinha BG, Ramesar J, Fonager J, van Gemert G-J, Luty AJ, Hermsen CC, Sauerwein RW, Baptista FG. Visualisation and quantitative analysis of the rodent malaria liver stage by real time imaging. PLoS One 2009;4:e7881.
- 28. Shio MT, Olivier M. Editorial: Leishmania survival mechanisms: the role of host phosphatases. J Leukoc Biol 2010;88:1-3.
- 29. Balestieri F, Queiroz A, Scavone C, Costa V, Barral-Netto M, Abrahamsohn IA. Leishmania (L.) amazonensis-induced inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis in host macrophages. Microb Infect 2002;4:23-29.
- 30. Pearson R, Harcus J, Symes P, Romito R, Donowitz G. Failure of the phagocytic oxidative response to protect human monocytederived macrophages from infection by Leishmania donovani. J Immunol 1982;129:1282-86.
- 31. Paloque L, Vidal N, Casanova M, Dumètre A, Verhaeghe P, Parzy D, Azas N. A new, rapid and sensitive bioluminescence assay for drug screening on Leishmania. J Microbiol Methods 2013;95:320-323.
- 32. Sereno D, Roy G, Lemesre JL, Papadopoulou B, Ouellette M. DNA transformation of Leishmania infantum axenic amastigotes and their use in drug screening. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2001;45:1168-1173.
- 33. Reimão JQ, Trinconi CT, Yokoyama-Yasunaka JK, Miguel DC, Kalil SP, Uliana SR. Parasite burden in Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis-infected mice: validation of luciferase as a quantitative tool. J Microbiol Methods 2013;93:95-101.