Abstract
Plasmodium falciparum can invade all stages of red blood cells, while Plasmodium vivax can invade only reticulocytes. Although many P. vivax proteins have been discovered, their functions are largely unknown. Among them, P. vivax reticulocyte binding proteins (PvRBP1 and PvRBP2) recognize and bind to reticulocytes. Both proteins possess a C-terminal hydrophobic transmembrane domain, which drives adhesion to reticulocytes. PvRBP1 and PvRBP2 are large (> 326 kDa), which hinders identification of the functional domains. In this study, the complete genome information of the P. vivax RBP family was thoroughly analyzed using a prediction server with bioinformatics data to predict B-cell epitope domains. Eleven pvrbp family genes that included 2 pseudogenes and 9 full or partial length genes were selected and used to express recombinant proteins in a wheat germ cell-free system. The expressed proteins were used to evaluate the humoral immune response with vivax malaria patients and healthy individual serum samples by protein microarray. The recombinant fragments of 9 PvRBP proteins were successfully expressed; the soluble proteins ranged in molecular weight from 16 to 34 kDa. Evaluation of the humoral immune response to each recombinant PvRBP protein indicated a high antigenicity, with 38-88% sensitivity and 100% specificity. Of them, N-terminal parts of PvRBP2c (PVX_090325-1) and PvRBP2 like partial A (PVX_090330-1) elicited high antigenicity. In addition, the PvRBP2-like homologue B (PVX_116930) fragment was newly identified as high antigenicity and may be exploited as a potential antigenic candidate among the PvRBP family. The functional activity of the PvRBP family on merozoite invasion remains unknown.
-
Key words: Plasmodium vivax, reticulocyte binding protein, recombinant protein, antigenicity
INTRODUCTION
An estimated 124-283 million of malaria clinical cases occur annually, and the disease continues to be a serious health threat in developing countries [
1]. Malaria is caused by
Plasmodium spp., and of them
Plasmodium vivax is geographically the most widely spread species [
2]. Moreover, control and understanding of vivax malaria have limitation from lack of
P. vivax continuous culture [
3-
5]. To overcome this constraint, various new approaches using bioinformatics data were tried and used for development of antimalarial drugs and vaccines [
6,
7].
In the blood stage,
Plasmodium spp. invade erythrocytes or reticulocytes by use of an actin-myosin motor [
8,
9]. This process internalizes the parasite in red blood cells (RBCs), followed by growth and replication to form the merozoites. The invasive merozoites egress from infected RBCs to invade new host cells [
10-
12]. In this step, specific receptors on the surface of host RBCs are required for interaction involved with attachment, reorientation, and junction formation for parasite invasion [
12]. During these multiple steps, many proteins mediate the interaction between RBCs and parasites [
13,
14]. One of these proteins is Duffy binding protein of
P. vivax (PvDBP), which is essential for invasion of vivax parasites into RBCs. The invasion utilizes the Duffy antigen/receptor for chemokines (DARC) on the surface of RBCs [
15,
16]. PvDBP and DARC were only one of the unique and essential ligand-receptors for erythrocyte invasion of
P. vivax [
17]. Recently, clinical vivax patients were observed in Duffy-negative populations of Madagascar, where mixture of Duffy-positive and Duffy-negative populations has lived together [
18]. Thus, new questions have arisen with regards to the Duffy-independent
P. vivax invasion of erythrocytes.
Reticulocyte binding-like (RBL) family proteins are possible candidates for alternative invasion pathway after PvDBP-DARC interaction. RBL proteins may interact with reticulocytes by an independent pathway with the Duffy phenotype, suggesting that the RBL family may use a novel receptor for reticulocyte invasion. RBL proteins feature a small and large exon separated by a small intron, and the small exon encodes the signal peptide [
19,
20]. The complete gene sequence of
P. vivax Salvador I (Sal-1) strain comprises genes for 11
P. vivax reticulocyte binding proteins (PvRBP) as well as 2 pseudogenes [
14,
21]. Five of these genes are highly expressed in schizont stage during the erythrocytic stage of
P. vivax parasites [
22,
23]. However, no studies have addressed the antigenicity of PvRBPs from vivax malaria patients in endemic countries.
In infectious diseases, identification of the antigenic domain(s) is important for diagnosis and vaccine development [
24,
25]. Numerous studies supported the accuracy of the specific domain prediction such as B-cell epitopes in infectious diseases [
24-
26]. Several B-cell epitope prediction systems based on bioinformatics data including ABCpred, BcePred, and BepiPred have been reported [
27-
33]. ABCpred predicts B-cell epitopes in an antigen sequence using an artificial recurrent neural network. This program is able to predict epitopes with 65.9% accuracy [
29,
31]. BcePred predicts linear B-cell epitopes on the basis of their physico-chemical properties (hydrophilicity, flexibility, mobility, accessibility, polarity, exposed surface, and turns) and produces epitopes with 58.7% accuracy using flexibility, hydrophilicity, polarity, and exposed surface factor score combined at a recommendation threshold of 2.38 [
28]. The BepiPred sever has been used to predict the location of linear B-cell epitopes using a combination of a hidden Markov model and propensity scale method [
30,
34]. This B-cell epitope prediction might be useful to decide antigenic domains in the
P. vivax RBL family proteins. This information would be helpful for increased understanding of the PvRBP family as a potential antigenic candidate.
In the present study, PvRBP family protein sequences were analyzed to predict B-cell epitope domains by in-silico data mining. Each recombinant PvRBP including B-cell epitope domains was expressed in a wheat germ cell-free expression system (WGCF). The humoral immune responses against PvRBPs were observed to evaluate the probability of a potential antigenic candidate by protein microarray-based serological screening.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Human serum and parasite samples
Human serum samples were collected from 16 P. vivax positive patients from an endemic area of Gangwon-do (Province), Republic of Korea (Korea). Vivax infections were confirmed by microscopic examination and detection of malaria antigen by P.f/Pan rapid diagnosis test kit (SDFK60) (SD Diagnostics, Giheung, Korea). Serum samples were collected from 8 healthy individuals with no history of malaria living in non-endemic areas of Gangwon-do. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at Kangwon National University Hospital. The individual serum samples were examined for humoral immune responses by protein array. Genomic DNA was extracted from 200 μl whole blood of the P. vivax patients using QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kits (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Prediction of linear B-cell epitopes for PvRBP family
The in-silico prediction of linear B-cell epitopes was conducted by ABCpred (
http://imtech.res.in/raghava/abcpred/), BcePred (
http://www.imtech.res.in/raghava/bcepred/), and BepiPred (
http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/BepiPred/) to heighten the accuracy. For prediction of B-cell epitopes, PvRBP family sequences were obtained from PlasmoDB (
http://plasmodb.org/plasmo/) (
Table 1). Each sequence was allowed in the B-cell epitope prediction with each prediction server. ABCpred setting was up to 20 mer peptides by overlapping filter and a threshold value of 0.51 (ABCpred base threshold value). The predicted B-cell epitopes were ranked according to their score obtained by a trained recurrent neural network. Higher scores (>0.90) were chosen for B-cell epitope combination analysis for each protein. BcePred predicted linear B-cell epitopes based on physico-chemical properties using values of hydrophilicity (2.0), flexibility (1.9), accessibility (2.0), turns (1.9), exposed surface value (2.4), polarity (2.3), and antigenic propensity (1.8) to calculate a threshold value at 1.9. BepiPred 1.0 was set for each PvRBPs sequence using a threshold value of 1.3, which represented B-cell epitope prediction sensitivity and specificity of 13% and 96%, respectively. Each
PvRBP family was analyzed for flexibility, antigenic index, and surface location by the Protean protein secondary structure prediction program (Lasergene, Madison, Wisconsin, USA). Finally, 20 PvRBP family fragments were selected from the combination of predicted B-cell epitopes listed from the highest scores for humoral immune response analysis.
PvRBP family sequences from PlasmoDB were used to design primers of gene amplification for B-cell epitope fragments (
Table 2). Expected molecular weight and isoelectric point for B-cell epitope fragments are shown in
Table 2. For recombinant protein expression vector construction, pEU-E01-His-TEV-MCS vector containing a 6× His tag at the N-terminus (CellFree Science, Matsuyama, Japan) was used. After restriction enzyme digestion of pEU vector with
XhoI and
BamHI, the target amplicon was cloned into the pEU vector by an Infusion cloning system (Clontech, Mountain View, California, USA). The sequences of each protein fragment were analyzed using an ABI 3700 genetic analyzer (Genotech, Daejeon, Korea) and were used for small-scale WGCF expression in the Cell-Free Expression Kit (CellFree Sciences) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Recombinant crude protein (10 μl) was mixed with reducing sample buffer and total and soluble fractions were obtained by centrifugation (12,000 g). For target protein detection, recombinant proteins were separated using 12% SDS-PAGE and detected by Western blot analysis. Briefly, the electrophoretically resolved proteins were transferred to polyvinyl difluoride membranes (Millipore, Bedford, Massachusetts, USA). Specific proteins were detected by mouse anti-penta-His antibody (Qiagen) in a 1:2,000 dilution of 0.2% Tween 20 in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS-T). The primary antibody reaction was detected by a 1:5,000 dilution of goat anti-mouse IRDye CW800 secondary antibody (LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, Nebraska, USA) in PBS-T. Western blot results were determined with an Odyssey infrared imaging system and incorporated software (LI-COR Biosciences) at a wavelength of 680 nm.
For humoral immune response analysis, the protein array analysis was done as follows. Tri-amine coated slides were prepared by trimethoxysilane (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, Missouri, USA) on the microscope slide (Marienfeld-Superior, Lauda, Germany). The crude recombinant protein fragment (1 μl) of PvRBP was reacted to the amine-coated slide surface. After washing and blocking with PBS-T containing 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA), the array was probed with serial dilution (1:100 to 1:10) of malaria patient or healthy individual sera and with a 1:100 dilution of wheat germ lysate in PBS. Array conditions were optimized using 1:10 dilution of mixed sera from patients and healthy individuals. Alexa Fluor 546 goat anti-human IgG (Invitrogen) in PBS-T containing 1% BSA was applied into each spots for detection of the antibody reaction. The fluorescent signals were detected using a ScanArray Express fluorescence scanner (PerkinElmer, Boston, Massachusetts, USA). The cut-off value was defined as 3 standard deviations (SDs) above the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the healthy individual samples. Recombinant P. vivax merozoite surface protein 1-19 (PvMSP1-19) was used as a positive control, and its MFIs were used for compensation in each slide.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, San Diego, California, USA) and Excel 2013 (Microsoft, Redmond, Washington, USA). Statistical analysis of significance between P. vivax parasite-infected patients and healthy individual samples was performed with 2-tailed non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test. A P-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Bioinformatics analysis of pvrbp gene sequences
A total of 11
pvrbps genes including 3 homologue gene subfamilies of the PvRBP family (
pvrbp1s, pvrbp2s, and
pvrbp3) (
Table 1) were selected for this study. The 3 pvrbp1 homologue genes in
P. vivax Sal-1 included
pvrbp1a (PVX_098585),
pvrbp1b (PVX_098582), and pvrbp1-like partial sequence (PVX_125738) (
Fig. 1).
Pvrbp1a and
pvrbp1b encoded signal sequence at the N-terminal region in a full-length sequence.
Pvrbp1a and
pvrbp1-like partial sequence displayed a transmembrane domain near the C-terminus (
Table 2). This
pvrbp1-like partial sequence had 95% similarity with the C-terminal sequence of
pvrbp1b, and was consistent with the typical RBL family structure.
The
pvrbp2 genes comprise 7 members that include
pvrbp2a (PVX_121920),
pvrbp2b (PVX_094255),
pvrbp2c (PVX_121920),
pvrbp2d (PVX_101585),
pvrbp2 like partial A (PVX_090330),
pvrbp2 like partial B (PVX_101590), and
pvrbp2 homologue B (PVX_116930) (
Fig. 1).
Pvrbp2d was identified as a pseudogene. The other 6
pvrbp2 homologue genes comprise 4 members with a full length sequence and 2 members with a partial sequence (
Table 1). Among the
pvrbp2 genes, signal sequence and transmembrane domain were identified in
pvrbp2c. Unlike other pvrbp genes, the
pvrbp2 homologue B gene consists of introns at both N-terminus and C-terminus, and displayed a shorter open reading frame (1,060 aa, 123.9 kDa) than those of other pvrbp sequences. Cysteine (Cys) residues and alpha helix coiled-coil region ectodomain structure were detected in
pvrbp2 homologue B. Accordingly, the
pvrbp2 homologue B was expected to evoke a higher immune response.
Pvrbp3 (PVX_101495) was observed as a pseudogene in the Sal-1 strain. All members of the pvrbps displayed large molecular weights exceeding 280 kDa and similar protein structure consisting of many Cys residues (
Table 1;
Fig. 1).
The prediction results of B-cell epitopes obtained by the 3 different B-cell prediction servers and protein fragment information are shown in
Table 2. The prediction results of linear B-cell epitopes for PvRBP family displayed a wide range of fragments (3 to 29; median 13.9). According to the protein secondary structures and high probability of surface exposure, 20 fragments were selected as the potential specific B-cell epitopes for further study. The prediction results revealed that 5 fragments were located in the N-terminal region (PVX_098582-1, PVX_121920-1, PVX_090325-1, PVX_090330-1, and PVX_101590-1) and another 5 at the C-terminus (PVX_098585-2, PVX_125738-2, PVX_121920-4, PVX_094255-2, and PVX_090325-3). The specific domain feature contained alpha helix coiled-coil domain in 4 PvRBPs (PVX_098582-2, PVX_125738-1, PVX_090325-2, and PVX_090330-2) and repeat sequence with low complexity in 5 PvRBPs (PVX_098585-1, PVX_121920-2, PVX_121920-3, PVX_094255-1, and PVX_116930-2). PvRBP2-like homologue B fragment 1 (PVX_116930-1) did not represent any specific feature on protein secondary structure prediction. According to the B-cell epitope prediction, all of the fragments were likely to be surface-exposed and expected to be potently antigenic.
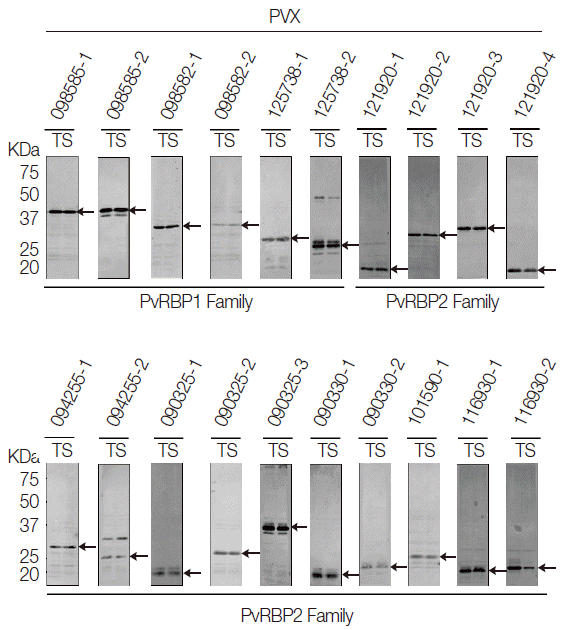
All the PvRBP recombinant proteins were expressed in the supernatant as the soluble fraction with variable expression level in the WGCF system. The expression level of the specific PvRBP proteins was confirmed by Western blot analysis with anti-His tag for detection of recombinant protein (
Fig. 2). Lower pI values of expressed PvRBP proteins were slower-migrating proteins on the SDS-PAGE analysis. The experimental positive control was PvMSP1-19, which was expressed by WGCF and purified by Ni-affinity chromatography as described previously [
35]. These recombinant proteins were used for further analysis.
The humoral immune responses of the PvRBP family fragment proteins were evaluated with sera from
P. vivax patients and healthy individuals by protein microarray (
Table 3). IgG prevalence to recombinant PVX_090325-1 and PVX_116930-2 fragments had the highest sensitivity (87.5%). Similarly, recombinant PvRBP2 fragments displayed high IgG positive responses; PVX_090330-1 (81.3%), PVX_094255-1 (75.0%), and PVX_116930-1 (75.0%) (
Table 3). Recombinant PvRBP proteins from 6 fragments involving 2 fragments of PVX_125738 (coiled-coil and putative C-terminal domains), PVX_121920-1, -2, and -3 (N-terminal fragment, low complexity sequence, and repeat sequence, respectively), and PVX_090325-3 (C-terminal fragment) showed a similarly of 68.8% IgG-positive responses. Other fragments including PVX_098585-1 (repeat sequence), PVX_098582-2 (coiled-coli domain), and PVX_094255-2 (C-terminal domain) were 62.5% IgG-positive responses. The IgG prevalence below 60.0% was detected in PVX_090325-2 (containing a short coiled-coil domain), PVX_101590-1 (N-terminal region), PVX_098585-2 (C-terminal region), PVX_090330-2 (contained short coiled-coil domain), PVX_098582-1 (N-terminal region), and PVX_121920-4 (C-terminal region) (
Table 3). The IgG prevalence of the overall PvRBP2s was higher than those of PvRBP1s. Recombinant PvRBP2 fragments displayed high positivity of IgG at the N-termini and repeat sequence regions. Most of recombinant PvRBP fragments showed high specificities and significantly different between
P. vivax patients and healthy individuals (
P <0.05;
Table 3).
DISCUSSION
In the post-genomic era, the
P. vivax complete genome sequences and bioinformatics information are available for various proteome-related approaches [
14,
34,
36-
38]. Bioinformatics tools for selection of proteins in
P. falciparum have been used for new malaria antigenic protein identification. Antigenic proteins were considered from secondary structures, such as the alpha helical coiled-coil domain [
36,
39]. In this study, humoral immune responses against recombinant PvRBP family proteins were evaluated by integration of bioinformatics with 3 prediction servers for B-cell epitopes, cell-free protein expression system, and protein microarray methods. The advantage of this strategy is easy selection of possible antigenic proteins and the ability to evaluate antigenicity in a small quantity of recombinant proteins.
A higher humoral immune response level was observed in PVX_116930-1 (391-510 aa) and PVX_116930-2 (635-769 aa) than those of the other PvRBP family genes (75.0% and 87.5%, respectively) (
Table 3). Especially, PVX_116930-2 contained the sequence (
663KSPEPL
692) that was repeated 5 times, possibly to elicit high antigenicity. Although this protein expression level was not specific in schizont stage, overall it was highly conserved regardless of the strain [
40]. BLAST analysis revealed a close relationship with
P. falciparum conserved protein (PF3D7_0305200) and PvRBP2 homologue B (PVX_116930) with a 41% sequence similarity in alpha helical coiled-coil domains. Although the exact function of the PF3D7_0305200 has not yet been defined, it has the expected high antigenicity [
13,
41-
43]. This evidence supports the potential of PvRBP2 homologue B (PVX_116930) as an antigenic serological marker. The alpha helical coiled-coil domain has demonstrated high antigenicity in a broad variety of antigens of parasites that include
Plasmodium spp. [
38,
39,
43]. The recombinant proteins as coiled-coil domain elicit the antigenicity, consistent with previous studies [
36,
38,
39,
44]. PvRBP2 homologue B may an important antigenic protein of the PvRBP family and could be useful serological markers for
P. vivax.
Although the similarity of PvRBP family gene sequence was low, these homologue genes presented a typical RBL family structure, which consisted of a large exon (ectodomain) and small cytoplasmic tails, such as type 1 transmembrane proteins. The PvRBP family has an expected specific function involved in reticulocyte recognition during host cell invasion [
19]. The typical RBL family proteins, PvRBP1a and PvRBP2c, bind to reticulocytes [
19,
20]. Transcription results of the PvRBP family indicate that RBP1a is highly expressed during blood stage parasites. Presently, a new antigenic RBP protein, PvRBP2 homologue B, was confirmed to be consistently expressed during blood stage parasite development. Localization, expression level and pattern, and reticulocyte binding ability of this protein need to be explored.
The sequence diversity analysis of PvRBP1 revealed that the N-terminal region of the protein contains polymorphic residues with non-synonymous polymorphisms relating with immune selection pressure [
44,
45]. In contrast, PvRBP2 homologue B is highly conserved in worldwide isolate; however, coiled-coil domain has immune selection. In this study, antigenicity of most of the PvRBP2 family including the PvRBP2 homologue B was higher than that of the PvRBP1 family. This result may reflect the high genetic diversity in PvRBP2 compared to PvRBP1 [
46]. Moreover, high prevalence of total IgG represents the repeat sequence and both termini of PvRBP2 family. Especially N-terminal part of PvRBP2c (PVX_090325-1) and PvRBP2 partial A (PVX_090330-1) represent high antigenicity (87.5% and 81.3%, respectively) with sequence similarity (60%). These domains may also play an important role for recognition of antibodies.
In summary, this study is the first evaluation of the humoral immune responses against fragments of PvRBP family proteins with predicted B-cell epitope regions in vivax malaria patients and healthy individuals. A high prevalence of total IgG against the fragment of PvRBP2 homologue B (PVX_116930) was detected, implicating the fragment as a potential serological marker. A high prevalence of total IgG in PvRBP2 family genes was observed in the alpha helical coiled-coil motif and at the N-terminus. The present findings will be valuable for serological marker candidates.
This work was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (A121180).
Fig. 1.Schematic protein features and secondary structures of the PvRBP family. The PvRBP family based on amino acid (aa) length. Black bar denotes fragment for recombinant protein expression, with the order of fragment number from the N-terminal region. RDG, arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid a cell adhesion motif.

Fig. 2.Recombinant protein expressions of PvRBP family fragments by Western blot analysis. All the PvRBP recombinant proteins were expressed in the supernatant as the soluble fraction with variable expression level in the wheat germ cell-free expression system. The expression level of each PvRBP protein was detected by Western blot analysis probed with anti-His tag. kDa, kilodalton; T, total crude protein; S, supernatant soluble fraction.
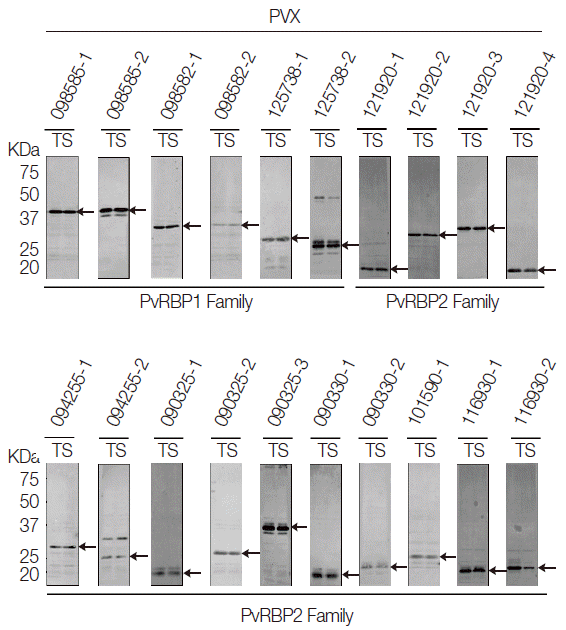
Table 1.General information of Plasmodium vivax reticulocyte binding like protein (PvRBP)
Table 1.
|
Name |
Gene ID (PVX_) |
Chromosome No. |
Length (aa) |
MW (kDa) |
SP |
TM |
Expression stage |
Note |
Reference |
|
PvRBP1a |
098585 |
7 |
2,833 |
326.2 |
Y |
Y |
Schizont |
Full length |
[19,23] |
|
PvRBP1b |
098582 |
7 |
2,608 |
303.3 |
Y |
N |
Unknown |
Full length |
[14] |
|
PvRBP1 like-partial |
125738 |
NA |
785 |
90.9 |
N |
Y |
Unknown |
Partial length |
[14] |
|
PvRBP2a |
121920 |
14 |
2,487 |
286.6 |
Y |
N |
Schizont |
Full length |
[14,21] |
|
PvRBP2b |
094255 |
8 |
2,806 |
325.5 |
Y |
N |
Schizont |
Full length |
[14,21] |
|
PvRBP2c |
090325 |
5 |
2,824 |
326.4 |
Y |
Y |
Schizont |
Full length |
[19,23] |
|
PvRBP2 like-partial A |
090330 |
5 |
623 |
72.8 |
Y |
N |
Schizont |
Partial length |
[14,21] |
|
PvRBP2 like-partial B |
101590 |
14 |
640 |
74.2 |
Y |
N |
Unknown |
Partial length |
[14,21] |
|
PvRBP2 like-homologue B |
116930 |
12 |
1,060 |
123.9 |
Y |
N |
Unknown |
Full length |
[14,21] |
|
PvRBP2d |
101585 |
14 |
2,829 |
329.1 |
Y |
Y |
Null |
Pseudogene |
[21] |
|
PvRBP3 |
101495 |
14 |
2,798 |
323.1 |
N |
Y |
Null |
Pseudogene |
[21] |
Table 2.Primer sequences for recombinant PvRBP family protein expressions
Table 2.
|
Fragment (PVX_) |
Forward primer (5ʹ→3ʹ) |
Reverse primer (5ʹ→3ʹ) |
Position (aa) |
Length (aa) |
pI |
MW (kDa) |
|
098585-1 |
CAAAACAGCATGCAGCAGTAC |
TTCGTCTACTTCCCTTTTGATGT |
804-1,073 |
270 |
5.1 |
34.4 |
|
098585-2 |
GAAATGAATTCTAAAAAGAGCGCT |
TTCTTCTTTGTTTTCTGGGTTCA |
2,619-2,822 |
204 |
4.2 |
25.6 |
|
098582-1 |
GTAGATTTAAATCGAGGGAAAAACAC |
GCAGCTGGATTGCTTCAAA |
15-289 |
273 |
6.7 |
34.7 |
|
098582-2 |
GATAAGTTGAAAGCAGAACTAGGAAGT |
GATCTGTTGTGTTTGCTCTTCC |
996-1,254 |
259 |
5.6 |
33.8 |
|
125738-1 |
CTAGAAAATGACAAAAGGAAAAAGAGC |
AATGTCTGTTTGAGGGGGTAGTC |
476-623 |
148 |
4.6 |
20.0 |
|
125738-2 |
AAAAATGACAGAAACGATCAAAAAT |
ATCTTTTACATTACGTTTTGAACCATT |
630-772 |
143 |
5.4 |
18.9 |
|
121920-1 |
TCAAGCAAAGAAAGCAATCG |
TATTTGATTCTTTGGTGTGAAGAGAA |
20-145 |
126 |
9.7 |
17.7 |
|
121920-2 |
AGCGAAAAAATAGATAAAAATTTGGA |
CATATCGTCGACTAATTCTTTTAAGTC |
453-713 |
261 |
5.2 |
33.3 |
|
121920-3 |
ACGGAAGCTAAAACACTCAGG |
TGTGTCGTAATTCTTATCATCCGT |
1,789-2,049 |
261 |
5.8 |
32.9 |
|
121920-4 |
GCTAAGGAAAACTCCATTAATATGC |
TTCTTCCTTATCTTGAAGATTTCCA |
2,330-2,474 |
145 |
7.4 |
19.0 |
|
094255-1 |
CAAGAAGCTTCCTACCAAAATGC |
TGCAATATTCACTTTCTTAATGGAGT |
728-965 |
238 |
4.7 |
30.7 |
|
094255-2 |
GATACCCAAGAGAACGATACAGAC |
TTCAGAATAATCGCTATTGTCGAA |
2,673-2,806 |
134 |
4 |
18.2 |
|
090325-1 |
AGGAATGGTCAACACAAATACAAC |
TACAATTTCAGGGGCCTCTG |
47-171 |
125 |
9.7 |
18.0 |
|
090325-2 |
CTAAAAGCAAGCTCGAACGATC |
GTATTTATCAGCATTTGATTTCATTTC |
2,115-2,314 |
200 |
5 |
25.7 |
|
090325-3 |
GCAAAAGTTGAGCCTGAAGC |
ATCTTCTTCATTAAAGCAAACTTCG |
2,652-2,824 |
173 |
3.9 |
22.3 |
|
090330-1 |
AGGGATGATCAAAACGGACA |
TGAATTTGGAACACTATGCAATTC |
47-145 |
99 |
8.4 |
14.4 |
|
090330-2 |
GAAAATCCAGAACACTATAAAAATAAGAGA |
AATTTCATCTATTACGAAATCTGCC |
242-370 |
129 |
6.8 |
18.5 |
|
101590-1 |
AAGGATGTCAATCGAAACAAACC |
ATGCAATTTTTTATTATCATCTTCCAT |
22-145 |
124 |
7.5 |
17.2 |
|
116930-1 |
TTGCACAATTCGACCTCC |
AACCATGCTGCCTTCGTAC |
359-477 |
119 |
6.3 |
16.6 |
|
116930-2 |
GATAACATCAAGAGGAGGAACGC |
CAGTTTGAAATTTTTATCGATGTTGT |
603-736 |
134 |
9.7 |
19.4 |
Table 3.Total IgG prevalence of each recombinant PvRBP protein including predicted B-cell epitope domain
Table 3.
|
Antigen (PVX_) |
No. of patients samples (n)
|
95% Cib (%) |
MFIc
|
No. of healthy samples (n)
|
95% CI (%) |
MFI |
P-valuee
|
Features/Structures |
|
Posit. |
Neg. |
Total (%)a
|
Posit. |
Neg. |
Total (%)d
|
|
098585-1 |
10 |
6 |
16 (62.5) |
38.6-81.5 |
6,429 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,139 |
0.0013 |
Repeat sequence |
|
098585-2 |
8 |
8 |
16 (50.0) |
28.0-72.0 |
5,480 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
2,943 |
0.0016 |
C-terminal |
|
098582-1 |
6 |
10 |
16 (37.5) |
18.5-61.4 |
5,806 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,275 |
0.0011 |
N-terminal |
|
098582-2 |
10 |
6 |
16 (62.5) |
38.6-81.5 |
6,566 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,181 |
0.0004 |
Coiled coil |
|
125738-1 |
11 |
5 |
16 (68.8) |
44.4-85.8 |
9,242 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,970 |
0.0002 |
Coiled coil |
|
125738-2 |
11 |
5 |
16 (68.8) |
44.4-85.8 |
10,280 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,741 |
0.0003 |
C-terminal |
|
121920-1 |
11 |
5 |
16 (68.8) |
44.4-85.8 |
11,283 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
4,628 |
0.0013 |
N-terminal |
|
121920-2 |
11 |
5 |
16 (68.8) |
44.4-85.8 |
9,232 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,863 |
0.0007 |
Low complexity |
|
121920-3 |
11 |
5 |
16 (68.8) |
44.4-85.8 |
8,821 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,010 |
0.0005 |
Repeat sequence |
|
121920-4 |
6 |
10 |
16 (37.5) |
18.5-61.4 |
6,947 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,710 |
0.0053 |
C-terminal |
|
094255-1 |
12 |
4 |
16 (75.0) |
50.5-89.8 |
13,325 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
5,163 |
0.0007 |
Repeat sequence |
|
094255-2 |
8 |
8 |
16 (62.5) |
28.0-72.0 |
6,307 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,394 |
0.0011 |
C-terminal |
|
090325-1 |
14 |
2 |
16 (87.5) |
64.0-96.5 |
17,597 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
6,257 |
0.0002 |
N-terminal |
|
090325-2 |
9 |
7 |
16 (56.3) |
33.2-76.9 |
19,179 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
7,226 |
0.0004 |
Short coiled coil |
|
090325-3 |
11 |
5 |
16 (68.8) |
44.4-85.8 |
18,615 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
6,095 |
0.0007 |
C-terminal |
|
090330-1 |
13 |
3 |
16 (81.3) |
57.0-93.0 |
12,413 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
4,455 |
0.0002 |
N-terminal |
|
090330-2 |
7 |
9 |
16 (43.8) |
23.1-66.8 |
12,149 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
6,072 |
0.0030 |
Short coiled coil |
|
101590-1 |
9 |
7 |
16 (56.3) |
33.1-76.9 |
7,223 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,299 |
0.0005 |
N-terminal |
|
116930-1 |
12 |
4 |
16 (75.0) |
50.5-89.8 |
12,407 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
4,522 |
0.0004 |
Short coiled coil |
|
116930-2 |
14 |
2 |
16 (87.5) |
64.0-96.5 |
11,332 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
3,346 |
0.0005 |
Repeat sequence |
|
PvMSP1-19 |
4 |
0 |
4 (100.0) |
51.0-100.0 |
9,987 |
0 |
8 |
8 (100.0) |
67.6-100.0 |
1,887 |
0.0286 |
|
References
- 1. World Health Organization. World Malaria Report (2014). 2014.
- 2. Gething PW, Elyazar IR, Moyes CL, Smith DL, Battle KE, Guerra CA, Patil AP, Tatem AJ, Howes RE, Myers MF, George DB, Horby P, Wertheim HF, Price RN, Mueller I, Baird JK, Hay SI. A long neglected world malaria map: Plasmodium vivax endemicity in 2010. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2012;6:e1814.
- 3. Birkett AJ, Moorthy VS, Loucq C, Chitnis CE, Kaslow DC. Malaria vaccine R&D in the Decade of Vaccines: breakthroughs, challenges and opportunities. Vaccine 2013;31(suppl 2):B233-B243.
- 4. Noulin F, Borlon C, Van Den Abbeele J, D'Alessandro U, Erhart A. 1912-2012: a century of research on Plasmodium vivax in vitro culture. Trends Parasitol 2013;29:286-294.
- 5. Udomsangpetch R, Kaneko O, Chotivanich K, Sattabongkot J. Cultivation of Plasmodium vivax. Trends Parasitol 2008;24:85-88.
- 6. Ubaida Mohien C, Colquhoun DR, Mathias DK, Gibbons JG, Armistead JS, Rodriguez MC, Rodriguez MH, Edwards NJ, Hartler J, Thallinger GG, Graham DR, Martinez-Barnetche J, Rokas A, Dinglasan RR. A bioinformatics approach for integrated transcriptomic and proteomic comparative analyses of model and non-sequenced anopheline vectors of human malaria parasites. Mol Cell Proteomics 2013;12:120-131.
- 7. Fard AT, Salman A, Kazemi B, Bokhari H. In silico comparative genome analysis of malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax chromosome 4. Parasitol Res 2009;104:1361-1364.
- 8. Jones ML, Kitson EL, Rayner JC. Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte invasion: a conserved myosin associated complex. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2006;147:74-84.
- 9. Keeley A, Soldati D. The glideosome: a molecular machine powering motility and host-cell invasion by Apicomplexa. Trends Cell Biol 2004;14:528-532.
- 10. Cowman AF, Crabb BS. Invasion of red blood cells by malaria parasites. Cell 2006;124:755-766.
- 11. Wright GJ, Rayner JC. Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte invasion: combining function with immune evasion. PLoS Pathog 2014;10:e1003943.
- 12. Cowman AF, Berry D, Baum J. The cellular and molecular basis for malaria parasite invasion of the human red blood cell. J Cell Biol 2012;198:961-971.
- 13. Gardner MJ, Hall N, Fung E, White O, Berriman M, Hyman RW, Carlton JM, Pain A, Nelson KE, Bowman S, Paulsen IT, James K, Eisen JA, Rutherford K, Salzberg SL, Craig A, Kyes S, Chan MS, Nene V, Shallom SJ, Suh B, Peterson J, Angiuoli S, Pertea M, Allen J, Selengut J, Haft D, Mather MW, Vaidya AB, Martin DM, Fairlamb AH, Fraunholz MJ, Roos DS, Ralph SA, McFadden GI, Cummings LM, Subramanian GM, Mungall C, Venter JC, Carucci DJ, Hoffman SL, Newbold C, Davis RW, Fraser CM, Barrell B. Genome sequence of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 2002;419:498-511.
- 14. Carlton JM, Adams JH, Silva JC, Bidwell SL, Lorenzi H, Caler E, Crabtree J, Angiuoli SV, Merino EF, Amedeo P, Cheng Q, Coulson RM, Crabb BS, Del Portillo HA, Essien K, Feldblyum TV, Fernandez-Becerra C, Gilson PR, Gueye AH, Guo X, Kang'a S, Kooij TW, Korsinczky M, Meyer EV, Nene V, Paulsen I, White O, Ralph SA, Ren Q, Sargeant TJ, Salzberg SL, Stoeckert CJ, Sullivan SA, Yamamoto MM, Hoffman SL, Wortman JR, Gardner MJ, Galinski MR, Barnwell JW, Fraser-Liggett CM. Comparative genomics of the neglected human malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax. Nature 2008;455:757-763.
- 15. Kappe SH, Noe AR, Fraser TS, Blair PL, Adams JH. A family of chimeric erythrocyte binding proteins of malaria parasites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998;95:1230-1235.
- 16. Adams JH, Sim BK, Dolan SA, Fang X, Kaslow DC, Miller LH. A family of erythrocyte binding proteins of malaria parasites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992;89:7085-7089.
- 17. Horuk R, Chitnis CE, Darbonne WC, Colby TJ, Rybicki A, Hadley TJ, Miller LH. A receptor for the malarial parasite Plasmodium vivax: the erythrocyte chemokine receptor. Science 1993;261:1182-1184.
- 18. Menard D, Barnadas C, Bouchier C, Henry-Halldin C, Gray LR, Ratsimbasoa A, Thonier V, Carod JF, Domarle O, Colin Y, Bertrand O, Picot J, King CL, Grimberg BT, Mercereau-Puijalon O, Zimmerman PA. Plasmodium vivax clinical malaria is commonly observed in Duffy-negative Malagasy people. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010;107:5967-5971.
- 19. Galinski MR, Medina CC, Ingravallo P, Barnwell JW. A reticulocyte-binding protein complex of Plasmodium vivax merozoites. Cell 1992;69:1213-1226.
- 20. Miller LH, Baruch DI, Marsh K, Doumbo OK. The pathogenic basis of malaria. Nature 2002;415:673-679.
- 21. Kosaisavee V, Lek-Uthai U, Suwanarusk R, Gruner AC, Russell B, Nosten F, Renia L, Snounou G. Genetic diversity in new members of the reticulocyte binding protein family in Thai Plasmodium vivax isolates. PLoS One 2012;7:e32105.
- 22. Li J, Han ET. Dissection of the Plasmodium vivax reticulocyte binding-like proteins (PvRBPs). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012;426:1-6.
- 23. Bozdech Z, Mok S, Hu G, Imwong M, Jaidee A, Russell B, Ginsburg H, Nosten F, Day NP, White NJ, Carlton JM, Preiser PR. The transcriptome of Plasmodium vivax reveals divergence and diversity of transcriptional regulation in malaria parasites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008;105:16290-16295.
- 24. List C, Qi W, Maag E, Gottstein B, Muller N, Felger I. Serodiagnosis of Echinococcus spp. infection: explorative selection of diagnostic antigens by peptide microarray. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2010;4:e771.
- 25. Noya O, Patarroyo ME, Guzman F, Alarcon de Noya B. Immunodiagnosis of parasitic diseases with synthetic peptides. Curr Protein Pept Sci 2003;4:299-308.
- 26. Assis LM, Sousa JR, Pinto NF, Silva AA, Vaz AF, Andrade PP, Carvalho EM, De Melo MA. B-cell epitopes of antigenic proteins in Leishmania infantum: an in silico analysis. Parasite Immunol 2014;36:313-323.
- 27. Singh H, Ansari HR, Raghava GP. Improved method for linear Bcell epitope prediction using antigen's primary sequence. PLoS One 2013;8:e62216.
- 28. Saha S, Raghava GPS. BcePred: Prediction of continuous B-cell epitopes in antigenic sequences using physico-chemical properties. Artificial Immune Systems, Proceedings 2004;3239:197-204.
- 29. Saha S, Raghava GP. Prediction of continuous B-cell epitopes in an antigen using recurrent neural network. Proteins 2006;65:40-48.
- 30. Larsen JE, Lund O, Nielsen M. Improved method for predicting linear B-cell epitopes. Immunome Res 2006;2:2.
- 31. Yang X, Yu X. An introduction to epitope prediction methods and software. Rev Med Virol 2009;19:77-96.
- 32. Mahdavi M, Mohabatkar H, Keyhanfar M, Dehkordi AJ, Rabbani M. Linear and conformational B cell epitope prediction of the HER 2 ECD-subdomain III by in silico methods. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2012;13:3053-3059.
- 33. Bouillon A, Giganti D, Benedet C, Gorgette O, Petres S, Crublet E, Girard-Blanc C, Witkowski B, Menard D, Nilges M, MercereauPuijalon O, Stoven V, Barale JC. In Silico screening on the threedimensional model of the Plasmodium vivax SUB1 protease leads to the validation of a novel anti-parasite compound. J Biol Chem 2013;288:18561-18573.
- 34. Restrepo-Montoya D, Becerra D, Carvajal-Patino JG, Mongui A, Nino LF, Patarroyo ME, Patarroyo MA. Identification of Plasmodium vivax proteins with potential role in invasion using sequence redundancy reduction and profile hidden Markov models. PLoS One 2011;6:e25189.
- 35. Cheng Y, Wang Y, Ito D, Kong DH, Ha KS, Chen JH, Lu F, Li J, Wang B, Takashima E, Sattabongkot J, Tsuboi T, Han ET. The Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein 1 paralog is a novel erythrocyte-binding ligand of P. vivax. Infect Immun 2013;81:1585-1595.
- 36. Cespedes N, Habel C, Lopez-Perez M, Castellanos A, Kajava AV, Servis C, Felger I, Moret R, Arevalo-Herrera M, Corradin G, Herrera S. Plasmodium vivax antigen discovery based on alpha-helical coiled coil protein motif. PLoS One 2014;9:e100440.
- 37. Crowther GJ, Shanmugam D, Carmona SJ, Doyle MA, HertzFowler C, Berriman M, Nwaka S, Ralph SA, Roos DS, Van Voorhis WC, Aguero F. Identification of attractive drug targets in neglected-disease pathogens using an in silico approach. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2010;4:e804.
- 38. Kulangara C, Kajava AV, Corradin G, Felger I. Sequence conservation in Plasmodium falciparum alpha-helical coiled coil domains proposed for vaccine development. PLoS One 2009;4:e5419.
- 39. Olugbile S, Villard V, Bertholet S, Jafarshad A, Kulangara C, Roussilhon C, Frank G, Agak GW, Felger I, Nebie I, Konate K, Kajava AV, Schuck P, Druilhe P, Spertini F, Corradin G. Malaria vaccine candidate: design of a multivalent subunit alpha-helical coiled coil poly-epitope. Vaccine 2011;29:7090-7099.
- 40. Neafsey DE, Galinsky K, Jiang RH, Young L, Sykes SM, Saif S, Gujja S, Goldberg JM, Young S, Zeng Q, Chapman SB, Dash AP, Anvikar AR, Sutton PL, Birren BW, Escalante AA, Barnwell JW, Carlton JM. The malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax exhibits greater genetic diversity than Plasmodium falciparum. Nat Genet 2012;44:1046-1050.
- 41. Bowman S, Lawson D, Basham D, Brown D, Chillingworth T, Churcher CM, Craig A, Davies RM, Devlin K, Feltwell T, Gentles S, Gwilliam R, Hamlin N, Harris D, Holroyd S, Hornsby T, Horrocks P, Jagels K, Jassal B, Kyes S, McLean J, Moule S, Mungall K, Murphy L, Oliver K, Quail MA, Rajandream MA, Rutter S, Skelton J, Squares R, Squares S, Sulston JE, Whitehead S, Woodward JR, Newbold C, Barrell BG. The complete nucleotide sequence of chromosome 3 of Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 1999;400:532-538.
- 42. Hall N, Pain A, Berriman M, Churcher C, Harris B, Harris D, Mungall K, Bowman S, Atkin R, Baker S, Barron A, Brooks K, Buckee CO, Burrows C, Cherevach I, Chillingworth C, Chillingworth T, Christodoulou Z, Clark L, Clark R, Corton C, Cronin A, Davies R, Davis P, Dear P, Dearden F, Doggett J, Feltwell T, Goble A, Goodhead I, Gwilliam R, Hamlin N, Hance Z, Harper D, Hauser H, Hornsby T, Holroyd S, Horrocks P, Humphray S, Jagels K, James KD, Johnson D, Kerhornou A, Knights A, Konfortov B, Kyes S, Larke N, Lawson D, Lennard N, Line A, Maddison M, McLean J, Mooney P, Moule S, Murphy L, Oliver K, Ormond D, Price C, Quail MA, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutter S, Rutherford KM, Sanders M, Simmonds M, Seeger K, Sharp S, Smith R, Squares R, Squares S, Stevens K, Taylor K, Tivey A, Unwin L, Whitehead S, Woodward J, Sulston JE, Craig A, Newbold C, Barrell BG. Sequence of Plasmodium falciparum chromosomes 1, 3-9 and 13. Nature 2002;419:527-531.
- 43. Villard V, Agak GW, Frank G, Jafarshad A, Servis C, Nebie I, Sirima SB, Felger I, Arevalo-Herrera M, Herrera S, Heitz F, Backer V, Druilhe P, Kajava AV, Corradin G. Rapid identification of malaria vaccine candidates based on alpha-helical coiled coil protein motif. PLoS One 2007;2:e645.
- 44. Tran TM, Oliveira-Ferreira J, Moreno A, Santos F, Yazdani SS, Chitnis CE, Altman JD, Meyer EV, Barnwell JW, Galinski MR. Comparison of IgG reactivities to Plasmodium vivax merozoite invasion antigens in a Brazilian Amazon population. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2005;73:244-255.
- 45. Rayner JC, Tran TM, Corredor V, Huber CS, Barnwell JW, Galinski MR. Dramatic difference in diversity between Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax reticulocyte binding-like genes. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2005;72:666-674.
- 46. Prajapati SK, Kumari P, Singh OP. Molecular analysis of reticulocyte binding protein-2 gene in Plasmodium vivax isolates from India. BMC Microbiol 2012;12:243.