Abstract
The sodium hydrogen exchanger 1 (NHE1), which functions in maintaining the ratio of Na+ and H+ ions, is widely distributed in cell plasma membranes. It plays a prominent role in pH balancing, cell proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, and migration. However, its exact subcellular location and biological functions in Toxoplasma gondii are largely unclear. In this study, we cloned the C-terminal sequence of T. gondii NHE1 (TgNHE1) incorporating the C-terminal peptide of NHE1 (C-NHE1) into the pGEX4T-1 expression plasmid. The peptide sequence was predicted to have good antigenicity based on the information obtained from an immune epitope database. After induction of heterologous gene expression with isopropyl-b-D-thiogalactoside, the recombinant C-NHE1 protein successfully expressed in a soluble form was purified by glutathione sepharose beads as an immunogen for production of a rabbit polyclonal antiserum. The specificity of this antiserum was confirmed by western blotting and immunofluorescence. The antiserum could reduce T. gondii invasion into host cells, indicated by the decreased TgNHE1 expression in T. gondii parasites that were pre-incubated with antiserum in the process of cell entry. Furthermore, the antiserum reduced the virulence of T. gondii parasites to host cells in vitro, possibly by blocking the release of Ca2+. In this regard, this antiserum has potential to be a valuable tool for further studies of TgNHE1.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, soluble expression, TgNHE1, polyclonal antiserum, Ca2+ release
INTRODUCTION
Toxoplasma gondii, a highly pathogenic intracellular parasite, causes a zoonotic disease referred to as toxoplasmosis, and infects a wide range of animals, including humans. About one-third of the global population carries dominant or recessive symptoms of toxoplasmosis, and pregnant women are highly susceptible to it [
1]. Currently, the leading therapy for this disease is the combination of pyrimethamine and sulfonamide drugs [
2]. However, the need for long-term treatment and untoward side effects are disadvantages of such treatment.
Membrane proteins are the first frontier of the interaction between parasites and hosts.
T. gondii contains 4 sodium hydrogen exchangers (NHEs): TgNHE1, TgNHE2, TgNHE3, and TgNHE4. Recent studies indicate that TgNHE1 and TgNHE2 are localized in the plasma membrane and rhoptry organelle, respectively [
3,
4]. TgNHE3 co-localizes with the PLV/VAC TgVP1 marker [
5], while the location of TgNHE4 in the parasite is still unclear. TgNHE1 functions mainly in Ca
2+ release from intracellular pools [
3]. As is known, Ca
2+ signaling plays a pivotal role in host cell invasion by parasites. Ca
2+-dependent secretion from apical micronemes mediates pH homeostasis, leading to suppression of potassium ions and promoting parasite motility [
6]. Ca
2+ ionophores ionomycin and A23187, which are 2 Ca
2+ elevating regents, stimulate microneme discharge of the transmembrane adhesin, MIC2 [
7,
8]. Apart from autogenous regulation of intracellular Ca
2+,
T. gondii invasion also induces significance alternations to the Ca
2+ concentration in host cells [
9,
10].
To the best of our knowledge, only a few studies have focused on TgNHE1, and the detailed mechanisms it takes part in remain largely unknown. In this study, we successfully designed and expressed a C-terminal peptide of TgNHE1 (C-TgNHE1) in a soluble form using a prokaryotic expression system. A total of 2 mg of purified protein was used for generating a polyclonal antiserum against TgNHE1 by immunizing New Zealand rabbits. The specificity of the polyclonal antiserum was confirmed by western blotting and immunofluorescence assays. This antiserum reduced T. gondii invasion and virulence markedly, as shown by the TgNHE1 expression in intracellular T. gondii, as well as measuring the number and area of cell plaques by T. gondii parasite infection, thus indicating that TgNHE1 could be a promising therapeutic target.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and regents
Male Kunming mice weighing 25-30 g were purchased from the Laboratory Animal Center of Southern Medical University (Guangzhou, China). The animal experiments were approved by the local Animal Ethics Committee of the Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, People’s Republic of China, following the rules relating to the ethics on experimental animals. SuperScript® II reverse transcriptase was purchased from Invitrogen (Grand Island, New York, USA). PrimeSTAR® HS, restriction endonuclease, and a DNA Ligation Kit were purchased from Takara (Dalian, China). The pGEX4T-1 vector, TOP10, and BL21 (DE3) competent cells were from TIANGEN Biotech (Beijing, China). PageRuler Prest Protein Ladder was from Fermentas (Ontario, Canada). Trizol and isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactoside (IPTG) were from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, Missouri, USA). Glutathione sepharose high-performance (GSH) beads were from BEAVER Nano (Suzhou, China). Goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP antibody was from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, Texas, USA). Alexa fluor 594 goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) secondary antibody conjugate was from Life Technologies (Grand Island). Bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA) protein assay kit was from Thermo Scientific (Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). Centrifugal filter units (30 kDa) were from Merck Millipore (Bedford, Massachusetts, USA).
Parasite culture
T. gondii, cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen in our laboratory, was recovered at a constant 37˚C. Parasites (1×10
5) suspended in 200 μl PBS were intraperitoneally injected into Kunming mice. When exhibiting obvious signs of infection, the mice were humanely killed. The parasites were collected from their peritoneal exudates and added to PBS.
T. gondii tachyzoites were purified using a method based on 3-μm filter purification, as described elsewhere [
11].
Primer design and plasmid construction
The 2 primers used for amplifying TgNHE1 cDNA were as follows. The forward primer sequence was 5´ ATTGGATCCATGGGGCATGTCCTCGCGT 3´ (restriction sites in bold); the reverse primer sequence was 5´ AATCTCGAGAACTGCATTCTGAAAGCTCGC 3´ (restriction sites in bold).
Total RNA was extracted from 1×107 purified T. gondii tachyzoites. The RNA-cDNA reaction was carried out by SuperScript® II reverse transcriptase following the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR amplification conditions were as follows: 34 cycles at 98˚C for 10 sec, 55˚C for 15 sec, 72˚C for 10 sec, and a final extension step at 72˚C for 5 min. After PCR product purification, the DNA insert and pGEX4T-1 vector were digested by BamH I and Xho I for 1 hr, respectively. For DNA ligation, the molar ratio of the DNA insert to linearized vector was 5 to 1, respectively, and the reaction proceeded at 16˚C for 30 min. Escherichia coli TOP10 competent cells were transformed with recombinant pGEX4T-1. Positive clones were confirmed by double-enzyme restriction and sequencing.
Protein expression and purification
The recombinant pGEX4T-1-C-TgNHE1 plasmid was transformed into 50 μl E. coli BL21 (DE3) and cultured in Luria-Bertani solid medium with 100 μg/ml ampicillin. A single clone was grown with shaking at 220 rpm at 37˚C until the OD600 reached 0.6. Bacteria were induced to express C-TgNHE1 by IPTG at a concentration of 24 μg/ml for 20 hr at 18˚C to obtain the target protein in a soluble form. The bacteria were collected by centrifuging at 10,000 g for 1 min followed by 3 freeze-thaw cycles and 30 min sonication on ice under 200 W for 2 sec with 8-sec intervals. After centrifuging at 14,000 g for 20 min, the supernatants containing the target protein were separated and stored at -70˚C.
For protein purification, GSH beads (BEAVER Nano) were used. First, the beads were washed in buffer A (140 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, and 1.8 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.4) 3 times. The soluble components (1 ml) supplemented with 1×protease inhibitor cocktail were mixed with the beads vertically at 4˚C for 1 hr. After 3 additional washes with buffer A, the GST-fusion proteins that had adsorbed to the GSH beads were eluted with 500 μl of buffer B (50 mM Tris-HCl, 10 mM reduced glutathione, pH 7.4) at ambient temperature for 6 min. The eluents were filtered through 0.22-μm membranes, and the protein concentration of the eluent was measured with a BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Scientific). Finally, the base solution of recombinant proteins was replaced with normal saline using 10 kDa centrifugal filter units (Merck Millipore).
Preparation of polyclonal antiserum
New Zealand white rabbits weighing about 1.5 kg were immunized subcutaneously with 500 μg of purified recombinant C-TgNHE1 emulsified in an equal volume of Freund’s complete adjuvant. To enhance the immune response, 500 μg of recombinant protein emulsified in Freund’s incomplete adjuvant was administered twice every 2 weeks. Afterwards, a blood sample was collected from the rabbit’s auricular vein to determine the titer of the antiserum by an indirect ELISA. When the titer reached a sufficiently high level, 100 μg of the immunogen was administered, and a blood sample was collected through carotid artery intubation. Serum was separated from whole blood by standing the blood sample at 4˚C overnight, and the antiserum was purified using protein A agarose (Sigma-Aldrich).
Western blotting and immunofluorescence
Denatured samples were subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE and electrotransferred to PVDF membranes (no. 162-0177, Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA) at 100 V for 90 min. Membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat milk at 4˚C overnight and incubated with antiserum at a dilution of 1:1,000 for 1.5 hr. After washing with Tris-buffered saline Tween-20 (TBST) 3 times, the membranes were incubated with a goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP antibody for 1 hr and then washed with TBST again, 3 times. Finally, chemiluminescent substrates (ECL, Thermo Scientific) were used to develop the immunoblots.
For the immunofluorescence assays, T. gondii RH tachyzoites cultured in Kunming mice were isolated and purified with a 3-μm filter, then placed on a cell culture dish and immobilized with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min. Parasite membranes were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 for 10 min and then washed with PBS 3 times for 5 min each time. Samples were blocked with PBST (PBS containing 1% BSA and 0.1% Tween 20) for 1 hr and incubated with antiserum at a 1:100 dilution at 4˚C overnight. The parasites were then incubated with anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 594 (red) antibody for 1 hr at ambient temperature. Unbound antibodies were washed 3 times with PBS and the cell nuclei were stained with 4, 6,-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). The fluorescent signals were visualized using an inverted fluorescence microscope (Leica, Brunswick, Germany).
CCK-8 assays
For the CCK-8 assays, ovine fetal turbinate (OFTu) cells were cultured in 96-well plates containing Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium (DMEM) plus 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (2×104/well/200 μl) for 24 hr. Different concentrations of antiserum were added to the cell medium for 72 hr. After treatment, the supernatant was removed, and the cells were washed with PBS and treated with 10 μl of CCK-8 for 2 hr. Finally, the absorbance of the cells was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader (Bio-Rad).
Plaque assays
Plaque assays were performed as described previously [
12]. In detail, 1×10
5 OFTu cells were cultured in 24-well plates in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS until confluent. Cells were infected with 5×10
5 T. gondii RH strain pre-incubated individually with various concentrations (0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 mg/ml) of antiserum or with normal rabbit serum for 12 hr. Cells were washed with PBS to remove any uninvaded parasites at 4 hr post infection and then cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS. Five days later, the cells were washed, fixed in 10% buffered formalin for 24 hr, and stained with 1% toluidine blue. The cells were visualized using a light microscope, and images of the microscopic fields were captured to quantify the number of plaques (no. of areas with lysed cells) and measure the plaque area (dimension of the areas with lysed cells).
RESULTS
Design of the antigenic epitope of TgNHE1
TgNHE1 (GenBank no. AAR85890.1) contains 12 possible transmembrane helices predicted by TMHMM Server v.2.0 (
http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-2.0/). The TgNHE1 internal and transmembrane domains are located mainly at the N-terminal of the amino acid (aa) sequence and the C-terminal region stretches out of the cell membrane. In consideration of the difficulty anticipated in expressing the complete high molecular-weight membrane protein (about 248 kDa) in
E. coli, we selected the C-terminal antigenic determinants of TgNHE1 for antibody preparation. The B-cell epitope of TgNHE1 was analyzed by Bepipred Linear Epitope Prediction from the IEDB analysis resource (
www.ideb.org). The peaks above the threshold were suggestive of promising regions with good immunogenicity. In view of avoiding the cross reaction with non-specific proteins from host cells (OFTu cells) in this research, the C-terminal sequence (2127 aa-2288 aa) with good predicted immunogenicity was determined for the follow-up expression experiments.
To obtain the coding sequence of the C-terminal of TgNHE1 (C-TgNHE1), total RNA was isolated from
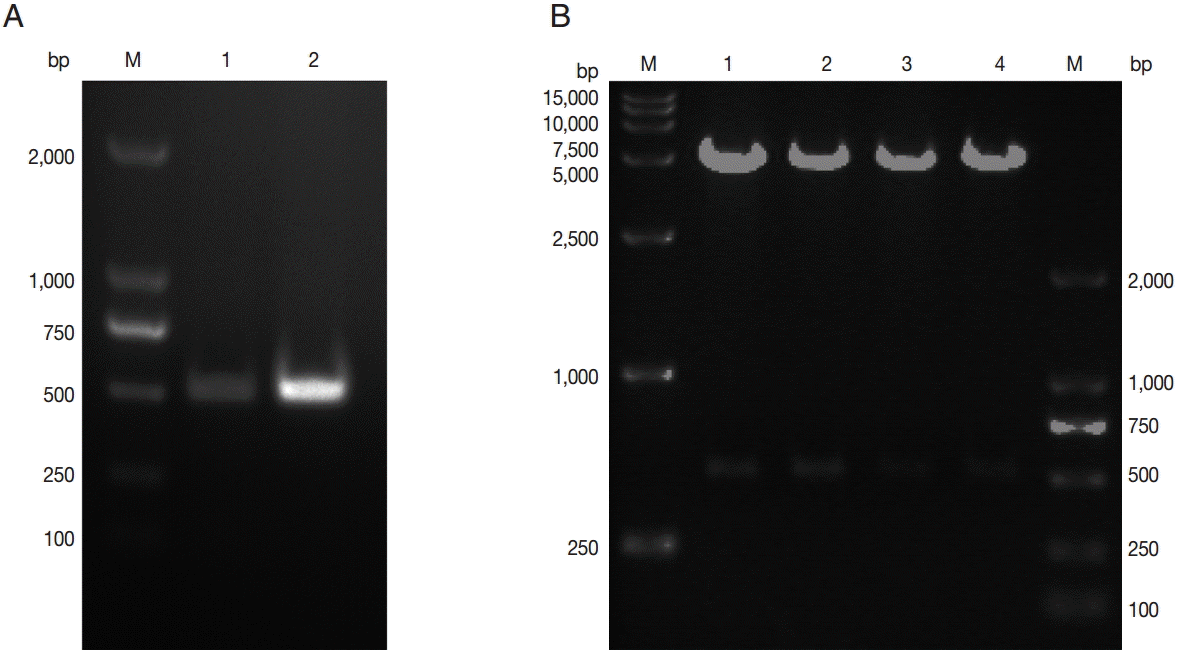
T. gondii RH strain, and the corresponding cDNA was synthesized. The 486-bp C-terminal-TgNHE1 coding sequence was amplified by PCR (
Fig. 1A). After double enzyme digestion with
BamH I and
Xho I, the purified PCR product and linearized vector pGEX4T-1 were ligated and transformed into
E. coli TOP10 cells. The pGEX4T-1-C-TgNHE1 recombination plasmid was identified by restriction digestion (
Fig. 1B) and DNA sequencing (data not shown).
The recombinant plasmid derived from
E. coli TOP10 cells was subsequently transformed into
E. coli BL21. A single clone was selected for IPTG induction. Compared with the mock-vehicle group, a GST fusion protein of about 43 kDa (26 kDa GST-tag plus 17 kDa C-TgNHE1) was expressed (
Fig. 2A). In addition, 2 more proteins of about 35 kDa and 26 kDa (possibly derived from the GST tag) were simultaneously expressed to a lesser extent. To obtain a prokaryotic protein with approximate native conformation, we employed a method favoring soluble protein expression where the bacteria were induced at 18˚C for 20 hr. After sonication, the soluble and pelleted fractions were separated by centrifuging at 14,000 g for 20 min and subjected to SDS-PAGE. The results showed that C-TgNHE1 existed in both components (
Fig. 2B). The soluble fraction was then purified by GSH beads. As indicated in
Fig. 3B, C-TgNHE1 was purified with high specificity and affinity. Western blotting confirmed that the purified protein of the expected size was a GST-tagged fusion protein (
Fig. 2C).
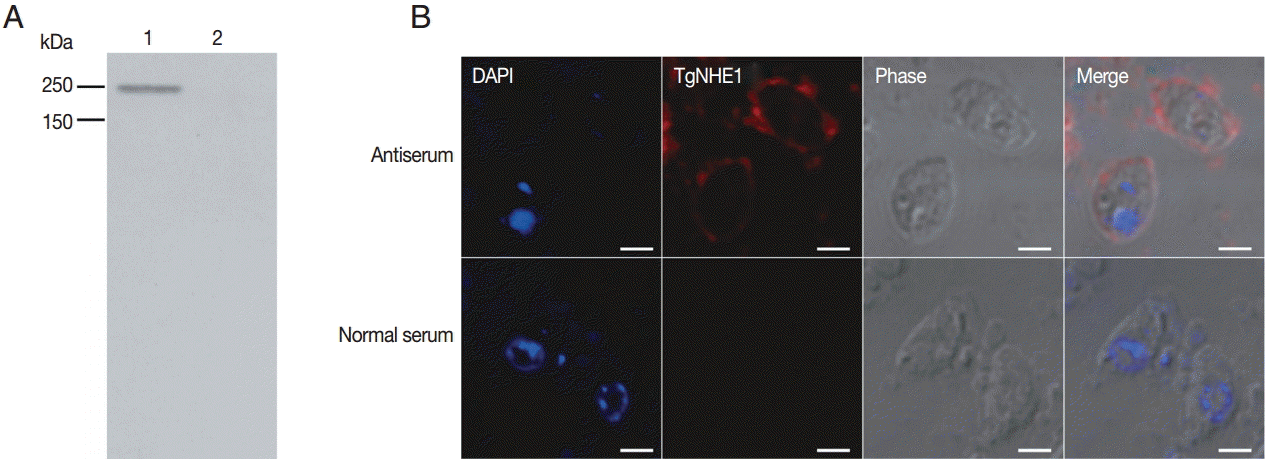
Polyclonal antibody production was induced in New Zealand white rabbits by immunization of multiple sites by subcutaneous injections. After a booster immunization, the rabbit polyclonal anti-serum was measured by indirect ELISA. The polyclonal anti-serum bound to the coating antigen with high affinity in a dose-dependent manner (anti-serum titer: 1:640,000) (data not shown). To detect the capacity of the antibody in recognizing natural TgNHE1 in
T. gondii RH strain, purified parasites were lysed and used for western blotting. The results showed that a single band was recognized by the antibody at the right location, while the normal rabbit serum failed to do so (
Fig. 3A). We also detected cross-reaction of this antiserum using an immunofluorescence assay. TgNHE1 showed a punctate pattern of distribution in the plasma membrane, while specific signals were not seen in the control group (
Fig. 3B). Above all, these results indicate that the antiserum is a potentially valuable tool for studying TgNHE1.
As the TgNHE1 membrane protein is involved in Ca
2+ egress, which is closely related to
T. gondii virulence, and the polyclonal antiserum binds to this protein, we speculated that this antiserum would reduce
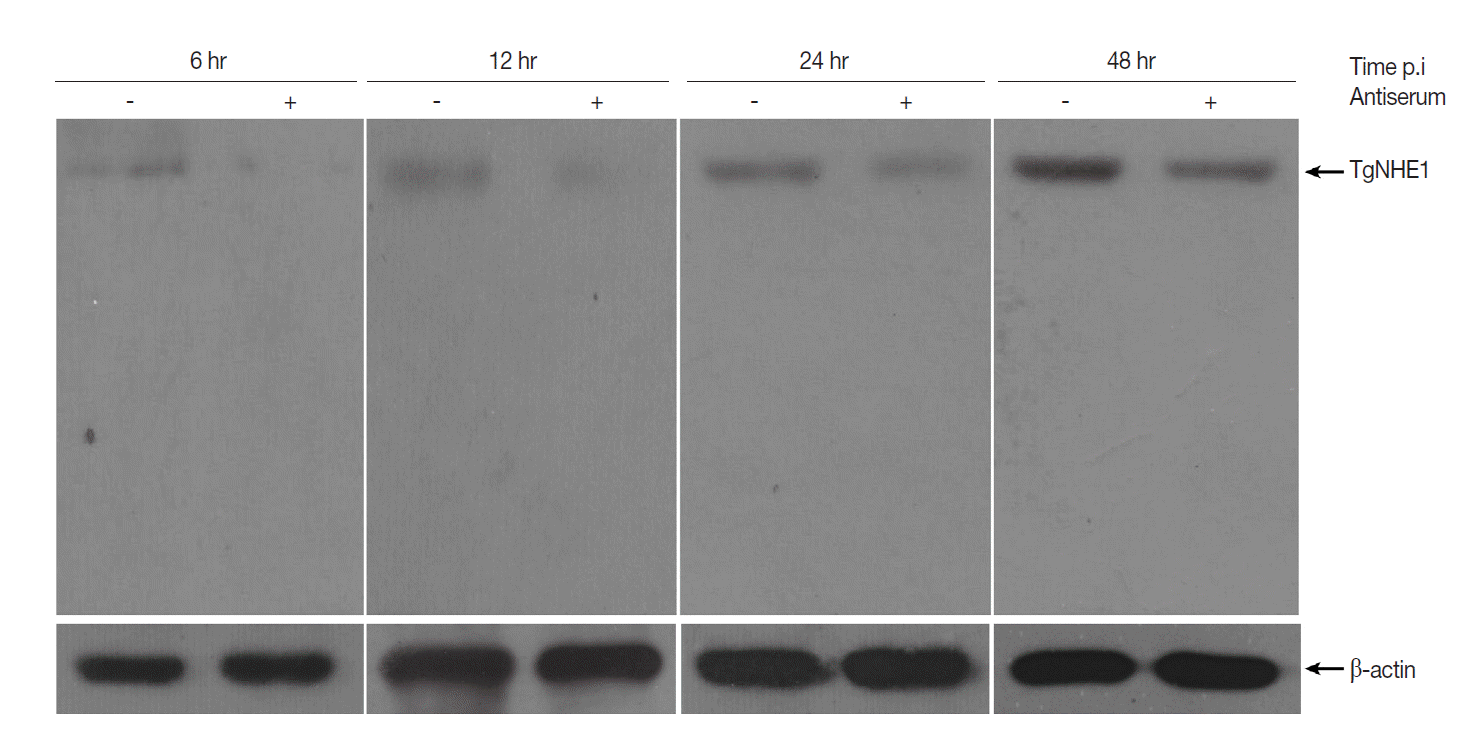
T. gondii invasion and virulence by blocking TgNHE1. To test this hypothesis, we first investigated TgNHE1 expression in intracellular
T. gondii RH strain that was pre-incubated with antiserum or normal serum at different time points post infection (p.i). Compared with controls, the expression of TgNHE1 was dramatically reduced shortly after parasites entered OFTu cells (6h) (
Fig. 4). Since
T. gondii started to proliferate between 12 hr and 24 hr, sustained lower TgNHE1 expression was still observed in antiserum-treated group, indicating that the antiserum prevented the cell entry of
T. gondii by blocking TgNHE1, and lower TgNHE1 expression was possibly due to the less number of
T. gondii that entered the host cell (
Fig. 4). To test the effect of the antiserum on
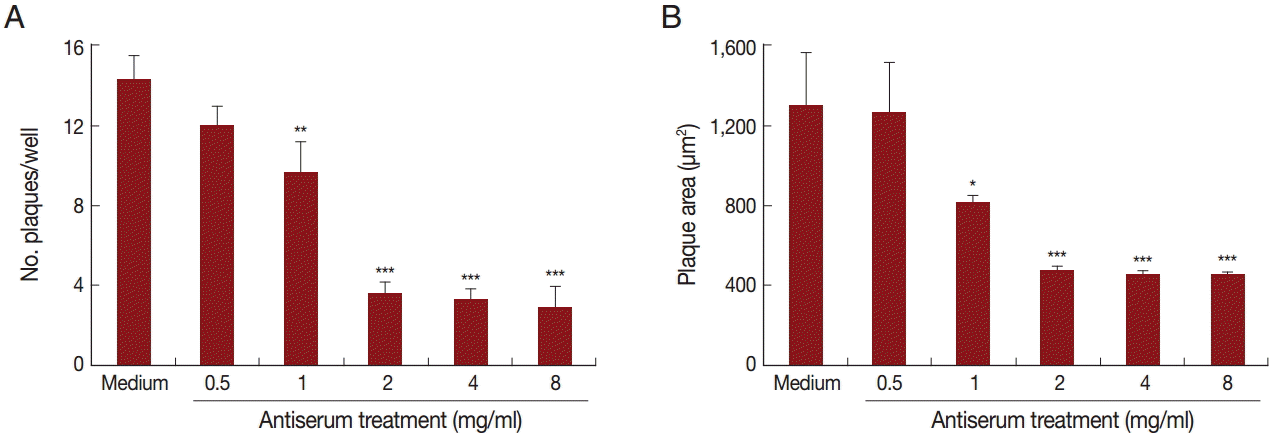
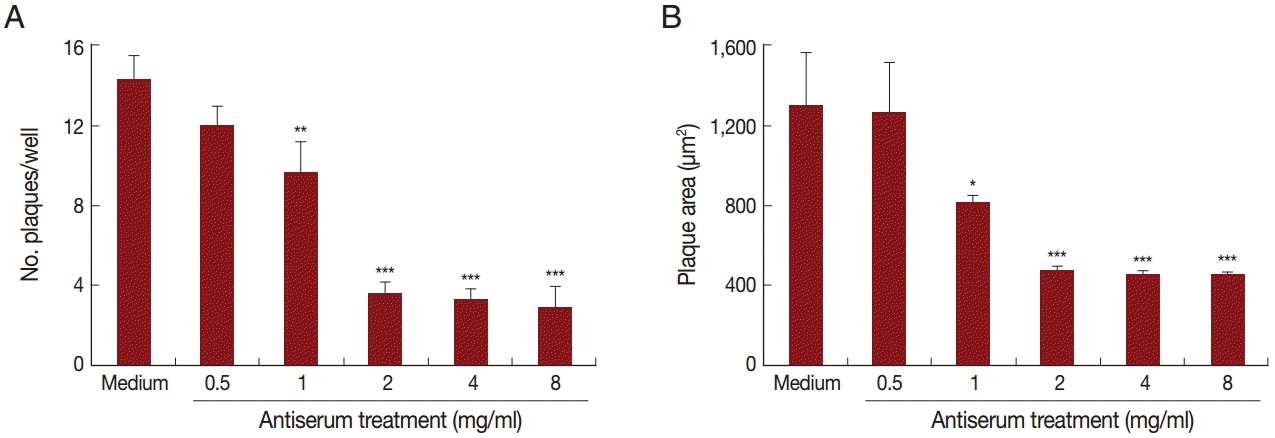
T. gondii virulence, we first measured the toxicity of the antiserum to host cells. Treatment with the antiserum at increasing concentrations did not reduce the cell viability using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), which was applied to detect cell proliferation and virulence (data not shown). We then employed a plaque assay to observe the number and area of plaques changed by pretreatment with the antiserum. Parasites that were pre-incubated with increasing levels of antiserum were used to infect OFTu cells. Normal rabbit serum served as a negative control. As shown in
Fig. 5A, antiserum treatment reduced the number of plaques compared with the untreated cells in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, the plaque areas were markedly reduced following antiserum treatment (
Fig. 5B). Taken together, antiserum treatment reduced
T. gondii entry and virulence to host cells.
DISCUSSION
T. gondii, a parasite of living cells, infects a wide range of warmblooded hosts, resulting in a serious zoonosis called toxoplasmosis.
T. gondii has high resistance to antiparasitic agents, causes severe pathogenicity in pregnant women, and is found worldwide but mainly in the USA and Europe among high-risk groups [
13]. The search for an effective therapeutic target is now urgent.
The homeostasis of intracellular pH is of great importance to a variety of biological processes such as cell growth, differentiation, internal enzymatic activity, and cytoskeleton assembly in apicomplexan parasites such as
T. gondii. NHEs, which are localized mainly in the plasma membrane, play an important role in such cellular events. TgNHE molecules possess 4 homologous series proteins: TgNHE1 to TgNHE4. TgNHE1 is a ubiquitous membrane protein involved not only in Na
+/H
+ exchange, but also in Ca
2+ egress [
14]. Studies showed that Ca
2+ signaling is crucial for protein secretion, motility, cell invasion, and differentiation of apicomplexan parasites [
15-
18]. When TgNHE1 is knocked out,
T. gondii is resistant to Ca
2+ ionophore A23187-induced egress and amiloride-induced proton efflux inhibition [
14]. Compared with TgNHE1, TgNHE3 also plays a role in Ca
2+ homeostasis and parasite invasion through mediating MIC2 secretion and maintaining intracellular Ca
2+ concentrations [
5]. In the closely related apicomplexan parasite
Plasmodium falciparum (Pf), PfNHE, which has been well characterized for its resistance to an anti-malarial drug, quinine, regulates H+ egress and cytosolic Ca
2+ concentrations [
19-
22]. Similarly, in both
Leishmania donovani and
Trypanosoma brucei, acidocalcisomal NHE facilities Ca
2+ release from the rhoptry organelle [
23,
24].
There is a wealth of evidence showing the importance of Ca
2+ release in the process of
T. gondii invasion of host cells. Calcium ionophores, such as ionomycin and A23187, or the endoplasmic reticulum Ca
2+ pump inhibitor thapsigargin, are capable of activate conoid extrusion of
T. gondii tachyzoites [
25]. Treatment of tachyzoites with the intracellular Ca
2+ chelator 1,2-bis (
o-aminophenoxy) ethane-
N,N,N,N-tetraacetic acid/tetraacetoxymethyl ester prevented ionomycin-induced conoid extrusion and inhibited parasite invasion [
25]. Ionomycin-induced conoid extrusion was also prevented by cytochalasin D, a drug that impairs
T. gondii motility and invasion capacity into host cells [
26-
29]. These results suggested that Ca
2+ release from tachyzoite internal stores has been identified as key players in activating the process of
T. gondii invasion.
In this research, we generated a polyclonal antibody that specifically recognizes TgNHE1, a plasma membrane controller of Ca2+ release. We expect this antibody to be a useful tool for studying TgNHE1 and also to weaken T. gondii invasion by blocking Ca2+ release from TgNHE1. As an initial step, based on TMHMM prediction, we found that the C-terminal peptide of TgNHE1 was fully exposed to the external cell surface, while the N-terminal part was not entirely exposed. Additionally, the B-cell epitopes were more concentrated in the C-terminus and had high scores. Therefore, C-TgNHE1 was selected for expression as an immunogen for antibody production.
The GST fusion system has been used extensively as a prokaryotic expression system in bacteria for its convenience at producing soluble heterologous proteins that are easy to purify [
30]. Here, GST was employed as a co-expression vehicle with C-TgNHE1, with the aim to generate a soluble functional fusion protein. After preparation of the antiserum triggered by administration of purified C-TgNHE1 in a rabbit, we identified the antibody by indirect ELISA, western blotting, and immunofluorescence. TgNHE1 was found to be embedded mainly in the cell membrane with some other dotted distribution in the cytoplasm. By indirect ELISA and western blotting analysis, we confirmed that this antibody was able to recognize natural TgNHE1 in
T. gondii with high affinity and specificity, indicating that it has potential to be a valuable tool for studying TgNHE1. We also observed that pre-incubation of
T. gondii RH strain with this antiserum reduced cell entry and plaque formation. These results show that besides binding to TgNHE1, this antibody might also block ion transport in the channel, especially invasion-related ion Ca
2+. Thus, TgNHE1 could be a promising therapeutic target against
T. gondii.
In conclusion, we successfully expressed a soluble C-terminal peptide of TgNHE1 and have used it as an immunogen to generate a polyclonal antiserum. The affinity and specificity of this antiserum against T. gondii was confirmed. We also tentatively explored the therapeutic effects of the antiserum in T. gondii infections in vitro. In future studies, we will explore more applications of this antiserum in research on T. gondii.
Notes
-
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
This work is funded by a grant (no. 81171608 to Wenbo Hao) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and by the Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (no. A2015348). We thank RayBiotech (Guangzhou, China), Inc. for antibody preparation.
Fig. 1.Construction of a recombinant plasmid harboring C-terminal TgNHE1. (A) PCR amplification of the C-TgNHE1 coding sequence. M, DNA marker; 1 and 2, PCR products of C-TgNHE1. (B) Restriction analysis of pGEX4T-1-C-TgNHE1.

Fig. 2.Expression, purification, and identification of the GST C-TgNHE1 fusion protein. (A) Expression of C-TgNHE1 in bacteria. M, pre-stained protein ladder; 1, non-induced BL21 harboring pGEX4T-1; 2, induced BL21 harboring pGEX4T-1; 3, non-induced BL21 harboring pGEX4T-1-C-TgNHE1; 4, induced BL21 harboring pGEX4T-1-C-TgNHE1. (B) Identification of soluble and insoluble fractions after sonication of induced BL21 cells and purification of C-TgNHE1 followed by SDS-PAGE. M, pre-stained protein ladder; 1, purified C-TgNHE1; 2, insoluble fraction of total cellular proteins; 3, soluble fraction of total cellular proteins. (C) Western blot analysis of samples from (B) using an anti-GST antibody. 1, soluble fraction; 2, insoluble fraction; 3, purified C-TgNHE1.
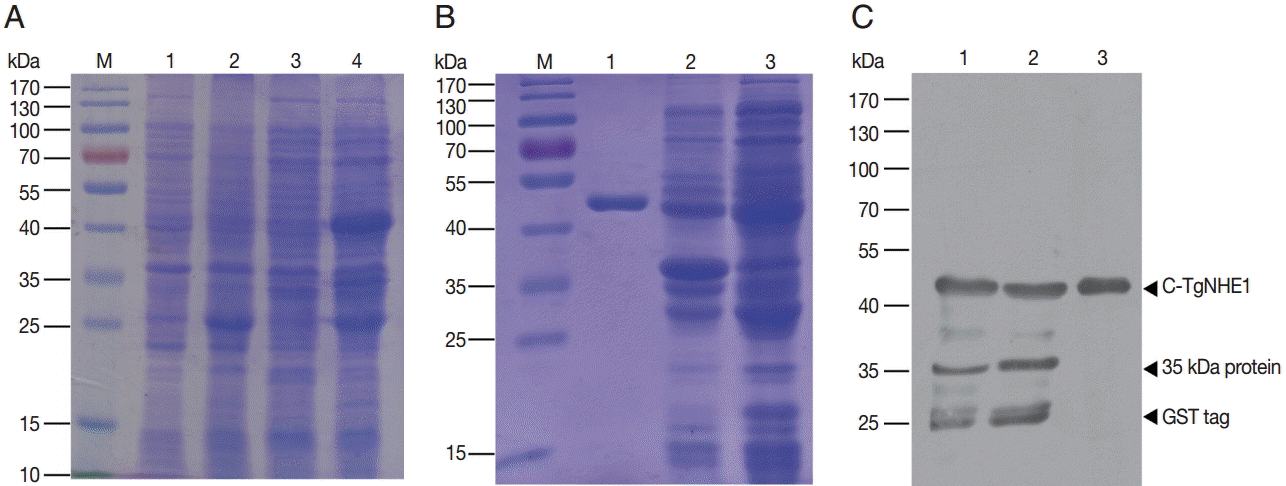
Fig. 3.The binding specificity of the polyclonal antibody against purified T. gondii following parasite lysis. (A) 1×107 parasites were subjected to SDS-PAGE and probed with the antibody against TgNHE1. Normal rabbit serum was used as a negative control. (B) The TgNHE1 signal, visualized by probing with the anti-TgNHE1 antiserum, was labeled with anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 594 (Red). Normal rabbit serum served as a negative control. Cell nuclei (blue) were stained with DAPI. Scale bar=2 μm.
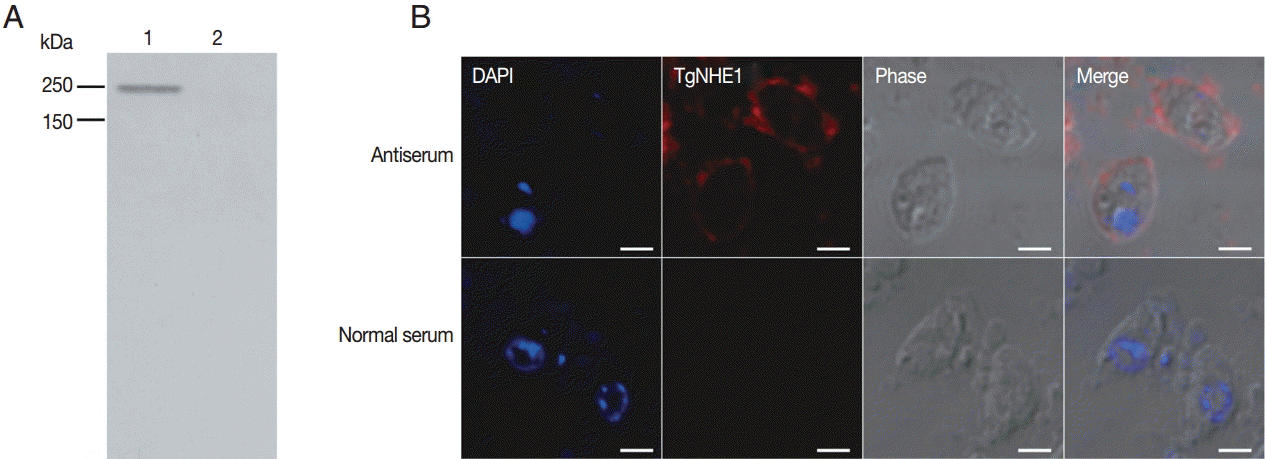
Fig. 4.Western blot analysis of TgNHE1 expression in intracellular T. gondii post infection. 1×106 OFTu cells cultured in 6-well plates were infected with 5×106 T. gondii RH strain pre-incubated either with antiserum or normal serum at a concentration of 4 mg/ml for 12 hr. Uninvaded parasites were washed by PBS at 4 hr post infection. Cells were harvested at indicated time points and subjected to western blot probed with TgNHE1 antiserum. The expression of β-actin served as a loading control. The experiment was repeated in triplicates.
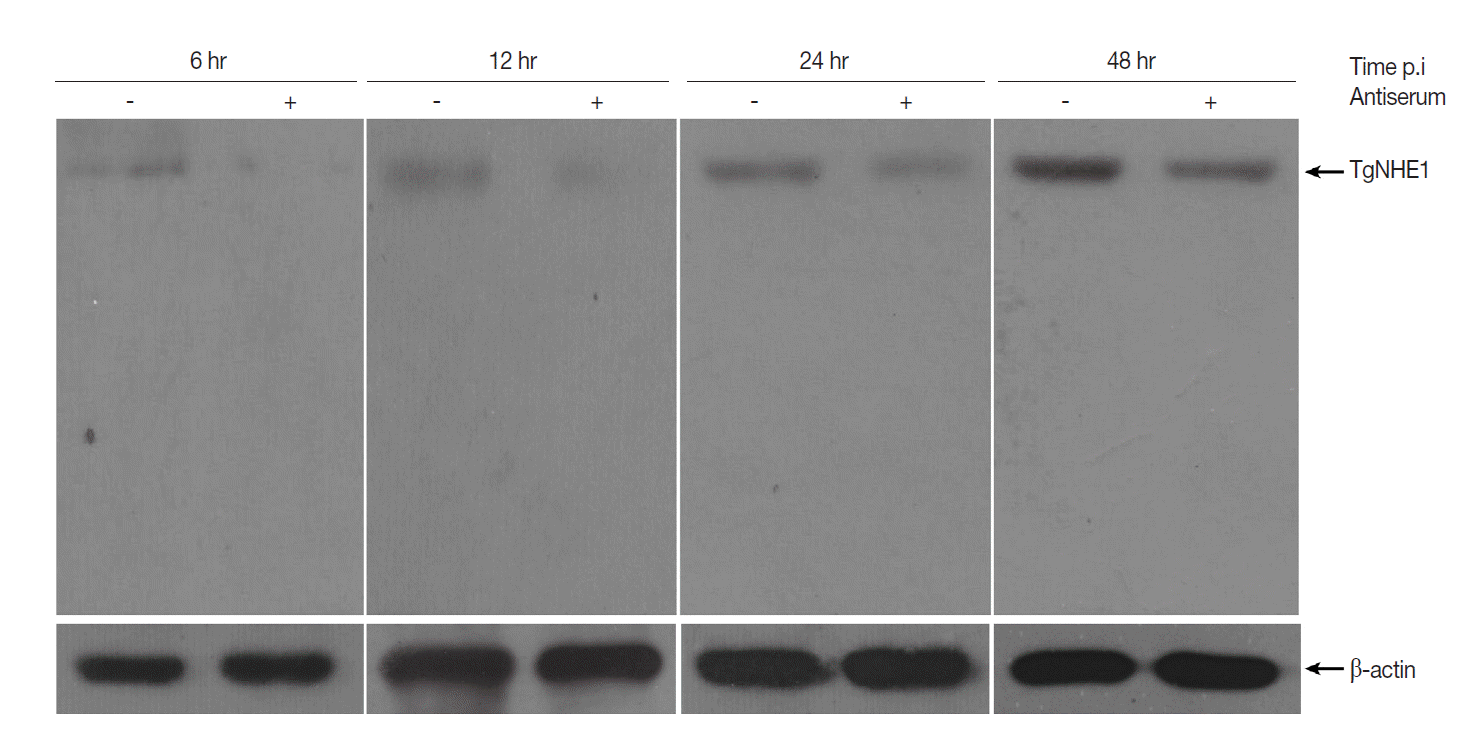
Fig. 5.The antiserum reduced T. gondii virulence in vitro. Number (A) and area (B) of plaques in OFTu cells infected with T. gondii pre-treated with medium (control) or different concentrations of anti-TgNHE1 antiserum. The OFTu cells were grown in 24-well plates in DMEM with 10% FBS at 37˚C and 5% CO2 for 72 hr until they reached confluence, when they were infected with T. gondii treated with the antiserum or with normal rabbit serum. After the parasites that had not invaded were washed away, the cells were cultured for an additional 5 days, when the number and area of plaques were determined. Mann-Whitney U-test, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, and *P<0.05 in comparison with medium-treated cells.
References
- 1. Montoya JG, Liesenfeld O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004;363:1965-1976.
- 2. Kaye A. Toxoplasmosis: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention in congenitally exposed infants. J Pediatr Health Care 2011;25:355-364.
- 3. Arrizabalaga G, Boothroyd JC. Role of calcium during Toxoplasma gondii invasion and egress. Int J Parasitol 2004;34:361-368.
- 4. Karasov AO, Boothroyd JC, Arrizabalaga G. Identification and disruption of a rhoptry-localized homologue of sodium hydrogen exchangers in Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol 2005;35:285-291.
- 5. Francia ME, Wicher S, Pace DA, Sullivan J, Moreno SN, Arrizabalaga G. A Toxoplasma gondii protein with homology to intracellular type Na+/H+ exchangers is important for osmoregulation and invasion. Exp Cell Res 2011;317:1382-1396.
- 6. Roiko MS, Svezhova N, Carruthers VB. Acidification activates Toxoplasma gondii motility and egress by enhancing protein secretion and cytolytic activity. PLoS Pathog 2014;10:e1004488.
- 7. Carruthers VB, Sibley LD. Mobilization of intracellular calcium stimulates microneme discharge in Toxoplasma gondii. Mol Microbiol 1999;31:421-428.
- 8. Carruthers VB, Moreno SN, Sibley LD. Ethanol and acetaldehyde elevate intracellular [Ca2+] and stimulate microneme discharge in Toxoplasma gondii. Biochem J 1999;342(Pt 2):379-386.
- 9. Lin J, Lin X, Yang GH, Wang Y, Peng BW, Lin JY. Toxoplasma gondii: expression of GRA1 gene in endoplasmic reticulum promotes both growth and adherence and modulates intracellular calcium release in macrophages. Exp Parasitol 2010;125:165-171.
- 10. Plattner H, Sehring IM, Mohamed IK, Kiranda K, De Souza W, Billington R, Genazzani A, Ladenburger EM. Calcium signaling in closely related protozoan groups (Alveolata): non-parasitic ciliates (Paramecium, Tetrahymena) vs. parasitic Apicomplexa (Plasmodium, Toxoplasma). Cell Calcium 2012;51:351-382.
- 11. Wu L, Chen SX, Jiang XG, Fu XL, Shen YJ, Cao JP. Separation and purification of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites from in vitro and in vivo culture systems. Exp Parasitol 2012;130:91-94.
- 12. Barbosa BF, Gomes AO, Ferro EA, Napolitano DR, Mineo JR, Silva NM. Enrofloxacin is able to control Toxoplasma gondii infection in both in vitro and in vivo experimental models. Vet Parasitol 2012;187:44-52.
- 13. Pappas G, Roussos N, Falagas ME. Toxoplasmosis snapshots: global status of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence and implications for pregnancy and congenital toxoplasmosis. Int J Parasitol 2009;39:1385-1394.
- 14. Arrizabalaga G, Ruiz F, Moreno S, Boothroyd JC. Ionophore-resistant mutant of Toxoplasma gondii reveals involvement of a sodium/hydrogen exchanger in calcium regulation. J Cell Biol 2004;165:653-662.
- 15. Masek KS, Fiore J, Leitges M, Yan SF, Freedman BD, Hunter CA. Host cell Ca2+ and protein kinase C regulate innate recognition of Toxoplasma gondii. J Cell Sci 2006;119(Pt 21):4565-4573.
- 16. Chini EN, Nagamune K, Wetzel DM, Sibley LD. Evidence that the cADPR signalling pathway controls calcium-mediated microneme secretion in Toxoplasma gondii. Biochem J 2005;389:269-277.
- 17. Nagamune K, Moreno SN, Chini EN, Sibley LD. Calcium regulation and signaling in apicomplexan parasites. Subcell Biochem 2008;47:70-81.
- 18. Bottova I, Sauder U, Olivieri V, Hehl AB, Sonda S. The P-glycoprotein inhibitor GF120918 modulates Ca2+-dependent processes and lipid metabolism in Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS One 2010;5:e10062.
- 19. Bennett TN, Patel J, Ferdig MT, Roepe PD. Plasmodium falciparum Na+/H+ exchanger activity and quinine resistance. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2007;153:48-58.
- 20. Vinayak S, Alam MT, Upadhyay M, Das MK, Dev V, Singh N, Dash AP, Sharma YD. Extensive genetic diversity in the Plasmodium falciparum Na+/H+ exchanger 1 transporter protein implicated in quinine resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2007;51:4508-4511.
- 21. Henry M, Briolant S, Zettor A, Pelleau S, Baragatti M, Baret E, Mosnier J, Amalvict R, Fusai T, Rogier C, Pradines B. Plasmodium falciparum Na+/H+ exchanger 1 transporter is involved in reduced susceptibility to quinine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2009;53:1926-1930.
- 22. Andriantsoanirina V, Menard D, Rabearimanana S, Hubert V, Bouchier C, Tichit M, Bras JL, Durand R. Association of microsatellite variations of Plasmodium falciparum Na+/H+ exchanger (Pfnhe-1) gene with reduced in vitro susceptibility to quinine: lack of confirmation in clinical isolates from Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2010;82:782-787.
- 23. Vercesi AE, Docampo R. Sodium-proton exchange stimulates Ca2+ release from acidocalcisomes of Trypanosoma brucei. Biochem J 1996;315(Pt 1):265-270.
- 24. Vercesi AE, Rodrigues CO, Catisti R, Docampo R. Presence of a Na+/H+ exchanger in acidocalcisomes of Leishmania donovani and their alkalization by anti-leishmanial drugs. FEBS Lett 2000;473:203-206.
- 25. Mondragon R, Frixione E. Ca++-dependence of conoid extrusion in Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1996;43:120-127.
- 26. Ryning FW, Remington JS. Effect of cytochalasin D on Toxoplasma gondii cell entry. Infect Immun 1978;20:739-743.
- 27. Silva SR, Meirelles SS, De Souza W. Mechanism of entry of Toxoplasma gondii into vertebrate cells. J Submicrosc Cytol 1982;14:471-482.
- 28. Schwartzman JD, Pfefferkorn ER. Immunofluorescent localization of myosin at the anterior pole of the coccidian, Toxoplasma gondii. J Protozool 1983;30:657-661.
- 29. Dobrowolski JM, Sibley LD. Toxoplasma invasion of mammalian cells is powered by the actin cytoskeleton of the parasite. Cell 1996;84:933-939.
- 30. Cole TR, Igumenova TI. Expression and purification of the N-terminal regulatory domain of protein kinase C for biophysical studies. Protein Expr Purif 2015;110:14-21.