Abstract
Trichomonas vaginalis causes the most prevalent sexually transmitted infection worldwide. Trichomonads have been detected in prostatic tissues from prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and prostate cancer. Chronic prostatic inflammation is known as a risk factor for prostate enlargement, benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms, and acute urinary retention. Our aim was to investigate whether T. vaginalis could induce inflammatory responses in cells of a benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelial cell line (BPH-1). When BPH-1 cells were infected with T. vaginalis, the protein and mRNA of inflammatory cytokines, such as CXCL8, CCL2, IL-1β, and IL-6, were increased. The activities of TLR4, ROS, MAPK, JAK2/STAT3, and NF-κB were also increased, whereas inhibitors of ROS, MAPK, PI3K, NF-κB, and anti-TLR4 antibody decreased the production of the 4 cytokines although the extent of inhibition differed. However, a JAK2 inhibitor inhibited only IL-6 production. Culture supernatants of the BPH-1 cells that had been incubated with live T. vaginalis (trichomonad-conditioned medium, TCM) contained the 4 cytokines and induced the migration of human monocytes (THP-1 cells) and mast cells (HMC-1 cells). TCM conditioned by BPH-1 cells pretreated with NF-κB inhibitor showed decreased levels of cytokines and induced less migration. Therefore, it is suggested that these cytokines are involved in migration of inflammatory cells. These results suggest that T. vaginalis infection of BPH patients may cause inflammation, which may induce lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS).
-
Key words: Trichomonas vaginalis, benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelial cell (BPH-1), inflammatory response
INTRODUCTION
Trichomonas vaginalis, a protozoan parasite, causes an estimated 274 million sexually transmitted infections (STI) worldwide annually [
1], and this frequency is higher than that of infections with
Chlamydia trachomatis and
Neisseria gonorrhea [
2]. In men,
T. vaginalis may lead to urethritis, epididymitis, prostatitis, and infertility [
3]. In addition, it may increase the transmission of human immunodeficiency virus by 2-3 folds [
4].
T. vaginalis infection rates were 21.2% in chronic prostatitis and urethritis, and 34% in benign prostatic hyperplasia, as measured by PCR, which is the most sensitive method for diagnosis of trichomoniasis [
5,
6]. Also
T. vaginalis was detected in the majority (71.7%) of the male partners of women diagnosed with trichomoniasis [
7]. In addition, in a previous study, we showed that when RWPE-1 prostate epithelial cells collected from normal prostates were incubated with
T. vaginalis, inflammatory responses, including cytokine production and inflammatory cell migration, were detected [
8].
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) predominantly affects men aged >50 years and represents the most common urologic disease among elderly males [
9,
10]. The histologic diagnosis of BPH is based on an overgrowth of the epithelial and stromal components of the transition zone and periurethral area, resulting in prostate enlargement, bladder outlet obstruction, and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) [
10,
11].
Aging and hormone imbalance have been considered as causative factors. In addition, inflammation was recently proposed as an important element in the development of BPH [
10,
12]. Indeed, chronic inflammation of the prostate has been seen as the major cause of the development and progression of BPH [
10]. Pathologic examinations of BPH tissues often show infiltration of lymphocytes and macrophages around the gland [
13]. These infiltrated cells produce cytokines, such as interleukine-6 and CXCL8, which may induce epithelial and stromal cell growth [
14].
A variety of microorganisms, including gram positive and negative bacteria and fungi, have been detected in BPH [
15,
16]. Moreover, it has been suggested that chronic retention of
T. vaginalis in the prostate is associated with BPH [
6]. The aim of this study was to investigate whether BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis can induce inflammatory responses. We show below that BPH-1 cells stimulated with
T. vaginalis produce proinflammatory cytokines and induce migration of monocytes and mast cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture
T. vaginalis (T016 isolate) was grown in trypticase-yeast extract-maltose medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated horse serum at 37°C. Cells of a benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelial cell line (BPH-1) were obtained from the Leibniz-Institut DSMZ - Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH (ACC-143; DSMZ, Braunschweig, Germany). The cells were maintained in BPH-1 culture medium consisting of RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with testosterone 20 ng/ml (TCI chemicals, Tokyo, Japan), transferrin 5 µg/ml, sodium selenite 5 ng/ml, insulin 5 µg/ml (from Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, Missouri, USA), 1% penicillin/streptomycin, and 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS, PAN Biotech, Aidenbach, Germany), at 37°C containing 5% CO2. Cells of the human mast cell line, HMC-1, was incubated in IMDM supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. Cells of the human monocyte cell line (THP-1) were grown in RPMI 1640 media supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. HMC-1 and THP-1 (1×106) cells were incubated in 20 ml medium in 75T culture flasks at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator.
Preparation of BPH-1-conditioned medium
For preparation of BPH-1-conditioned medium, BPH-1 cells (2×105) were cultured in the absence or presence of T. vaginalis (1.0×106) for 3 hr at 37°C in a 24 well plate. Supernatants were obtained by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm and 4°C for 30 min and filtered using a 0.2 μm syringe filter (Millipore, Billerica, Massachusetts, USA). Culture supernatants of BPH-1 incubated with and without trichomonads were named trichomonads conditioned medium (TCM) and conditioned medium (CM), respectively.
Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Intracellular ROS were measured by spectrofluorometer using 2´,7´-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCF-DA, Molecular Probes, Eugene, Oregon, USA). Briefly, BPH-1 cells with or without diphenyleneiodonium (DPI, Sigma Aldrich) pretreatment were co-cultured with
T. vaginalis. The cells were washed and stained with 30 μM DCF-DA for 1 hr at 37°C. Intracellular ROS were determined with a VICTOR X spectrofluorometer (Perkin-Elmer, Boston, Massachusetts, USA) at excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 530 nm, respectively [
8].
To examine cytokine production of BPH-1 cell infected with live T. vaginalis, BPH-1 cells (2×105) were cultured in BPH-1 culture medium FBS in 24-well plates (Corning, New York, USA). After 24 hr, the cells were washed twice with PBS, suspended in serum free-BPH-1 culture medium and incubated with T. vaginalis (BPH-1: T. vaginalis, 1:1, 1:5, and 1:10) for 3 hr, 6 hr, and 12 hr, respectively. Signaling pathway inhibitors used (all at 30 μM) were DPI, SB203580 (Sigma Aldrich), PD98059, SP600125 (Calbiochem, San Diego, California, USA), BAY11-7082 (Enzo Life Science, Farmingdale, New York, USA), Ruxolitinib, Wortmannin (Selleckchem, Houston, Texas, USA), and anti-TLR4 antibody 1:200 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK). Concentrations of cytokines (CXCL8, CCL2, IL-1β, and IL-6) in culture supernatants were measured with an OptEIA ELISA Set (BD Bioscience, San Diego, California, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
RT-PCR for cytokine mRNAs
Total cellular RNA was extracted from BPH-1 cells using Trizol reagent (Favorgen, Ping-tung, Taiwan), and cDNA was synthesized using a Maxime RT Premix kit (iNtRON, Seongnam, Korea). Amplification was carried out in final volumes of 20 µl in reaction mixtures containing 1 µl forward primer, 1 µl reverse primer, 1 µg cDNA sample, and DEPC water. They were run on a Mastercycler (Eppendorf, Westbury, New York, USA) using the following program: 10 sec at 95°C for cDNA denaturation, 5 sec at 60°C for annealing and 10 sec at 72°C for extension, followed by 40 repeat cycles. Forward and reverse primers used were as follows: for IL-6, forward primer was 5´-TGGCTGCAGGACATGACAACT-3´ and reverse primer 5´-ATCTGAGGTGCCCATGCTACA-3´. For CXCL8, forward primer was 5´-GGCAGCTTCCTGATTTCTG and reverse primer 5´-CGCAGTGTGGTCCACTCTCA-3´. For CCL2, forward primer was 5´-CAAGCAGAAGTGGGTTCAGGA-3´ and reverse primer 5´-TCTTCGGAGTTTGGGTTTGC-3´. For IL-1β, forward primer was 5´-CTGATGGCCCTAAACAGATGAAG and reverse primer 5´-GGTCGGAGATTCGTAGCAGCTGGAT-3´.
Western blotting
BPH-1 cells were lysed using Pro-prep TM protein extraction solution (iNtRON). Lysates were mixed with SDS-PAGE sample buffer and boiled at 100°C for 5 min. Equal amounts of protein samples were run on 10% SDS-PAGE gel and transferred onto PVDF membranes, which were incubated with the following primary antibodies (all at 1:1,000) overnight at 4°C: phospho-p38 antibody, phospho-JNK antibody, phospho-ERK antibody, anti-TLR4 antibody, phospho-STAT3 antibody (all from Cell Signaling, Beverly, Massachusetts, USA); also phospho-JAK2 antibody, phospho-NF-κB antibody, β-actin antibody (all from Abcam). After 3 washes with Tween 20-Tris buffered saline (T-TBS, Biosesang, Seongnam, Korea), proteins were probed with anti-rabbit HRP-conjugated secondary antibody 1:10,000 (Abcam). Proteins were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) using a ChemiDoc MP detection system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA).
Chemotaxis assay
The 24-well plates fitted with polycarbonate membrane inserts (8 μm, Corning) were used to measure mast cell (HMC-1) and monocyte (THP-1) chemotaxis. To promote adhesion of the cells, the filters were pretreated with human plasma fibronectin (100 µg/ml) overnight at 4°C and air-dried for 30 min. The lower well was filled with CM (culture supernatant of BPH-1 cell alone for 3 hr) or TCM (culture supernatant of BPH-1 infected with
T. vaginalis for 3 hr), and 2.0×10
5 monocytes or mast cells were placed in the upper well. Recombinant human CCL2 (100 ng/ml, ProSpec, East Brunswick, New Jersey, USA), and stem cell factor (100 ng/ml, Enzo Life Science) were used as positive controls. The plates were incubated for 3 hr at 37°C, the membrane inserts were removed, and cells adhering to their upper surfaces were wiped off with cotton swab. The membranes were dried, fixed with methanol, and stained with Giemsa, and the cells in 5 randomly selected fields per well were counted under a light microscope. The chemotactic index was calculated from the number of cells that migrated in response to the control (RPMI1640 medium). To investigate the effects of cytokines (CXCL8, CCL2, IL-1β, and IL-6) contained in the BPH-1 cell conditioned medium on migration, cell culture supernatant of BPH-1 cells pretreated with NF-κB inhibitor (BAY11-7082, Enzo Life Science) before incubation with
T. vaginalis were placed in the lower well [
8].
The data are expressed as means±SDs of 3-4 independent experiments. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to analyze the significance of differences, and P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
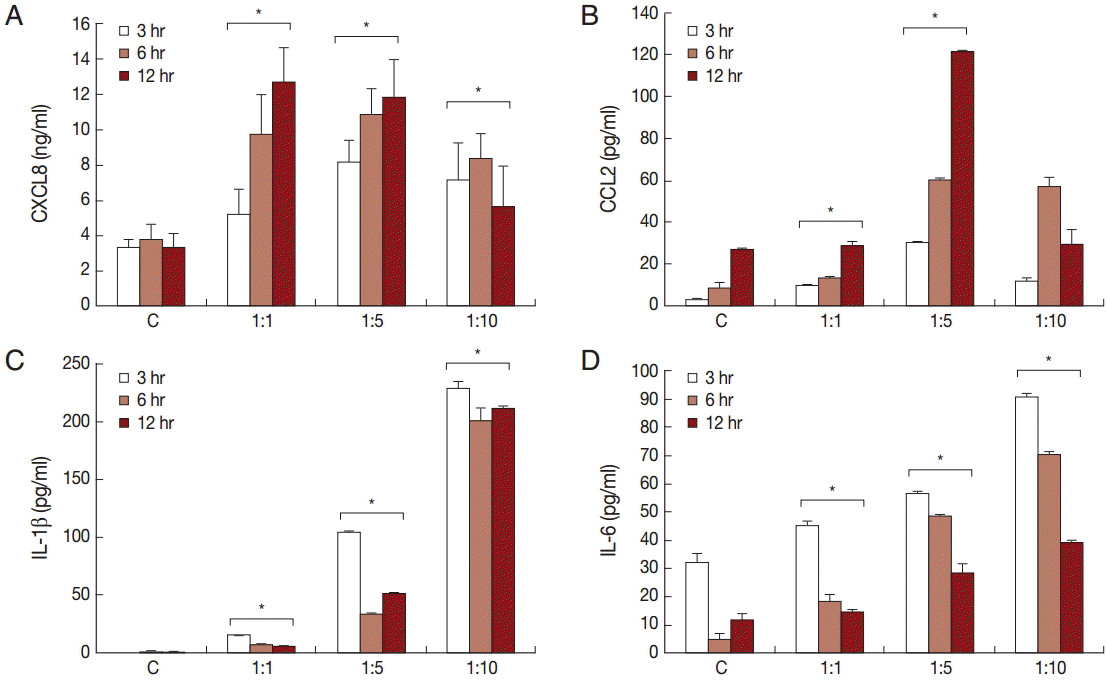
Chemokine and cytokine production by BPH-1 cells infected with T. vaginalis
To investigate the production of chemokines and cytokines by BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis, BPH-1 cells were incubated with different ratios of live trichomonads (1:1, 1:5, and 1:10) for 3 hr, 6 hr, and 12 hr, respectively. As shown in
Fig. 1, BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis produced 2 chemokines and 2 cytokines (CXCL8, CCL2, IL-1β, and IL-6). CXCL8 and CCL2 levels peaked at the 1:5 ratio of cells to trichomonads (
Fig. 1A,
B). IL-1β and IL-6 production was increased with increasing numbers of trichomonads (
Fig. 1C,
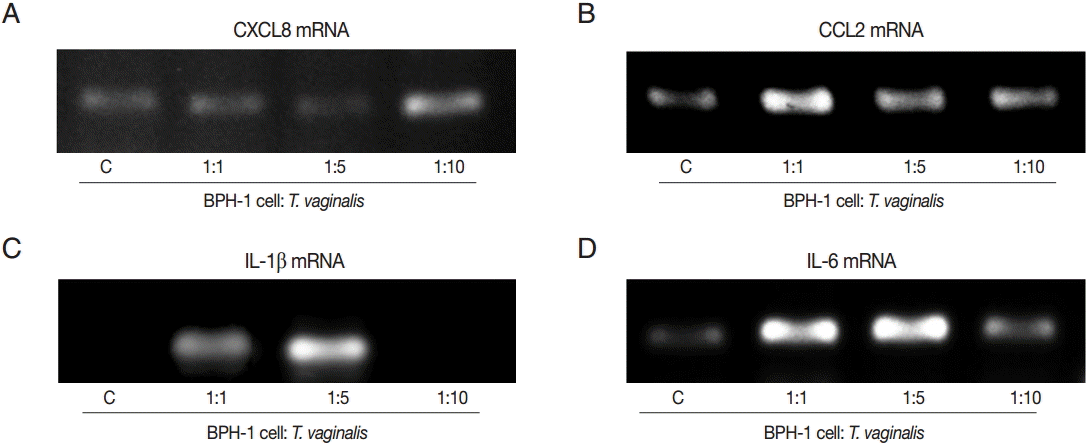
D). Next, we investigate the levels of transcripts of the 4 cytokines. IL-1β and IL-6 were maximal at the 1:5 ratio (
Fig. 2C,
D), whereas transcripts of CXCL8 and CCL2 peaked at the 1:10 and 1:1 ratios, respectively (
Fig. 2A,
B).
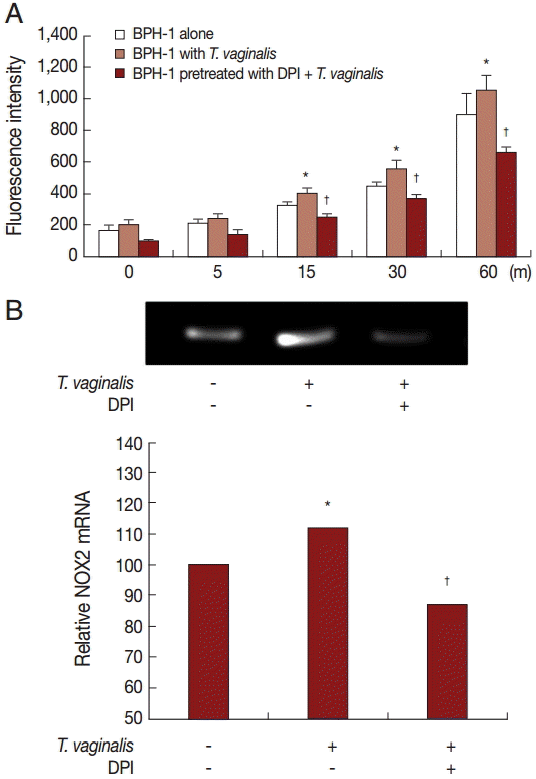
Production of hydrogen peroxide by BPH-1 incubated with
T. vaginalis was measured using a spectrofluorometer after staining with DCF-DA. We determined whether ROS production by BPH-1 cells incubated with
T. vaginalis was related to NADPH oxidase (NOX) activity. ROS production was stimulated by incubating BPH-1 cells with
T. vaginalis, and pretreatment with the NOX inhibitor (DPI) decreased the production of ROS (
Fig. 3A). NOX2 mRNA levels also increased (
Fig. 3B). Therefore, DPI may block hydrogen peroxide production through inhibition of NOX2.
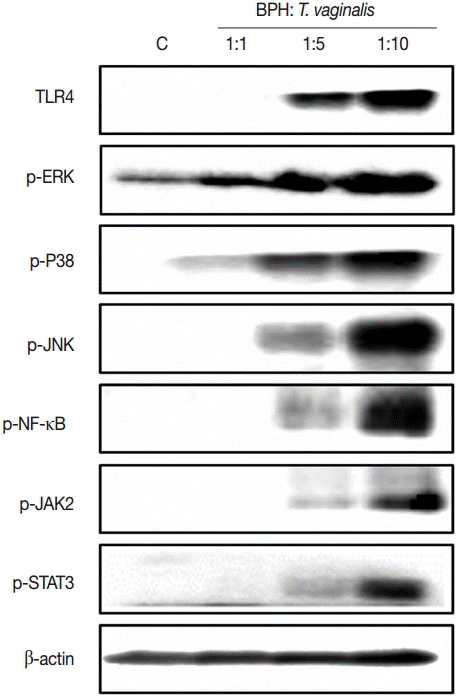
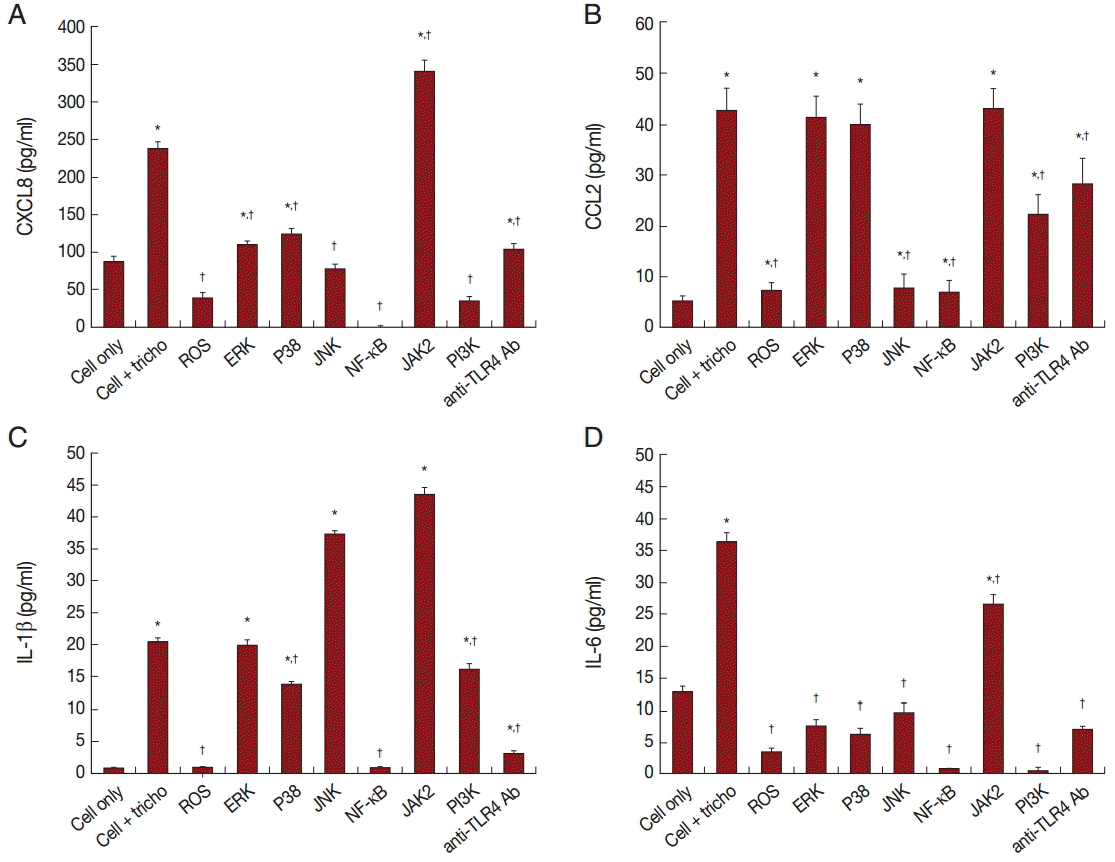
To investigate the signaling molecules related to cytokine production by BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis, we used western blotting. Our results demonstrated that incubation of BPH-1 with
T. vaginalis increased the phosphorylation levels of MAPK, NF-κB, JAK2, STAT3, and the expression of TLR4 (
Fig. 4). The signaling molecule levels peaked at the 1:10 ratio of cells to trichomonads.
In order to assess the effect of signaling molecules on cytokine production by BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis, BPH-1 cells were pretreated with the appropriate inhibitors before stimulation with
T. vaginalis. ROS and NF-κB inhibitors markedly decreased the production of the 4 kinds of cytokines (
Fig. 5A-
D). The MAPK inhibitor reduced CXCL8 and IL-6 production. However, CCL2 and IL-1β production were affected only by JNK and P38 inhibitors, respectively. The JAK2 inhibitor decreased production of IL-6, although it increased the production of the other cytokines. The PI3-kinase inhibitor and anti-TLR4 antibody decreased all 4 cytokines. Our results suggest that these signaling molecules are related to the inflammation. In particular, we confirmed that IL-6 production was dependent on the JAK2 signaling pathway (
Fig. 5).
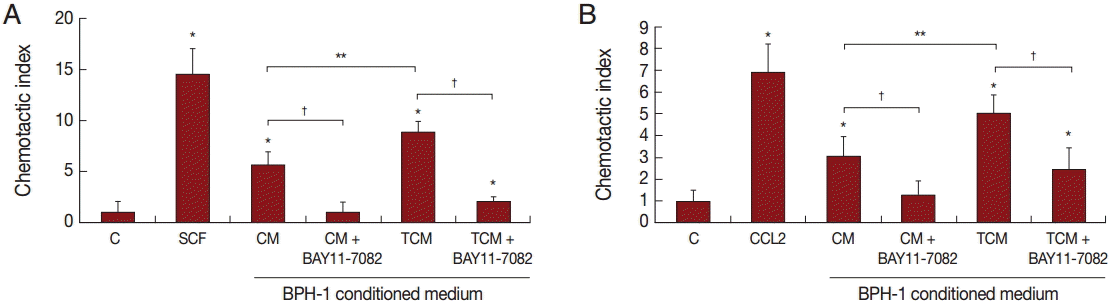
Migration of inflammatory cells plays an important role in the inflammatory response. We investigated whether BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis recruit inflammatory cells, such as mast cells and monocytes. We performed chemotaxis assay using culture supernatants of BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis. Stem cell factor (SCF) and CCL2 are known to be chemotactic factors for mast cells and monocytes, respectively, and were used as positive controls. Migration was increased by culture supernatants of BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis (TCM) more than by control supernatant (CM) (
Fig. 6A,
B). BPH-1 cell was pretreated with an NF-κB inhibitor before stimulation with
T. vaginalis, and the culture supernatant was collected. Migration of mast cells and monocytes in response to their supernatant was decreased (
Fig. 6A,
B). These results suggested that factors, possible cytokines or chemokines, in BPH-1 culture supernatants are responsible for stimulating the migration of inflammatory cells.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we showed that incubation of BPH-1 cells with T. vaginalis induced production of inflammatory cytokines and migration of inflammatory cells. This indicates that T. vaginalis can trigger inflammatory responses in BPH-1 cells.
T. vaginalis is a flagellated, protozoan parasite that causes trichomoniasis by sexual contact. The complications induced by
T. vaginalis infection include low birth weight and preterm delivery in pregnant women and chronic prostatitis, urethritis, and infertility in men [
3,
17].
The adhesion of
T. vaginalis to vaginal epithelial cells plays an important role in the pathogenesis of trichomoniasis through production of CXCL8, CCL2, and IL-6 [
18]. Also prostatic epithelial cells (RWPE-1 cells) infected with
T. vaginalis produce CCL2, CXCL8, and IL-1β [
8]. Similarly, in the present study,
T. vaginalis-infected BPH-1 cells produced pro-inflammatory cytokines CXCL8, CCL2, IL-1β, and IL-6 that increased the migration of monocytes and mast cells. This finding is significant since such an inflammatory response would be expected to cause lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in BPH patients.
CCL2, also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), is a member of the chemokine superfamily that plays an important role in the recruitment and activation of monocytes during inflammation [
19]. Moreover, CCL2 has been associated with the development of BPH and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) [
20,
21]. In this context, Fujita et al. [
14] reported that multiplication of prostate epithelial cells was stimulated by exogenous CCL2, and human prostate volume and numbers of macrophages were correlated with CCL2 levels in expressed prostatic secretion (EPS). Hence, elevated CCL2 levels in the prostate may contribute to a positive feedback loop provoking BPH [
14]. Infiltrating cells in BPH are reported to consist of T lymphocytes, B cells, and macrophages as well as mast cells [
22]. It will be of interest to determine whether CCL2 is involved in the proliferation of prostate stromal cells.
IL-1β is a potent proinflammatory cytokine that is produced by a variety of cells and acts on almost every organ system of the body [
23]. A previous study reported that it is associated with inflammatory diseases such as fever and septic shock, and plays an important role in inflammatory responses [
24]. In the present study, the increase of IL-1β induced in the infected BPH-1 cells paralleled Hamakawa et al.’s report based on immunohistochemistry that IL-1β expression was elevated in prostate tissues from BPH patients [
25]. We showed previously that IL-1β was produced via the NLRP3 inflammasome by prostate epithelial cells infected with
T. vaginalis [
8,
25]. In addition, inflammation in a rat BPH model was induced by IL-1β and IL-18 via the NLRP1 inflammasome [
26]. It remains to be seen which type of inflammasome is associated with IL-1β production in the present context.
CXCL8, alternatively known as IL-8, is a proinflammatory cytokine and acts mainly on neutrophils [
19]. Castro et al. [
27] reported that CXCL8 production was upregulated in tissue extracts of BPH patients, and CXCL8 levels were correlated with prostate weight and the age of BPH patients. Also, exogenous CXCL8 caused proliferation of prostate epithelial cells. In addition, CXCL8 in EPS was reported to serve as a reliable biomarker of BPH with chronic prostatitis [
28]. Here, BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis increased CXCL8 production as seen in prostate epithelial cells stimulated with
T. vaginalis [
8].
IL-6, a member of the Gp130 family, is a proinflammatory cytokine that acts on the innate immune response [
29]. Increased IL-6 production is a hallmark of many human chronic inflammatory states, including sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease/colitis [
30]. Moreover, IL-6 is considered to be a factor promoting the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer [
31,
32]. When BPH-1 and prostate epithelial cells were treated with IL-6, cell proliferation was increased. IL-6 levels in sera were increased in patients with prostate cancer [
33], and this was associated with poor outcomes of prostate disease, such as prostate cancer and BPH [
34]. IL-6 activates prosurvival signaling by JAK/STAT, Ras/ERK or PI3K/Akt, but mainly via Janus kinases (JAK) and signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) [
30,
35]. In the present study, we demonstrated that BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis had elevated levels of IL-6, and treatment with a JAK2 inhibitor reduced IL-6 production. Also, expression of JAK2 and phospho STAT3 was significantly increased by
T. vaginalis. These results suggest that the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is involved in the production of IL-6.
PI3K/Akt is associated with mitogenesis, cell transformation, and other key cell cycle regulatory processes in prostate cancer cells [
36]. PI3-kinase is activated in response to ligand-binding, and the resulting second messenger recruits the protein kinase Akt to the plasma membrane. Phosphorylated Akt then translocates to the nucleus and other subcellular components, where it regulates an array of biological activities, most notably anti-apoptotic and proliferative processes [
37]. We found that production of all 4 cytokines was reduced by treatment with a PI3-kinase inhibitor.
An increase of ROS has been shown to activate transcription factors, mitogen activated protein kinases, and protein kinase C, and to stimulate cell proliferation or death. [
38]. Also, ROS production by membrane-localized NOX2 is a major cell signaling mechanism concerned with tissue inflammation [
39]. NADPH oxidase has been established as an important enzyme in the production of intracellular ROS [
40]. We observed that BPH-1 cells stimulated with
T. vaginalis released increased ROS and expressed NOX2 mRNA. When BPH-1 cells were pretreated with DPI (a NOX inhibitor), ROS and NOX2 expression were significantly reduced. Therefore, NOX2 is involved in ROS production. Also, DPI decreased production of the 4 cytokines. This result suggests that ROS are involved in cytokine production by the BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis.
The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade plays a key role in immune responses [
41,
42]. There are 3 major subfamilies of MAPK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38 map kinase, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). All 3 increased when BPH-1 cells were incubated with
T. vaginalis. Inhibitors of ERK, P38 and JNK suppressed CXCL8 and IL-6 production. In contrast, only JNK appeared to be involved in CCL2 production and only p38 showed to be associated with IL-1β.
Recruitment into tissues of large numbers of neutrophils followed by monocytes occurs as part of the acute inflammatory response to infection and tissue injury [
19]. We reported previously that migration of neutrophils and monocytes was observed in the inflammatory response by prostate epithelial cells to
T. vaginalis [
8]. Also, medium conditioned by vaginal epithelial cells incubated with
T. vaginalis (TCM) induced the migration of mast cells, and, in turn, the mast cells caused more neutrophil migration via CXCL8 and TNF-α. In the present study, we showed that medium conditioned by BPH-1 cells infected with
T. vaginalis induced the migration of monocytes and mast cells. The recruited monocytes and mast cells would presumably activate the inflammatory response and induce cell proliferation.
Our results indicate that BPH-1 cells infected with T. vaginalis produced cytokines, such as CXCL8, CCL2, IL-1β, and IL-6 via cellular signaling pathways involving ROS, MAPK, and NF-κB. These cytokines induced migration of monocytes and mast cells, thereby, caused inflammatory responses of the BPH-1 cells. We suggest that T. vaginalis infection of BPH patients may induce inflammatory responses that contribute to the development of lower urinary tract symptoms.
Notes
-
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
This research was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Government (MSIP) (NRF-2014R1A2A2A01005449).
Fig. 1.Production of cytokines by benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelial cells (BPH-1) infected with T. vaginalis. Production of inflammatory cytokines CXCL8 (A), CCL2 (B), IL-1β (C), and IL-6 (D) by BPH-1 cells incubated with increasing numbers of live trichomonads for 3 hr, 6 hr, and 12 hr, respectively, was measured using ELISA. C, BPH-1 cell alone. *P<0.05 vs untreated BPH-1 cells.
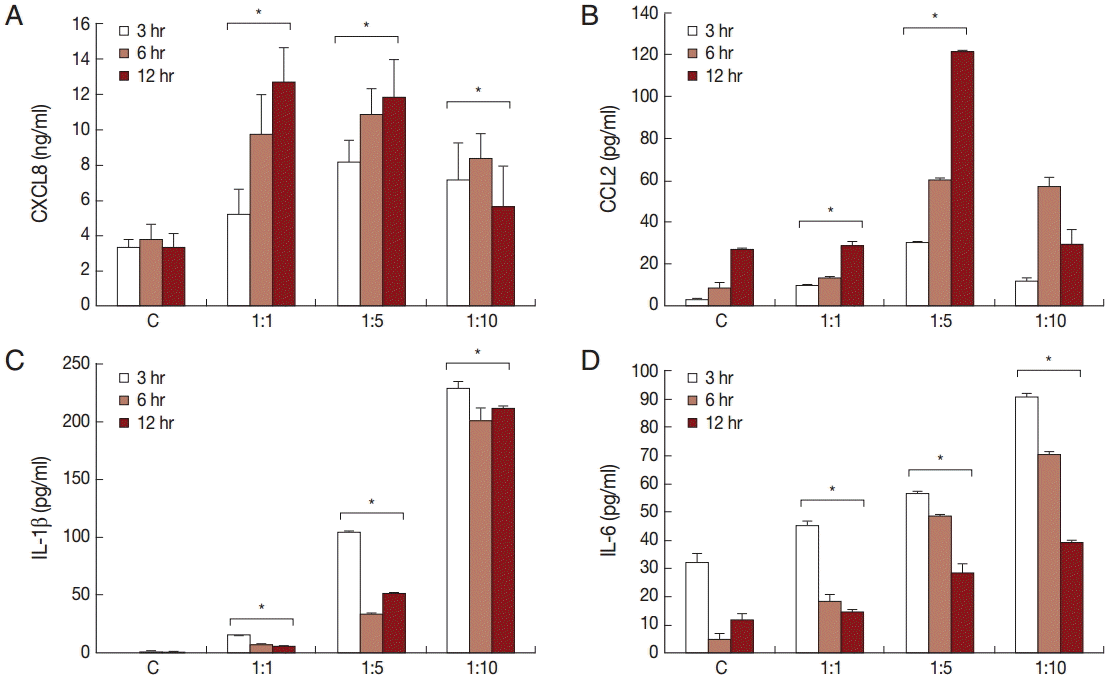
Fig. 2.PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokine mRNA levels in BPH-1 cells infected with T. vaginalis (A-D: CXCL8, CCL2, IL-1β, and IL-6). BPH-1 cells (2×105) were incubated with increasing numbers of live trichomonads (BPH-1: T. vaginalis=1:1, 1:5, and 1:10), for 45 min (CXCL8, CCL2, and IL-6) or 30 min (IL-1β). C, BPH-1 cells alone.
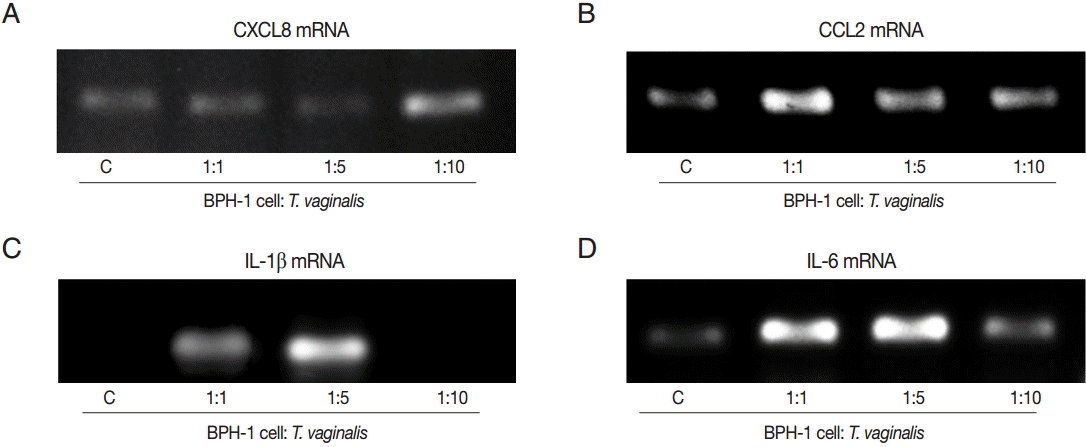
Fig. 3.ROS production by BPH-1 cells infected with T. vaginalis. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) production was measured by a spectrofluorometer using DCF-DA. (A) ROS production by BPH-1 cells infected with T. vaginalis for 5 to 60 min was detected by a spectrofluorometer. DPI was used as a ROS inhibitor. (B) mRNA levels of NOX2 were determined by RT-PCR. Numerical values of PCR band densities are shown below the graph. *P<0.05 vs untreated BPH-1 cells. †P<0.05 versus BPH-1 cells treated with T. vaginalis.
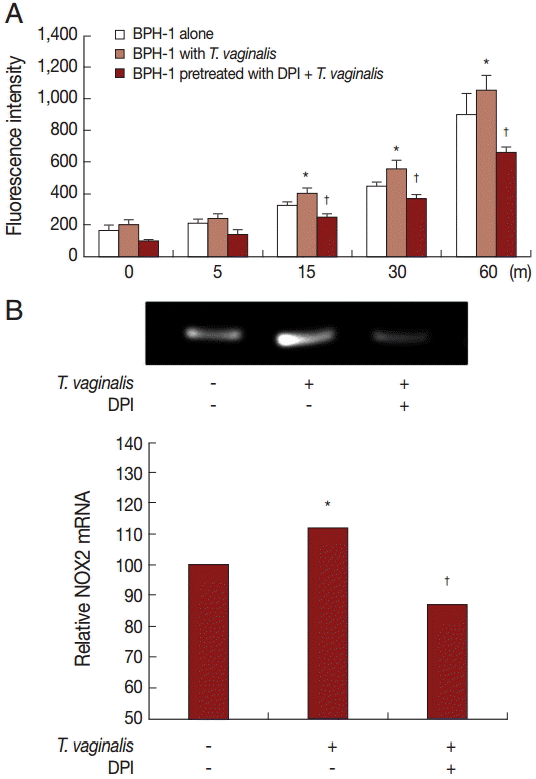
Fig. 4.Levels of signaling molecules in BPH-1 cells incubated with or without live T. vaginalis for 3 hr were determined by western blotting. Signaling molecules activation peaked at the 1:10 ratio of cells to trichomonads. C, BPH-1 cells alone.
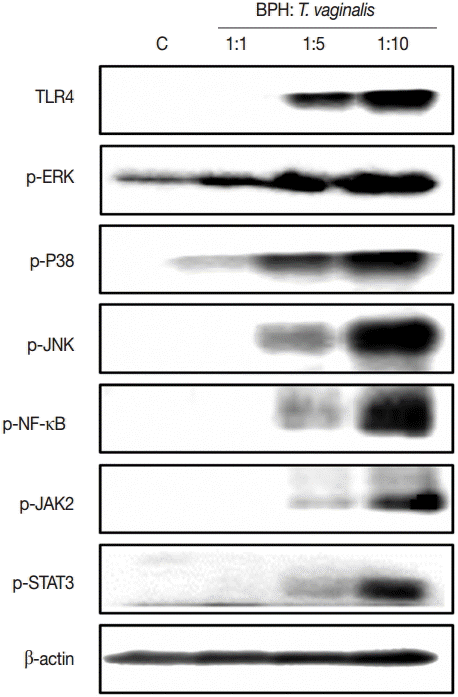
Fig. 5.BPH-1 cells were pretreated with inhibitors of signaling molecules before treatment with T. vaginalis. Production of cytokines was measured in supernatant of cells pretreated with inhibitors of ROS, MAPK, NF-κB, JAK2, and PI3K, and with anti-TLR4 antibody. Cytokine production by BPH-1 incubated with T. vaginalis was significantly increased compared with that of BPH-1 alone (*P<0.05). †P<0.05 vs BPH-1 cells treated with T. vaginalis.
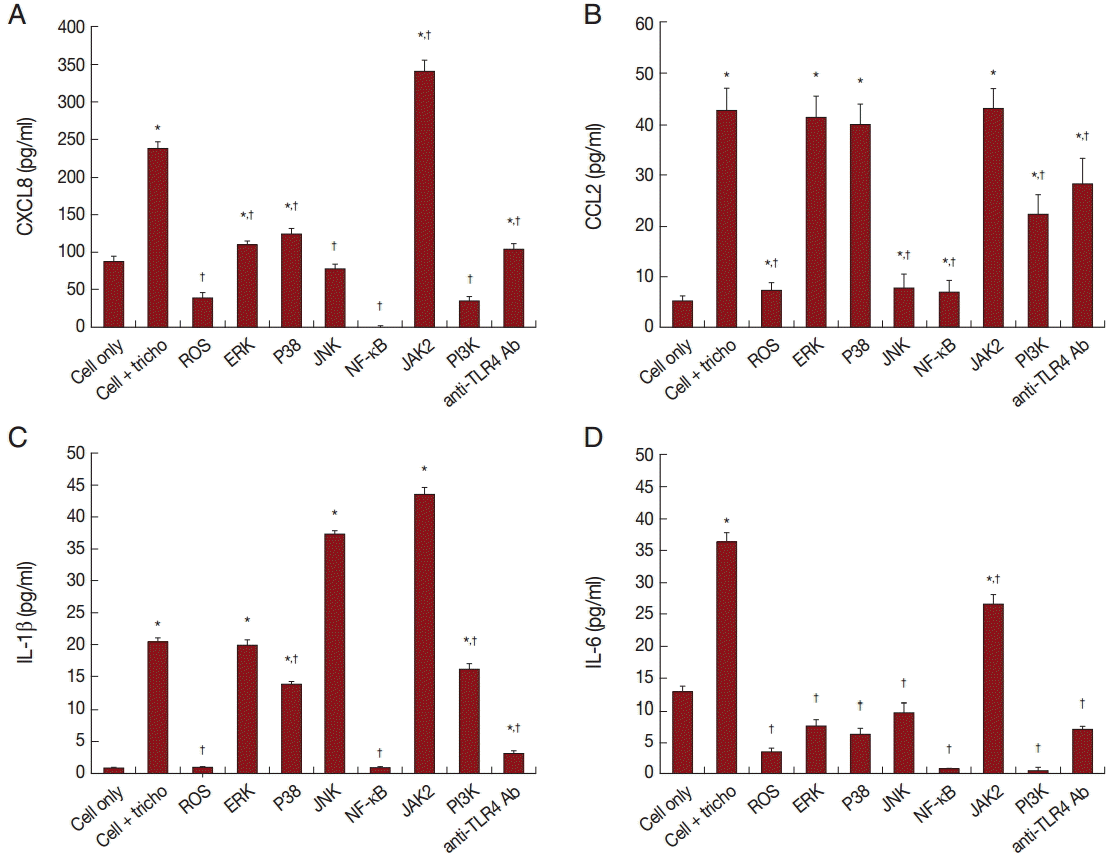
Fig. 6.Migration of mast cells (A, HMC-1 cells) and monocytes (B, THP-1 cells) induced by conditioned medium of BPH-1 cells infected with T. vaginalis. RPMI 1640 medium was used as negative control (C), and stem cell factor (SCF) and CCL2 were used as positive controls for mast cells or monocytes, respectively. To identify the effect of cytokines on the migration of mast cells and monocytes, BPH-1 cells were pretreated with BAY11-7082 before incubation with T. vaginalis, and then the culture supernatant was used for migration assay. *P<0.05 vs RPMI 1640 medium. **P<0.05 vs CM. †P<0.05 vs TCM (or CM).
References
- 1. World Health Organization (WHO). Global incidence and prevalence of selected curable sexually transmitted infections - 2008. Geneva. Switzerland. WHO. 2012.
- 2. Hobbs MM, Sena AC. Modern diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis infection. Sex Transm Infect 2013;89:434-438.
- 3. Krieger JN. Trichomoniasis in men: old issues and new data. Sex Transm Dis 1995;22:83-96.
- 4. Quinlivan EB, Patel SN, Grodensky CA, Golin CE, Tien HC, Hobbs MM. Modeling the impact of Trichomonas vaginalis infection on HIV transmission in HIV-infected individuals in medical care. Sex Transm Dis 2012;39:671-677.
- 5. Lee JJ, Moon HS, Lee TY, Hwang HS, Ahn MH, Ryu JS. PCR for diagnosis of male Trichomonas vaginalis infection with chronic prostatitis and urethritis. Korean J Parasitol 2012;50:157-159.
- 6. Mitteregger D, Aberle SW, Makristathis A, Walochnik J, Brozek W, Marberger M, Kramer G. High detection rate of Trichomonas vaginalis in benign hyperplastic prostatic tissue. Med Microbiol Immunol 2012;201:113-116.
- 7. Sena AC, Miller WC, Hobbs MM, Schwebke JR, Leone PA, Swygard H, Atashili J, Cohen MS. Trichomonas vaginalis infection in male sexual partners: implications for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Clin Infect Dis 2007;44:13-22.
- 8. Seo MY, Im SJ, Gu NY, Kim JH, Chung YH, Ahn MH, Ryu JS. Inflammatory response of prostate epithelial cells to stimulation by Trichomonas vaginalis. Prostate 2014;74:441-449.
- 9. Garraway WM, Collins GN, Lee RJ. High prevalence of benign prostatic hypertrophy in the community. Lancet (London, England) 1991;338:469-471.
- 10. Robert G, Descazeaud A, Allory Y, Vacherot F, de la Taille A. Should we investigate prostatic inflammation for the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia? Eur Urol Suppl 2009;8:879-886.
- 11. Wei JT, Calhoun E, Jacobsen SJ. Urologic diseases in America project: benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2005;173:1256-1261.
- 12. Wang X, Lin WJ, Izumi K, Jiang Q, Lai KP, Xu D, Fang LY, Lu T, Li L, Xia S, Chang C. Increased infiltrated macrophages in benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): role of stromal androgen receptor in macrophage-induced prostate stromal cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 2012;287:18376-18385.
- 13. Theyer G, Kramer G, Assmann I, Sherwood E, Preinfalk W, Marberger M, Zechner O, Steiner GE. Phenotypic characterization of infiltrating leukocytes in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Lab Invest 1992;66:96-107.
- 14. Fujita K, Ewing CM, Getzenberg RH, Parsons JK, Isaacs WB, Pavlovich CP. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2) is associated with prostatic growth dysregulation and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate 2010;70:473-481.
- 15. Nickel JC, Downey J, Young I, Boag S. Asymptomatic inflammation and/or infection in benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int 1999;84:976-981.
- 16. Bedalov G, Vuckovic I, Fridrih S, Bruk M, Puskar D, Bartolin Z. Prostatitis in benign prostatic hyperplasia: a histological, bacteriological and clinical study. Acta Med Croatica 1994;48:105-109.
- 17. Moodley P, Wilkinson D, Connolly C, Moodley J, Sturm AW. Trichomonas vaginalis is associated with pelvic inflammatory disease in women infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infec Dis 2002;34:519-522.
- 18. Han IH, Park SJ, Ahn MH, Ryu JS. Involvement of mast cells in inflammation induced by Trichomonas vaginalis via crosstalk with vaginal epithelial cells. Parasite Immunol 2012;34:8-14.
- 19. Abbas AK, Lichtman AH, Pillai S. Cellular and molecular immunology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, USA. Elsevier Saunders. 2012, pp 76-78.
- 20. Desireddi NV, Campbell PL, Stern JA, Sobkoviak R, Chuai S, Shahrara S, Thumbikat P, Pope RM, Landis JR, Koch AE, Schaeffer AJ. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha as possible biomarkers for the chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Urol 2008;179:1857-1861.
- 21. Mazzucchelli L, Loetscher P, Kappeler A, Uguccioni M, Baggiolini M, Laissue JA, Mueller C. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene expression in prostatic hyperplasia and prostate adenocarcinoma. Am J Pathol 1996;149:501-509.
- 22. Kramer G, Mitteregger D, Marberger M. Is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) an immune inflammatory disease? Eur Urol 2007;51:1202-1216.
- 23. Schmitz N, Kurrer M, Bachmann MF, Kopf M. Interleukin-1 is responsible for acute lung immunopathology but increases survival of respiratory influenza virus infection. J Virol 2005;79:6441-6448.
- 24. Abbott DW, Wilkins A, Asara JM, Cantley LC. The Crohn’s disease protein, NOD2, requires RIP2 in order to induce ubiquitinylation of a novel site on NEMO. Curr Biol 2004;14:2217-2227.
- 25. Gu NY, Kim JH, Han IH, Im SJ, Seo MY, Chung YH, Ryu JS. Trichomonas vaginalis induces IL-1β production in a human prostate epithelial cell line by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome via reactive oxygen species and potassium ion efflux. Prostate 2016;DOI: 10.1002/pros.23178
- 26. Kashyap M, Pore S, Wang Z, Gingrich J, Yoshimura N, Tyagi P. Inflammasomes are important mediators of prostatic inflammation associated with BPH. J Inflamm 2015;12:DOI: 10.1186/s12950-12015-10082-12953
- 27. Castro P, Xia C, Gomez L, Lamb DJ, Ittmann M. Interleukin-8 expression is increased in senescent prostatic epithelial cells and promotes the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate 2004;60:153-159.
- 28. Liu L, Li Q, Han P, Li X, Zeng H, Zhu Y, Wei Q. Evaluation of interleukin-8 in expressed prostatic secretion as a reliable biomarker of inflammation in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 2009;74:340-344.
- 29. Heinrich P, Castell JV, Andus T. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem J 1990;265:621-636.
- 30. Greenhill CJ, Rose-John S, Lissilaa R, Ferlin W, Ernst M, Hertzog PJ, Mansell A, Jenkins BJ. IL-6 trans-signaling modulates TLR4-dependent inflammatory responses via STAT3. J Immunol 2011;186:1199-1208.
- 31. Kramer G, Marberger M. Could inflammation be a key component in the progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia? Curr Opin Urol 2006;16:25-29.
- 32. Bouraoui Y, Ricote M, Garcia-Tunon I, Rodriguez-Berriguete G, Touffehi M, Rais NB, Fraile B, Paniagua R, Oueslati R, Royuela M. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and prostate-specific antigen in hyperplasia and human prostate cancer. Cancer Detect Prev 2008;32:23-32.
- 33. Adler HL, McCurdy MA, Kattan MW, Timme TL, Scardino PT, Thompson TC. Elevated levels of circulating interleukin-6 and transforming growth factor-beta1 in patients with metastatic prostatic carcinoma. J Urol 1999;161:182-187.
- 34. Daniel J, George SH, Timothy F, Shepard BS, Nicholas J, Vogelzang EJS, Kantoff PW. The prognostic significance of plasma interleukin-6 levels in patients with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer: results from cancer and leukemia group B 9480. Clin Cancer Res 2005;11:1815-1820.
- 35. Ernst M, Jenkins BJ. Acquiring signalling specificity from the cytokine receptor gp130. Trends Genet 2004;20:23-32.
- 36. Li L, Ittmann MM, Ayala G, Tsai MJ, Amato RJ, Wheeler TM, Miles BJ, Kadmon D, Thompson TC. The emerging role of the PI3-K-Akt pathway in prostate cancer progression. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2005;8:108-118.
- 37. Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns HM, Muller-newen G, Schaper F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J 2003;374:1-20.
- 38. Forman HJ, Torres M. Reactive oxygen species and cell signaling: respiratory burst in macrophage signaling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;166:S4-S8.
- 39. Min A, Lee YA, Kim KA, El-Benna J, Shin MH. NOX2-derived ROS-mediated surface translocation of BLT1 is essential for exocytosis in human eosinophils induced by LTB4. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2014;165:40-51.
- 40. Makni-Maalej K, Chiandotto M, Hurtado-Nedelec M, Bedouhene S, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Dang PM, El-Benna J. Zymosan induces NADPH oxidase activation in human neutrophils by inducing the phosphorylation of p47phox and the activation of Rac2: involvement of protein tyrosine kinases, PI3Kinase, PKC, ERK1/2 and p38 MAPkinase. Biochem Pharmacol 2013;85:92-100.
- 41. Min YD, Choi CH, Bark H, Son HY, Park HH, Lee S, Park JW, Park EK, Shin HI, Kim SH. Quercetin inhibits expression of inflammatory cytokines through attenuation of NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK in HMC-1 human mast cell line. Inflamm Res 2007;56:210-215.
- 42. Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang DG, Pae HO. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: how can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J Signal Transduct 2011;2011:DOI: 10.1155/2011/792639.