Abstract
Cryptosporidium and Cyclospora are well-known coccidian protozoa that can cause waterborne and foodborne diarrheal illnesses. There have been a few reports regarding contamination in different vegetables with Cryptosporidium, but no data are available regarding the sources of Cyclospora infections in Korea. In the present study, we collected 6 kinds of vegetables (perilla leaves, winter-grown cabbages, chives, sprouts, blueberries, and cherry tomatoes) from July 2014 to June 2015, and investigated contamination by these 2 protozoa using multiplex quantitative real-time PCR. Among 404 vegetables, Cryptosporidium and Cyclospora were detected in 31 (7.7%) and 5 (1.2%) samples, respectively. In addition, Cryptosporidium was isolated from all 6 kinds of vegetables, whereas Cyclospora was detected in 4 kinds of vegetables (except perilla leaves and chives). Cryptosporidium (17.8%) and Cyclospora (2.9%) had the highest detection rates in chives and winter-grown cabbages, respectively. Cryptosporidium was detected all year long; however, Cyclospora was detected only from October to January. In 2 samples (sprout and blueberry), both Cryptosporidium and Cyclospora were detected. Further investigations using TaqI restriction enzyme fragmentation and nested PCR confirmed Cryptosporidium parvum and Cyclospora cayetanensis, respectively. In conclusion, we detected C. cayetanensis in vegetables for the first time in Korea. This suggests that screening should be employed to prevent these protozoal infections in Korea.
-
Key words: Cryptosporidium parvum, Cyclospora cayetanensis, vegetable, real-time PCR, Korea
INTRODUCTION
Cryptosporidium parvum is a zoonotic protozoan parasite that causes severe enteritis in immunocompromised patients. Numerous outbreaks have been reported worldwide [
1–
3]. The coccidian parasite
Cyclospora cayetanensis has been recently recognized as a cause of prolonged diarrhea in children and immunodeficient patients in developing countries [
4–
7]. These 2 organisms produce environment-resistant oocysts that are excreted in the feces of infected individuals. The major risk factor associated with transmission of these parasites has been identified as consumption of oocysts in contaminated water or foods [
8–
11].
Although risks for massive waterborne cryptosporidiosis outbreaks have been present since 1990 in western countries, there was no outbreak in Korea for several decades. However, the first water-borne outbreak of cryptosporidiosis was reported in Korea in 2012 [
12], and soil and vegetable samples have been reported to be contaminated with
C. parvum oocysts [
13]. In contrast, since the first human case of
Cyclospora was reported in 2003 in travelers who had visited Indonesia [
14], information regarding other indigenous cases and environmental sources of
Cyclospora oocysts was not available in Korea. In this study, we investigated several food samples to assess contamination by
Cryptosporidium and
Cyclospora oocysts using multiplex quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). This information could be useful for preventing food poisoning due to infections by these protozoa.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Food sample collection and pretreatment
Six kinds of food samples (perilla leaves, winter-grown cabbages, chives, sprouts, blueberries, and cherry tomatoes) were purchased from local groceries in Seoul from July 2014 to June 2015. For perilla leaves and sprouts, 20 and 30 g samples were used for examination, respectively. For other vegetables, 50 g fresh samples were used. For sample wash preparation, we followed the method reported previously by Hong et al. [
13]. Briefly, each sample was placed in a zipper bag (Cleanwrap Inc., Hwaseong, Korea) and 2–3 volumes of 0.1% liquinox
TM (Alconox Inc., New York, USA) in 0.01 M PBS (pH 7.4) was added. Samples were shaken on an orbital shaker (Red Roter, Hoefer, California, USA) for 15 min and were shaken repeatedly in an upside down position. Subsequently, the washing solution was collected and pellets were saved after centrifugation at 5,000 g for 20 min. Food samples were rewashed and pellets were added to the bottle used for the first wash. The pellets were moved into microcentrifuge tubes and kept at −20°C until DNA extraction using QIAquick stool mini kit (QIAGEN Inc., Valencia, California, USA).
All purchased vegetables were produced domestically, except blueberries. Blueberries were imported from the United States (August) and Chile (from December to April) or domestically produced (from May to July).
Real-time PCR
The extracted DNA was used as a template for qPCR. For a positive DNA control,
C. parvum oocysts (KKU isolates) were used as described by Lee et al. [
15]. The primers and probes used for qPCR were designed using the Swi2/SNF2 ATPase,
Rad 16 ortholog gene (
Rad 16, GenBank no. XM_625623.1) of
Cryptosporidium [
13] and the internal transcribed spacer 2 gene (
ITS2, GenBank no. AF301386.1) of
Cyclospora [
16] (
Table 1).
Absolute qPCR reactions were performed using the method of Lee et al. [
15]. Briefly, reaction mixtures included 0.1×LightCycler® FastStart HybProbe master mix (Roche, Mannheim, Germany), each
C. parvum primer set at 0.5 μM (Bioneer, Daejeon, Korea), and the probe set at 0.1 μM (TIB MOLBIO, Berlin, Germany). qPCR was performed using a LightCycler® 480 device (Roche), and each qPCR mixture was denatured at 95°C for 10 min, followed by 45 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 10 sec, annealing at 60°C for 30 sec, and extension at 72°C for 3 sec, with a final cooling step at 40°C for 30 sec. DNase/RNase-free water was used in place of template DNA as a negative control. The plasmid DNA standard for real-time PCR was prepared as described previously using the
Rad 16 gene of
Cryptosporidium and
ITS2 gene of
Cyclospora as targets [
15].
Sequences of qPCR products were confirmed using an ABI 7700 model sequence detector with SDS v.-1.6.3 software (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA) at the Cosmo sequence facility service (Seoul, Korea) after electrophoresis using a 2% agarose gel; gene sequences were aligned using Clone Manager suite 7 (Sci-Ed Software, Cary, North Carolina, USA). To differentiate
Cryptosporidium species, the qPCR products were digested with the
TaqI restriction enzyme (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan) at 65°C for 2 hr, and analyzed using 2% agarose gels [
13]. For
Cyclospora species identification, we performed nested PCR as described by Orlandi and Lampel [
17] with qPCR positive vegetable samples and the 18S ribosomal DNA gene as the target.
RESULTS
We examined 404 samples representing 6 kinds of popular vegetables to simultaneously detect
Cryptosporidium and
Cyclospora. As a result,
Cryptosporidium spp. was detected in 31 samples of all 6 types of vegetables (7.7%;
Table 2). In contrast,
Cyclospora spp. were identified in 5 samples comprising of 4 types of vegetables (1.2%;
Table 2). The number of oocysts per gram of vegetables ranged from 25 to 783 and from 13 to 348 for
Cryptosporidium and
Cyclospora, respectively (data not shown).
Among the 6 types of vegetables, chives showed the highest contamination rates (17.8%), and sprouts (baby bok choy, chicory, beet, and fushun) showed the lowest contamination rates (1.4%) for
Cryptosporidium (
Table 3). Perilla leaves, winter-grown cabbages, blueberries, and cherry tomatoes showed a similar range of contamination (5.7–6.9%). Among 3 positive blueberry samples, 2 samples were imported from Chile, and 1 was domestic. In terms of seasonal variation, there was no specific seasonal dependence observed for
Cryptosporidium.
Cyclospora was detected in winter-grown cabbages, sprouts, blueberries, and cherry tomatoes with contamination rates ranging from 1.4% to 2.9% (
Table 2). These rates were much lower than those of
Cryptosporidium. Especially, both
Cryptosporidium and
Cyclospora were detected in 1 blueberry and 1 sprout sample. The blueberry sample was imported from Chile, and the sprout sample was a domestic product. In terms of seasonal variation,
Cyclospora was detected in samples collected from October to January (
Table 4).
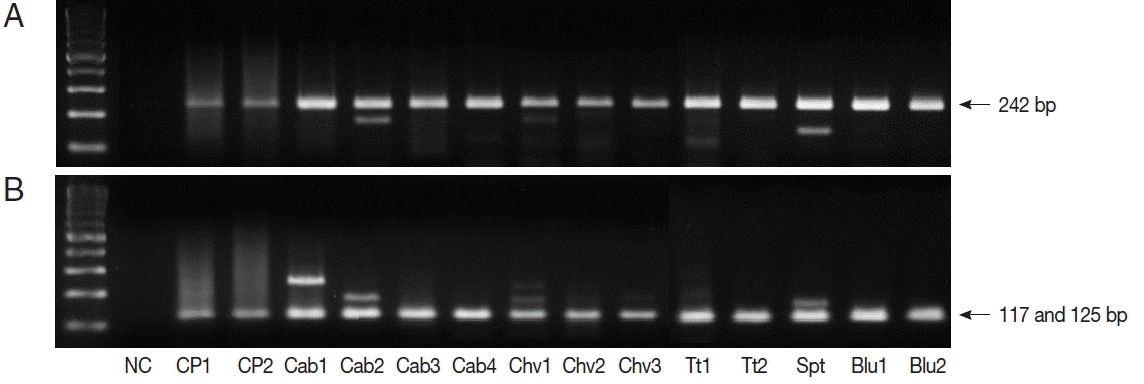
TaqI restriction enzyme digestion of qPCR products (242 bp) from
Cryptosporidium spp. resulted in 2 bands (117 and 125 bp); therefore, all qPCR positive samples were
C. parvum (
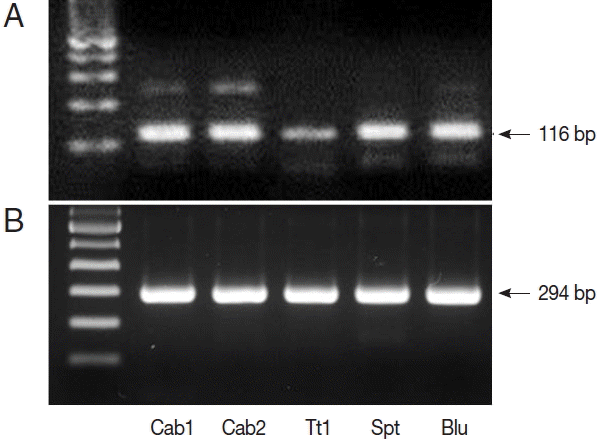
Fig. 1). We also performed nested PCR targeting 18S ribosomal DNA of
Cyclospora using vegetable DNA that was positive for
Cyclospora by qPCR as the template. The nested PCR products were 294 bp bands, thus confirming the presence of
Cyclospora spp. in these vegetable samples (
Fig. 2). Sequencing data from nested PCR products were consistent with the presence of
C. cayetanensis.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, we established a qPCR method to detect both Cryptosporidium and Cyclospora simultaneously using fresh farm produce. We identified 2 samples, blueberry and sprout, which were simultaneously contaminated with C. parvum and C. cayetanensis. This technique could be useful to save time and materials, especially those that are available in limited amounts. All vegetable items examined in this study are popular, edible raw, and easily purchased from the grocery markets in town.
The management of opportunistic infections is important because the population of immunocompromised hosts, accompanied by the progress made in transplantation methods, has increased [
18]. A recent review article found that in the last decade, only 15 of 71 worldwide
Cryptosporidium-linked outbreaks were correlated to foodborne transmission [
9]. Reports on foodborne cryptosporidiosis were mainly from the US, UK, and Nordic countries, and various types of food were associated with these outbreaks [
19]. In Korea, only 1 waterborne outbreak of
Cryptosporidium had been reported until now [
12], and there had been no reports of foodborne outbreaks of
Cryptosporidium.
In addition, regarding
Cyclospora, there had been no cases of indigenous human infections, and there were no reports regarding infection sources in Korea, as only 1 case was reported from an individual infected after visiting Indonesia [
14]. It is difficult to explain why cases of cyclosporiasis had not been reported in Korea. This is different from incidence rates in western countries where
Cyclospora is considered a major waterborne and foodborne protozoan that is routinely monitored (
https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/outbreaks/2016/index.html). Actually, since 1990, more than a half of the foodborne outbreaks by
Cyclospora were reported in the US, and several other countries, including Nepal, Canada, Germany, Mexico, Peru, Colombia, Indonesia, and Turkey [
20]. Vehicles for most reported outbreaks included various types of berries, salad mixes, and leafy herbs [
20]. These are quite similar to the items tested in this study. Perhaps one of the reasons for the absence of cyclosporiasis in Korea is because
Cyclospora is frequently neglected as a causative organism of food poisoning. Therefore, it is not screened routinely when foodborne outbreaks occur in Korea.
The increased globalization of the food supply also increases the chances of endemic parasites coming into contact with consumers from other nations. Changes in nutritional habits have resulted in increased consumption of undercooked or raw foods, exposing consumers to parasites that proper food processing would otherwise reduce or eliminate [
20,
21]. Leafy vegetables are an essential component of a healthy diet but they have been associated with high-profile outbreaks causing severe illnesses [
22]. In addition, the consumption of fresh vegetables without proper washing is a risk factor for
Cyclospora infection [
23].
In the present study, we detected
C. parvum and
C. cayetanensis in daily edible vegetables, such as winter-grown cabbages, sprouts, blueberries, and cherry tomatoes. This finding is the first report of the infection source of
Cyclospora in Korea, whereas
C. parvum has been previously reported [
13]. Although there have been no reports of
Cryptosporidium or
Cyclospora foodborne outbreaks, the results suggest that these are possible in Korea. In this report,
Cyclospora was detected in samples collected from autumn to winter. The prevalence of
Cyclospora infection increased during the warm and rainy season [
6,
24,
25]. In contrast, infection has been reported more prevalent in cool and/or dry season [
26,
27]. The seasonal trend of
Cyclospora infection is not uniform among different regions.
Both
Cryptosporidium and
Cyclospora can cause infection after consumption of contaminated agricultural water and food [
8,
20]. In Korea,
Cryptosporidium oocysts were found in 22.5% of water samples from the Han River [
28], and
C. parvum was reported in 10.5% of pigs in Chungcheongbuk-do [
29] and 94% of livestock in Gokseong-gun, Jeollanam-do [
30]. Such high livestock infection rates suggest that farming areas nearby stables could be contaminated by agricultural runoff. The finding of vegetables positive for
Cyclospora suggests the presence of infected hosts as the source of oocysts, because
Cyclospora is an anthroponotic pathogen requiring fecal-oral transmission [
20]. A limitation of our study is that although we detected both
Cryptosporidium and
Cyclospora from several types of fresh produce, it is unknown whether the parasites were infective based on the methods used in this study.
In conclusion, we simultaneously detected C. parvum and C. cayetanensis in several types of fresh produce in Korea using qPCR. Although there have been no foodborne outbreaks caused by these 2 protozoa, this study implies a risk for such occurrences. Therefore, we suggest that fresh vegetables should be carefully washed and care should be taken when eating raw produce to prevent Cryptosporidium and Cyclospora infection, especially in children and immunocompromised individuals. In addition, implementation of monitoring strategies is needed in Korea.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by Konkuk University in 2014.
Fig. 1Restriction enzyme fragmentation profiles of Cryptosporidium. Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) products in positive samples were cut with TaqI restriction enzyme. (A) DNA of qPCR product. (B) fragmented DNA after TaqI digestion of qPCR product. NC, negative control; CP1 & CP2, C. parvum DNA (for positive controls); Cab, winter-grown cabbages; Chv, chives; Tt, cherry tomatoes; Spt, sprouts; Blu, blueberries.
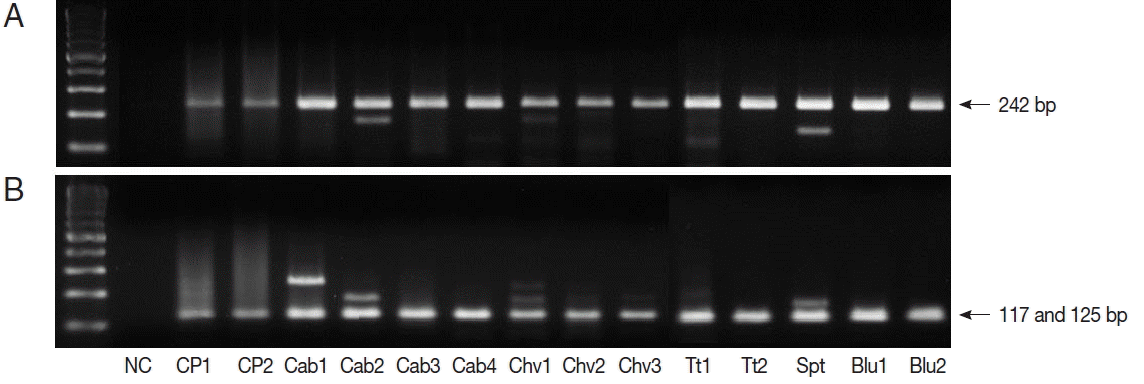
Fig. 2PCR results from Cyclospora positive samples. (A) DNA products after quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). (B) DNA products after nested PCR. The target gene was internal transcribed spacer 2 (GenBank no. AF301386.1, for qPCR) and 18S rRNA (GenBank no. AF111183.1, for nested PCR). Cab, winter-grown cabbages; Tt, cherry tomatoes; Spt, sprouts; Blu, blueberries.
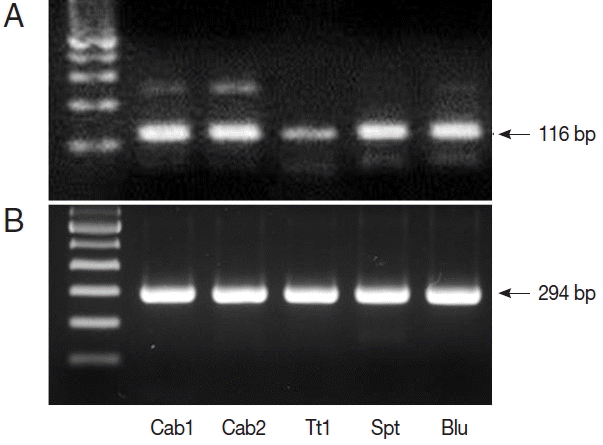
Table 1Primers and probes used for multiplex real-time PCR to detect Cryptosporidium and Cyclospora simultaneously in vegetables examined from 2014 to 2015
Table 1
|
Parasites |
|
Nucleotide position |
Sequences (5′→3′) |
Size (bp) |
|
Cryptosporidium
|
Forward primer |
2,930–2,950 |
CTCCCCAGGAAGACGAAATAA |
242 |
|
Reverse primer |
3,171–3,148 |
TTCAAGCTCTCTTTCAATTTGCTC |
|
Probe-FAM |
3,013–2,987 |
AGCAAACAGGGCATCCAAGAACTCCTC |
|
|
Cyclospora
|
Forward primer |
918–940 |
GCAGTCACAGGAGGCATATATCC |
116 |
|
Reverse primer |
1,033–1,012 |
ATGAGAGACCTCACAGCCAAAC |
|
Probe-HEX |
1,005–981 |
CGACGAACAGCCACGCACGCACTTG |
Table 2Positive rates of Cryptosporidium spp. and Cyclospora spp. in various vegetable samples examined from 2014 to 2015
Table 2
|
Vegetables |
No. examined |
No. of positive samples (%) |
|
Cryptosporidium spp. |
Cyclospora spp. |
|
Perilla leaves |
72 |
5 (6.9) |
0 |
|
Winter-grown cabbage |
70 |
4 (5.7) |
2 (2.9) |
|
Chives |
73 |
13 (17.8) |
0 |
|
Sprouts |
72 |
1 (1.4) |
1 (1.4) |
|
Blueberries |
44 |
3 (6.8) |
1 (2.3) |
|
Cherry tomatoes |
73 |
5 (6.8) |
1 (1.4) |
|
Total |
404 |
31 (7.7) |
5 (1.2) |
Table 3Positive rates of Cryptosporidium spp. in various vegetable samples examined from 2014 to 2015 by month
Table 3
|
Month |
Perilla leaves no. |
Winter-grown cabbage no. |
Chives no. |
Sprouts no. |
Blueberries no. |
Cherry tomatoes no. |
Total no. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
|
July |
10 |
|
10 |
|
10 |
|
10 |
|
10 |
|
10 |
|
60 |
0 |
|
|
August |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
3 |
|
6 |
|
33 |
0 |
|
|
September |
6 |
|
6 |
3 |
6 |
4 |
6 |
|
nda
|
|
6 |
2 |
30 |
9 |
|
|
October |
6 |
2 |
3 |
|
6 |
1 |
6 |
|
nda
|
|
6 |
1 |
27 |
4 |
|
|
November |
6 |
|
6 |
1 |
6 |
5 |
5 |
|
nda
|
|
6 |
|
29 |
6 |
|
|
December |
5 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
1 |
3 |
|
6 |
|
32 |
1 |
|
|
January |
3 |
|
3 |
|
3 |
1 |
3 |
|
3 |
2 |
3 |
|
18 |
3 |
|
|
February |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
1 |
36 |
1 |
|
|
March |
6 |
1 |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
35 |
1 |
|
|
April |
6 |
2 |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
2 |
|
6 |
|
32 |
2 |
|
|
May |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
36 |
0 |
|
|
June |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
2 |
6 |
|
6 |
1 |
6 |
1 |
36 |
4 |
|
|
Total |
72 |
5 (6.9) |
70 |
4 (5.7) |
73 |
13 (17.8) |
72 |
1 (1.4) |
44 |
3 (6.8) |
73 |
5 (6.8) |
404 |
31 (7.7) |
Table 4Positive rates of Cyclospora spp. in various vegetable samples examined from 2014 to 2015 by month
Table 4
|
Month |
Perilla leaves no. |
Winter-grown cabbage no. |
Chives no. |
Sprouts no. |
Blueberries no. |
Cherry tomatoes no. |
Total no. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
Tested |
Positive (%) |
|
July |
10 |
|
10 |
|
10 |
|
10 |
|
10 |
|
10 |
|
60 |
0 |
|
|
August |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
3 |
|
6 |
|
33 |
0 |
|
|
September |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
nda
|
|
6 |
|
30 |
0 |
|
|
October |
6 |
|
3 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
nda
|
|
6 |
1 |
27 |
1 |
|
|
November |
6 |
|
6 |
1 |
6 |
|
5 |
|
nda
|
|
6 |
|
29 |
1 |
|
|
December |
5 |
|
6 |
1 |
6 |
|
6 |
1 |
3 |
|
6 |
|
32 |
2 |
|
|
January |
3 |
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
3 |
1 |
3 |
|
18 |
1 |
|
|
February |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
36 |
0 |
|
|
March |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
35 |
0 |
|
|
April |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
2 |
|
6 |
|
32 |
0 |
|
|
May |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
36 |
0 |
|
|
June |
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
36 |
0 |
|
|
Total |
72 |
0 (0.0) |
70 |
2 (2.9) |
73 |
0 (0.0) |
72 |
1 (1.4) |
44 |
1 (2.3) |
73 |
1 (1.4) |
404 |
5 (1.2) |
References
- 1. Mac Kenzie WR, Hoxie NJ, Proctor ME, Gradus MS, Blair KA, Peterson DE, Kazmierczak JJ, Addiss DG, Fox KR, Rose JB, Davis JP. A massive outbreak in Milwaukee of Cryptosporidium infection transmitted through the public water supply. N Engl J Med 1994;331:161-167.
- 2. Baldursson S, Karanis P. Waterborne transmission of protozoan parasites: review of worldwide outbreaks - an update 2004–2010. Water Res 2011;45:6603-6614.
- 3. Smith HV, Rose JB. Waterborne cryptosporidiosis: current status. Parasitol Today 1998;14:14-22.
- 4. Agholi M, Shahabadi SN, Motazedian MH, Hatam GR. Prevalence of enteric protozoan oocysts with special reference to Sarcocystis cruzi among fecal samples of diarrheic immunodeficient patients in Iran. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:339-344.
- 5. Ortega YR, Sterling CR, Gilman RH. Cyclospora cayetanensis. Adv Parasitol 1998;40:399-418.
- 6. Chacín-Bonilla L. Epidemiology of Cyclospora cayetanensis: a review focusing in endemic areas. Acta Trop 2010;115:181-193.
- 7. Abdel-Hafeez EH, Ahmad AK, Ali BA, Moslam FA. Opportunistic parasites among immunosuppressed children in Minia District, Egypt. Korean J Parasitol 2012;50:57-62.
- 8. Fayer R. Cryptosporidium: a water-borne zoonotic parasite. Vet Parasitol 2004;126:37-56.
- 9. Putignani L, Menichella D. Global distribution, public health and clinical impact of the protozoan pathogen Cryptosporidium. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis 2010;2010:753512.
- 10. Herwaldt BL, Ackers ML. An outbreak in 1996 of cyclosporiasis associated with imported raspberries. The Cyclospora Working Group. N Engl J Med 1997;336:1548-1556.
- 11. Mansfield LS, Gajadhar AA. Cyclospora cayetanensis, a food- and waterborne coccidian parasite. Vet Parasitol 2004;126:73-90.
- 12. Moon S, Kwak W, Lee S, Kim W, Oh J, Youn SK. Epidemiological characteristics of the first water-borne outbreak of cryptosporidiosis in Seoul, Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2013;28:983-989.
- 13. Hong S, Kim K, Yoon S, Park WY, Sim S, Yu JR. Detection of Cryptosporidium parvum in environmental soil and vegetables. J Korean Med Sci 2014;29:1367-1371.
- 14. Yu JR, Sohn WM. A case of human cyclosporiasis causing traveler’s diarrhea after visiting Indonesia. J Korean Med Sci 2003;18:738-741.
- 15. Lee SU, Joung M, Ahn MH, Huh S, Song H, Park WY, Yu JR. CP2 gene as a useful viability marker for Cryptosporidium parvum. Parasitol Res 2008;102:381-387.
- 16. Kitajima M, Haramoto E, Iker BC, Gerba CP. Occurrence of Cryptosporidium, Giardia, and Cyclospora in influent and effluent water at wastewater treatment plants in Arizona. Sci Total Environ 2014;484:129-136.
- 17. Orlandi PA, Lampel KA. Extraction-free, filter-based template preparation for rapid and sensitive PCR detection of pathogenic parasitic protozoa. J Clin Microbiol 2000;38:2271-2277.
- 18. Yoo JH. Emerging infectious disease by industrialization and technology. Korean J Infect Dis 1999;31:65-78.
- 19. Robertson LJ, Chalmers RM. Foodborne cryptosporidiosis: is there really more in Nordic countries? Trends Parasitol 2013;29:3-9.
- 20. Ortega YR, Sanchez R. Update on Cyclospora cayetanensis, a food-borne and waterborne parasite. Clin Microbiol Rev 2010;23:218-234.
- 21. Orlandi PA, Chu D-M, Bier JW, Jackson GJ. Parasites and the food supply. Food Technol 2002;56:72-81.
- 22. Herman KM, Hall AJ, Gould LH. Outbreaks attributed to fresh leafy vegetables, United States, 1973–2012. Epidemiol Infect 2015;143:3011-3021.
- 23. Bhandari D, Tandukar S, Parajuli H, Thapa P, Chaudhary P, Shrestha D, Shah PK, Sherchan JB, Sherchand JB. Cyclospora infection among school children in Kathmandu, Nepal: prevalence and associated risk factors. Trop Med Health 2015;43:211-216.
- 24. Kimura K, Rai SK, Rai G, Insisiengmay S, Kawabata M, Karanis P, Uga S. Study on Cyclospora cayetanensis associated with diarrheal disease in Nepal and Loa PDR. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2005;36:1371-1376.
- 25. Kaminsky RG, Lagos J, Raudales Santos G, Urrutia S. Marked seasonality of Cyclospora cayetanensis infections: ten-year observation of hospital cases, Honduras. BMC Infect Dis 2010;16:66.
- 26. Eberhard ML, Nace EK, Freeman AR, Streit TG, da Silva AJ, Lammie PJ. Cyclospora cayetanensis infections in Haiti: a common occurrence in the absence of watery diarrhea. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1999;60:584-586.
- 27. Giangaspero A, Marangi M, Koehler AV, Papini R, Normanno G, Lacasella V, Lonigro A, Gasser RB. Molecular detection of Cyclospora in water, soil, vegetables and humans in southern Italy signals a need for improved monitoring by health authorities. Int J Food Microbiol 2015;211:95-100.
- 28. Lee MY, Cho EJ, Lee JH, Han SH, Park YS. A survey of Cryptosporidium oocysts in water supplies during a 10-year period (2000–2009) in Seoul. Korean J Parasitol 2010;48:219-224.
- 29. Yu JR, Seo M. Infection status of pigs with Cryptosporidium parvum. Korean J Parasitol 2004;42:45-47.
- 30. Yu JR, Lee JK, Seo M, Kim SI, Sohn WM, Huh S, Choi HY, Kim TS. Prevalence of cryptosporidiosis among the villagers and domestic animals in several rural areas of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2004;42:1-6.