Abstract
Codon usage bias (CUB) is a unique property of genomes and has contributed to the better understanding of the molecular features and the evolution processes of particular gene. In this study, genetic indices associated with CUB, including relative synonymous codon usage and effective numbers of codons, as well as the nucleotide composition, were investigated in the Clonorchis sinensis tyrosinase genes and their platyhelminth orthologs, which play an important role in the eggshell formation. The relative synonymous codon usage patterns substantially differed among tyrosinase genes examined. In a neutrality analysis, the correlation between GC12 and GC3 was statistically significant, and the regression line had a relatively gradual slope (0.218). NC-plot, i.e., GC3 vs effective number of codons (ENC), showed that most of the tyrosinase genes were below the expected curve. The codon adaptation index (CAI) values of the platyhelminth tyrosinases had a narrow distribution between 0.685/0.714 and 0.797/0.837, and were negatively correlated with their ENC. Taken together, these results suggested that CUB in the tyrosinase genes seemed to be basically governed by selection pressures rather than mutational bias, although the latter factor provided an additional force in shaping CUB of the C. sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini genes. It was also apparent that the equilibrium point between selection pressure and mutational bias is much more inclined to selection pressure in highly expressed C. sinensis genes, than in poorly expressed genes.
-
Key words: Clonorchis sinensis, tyrosinase, codon usage bias, selection pressure, mutational bias
INTRODUCTION
Tyrosinases (EC 1.14.18.1) comprise the type-3 copper protein family, which contain an active di-copper center, together with catecholoxidases [
1,
2]. The enzymes mediate the biochemical conversion of tyrosine into dihydrophenylalnine (DOPA; monophenol oxidase activity) and DOPA into DOPA quinone (diphenol oxidase activity) [
3,
4]. Tyrosinases are ubiquitously distributed across taxa ranging from bacteria to mammals and engaged in diverse biological events, such as pigmentations, innate immunity, sclerotization, and wound healing, depending on their primary structures [
2]. In parasitic trematodes, tyrosinases are produced in the mature vitellocytes and packed within secreting vacuoles termed vitelline droplets, together with eggshell precursor proteins [
5]. Following secretion in the ootype, the tyrosinases convert tyrosine residues on the eggshell proteins into DOPA quinones, which are then cross linked to other amino acids, such as tyrosine and lysine, on adjacent proteins to make the sclerotized eggshell [
6].
Clonorchis sinensis is the causative agent of clonorchiasis in humans, of which clinical manifestations are represented by abdominal pain, mechanical obstruction of the hepatobiliary ducts, cholangiectasis, and biliary stones [
7]. Chronic infection of
C. sinensis also appears to lead to high incidences of cholangiocarcinoma [
8,
9]. Human infection occurs by eating raw or undercooked freshwater fish containing
C. sinensis metacercariae. Clonorchiasis is highly endemic in Asian countries, such as China, Vietnam, and Korea, where it causes great socio-economic and public health burdens [
7]. In a previous report [
10], the structural and biochemical properties of multiple tyrosinases, as well as their spatiotemporal expression patterns, have been investigated in the liver fluke. Expression of these vitellocyte-specific tyrosinase genes was tightly related to the sexual maturation of
C. sinensis. However, the relative expression levels of these tyrosinase paralogs were substantially different, although any molecular evidence demonstrating functional diversification could not be detected among them [
10].
In general, gene expression level is regulated by multiple factors, such as promoter activity [
11], open reading frame (ORF) length and amino acid composition [
12], intron length [
13], and codon usage pattern [
14]. Unequal usage of synonymous codons encoding the same amino acid during translation of a gene, which is known as codon usage bias (CUB), is a commonly observed phenomenon in a wide variety of organisms. The codon usage pattern is a unique property of a genome, and it may vary between genomes and genes from the same genome [
15,
16]. Many genomic factors, such as gene length and GC-content, have been known to be highly associated with CUB [
15]. Comprehensive studies with various organisms further demonstrated that multiple factors, including mutation pressure, natural/translational selection, secondary structure of protein, hydropathic character of protein, and numbers of tRNA gene copies, influence on the codon usage patterns [
15,
17]. It is also likely that highly expressed genes exhibit significant bias in their codon usage toward those with abundant tRNA gene copy numbers. Therefore, the codon usage patterns of genes may be applied in the prediction of expression level of relevant genes [
16,
18].
In this study, the CUB of C. sinensis tyrosinase genes and their trematode orthologs was analyzed to understand the process of molecular evolution and the probable factors influencing the codon usage profile, which is ultimately related to the expression level of the corresponding gene.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sequence data
The genomic and proteomic databases of platyhelminths, of which the whole genome drafts were available, were selected for the screening of tyrosinase genes as follows:
C. sinensis in the GenBank (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/),
Opisthorchis viverrini in the GenBank,
Schistosoma japonicum in the GenBank and the Chinese National Human Genome Center at Shanghai (
http://lifecenter.sgst.cn/schistosoma/cn/schistosomaCnIndexPage.do), and
Schistosoma mansoni in the GenBank and the Sanger Institute. Tyrosinase sequences in the respective databases were identified using the tBLASTn program with the amino acid sequences of
C. sinensis tyrosinases (AGG11797-AGG11800 [
10]). The genomic and expressed sequence tag (EST) sequences of
Schmidtea mediterranea in the GenBank and the SmedGD (
http://smedgd.neuro.utah.edu/), as well as the GenBank databases of other platyhelminths, were also targeted during the BLAST examinations. The retrieved sequences were finally filtered to eliminate redundant sequences by comparing chromosomal locations of the respective genes. Otherwise, 95% similarity cutoff was taken for speciation of paralogous genes at the amino acid sequence level. The translated amino acid sequences of matched ESTs were predicted using the ORF Finder (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The similarity pattern and specific hidden Markov model (HMM) profiles were examined from the theoretical amino acid sequences using the BLASTp (
E-value cutoff, 1e-5) and InterProScan (version 5.0;
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/pfa/iprscan5/), respectively.
The frequencies of nucleotide G+C at the first (GC
1), second (GC
2), and third (GC
3) positions of tyrosinase gene codons were calculated using CAIcal (
http://genomes.urv.cat/CAIcal/) to quantify the extent of base composition bias. Codon adaptation index (CAI), which reflected the transcriptional activity of relevant gene [
19], and effective number of codons (ENC), which was used to quantify the codon usage bias of a gene unconcerned to its length [
20], were similarly determined with the program. The CAI values ranged from 0.0 to 1.0, and the higher value meant a likely stronger bias in codon usage and a potential higher expression level [
21]. During estimation of the CAI values, genes of
Caenorhabditis elegans and
Escherichia coli were used as reference groups. The ENC values were between 20 indicating that the gene used only 1 synonymous codon for the corresponding amino acid and 61 indicating that the gene used all the synonymous codons equally for the corresponding amino acid [
20].
Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) was defined as the observed frequency of a codon divided by the expected frequency, if all synonymous codons were used equally to encode any particular amino acid [
22]. Therefore, a codon with a RSCU value greater than 1 was used more frequently than expected, whereas that with a value smaller than 1 was used less frequently than expected. The RSCU values of tyrosinase gene codons were calculated using CodonW (
http://mobyle.pasteur.fr/cgi-bin/portal.py?#forms::CodonW). The RSCU values were further applied either in the correspondence analysis using identical program, which partitions the variation along 59 orthogonal axes.
RESULTS
Tyrosinase genes and their nucleotide contents
A total of 5 tyrosinase paralogs were identified in the genomes of
C. sinensis and
O. viverrini, while those of
Schistosoma spp. encoded only 2 paralogous tyrosinase genes. The free-living turbellarian,
S. mediterranea, possessed 6 genes homologous to the trematode tyrosinases. In addition to these genes in platyhelminths, of which whole genomic sequence information was available, a single tyrosinase ortholog was further retrieved from the GenBank database of other platyhelminths, such as
Paragonimus westermani and
Spirometra erinaceieuropaei, as well as
Capitella teleta (Annelida). The
Capitella tyrosinase information was taken to use as a outgroup gene (
Table 1). The similarity patterns of these tyrosinases toward the γ-subclass of type-3 copper protein family [
2] and the functional domains conserved in the subclass members, such as epidermal growth factor-like domain and di-copper center [
10], were verified by sequence analyses using the BLAST and InterProScan programs (data not shown).
The genome-wide G+C content (GC) varied from 28.7 (
S. mediterranea) to 44.8 (
C. sinensis) across platyhelminth genomes [
23,
24]. The values in the whole coding DNA sequences (CDSs) were found to be higher than the genome-wide values (36.2–48.0;
Table 1). GC values in tyrosinase genes ranging from 31.1±0.21 (
S. mansoni) to 47.2±1.41 (
O. viverrini) were approximate to the values of CDSs in the respective genomes. The tyrosinase genes of
C. sinensis (46.9±1.54) and other schistosomes (32.5±2.55 in
S. japonicum and 31.7±0.42 in
S. haematobium) showed GC contents similar to those of the
O. viverrini and
S. mansoni genes, respectively. The
S. mediterranea genes exhibited an average GC content of 35.6. The GC contents of
P. westermani, S. erinaceieuropaei, and
C. teleta genes were estimated as 46.9, 49.8, and 53.6, respectively.
The GC
1, GC
2, and GC
3 were also quite different among the tyrosinase genes. In
C. sinensis and
O. viverrini genes, the average values of GC
1 and GC
3 were similar to or slightly higher than that in total codon positions (51.0/47.8 vs 46.6 in
C. sinensis and 51.0/48.3 vs 47.2 in
O. viverrini), whereas the values were significantly reduced in the second positions (41.9 and 42.4 in
C. sinensis and
O. viverrini genes;
P<0.01). The nucleotide composition patterns in the
P. westermani and
S. erinaceieuropaei tyrosinase codons were similar to those of the opisthorchiid genes. However, the values were found to be the lowest in the third codon positions in the
Schistosoma spp. and
S. mediterranea tyrosinase genes (
P<0.05) (
Table 1). In order to estimate the relationship of the GC content at the 3 codon positions, neutrality plots, i.e., GC
3 vs GC
12 (average GC content in the first and second codon positions), were drawn for the platyhelminth tyrosinase genes. As shown in
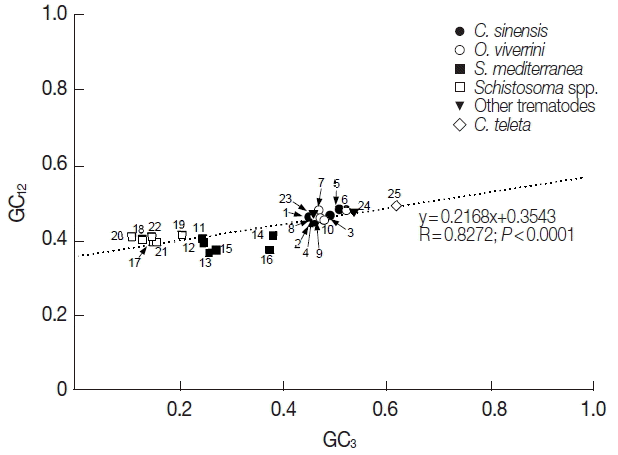
Fig. 1, the correlation between GC
12 and GC
3 was statistically significant (R=0.8272,
P<0.0001), and the slope of the regression line was 0.2168.
The patterns of synonymous codon usage were analyzed in the 5
C. sinensis tyrosinase genes (
Table 2). The usage patterns were found to be slightly different among the
Clonorchis genes. Codons with a RSCU value greater than 1.0, which meant that the particular codon was used more frequently than the other synonymous codons for the corresponding amino acid, were counted as 28, 29, 29, 30, and 28 in GAA27975, GAA32069, GAA48882, GAA48883, and GAA54899, respectively. Of these preferred codons, 9 (32.1%), 10 (34.5%), 13 (44.8%), 8 (26.7%), and 13 (46.4%) codons were ended with G or C.
The ENC values of tyrosinase genes ranged from 32.8 (AAW 26996 of
S. japonicum) to 61.0 (AJE29953 of
P. westermani) demonstrating that there were significant differences in codon bias among these genes (
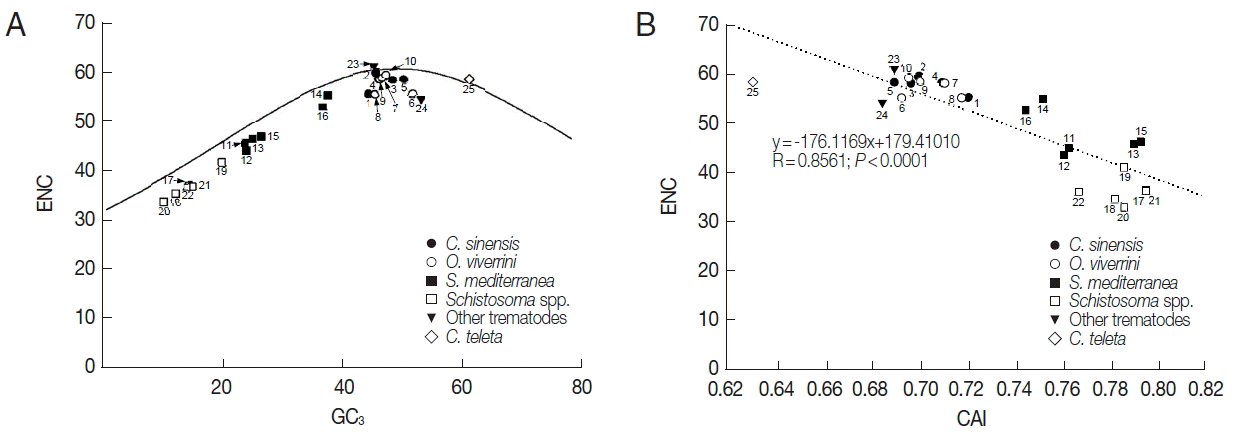
Table 1). The relationship between the codon bias and nucleotide composition was examined by NC plot analysis (GC
3 vs ENC) of the platyhelminth tyrosinase genes. As shown in
Fig. 2A, the NC plots of most tyrosinase genes fell below a reference line showing the expected position of gene, of which codon bias was constrained solely by the nucleotide composition at the third codon positions. Only a few platyhelminth genes, such as GAA32069 of
C. sinensis, AJE29953 of
P. westermani, and ELU13195 of
C. telleta, lay on the expected curve.
Unlike ENC depending upon nucleotide composition in a gene, CAI was a directional measure of codon usage bias, which was highly related to the degree of translational selection acting upon the gene and relative expression level of corresponding gene [
20,
21]. Therefore, comparison between ENC and CAI values provided insights into the relationship between nucleotide composition and selection pressure affecting CUB. The CAI values of platyhelminth genes obtained by referencing
C. elegans and
E. coli gene sets (CAI-1 and CAI-2 in
Table 1) had a relatively narrow distribution between 0.685/ 0.714 and 0.797/0.837, and were negatively correlated with their ENC (R=0.8561,
P<0.0001;
Fig. 2B).
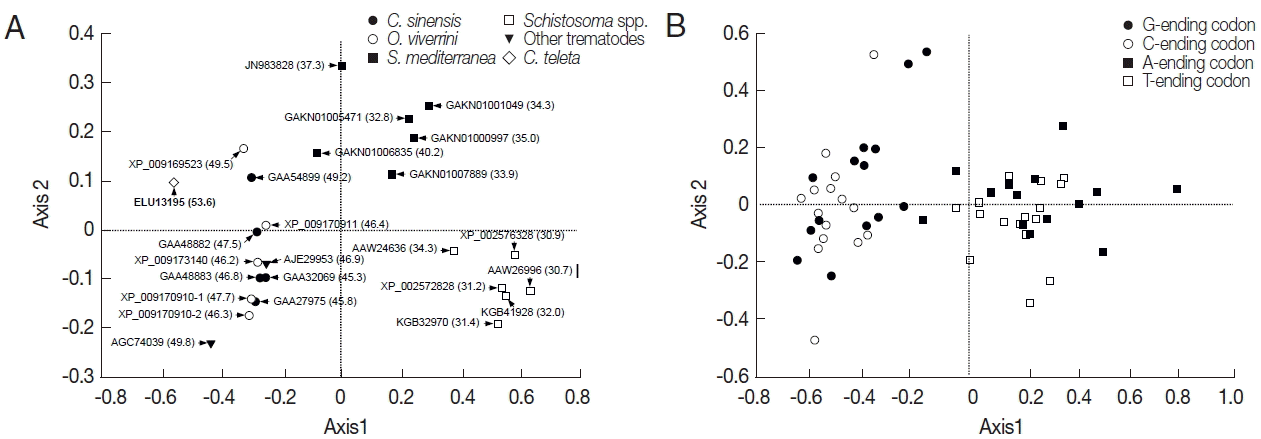
The RSCU values of platyhelminth tyrosinase genes were computed using the CodonW program, and the values were used in a correspondence analysis to investigate synonymous codon usage variation. The corresponding analysis of these genes generated a series of orthogonal axes to reflect the trends responsible for variation in codon usage, of which the first 2 principle axes accounted for 55.0% and 10.0% of the overall variation observed in RSCU of platyhelminth tyrosinase genes. As shown in
Fig. 3A, the tyrosinase orthologs were widely scattered along with the primary axis related to their donor organisms, while genes with paralogous relationship were properly resolved along the second axis. The correspondence analysis of synonymous codons also separated G-/C-ending codons from A-/T-ending codons largely along the first axis (
Fig. 3B). Correlation analyses between the position of genes along the axes and the nucleotide composition of respective genes demonstrated that the first axis has strong negative correlation with the nucleotide chemistry (correlation coefficient=−0.972), especially with the GC contents at the first (correlation coefficient=−0.887) and third (correlation coefficient=−0.995) codon positions (
Table 3). ENC values depending on nucleotide composition as described above were similarly correlated to the primary axis (correlation coefficient=−0.961). Of these compositional criteria of nucleobases, GC
2 exhibited the strongest correlation with gene positions along the second axis (correlation coefficient=−0.409).
DISCUSSION
CUB, which depicts unequal usage of synonymous codons to encode identical amino acid, is a unique property of genomes, and it may differ even between paralogous genes [
15,
16]. Of the diverse factors associated with CUB, compositional constraints under mutational bias and selection pressures, including translational selection, were considered to be the major determinants of codon usage variation among different organisms [
15,
25,
26]. Translational selection was extrapolated from the number of tRNA copies and inevitably from the expression level of respective genes [
25], while the mutational bias was largely associated with the GC content of donor genome. Genes encoded in a GC-rich genome tended to use synonymous codons ending with G and C, whereas those in an AT-rich genome preferred codons with A and T at the third position [
27]. The fraction of G- and C-ending codons (34.5±6.6) among the frequently used ones in
Clonorchis tyrosinase genes was significantly smaller than the average GC
3 content (47.8±2.4) of corresponding genes (
P<0.05), while the average GC
3 content was similar to that of all CDSs encoded in the liver fluke genome (48.0) (
Tables 1 and
2). As was in the
Clonorchis genes, the average GC
3 content of
O. viverrini tyrosinase genes (48.3±2.5) was also similar to that of whole CDSs (47.8). However, the values were greatly reduced in the
S. mediterranea (29.6±6.5) and
Schistosoma spp. (14.7± 3.3) genes compared to the respective GC contents of whole CDSs (36.0 and 36.5±0.36;
P<0.05) (
Table 1). In the correspondence analysis of RSCU, the tyrosinase gene positions moved toward the right side of the primary axis, which had strong negative correlation with the GC
3 content, compared to codons (
Fig. 3;
Table 3). These facts seemed to demonstrate that codon usage pattern, or that of frequently used synonymous codons, was biased to some extent toward A- and T-ending codons in the platyhelminth tyrosinase genes.
The mutation-selection equilibrium in shaping CUB could be estimated by neutrality analysis, which examined relationship between GC
12 and GC
3 of respective genes [
28]. If the relationship was statistically significant and the slope of the best-fitting line was close to 1.0, mutational bias was taken as the main force that affects CUB. Conversely, selection predominating against mutational bias caused no correlation between GC
12 and GC
3 and/or the smaller slope of their regression line [
29,
30]. The GC
12 and GC
3 were significantly correlated in platyhelminth tyrosinase genes, although the slope was much closer to 0.0 than 1.0 (a=0.2168, R=0.8272,
P<0.0001;
Fig. 1). Interestingly, the relationship was found to be quite different among paralogous gene sets. In the neutrality analyses performed at the intragenome level, the slope of regression line was slightly increased among
C. sinensis (a=0.3825; R=0.7693) and
O. viverrini (a=0.2284; R=0.4475) genes. However, the value came close to 0.0 among genes encoded in
Schistosoma spp. (a=0.0580; R=0.2391) and
S. mediterranea (a=0.0508; R=0.1690). Taken together, these data strongly suggested that the selection pressure, such as translational selection rather than mutational bias, was the main force governing bias in nucleotide composition of tyrosinase codons (refer [
31] and references therein), even though it was apparent that mutational bias also provided significant force causing the bias at least in the
C. sinensis and
O. viverrini genes. The predominant impact of selection pressure on CUB of tyrosinase genes was further supported by plots between ENC and GC
3, and between ENC and CAI (
Fig. 2) [
20,
31].
The expression of tyrosinase genes was specific to the vitellocytes and thus, coincided with the sexual maturation in trematodes, including
C. sinensis [
10,
32–
34]. Structural and biochemical analyses of the
Clonorchis tyrosinases did not show any evidence revealing functional diversification, while the relative expression levels were found to be quite different among them (GAA27975>GAA32069>GAA48883>GAA48882; [
10]). CUB-related criteria, such as ENC and CAI, had been known to be reflective of the expression level of corresponding gene [
20,
35,
36]. However, the ENC and CAI values of
Clonorchis genes did not have strong relation to their expression levels, which were empirically determined (
Table 1). Meanwhile,
C. sinensis tyrosinase genes, as well as
O. viverrini orthologs, were widely scattered only along the second axis in the correspondence analysis of their RSCU values (
Fig. 3A). Correlation analysis between the
Clonorchis gene positions along the axis and nucleotide compositions demonstrated that the positions were positively correlated with the GC contents of codons (correlation coefficient=0.971), especially at the third positions (correlation coefficient=0.933). Therefore, the highly expressed tyrosinase genes of
C. sinensis, such as GAA27975 and GAA32069, were likely to prefer synonymous codons with the lower GC content, which was also governed by selection pressures, including translational selection [
37]. Investigations on the relationship between tRNA gene copy numbers and CUB of tyrosinase genes will be helpful to address the issue in various platyhelminth species.
In conclusion, the codon usage patterns of tyrosinase genes identified in the genomes of diverse platyhelminths, including C. sinensis, were comparatively analyzed to gain insights on the evolutionary process and molecular clues related to the differential expressions of paralogous genes. The CUB detected in the platyhelminth tyrosinase genes was basically governed by selection pressures, rather than mutational bias, although the latter factor provided an additional force in shaping CUB of the C. sinensis and O. viverrini genes. It was also apparent that the equilibrium point between selection pressure and mutational bias was much skewed toward selection pressure in the highly expressed C. sinensis genes than that of poorly expressed paralogs. Further studies on physicochemical properties of tyrosinase proteins, tRNA gene copy numbers, and promoter activity of respective genes will be needed to confirm these results.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The auther has no conflict of interest related to this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), which was funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (no. NRF-2013R1A1A2012011).
Fig. 1Neutrality plots (GC12 against GC3) of platyhelminth tyrosinase genes. The dotted line was obtained by a regression analysis. Identity of each genes was distinguished with the GenBank accession no. of corresponding protein or cDNA (italicized) as follows: 1, GAA27975; 2, GAA32069; 3, GAA48882; 4, GAA48883; 5, GAA54899; 6, XP_009169523; 7, XP_009170910-1; 8, XP_009170910-2; 9, XP_009170911; 10, XP_009173140; 11, GAKN01000997, 12, GAKN01001049; 13, GAKN01005471; 14, GAKN01006835; 15, GAKN01007889; 16, JN983828; 17, XP_002572828; 18, XP_002576328; 19, AAW24636; 20, AAW26996; 21, KGB32970; 22, KGB41928; 23, AJE29953; 24, AGC74039; 25, ELU13195.
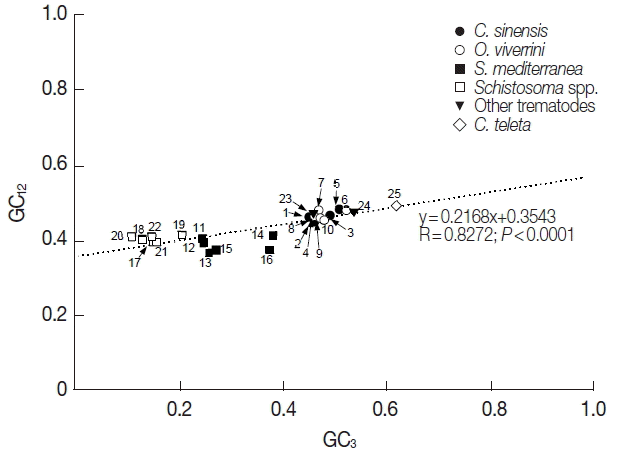
Fig. 2Scatter plots of GC
3 (A) and codon adaptation index (CAI, B) vs effective number of codons (ENC) of the platyhelminth tyrosinase genes. The continuous curve in panel A symbolizes the null hypothesis that the GC bias at the synonymous site is solely due to mutation but not selection. The hypothetical ENC values used in the curve were calculated by an equation, ENC=2+S+29/(S
2+(1−S)
2), where S represents the given GC
3 value. The dotted line in panel B was obtained by a regression analysis between ENC and CAI. For gene identities, refer to the legend for
Fig. 1.
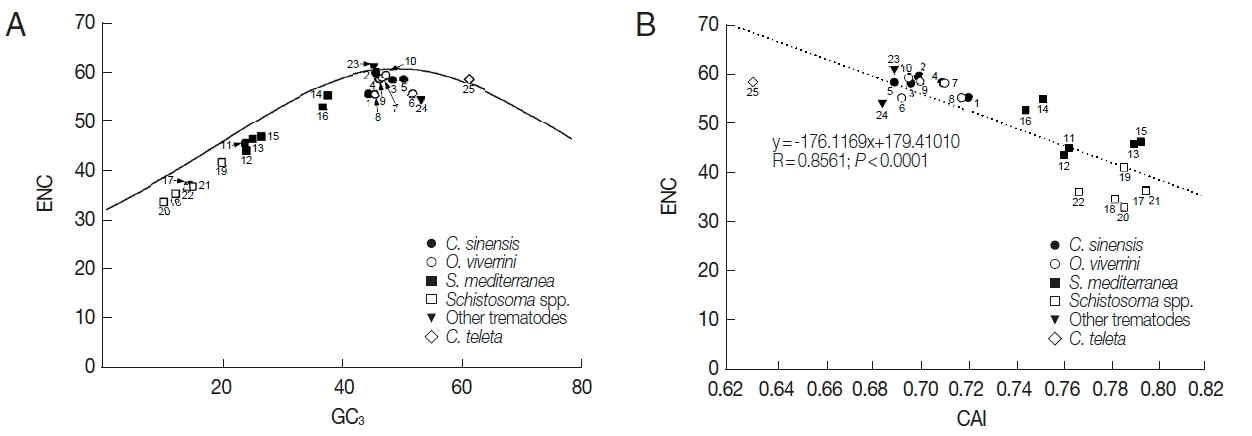
Fig. 3Correspondence analysis of relative synonymous codon usage. The distribution of genes (A) and codons (B) is shown along the first and second axes. Numerals in parenthesis in panel A indicate GC contents of all codons encoded in each of the respective genes.
Table 1G+C content of platyhelminth tyrosinase gene sequences
Table 1
|
Species |
Accession no.b
|
Length in bp (codon no.) |
GC |
GC1
|
GC2
|
GC3
|
CAI-1d
|
CAI-2d
|
ENCe
|
|
Clonorchis sinensis (44.8%, 48.0%)a
|
GAA27975 |
1431 (477) |
45.8 |
48.6 |
43.6 |
45.3 |
0.721 |
0.752 |
55.1 |
|
GAA32069 |
1449 (483) |
45.3 |
50.7 |
38.9 |
46.4 |
0.700 |
0.730 |
59.4 |
|
GAA48882 |
1434 (478) |
47.5 |
52.5 |
40.6 |
49.4 |
0.697 |
0.742 |
58.0 |
|
GAA48883 |
1419 (473) |
46.8 |
51.0 |
42.5 |
46.9 |
0.710 |
0.740 |
58.2 |
|
GAA54899c
|
978 (326) |
49.2 |
52.1 |
44.2 |
51.2 |
0.690 |
0.756 |
58.2 |
|
|
Opisthorchis viverrini (43.7%, 47.8%) |
XP_009169523c
|
1038 (346) |
49.5 |
50.9 |
45.1 |
52.6 |
0.693 |
0.755 |
55.1 |
|
XP_009170910-1 |
1419 (473) |
47.7 |
52.4 |
43.6 |
47.1 |
0.711 |
0.746 |
58.1 |
|
XP_009170910-2 |
1431 (477) |
46.3 |
49.7 |
43.0 |
46.3 |
0.718 |
0.744 |
55.0 |
|
XP_009170911 |
1434 (478) |
46.4 |
51.3 |
40.4 |
47.5 |
0.701 |
0.748 |
58.4 |
|
XP_009173140 |
1449 (483) |
46.2 |
50.7 |
39.8 |
48.2 |
0.696 |
0.736 |
59.1 |
|
|
Schmidtea mediterranea (28.7%, 36.0%) |
GAKN01000997
|
1494 (498) |
35.0 |
42.2 |
38.6 |
24.3 |
0.763 |
0.810 |
44.9 |
|
GAKN01001049
|
1380 (460) |
34.3 |
39.1 |
39.1 |
24.6 |
0.761 |
0.815 |
43.4 |
|
GAKN01005471
|
1425 (475) |
32.8 |
36.4 |
36.2 |
25.7 |
0.790 |
0.820 |
45.7 |
|
GAKN01006835
|
1437 (479) |
40.2 |
43.2 |
39.0 |
38.2 |
0.752 |
0.771 |
54.8 |
|
GAKN01007889
|
1545 (515) |
33.9 |
38.3 |
36.1 |
27.2 |
0.793 |
0.791 |
46.2 |
|
JN983828
|
1647 (549) |
37.3 |
39.5 |
34.8 |
37.5 |
0.745 |
0.761 |
52.5 |
|
|
Schistosoma mansoni (37.2%, 36.9%) |
XP_002572828 |
1437 (479) |
31.2 |
39.7 |
39.0 |
14.8 |
0.795 |
0.820 |
36.4 |
|
XP_002576328 |
1446 (482) |
30.9 |
38.4 |
41.7 |
12.7 |
0.782 |
0.825 |
34.5 |
|
|
Schistosoma japonicum (35.9%, 36.2%) |
AAW24636 |
1458 (486) |
34.3 |
41.8 |
40.7 |
20.4 |
0.786 |
0.805 |
40.9 |
|
AAW26996 |
1416 (472) |
30.7 |
39.8 |
41.7 |
10.6 |
0.786 |
0.827 |
32.8 |
|
|
Schistosoma haematobium (35.4%, 36.4%) |
KGB32970 |
1458 (486) |
31.4 |
40.1 |
38.7 |
15.4 |
0.795 |
0.826 |
36.1 |
|
KGB41928c
|
1140 (380) |
32.0 |
41.6 |
40.0 |
14.5 |
0.767 |
0.837 |
35.9 |
|
|
Paragonimus westermani
|
AJE29953 |
1425 (475) |
46.9 |
51.4 |
43.2 |
46.1 |
0.690 |
0.741 |
61.0 |
|
|
Spirometra erinaceieuropaei
|
AGC74039 |
1509 (503) |
49.8 |
53.3 |
42.1 |
54.1 |
0.685 |
0.714 |
54.1 |
|
|
Capitella teleta
|
ELU13195 |
1602 (534) |
53.6 |
53.6 |
44.9 |
62.4 |
0.631 |
0.717 |
58.3 |
Table 2Relative usage of synonymous codons in Clonorchis sinensis tyrosinase genes
Table 2
|
Amino acid |
Codon |
Relative synonymous codon usage (no.) |
|
|
GAA27975 |
GAA32069 |
GAA48882 |
GAA48883 |
GAA54899 |
|
Ala |
GCG |
0.14 (1) |
0.60 (3) |
0.60 (3) |
0.67 (4) |
0.71 (3) |
|
GCC |
1.10 (8) |
0.80 (4) |
1.40 (7) |
1.33 (8) |
1.18 (5) |
|
GCA |
1.79 (13) |
1.20 (6) |
1.80 (9) |
0.67 (4) |
0.94 (4) |
|
GCT |
0.97 (7) |
1.40 (7) |
0.20 (1) |
1.33 (8) |
1.18 (5) |
|
|
Cys |
TGC |
0.84 (8) |
0.64 (7) |
0.73 (8) |
0.74 (7) |
0.86 (3) |
|
TGT |
1.16 (11) |
1.36 (15) |
1.27 (14) |
1.26 (12) |
1.14 (4) |
|
|
Asp |
GAC |
0.83 (12) |
1.04 (14) |
1.00 (16) |
0.73 (12) |
1.03 (15) |
|
GAT |
1.17 (17) |
0.96 (13) |
1.00 (16) |
1.27 (21) |
0.97 (14) |
|
|
Glu |
GAG |
0.62 (5) |
0.95 (10) |
0.93 (13) |
0.87 (10) |
1.50 (6) |
|
GAA |
1.38 (11) |
1.05 (11) |
1.07 (15) |
1.13 (13) |
0.50 (2) |
|
|
Phe |
TTC |
1.13 (13) |
1.17 (17) |
0.94 (15) |
0.97 (14) |
0.76 (8) |
|
TTT |
0.87 (10) |
0.83 (12) |
1.06 (17) |
1.03 (15) |
1.24 (13) |
|
|
Gly |
GGG |
0.00 (0) |
0.33 (3) |
0.69 (5) |
0.35 (3) |
1.05 (5) |
|
GGC |
0.71 (6) |
0.67 (6) |
0.28 (2) |
0.94 (8) |
0.84 (4) |
|
GGA |
1.41 (12) |
1.78 (16) |
1.66 (12) |
1.12 (9) |
1.26 (6) |
|
GGT |
1.88 (16) |
1.22 (11) |
1.38 (10) |
1.65 (14) |
0.84 (4) |
|
|
His |
CAC |
1.47 (11) |
1.21 (17) |
1.10 (11) |
1.22 (11) |
0.67 (3) |
|
CAT |
0.53 (4) |
0.79 (11) |
0.90 (9) |
0.78 (7) |
1.33 (6) |
|
|
Ile |
ATC |
0.92 (8) |
0.80 (8) |
1.04 (8) |
1.14 (8) |
1.09 (4) |
|
ATA |
0.35 (3) |
0.90 (9) |
0.78 (6) |
0.29 (2) |
0.82 (3) |
|
ATT |
1.73 (15) |
1.30 (13) |
1.17 (9) |
1.57 (11) |
1.09 (4) |
|
|
Lys |
AAG |
0.72 (9) |
0.74 (10) |
0.55 (3) |
0.70 (8) |
0.20 (1) |
|
AAA |
1.28 (16) |
1.26 (17) |
1.45 (8) |
1.30 (15) |
1.80 (9) |
|
|
Leu |
TTG |
2.17 (13) |
1.59 (9) |
1.89 (12) |
2.06 (12) |
1.82 (10) |
|
CTG |
0.83 (5) |
1.94 (11) |
1.42 (9) |
0.86 (5) |
1.27 (7) |
|
CTC |
0.83 (5) |
0.53 (3) |
0.95 (6) |
0.69 (4) |
1.27 (7) |
|
TTA |
0.67 (4) |
0.35 (2) |
0.47 (3) |
0.51 (3) |
0.36 (2) |
|
CTA |
0.33 (2) |
0.71 (4) |
0.79 (5) |
0.69 (4) |
0.18 (1) |
|
CTT |
1.17 (7) |
0.88 (5) |
0.47(3) |
1.20 (7) |
1.09 (6) |
|
|
Met |
ATG |
1.00 (11) |
1.00 (11) |
1.00 (14) |
1.00 (15) |
1.00 (5) |
|
|
Asn |
AAC |
0.89 (12) |
1.14 (12) |
0.82 (9) |
0.87 (10) |
0.82 (7) |
|
AAT |
1.11 (15) |
0.86 (9) |
1.18 (13) |
1.13 (13) |
1.18 (10) |
|
|
Pro |
CCG |
0.69 (5) |
0.59 (4) |
1.03 (8) |
0.65 (5) |
0.89 (6) |
|
CCC |
0.83 (6) |
1.04 (7) |
1.03 (8) |
0.77 (6) |
0.44 (3) |
|
CCA |
0.97 (7) |
1.19 (8) |
1.55 (12) |
1.42 (11) |
1.78 (12) |
|
CCT |
1.52 (11) |
1.19 (8) |
0.39 (3) |
1.16 (9) |
0.89 (6) |
|
|
Gln |
CAG |
0.62 (4) |
0.59 (5) |
1.25 (10) |
0.89 (4) |
0.40 (4) |
|
CAA |
1.38 (9) |
1.41 (12) |
0.75 (6) |
1.11 (5) |
1.20 (6) |
|
|
Arg |
AGG |
0.39 (2) |
1.00 (5) |
0.39 (2) |
0.38 (2) |
0.40 (1) |
|
CGG |
1.35 (7) |
0.80 (4) |
1.16 (6) |
0.94 (5) |
0.80 (2) |
|
CGC |
0.58 (3) |
1.20 (6) |
0.39 (2) |
0.38 (2) |
0.40 (1) |
|
AGA |
1.16 (6) |
0.60 (3) |
0.97 (5) |
1.12 (6) |
2.00 (5) |
|
CGA |
1.55 (8) |
1.60 (8) |
1.74 (9) |
1.88 (10) |
0.40 (1) |
|
CGT |
0.97 (5) |
0.80 (4) |
1.35 (7) |
1.31 (7) |
2.00 (5) |
|
|
Ser |
AGC |
0.64 (3) |
0.90 (3) |
0.55 (2) |
1.14 (4) |
1.11 (5) |
|
TCG |
1.29 (6) |
0.30 (1) |
0.00 (0) |
1.14 (4) |
0.89 (4) |
|
TCC |
0.64 (3) |
0.30 (1) |
1.36 (5) |
0.29 (1) |
1.11 (5) |
|
AGT |
1.29 (6) |
2.10 (7) |
1.36 (5) |
0.86 (3) |
1.11 (5) |
|
TCA |
1.29 (6) |
0.90 (3) |
1.36 (5) |
0.86 (3) |
1.78 (8) |
|
TCT |
0.86 (4) |
1.50 (5) |
1.36 (5) |
1.71 (6) |
0.00 (0) |
|
|
Thr |
ACG |
0.87 (5) |
1.05 (5) |
1.00 (7) |
0.83 (5) |
1.09 (6) |
|
ACC |
1.04 (6) |
0.84 (4) |
1.14 (8) |
0.83 (5) |
1.82 (10) |
|
ACA |
0.35 (2) |
1.05 (5) |
1.00 (7) |
1.17 (7) |
0.55 (3) |
|
ACT |
1.74 (10) |
1.05 (5) |
0.86 (6) |
1.17 (7) |
0.55 (3) |
|
|
Val |
GTG |
1.60 (10) |
1.33 (8) |
1.57 (11) |
1.12 (7) |
1.71 (9) |
|
GTC |
0.16 (1) |
0.50 (3) |
0.86 (6) |
0.48 (3) |
0.95 (5) |
|
GTA |
0.32 (2) |
1.00 (6) |
0.71 (5) |
0.64 (4) |
0.38 (2) |
|
GTT |
1.92 (12) |
1.17 (7) |
0.86 (6) |
1.76 (11) |
0.95 (5) |
|
|
Trp |
TGG |
1.00 (15) |
1.00 (13) |
1.00 (11) |
1.00 (15) |
1.00 (10) |
|
|
Tyr |
TAC |
1.18 (13) |
0.77 (10) |
0.84 (8) |
1.67 (15) |
0.75 (3) |
|
TAT |
0.82 (9) |
1.23 (16) |
1.16 (11) |
0.33 (3) |
1.25 (5) |
|
|
Stop |
TAG |
0.00 (0) |
0.00 (0) |
3.00 (1) |
0.00 (0) |
NDa
|
|
TGA |
0.00 (0) |
3.00 (1) |
0.00 (0) |
3.00 (1) |
|
TAA |
3.00 (1) |
0.00 (0) |
0.00 (0) |
0.00 (0) |
Table 3Correlation between tyrosinase gene position on axis 1 and axis 2 and nucleotide compositions in different codon positions
Table 3
|
Axis |
GC |
GC1
|
GC2
|
GC12
|
GC3
|
ENCa
|
|
1 |
−0.972 |
−0.887 |
−0.482 |
−0.814 |
−0.995 |
−0.961 |
|
2 |
−0.116 |
−0.323 |
−0.409 |
−0.375 |
0.022 |
0.080 |
References
- 1. Decker H, Tuczek F. Tyrosinase/catecholoxidase activity of hemocyanins: structural basis and molecular mechanism. Trends Biochem Sci 2000;25:392-397.
- 2. Aguilera F, McDougall C, Degnan BM. Origin, evolution and classification of type-3 copper proteins: lineage-specific gene expansions and loss across the Metazoa. BMC Evol Biol 2013;13:96.
- 3. Sánchez-Ferrer A, Rodríguez-López JN, García-Cánovas F, García-Carmona F. Tyrosinase: a comprehensive review of its mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1995;1247:1-11.
- 4. Decker H, Dillinger R, Tuczek F. How does tyrosinase work? Recent insights from model chemistry and structural biology. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2000;39:1591-1595.
- 5. Smyth JD, Halton DW. The Physiology of Trematodes. 2nd ed. Cambridge, UK. Cambridge University; 1983.
- 6. Cordingley JS. Trematode eggshells: novel protein biopolymers. Parasitol Today 1987;3:341-344.
- 7. Lun ZR, Gasser RB, Lai DH, Li AX, Zhu XQ, Yu XB, Fang YY. Clonorchiasis: a key foodborne zoonosis in China. Lancet Infect Dis 2005;5:31-41.
- 8. Bouvard V, Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Freeman C, Galichet L, Cogliano V. WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group. A review of human carcinogens. Part B: Biological agents. Lancet Oncol 2009;10:321-322.
- 9. Shin HR, Oh JK, Masuyer E, Curado MP, Bouvard V, Fang YY, Wianqnon S, Sripa B, Hong ST. Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma: an update focusing on risk factors. Cancer Sci 2010;101:579-585.
- 10. Bae YA, Cai GB, Kim SH, Sohn WM, Kong Y. Expression pattern and substrate specificity of Clonorchis sinensis tyrosinases. Int J Parasitol 2013;43:891-900.
- 11. Papadakis ED, Nicklin SA, Baker AH, White SJ. Promoters and control elements: designing expression cassettes for gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther 2004;4:89-113.
- 12. Raghava GP, Han JH. Correlation and prediction of gene expression level from amino acid and dipeptide composition of its protein. BMC Bioinformatics 2005;6:59.
- 13. Castillo-Davis CI, Mekhedov SL, Hartl DL, Koonin EV, Kondrashov FA. Selection for short introns in highly expressed genes. Nat Genet 2002;31:415-418.
- 14. Hiraoka Y, Kawamata K, Haraguchi T, Chikashige Y. Codon usage bias is correlated with gene expression levels in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genes Cells 2009;14:499-509.
- 15. Duret L, Mouchiroud D. Expression pattern and, surprisingly, gene length shape codon usage in Caenorhabditis, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999;96:4482-4487.
- 16. Supek F, Vlahovicek K. Comparison of codon usage measures and their applicability in prediction of microbial gene expressivity. BMC Bioinformatics 2005;6:182.
- 17. Xu C, Cai X, Chen Q, Zhou H, Cai Y, Ben A. Factors affecting synonymous codon usage bias in chloroplast genome of oncidium gower ramsey. Evol Bioinform Online 2011;7:271-278.
- 18. Duret L. tRNA gene number and codon usage in the C. elegans genome are co-adapted for optimal translation of highly expressed genes. Trends Genet 2000;16:287-289.
- 19. Goetz RM, Fuglsang A. Correlation of codon bias measures with mRNA levels: analysis of transcriptome data from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005;327:4-7.
- 20. Wright F. The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene 1990;87:23-29.
- 21. Sharp PM, Li WH. The codon adaptation index--a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res 1987;15:1281-1295.
- 22. Sharp PM, Li WH. Codon usage in regulatory genes in Escherichia coli does not reflect selection for ‘rare’ codons. Nucleic Acids Res 1986;14:7737-7749.
- 23. Abril JF, Cebrià F, Rodríguez-Esteban G, Horn T, Fraguas S, Calvo B, Bartscherer K, Saló E. Smed454 dataset: unravelling the transcriptome of Schmidtea mediterranea. BMC Genomics 2010;11:731.
- 24. Young ND, Nagarajan N, Lin SJ, Korhonen PK, Jex AR, Hall RS, Safavi-Hemami H, Kaewkong W, Bertrand D, Gao S, Seet Q, Wongkham S, Teh BT, Wongkham C, Intapan PM, Maleewong W, Yang X, Hu M, Wang Z, Hofmann A, Sternberg PW, Tan P, Wang J, Gasser RB. The Opisthorchis viverrini genome provides insights into life in the bile duct. Nat Commun 2014;5:4378.
- 25. Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol 1981;151:389-409.
- 26. Nair RR, Nandhini MB, Sethuraman T, Doss G. Mutational pressure dictates synonymous codon usage in freshwater unicellular α-cyanobacterial descendant Paulinella chromatophora and β-cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus PCC6301. Springerplus 2013;2:492.
- 27. Hershberg R, Petrov DA. General rules for optimal codon choice. PLoS Genet 2009;5:e1000556.
- 28. Sueoka N. Directional mutation pressure and neutral molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988;85:2653-2657.
- 29. Nie X, Deng P, Feng K, Liu P, Du X, You FM, Weining S. Comparative analysis of codon usage patterns in chloroplast genomes of the Asteraceae family. Plant Mol Biol Rep 2014;32:828-840.
- 30. Yang X, Luo X, Cai X. Analysis of codon usage pattern in Taenia saginata based on a transcriptome dataset. Parasit Vectors 2014;7:527.
- 31. Subramanian A, Sarkar RR. Comparison of codon usage bias across Leishmania and Trypanosomatids to understand mRNA secondary structure, relative protein abundance and pathway functions. Genomics 2015;106:232-241.
- 32. Cai GB, Bae YA, Zhang Y, He Y, Jiang MS, He L. Expression and characterization of two tyrosinase from the trematode Schistosoma japonicum. Parasitol Res 2009;104:601-609.
- 33. Fitzpatrick JM, Hirai Y, Hirai H, Hoffmann KF. Schistosome egg production is dependent upon the activities of two developmentally regulated tyrosinases. FASEB J 2007;21:823-835.
- 34. Bae YA, Kim SH, Ahn CS, Kim JG, Kong Y. Molecular and biochemical characterization of Paragonimus westermani tyrosinase. Parasitology 2015;142:807-815.
- 35. Naya H, Romero H, Carels N, Zavala A, Musto H. Translational selection shapes codon usage in the GC-rich genome of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. FEBS Lett 2001;501:127-130.
- 36. Gupta SK, Bhattacharyya TK, Ghosh TC. Synonymous codon usage in Lactococcus lactis: mutational bias versus translational selection. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2004;21:527-535.
- 37. Yang X, Ma X, Luo X, Ling H, Zhang X, Cai X. Codon usage bias and determining forces in Taenia solium genome. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:689-697.