Abstract
Infections of Toxoplasma gondii and Babesia microti are reported in many wild animals worldwide, but information on their incidence and molecular detection in Korean wild fields is limited. In this study, the prevalence of T. gondii and B. microti infection in blood samples of 5 animal species (37 Chinese water deer, 23 raccoon dogs, 6 roe deer, 1 wild boar, and 3 Eurasian badgers) was examined during 2008–2009 in Gangwon-do (Province), the Republic of Korea (=Korea) by using serological and molecular tests. The overall seropositivity of T. gondii was 8.6% (6/70); 10.8% in Chinese water deer, 4.3% in raccoon dogs, and 16.7% in roe deer. PCR revealed only 1 case of T. gondii infection in Chinese water deer, and phylogenic analysis showed that the positive isolate was practically identical to the highly pathogenetic strain type I. In B. microti PCR, the positive rate was 5.7% (4/70), including 2 Chinese water deer and 2 Eurasian badgers. Phylogenetic analysis results of 18S rRNA and the β-tubulin gene showed that all positive isolates were US-type B. microti. To our knowledge, this is the first report of B. microti detected in Chinese water deer and Eurasian badger from Korea. These results indicate a potentially high prevalence of T. gondii and B. microti in wild animals of Gangwon-do, Korea. Furthermore, Chinese water deer might act as a reservoir for parasite infections of domestic animals.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, Babesia microti, wild animal, zoonotic pathogen, blood, Korea
Transmission of zoonotic pathogens between animals and humans is well documented, occurring through direct routes, such as contact or consumption of meat products, or indirect routes via an intermediate vector such as an arthropod [
1,
2]. Wild animals also play a role in the transmission of zoonosis as intermediators, reservoirs, amplifiers, or final hosts for pathogens. Because it is hard to recognize specific clinical symptoms or representative signs of zoonosis in wild animals, continuous surveys of the prevalence of zoonotic pathogens in wild animals are important from the perspectives of public health, to serve as a warning and to establish prevention strategies for the outbreak of critical zoonotic diseases [
3]. In this regard, among various types of zoonotic pathogens, focusing on parasitic infections in the wild animal population is particularly important, because parasites tend to have longer periods of infection establishment with more complex transmission routes compared to those of bacteria and viruses [
4].
Toxoplasma gondii, Babesia microti, Dirofilaria immitis, Dirofilaria repens, and
Cryptosporidium are well known as representative zoonotic parasites [
5]. Previous studies of zoonotic parasitoses in wild animals in the Republic of Korea (=Korea) have reported the prevalence of
T. gondii and
Trichinella in wild boars,
B. microti-like parasites in wild raccoon dogs [
6,
7]. Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease caused by the protozoan parasite
T. gondii [
8], and babesiosis, a well-known disease of domestic animals caused by
Babesia spp., has attracted increased attention as an emerging zoonotic disease [
9]. The prevalence of
T. gondii infection in wild boars in Korea was found to be relatively high compared to that reported in Japan, Austria, and Germany [
10].
B. microti infections were detected in raccoon dogs and small wild mammals in Korea [
6,
11,
12]. Although the consumption of undercooked meat may expose humans to a high risk of
T. gondii infection [
13], tick vectors are essential for the transmission of
B. microti, thereby requiring implementation of efficient vector control strategies [
14]. In particular, several wild animals, such as raccoons, foxes, and deer, are important for the maintenance of these ticks [
15].
However, surveillance of pathogen infections in wild animals has thus far been very limited in Korea. Therefore, the aim of the present survey was to investigate the prevalence of T. gondii and B. microti among wild animals in Gangwon-do (Province), via evaluation of blood samples provided by the Gangwon branch of the Korea Wildlife Rescue and Management Association in 2008–2009, as a representative mountainous region in Korea. The results of this study will prove to be valuable for evaluating the risk of exposure to these parasites from wild animals to humans and other animals in Korea.
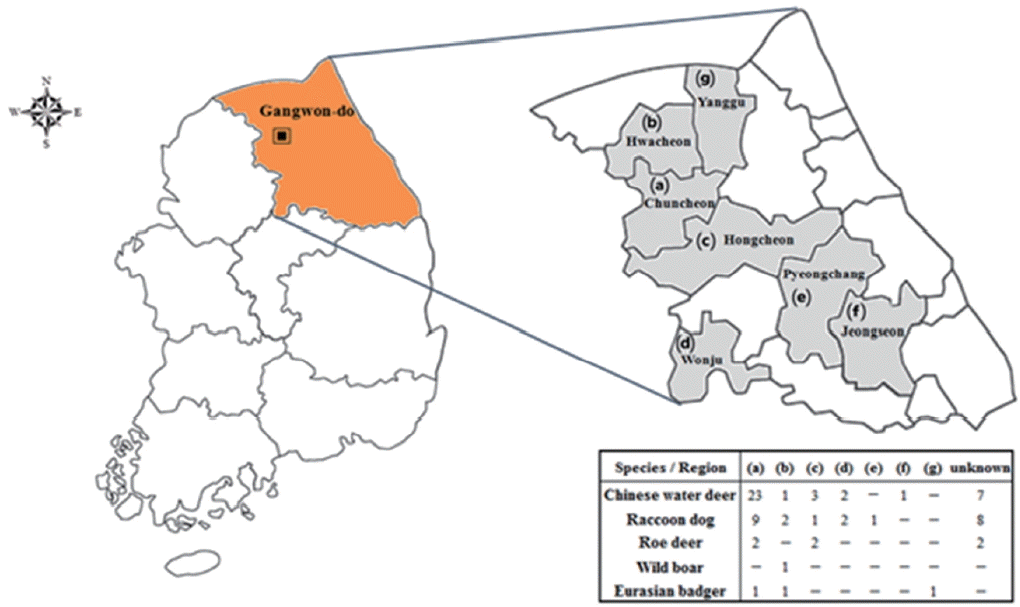
Total 70 blood samples of 5 animal species (37 Chinese water deer, 23 raccoon dogs, 6 roe deer, 1 wild boar, and 3 Eurasian badgers) were collected from the jugular vein of each animal in Gangwon-do (
Fig. 1). Sera were separated by centrifugation at 2,000 g for 5 min. Genomic DNA was also extracted from blood samples using a DNeasy tissue kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer instructions. Genomic DNA was resolved in 100 μL Tris-EDTA buffer and stored at −20°C until used.
T. gondii was detected by PCR targeting the
GRA5 and
GRA6 gene according to a previously described method [
16,
17].
B. microti was detected using nested PCR targeting the 18S rRNA and β-tubulin genes as previously described [
11]. Amplified products were size-fractionated by electrophoresis on agarose gels containing SafePinky DNA gel staining solution (GenDEPOT, Katy, Texas, USA). The PCR products were then purified using an agarose gel DNA purification kit (Qiagen). TA cloning was performed using the TOPO TA cloning kit with isolated PCR products for sequencing (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA). These samples were sequenced using an ABI PRISM 3730xl Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA). In addition, antibodies against
T. gondii were detected using a commercial toxoplasmosis multi-species ELISA kit (ID Vet, Montpellier, France). All procedures were carried out according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The samples were tested twice for the most part, and any samples showing inconsistent results were examined once more. The reference sequences of
GRA6 of
T. gondii strains and of 18S rRNA and β-tubulin for
B. microti strains were obtained from GenBank [
17,
18]. Sequence alignment was performed using CLUSTAL W (Multiple sequence alignment computer programs Histon, Cambridgeshire, UK). Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining method [
19] with maximum composite likelihood distance correction in the molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA6) program [
20]; the robustness of groupings was assessed using 1,000 bootstrap replicates [
21].
Six out of 70 serum samples examined in wild animals were positive for
T. gondii antibodies, with the highest positive rate observed in roe deer (16.7%, 1/6), despite the small sample number, followed by Chinese water deer (10.8%, 4/37), and raccoon dog (4.3%, 1/23) in ELISA (
Table 1). Only 1 sample of the positives for
T. gondii antibodies was positive for
GRA5 and
GRA6 genes in PCR which was from a Chinese water deer (2.7%, 1/37). The analysis of sequence polymorphism about
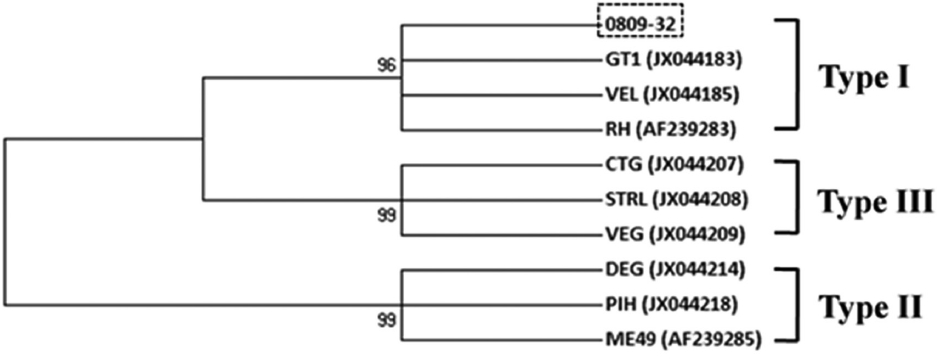
GRA6 showed the highest identities with the GT1, VEL, and RH (Type I) strains in the phylogenic analysis (
Fig. 2). This result revealed that the
T. gondii isolate detected in Chinese water deer belonged to a high-virulence type (type I).
The population structure of
T. gondii in Europe and North America consists of 3 different clonal lineages known as types I, II, and III [
22]. The type I has been detected in wild boars and foxes, which is a significant finding, because this genotype is not frequently reported in animals in Europe [
23,
24]. This finding is similar to previous reports showing that the
T. gondii antigen detected from small mammals captured in Gyeonggi-do and Gangwon-do of Korea belonged to the clonal type I group [
12]. Moreover, the possible overlap between the wild and domestic cycles of
T. gondii could have implications for the possible infection of farm animals and humans. Although specific transmission routes could not be identified in the present survey, stray cats may be presumed to be one of the main sources of
T. gondii transmission. Most of the recent investigations of
T. gondii have focused on humans or domestic animals [
25–
27]. The increasing urbanization of Korea has resulted in more interactions between humans and wild animals, including raccoons, wild boars, and Chinese water deer, which can survive well in close contact with humans. Furthermore, a recent review summarized the worldwide prevalence of
T. gondii infection in wild pigs and deer [
28], and human infections have been shown to be related to the consumption of the meat of wild animals [
13,
29]. Recently, consumption of raw pork was also identified as a critical dietary risk factor contributing to the seropositivity of
T. gondii infection [
27]. In addition, the seropositivity of
T. gondii infection among veterinarians in a public professional activities group was significantly related to contact with animals infected with zoonotic pathogens [
27]. Hence, the generally high prevalence of
T. gondii in wild animals suggests that transmission from wild animals via consumption of raw or undercooked meat or direct contact with wild animals may be the main route of human infections.
B. microti can infect a variety of animal species, but the reservoir competence of numerous wildlife hosts in Korea is not well known.
B. microti or
B. microti-like infection has been observed in other widespread mammalian species of the eastern Unites States, such as short-tailed shrews [
30], eastern cottontail rabbits, eastern chipmunks [
31], raccoons [
32], and foxes [
33]. In Korea,
B. microti infection has been reported in wild raccoon dogs [
7] and small wild mammals [
12]. However, the present results represented the first detection of
B. microti infection in Chinese water deer (5.4%, 2/37) and Eurasian badgers (66.7%, 2/3). Thus,
B. microti has been recognized as a genetically various species complex that consists of several clusters. Analysis of
B. microti genes showed sequence variations from geographically distant areas, such as Kobe (Japan), Hobetsu (Japan), G1 (USA), Gray (USA), and HK (Germany) [
11].
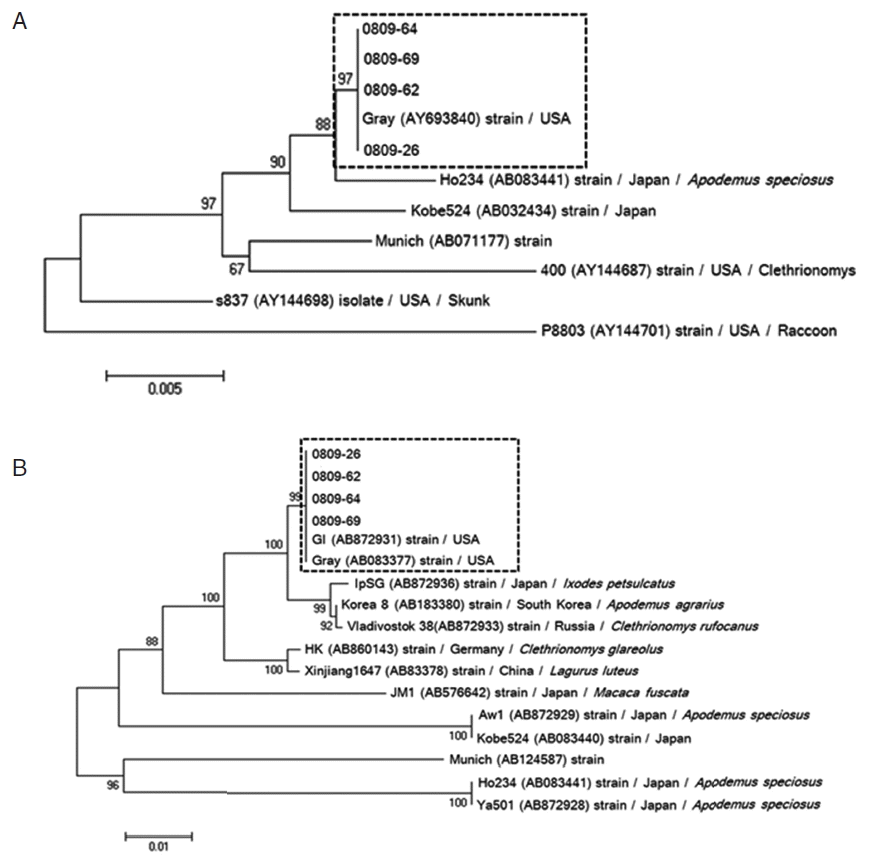
Phylogenetic reconstruction based on 18S rRNA and β-tubulin sequence data of 4
B. microti-positive samples showed that all positive samples of 18S rRNA (0809-26, 0809-62, 0809-64, and 0809-69) were most similar to the US-type
B. microti (
Fig. 3A). In addition, the β-tubulin sequence in our positive samples was strongly related to those previously reported in Korea and Russia (
Fig. 3B). Similar to the results for 18S rRNA, β-tubulin sequence analysis showed that
B. microti detected in small mammals in Korea most closely aligned with the US-type strain. Furthermore, US-type
B. microti is commonly distributed among small wild mammals in China and Russia [
11]. Therefore, our report shows that the US-type of
B. microti in Korea may distribute in wild animals, and that both small and large zoonotic mammals can be reservoirs of
B. microti, facilitating maintenance of the pathogen in nature. Moreover, ixodid ticks can transmit the pathogen to zoonotic and domestic hosts, and incidentally to humans [
30]; thus, further studies are needed to identify the specific tick species involved in its transmission.
One of the main limitations of the present study is that these data may not be representative of the overall prevalence of T. gondii and B. microti infections in wild animals of Korea because of insufficient sample numbers and the limited study area. However, in spite of these limitations, this is the first record of T. gondii and B. microti infections in wild animals, including Chinese water deer, raccoon dog, roe deer, and Eurasian badger, inhabiting a mountainous region of Gangwon-do, as detected by serological and molecular screening. Genotyping of the T. gondii isolate revealed a type I genotype, whereas B. microti more closely aligned with the US-type. To our knowledge, this is the first report of B. microti detected in Chinese water deer and Eurasian badgers from Korea. These results suggested that these species might serve as an important reservoir for the transmission of T. gondii and B. microti, highlighting the need for closer monitoring of zoonotic infections in wild animals of Korea.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was performed in collaboration with the Korea CDC and Mongolia NCCD and funded by a grant (no. 4847-302-210-13, 2013) from the Korea National Institute of Health, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Fig. 1Location surveyed for Toxoplasma gondii and Babesia microti infections in Gangwon-do (Province), Korea.
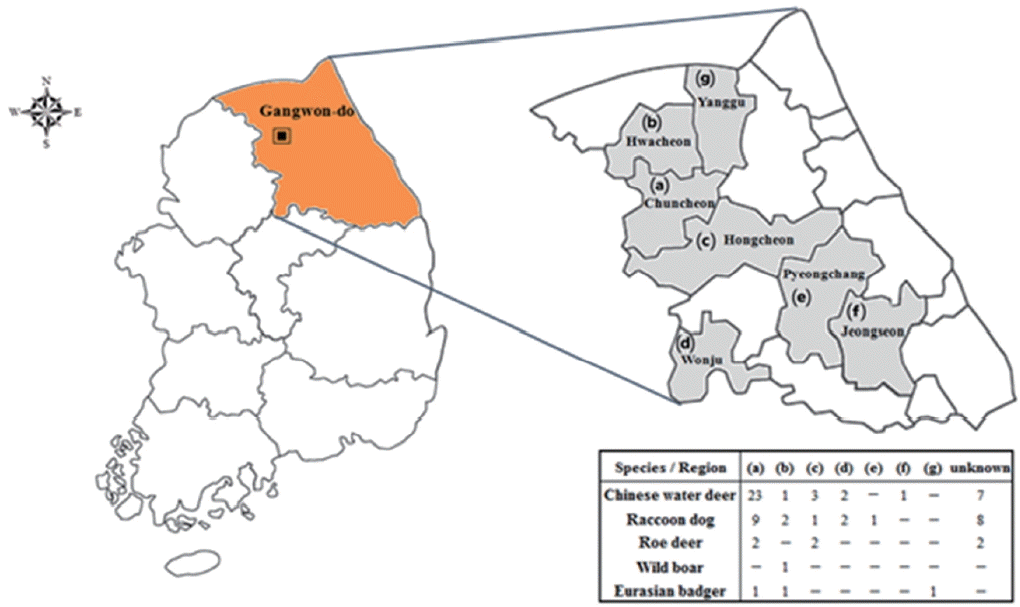
Fig. 2Phylogenetic relationships among Toxoplasma gondii species and genotypes according to neighbor-joining analysis with maximum composite likelihood distance correction, implemented with MEGA (version 6), using a fragment from the partial GRA6 gene. Sequences of other T. gondii isolates and genotypes were obtained from GenBank (accession numbers are indicated in parentheses). The genotype of 0809-32 in this study was type I.

Fig. 3Phylogenic relationships among Babesia species and genotypes according to neighbor-joining analysis with maximum composite likelihood distance correction, implemented with MEGA (version 6), using a fragment of the partial 18S rRNA (A) and β-tubulin (B) sequences of Babesia microti. Sequences of other Babesia species and genotypes were obtained from GenBank (accession numbers are indicated in parentheses). All positive isolates of B. microti are identified as the Gray (US-type).
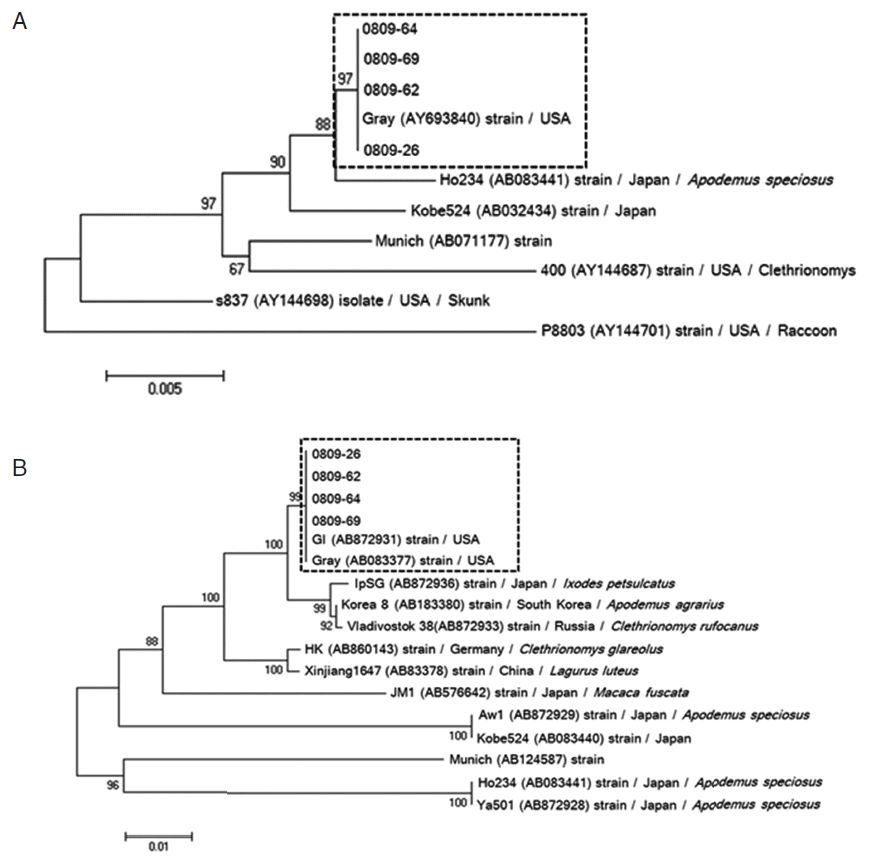
Table 1Positive number of serologic and molecular detection for T. gondii and B. microti in wild animals
Table 1
|
Wild animal species |
No. |
T. gondii
|
B. microti
|
|
|
|
ELISA (%) |
PCR (%) |
PCR (%) |
|
Chinese water deer |
37 |
4 (10.8) |
1 (2.7) |
2 (5.4) |
|
|
Raccoon dog |
23 |
1 (4.3) |
- |
- |
|
|
Roe deer |
6 |
1 (16.7) |
- |
- |
|
|
Wild boar |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Eurasian badger |
3 |
- |
- |
2 (66.7) |
|
|
Total |
70 |
6 (8.6) |
1 (1.4) |
4 (5.7) |
References
- 1. Chomel BB, Belotto A, Meslin FX. Wildlife, exotic pets, and emerging zoonoses. Emerg Infect Dis 2007;13:6-11.
- 2. Mackenstedt U, Jenkins D, Romig T. The role of wildlife in the transmission of parasitic zoonoses in peri-urban and urban areas. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl 2015;4:71-79.
- 3. Cutler SJ, Fooks AR, van der Poel WH. Public health threat of new, reemerging, and neglected zoonoses in the industrialized world. Emerg Infect Dis 2010;16:1-7.
- 4. Fèvre EM, Bronsvoort BM, Hamilton KA, Cleaveland S. Animal movements and the spread of infectious diseases. Trends Microbiol 2006;14:125-131.
- 5. Youn HJ. Review of Zoonotic Parasites in Medical and Veterinary Fields in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2009;47:133-141.
- 6. Kang SW, Doan HT, Noh JH, Choe SE, Yoo MS, Kim YH, Reddy KE, Nguyen TT, Van , Quyen D, Nguyen LT, Kweon CH, Jung SC. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondi and Trichinella spiralis infections in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Korea. Parasitol Int 2013;62:583-585.
- 7. Han JI, Lee SJ, Jang HJ, Na KJ. Asymptomatic Babesia microti-like parasite infection in wild raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in South Korea. J Wildl Dis 2010;46:632-635.
- 8. Dubey JP, Jones JL. Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans and animals in the United States. Int J Parasitol 2008;38:1257-1278.
- 9. Kjemtrup AM, Conrad PA. Human babesiosis: an emerging tick-borne disease. Int J Parasitol 2000;30:1323-1337.
- 10. Jeong W, Yoon H, Kim YK, Moon OK, Kim DS, An DJ. Prevalence of Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in South Korean Wild Boar (Sus scrofa coreanus). J Wildl Dis 2014;50:902-905.
- 11. Zamoto A, Tsuji M, Wei Q, Cho SH, Shin EH, Kim TS, Leonova GN, Hagiwara K, Asakawa M, Kariwa H, Takashima I, Ishihara C. Epizootiologic survey for Babesia microti among small wild mammals in Northeastern Eurasia and a geographic diversity in the β-tubulin gene sequences. J Vet Med Sci 2004;66:785-792.
- 12. Hong SH, Lee SE, Jeong YI, Kim HC, Chong ST, Klein TA, Song JW, Gu SH, Cho SH, Lee WJ. Prevalence and molecular characterizations of Toxoplasma gondii and Babesia microti from small mammals captured in Gyeonggi and Gangwon Provinces, Republic of Korea. Vet Parasitol 2014;205:512-517.
- 13. Choi WY, Nam HW, Kwak NH, Huh W, Kim YR, Kang MW, Cho SY, Dubey JP. Foodborne outbreaks of human toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis 1997;175:1280-1282.
- 14. Morzaria S, Katende J, Kairo A, Nene V, Musoke A. New methods for the diagnosis of Babesia bigemina infection. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 1992;87( Suppl):201-205.
- 15. Kawabuchi T, Tsuji M, Sado A, Matoba Y, Asakawa M, Ishihara C. Babesia microti-like parasites detected in feral raccoons (Procyon lotor) captured in Hokkaido, Japan. J Vet Med Sci 2005;67:825-827.
- 16. Chen J, Li ZY, Zhou DH, Liu GH, Zhu XQ. Genetic diversity among Toxoplasma gondii strains from different hosts and geographical regions revealed by sequence analysis of GRA5 gene. Parasit Vectors 2012;5:279.
- 17. Su C, Zhang X, Dubey JP. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii by multilocus PCR-RFLP markers: a high resolution and simple method for identification of parasites. Int J Parasitol 2006;36:841-848.
- 18. Tsuji M, Zamoto A, Kawabuchi T, Kataoka T, Nakajima R, Asakawa M, Ishihara C. Babesia microti-like parasites detected in Eurasian red squirrels (Sciurus vulgaris orientis) in Hokkaido, Japan. J Vet Med Sci 2006;68:643-646.
- 19. Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 1987;4:406-425.
- 20. Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K. MEGA: A biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 2008;9:299-306.
- 21. Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985;39:783-791.
- 22. Sibley LD, Boothroyd JC. Virulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii comprise a single clonal lineage. Nature 1992;359:82-85.
- 23. Berger-Schoch AE, Herrmann DC, Schares G, Müller N, Bernet D, Gottstein B, Frey CF. Prevalence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii in feline faeces (oocysts) and meat from sheep, cattle and pigs in Switzerland. Vet Parasitol 2011;177:290-297.
- 24. De Craeye S, Speybroeck N, Ajzenberg D, Dardé ML, Collinet F, Tavernier P, Van Gucht S, Dorny P, Dierick K. Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in wildlife: common parasites in Belgian foxes and Cervidae? Vet Parasitol 2011;178:64-69.
- 25. Hong SH, Jeong YI, Kim JY, Cho SH, Lee WJ, Lee SE. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in household cats in Korea and risk factors. Korean J Parasitol 2013;51:357-361.
- 26. Jung BY, Gebeyehu EB, Lee SH, Seo MG, Byun JW, Oem JK, Kim HY, Kwak D. Detection and determination of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence in native Korean goats (Capra hircus coreanae). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2014;14:374-377.
- 27. Lee SE, Hong SH, Jeong YI, Lee JH, Yoo SJ, Lim HS, Lee WJ, Cho SH. Cross-sectional analysis of the seropositivity and risk factors of Toxoplasma gondii infection among veterinarians, in relation to their public professional activities. Vet Parasitol 2014;203:29-34.
- 28. Dubey JP. Review of “Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans (Second Edition)” by J.P. Dubey. Parasit Vectors 2010;3:112.
- 29. Ross RD, Stec LA, Werner JC, Blumenkranz MS, Glazer L, Williams GA. Presumed acquired ocular toxoplasmosis in deer hunters. Retina 2001;21:226-229.
- 30. Telford SR 3rd, Mather TN, Adler GH, Spielman A. Short-tailed shrews as reservoirs of the agents of lyme disease and human babesiosis. J Parasitol 1990;76:681-683.
- 31. Spielman A, Etkind P, Piesman J, Ruebush TK 2nd, Juranek DD, Jacobs MS. Reservoir hosts of human babesiosis on Nantucket Island. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1981;30:560-565.
- 32. Birkenheuer AJ, Marr HS, Hladio N, Acton AE. Molecular evidence of prevalent dual piroplasma infections in North American raccoons (Procyon lotor). Parasitology 2008;135:33-37.
- 33. Birkenheuer AJ, Horney B, Bailey M, Scott M, Sherbert B, Catto V, Marr HS, Camacho AT, Ballman AE. Babesia microti-like infections are prevalent in North American foxes. Vet Parasitol 2010;172:179-182.