Abstract
Pathogenic Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba castellanii, and Acanthamoeba polyphaga, are distributed worldwide. They are causative agents of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis or acanthamoebic keratitis in humans, respectively. Trophozoites encyst in unfavorable environments, such as exhausted food supply and desiccation. Until recently, the method of N. fowleri encystation used solid non-nutrient agar medium supplemented with heat-inactivated Escherichia coli; however, for the amoebic encystment of Acanthamoeba spp., a defined, slightly modified liquid media is used. In this study, in order to generate pure N. fowleri cysts, a liquid encystment medium (buffer 1) modified from Page’s amoeba saline was applied for encystation of N. fowleri. N. fowleri cysts were well induced after 24 hr with the above defined liquid encystment medium (buffer 1). This was confirmed by observation of a high expression of differential mRNA of nfa1 and actin genes in trophozoites. Thus, this liquid medium can replace the earlier non-nutrient agar medium for obtaining pure N. fowleri cysts. In addition, for cyst formation of Acanthamoeba spp., buffer 2 (adjusted to pH 9.0) was the more efficient medium. To summarize, these liquid encystment media may be useful for further studies which require axenic and pure amoebic cysts.
-
Key words: Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba castellanii, Acanthamoeba polyphaga, encystation, encystment medium
INTRODUCTION
Pathogenic free-living amoebae,
Naegleria fowleri,
Acanthamoeba castellanii, and
Acanthamoeba polyphaga, are distributed worldwide, and are the known causative agents of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) or acanthamoebic keratitis (AK) in humans, respectively [
1]. PAM cases are associated with recreational activities in freshwater, whereas AK cases have become a concern in people wearing contact lenses. The ubiquitous distribution in nature of these free-living amoebae shows 2 distinct forms in their life-cycle: trophozoites and cysts (sometimes flagellate in
Naegleria). In unfavorable environments, such as exhausted food supply, desiccation, and low temperature, amoebic trophozoites are known to undergo encystation. The cysts are characterized by a round shape and the presence of 2 cyst walls (endo- and ectocyst), especially distinct in the wrinkled ectocyst in
Acanthamoeba spp. [
2]. The encystation is an important event for the survival, resistance, and ability of disease induction of these free-living amoebae [
3–
6].
Until recently, a useful method of
N. fowleri encystation was the use of solid non-nutrient agar medium supplied with heat-inactivated
Escherichia coli. The solid medium has a limitation for cultivation and harvesting axenic and massive amoebic cysts. Current studies in
Naegleria infection indicate that the encystation of
N. fowleri trophozoites is required to study the pathophysiology, pathogenic mechanisms, immunology, and genomics. On the other hand, since a defined liquid media for the encystment of
Acanthamoeba spp. has been established [
6], many researchers have lately applied acanthamoebic encystation with a little modification [
7–
10].
To obtain a large amount of pure
N. fowleri cysts (or precysts), a liquid encystment medium modified from Page’s amoeba saline [
1] was applied on encystation of
N. fowleri trophozoites. In addition, the efficient usage of 2 liquid encystment media generally used for the cyst formation of
Acanthamoeba spp. [
6,
11] was compared.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Free-living amoebae cultivation
Trophozoites of
N. fowleri (Cater NF69 strain, ATCC No. 30215, Manassas, Virginia, USA) were axenically cultured at 37°C in Nelson’s medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum [
12], and
A. castellanii and
A. polyphaga were axenically cultured at 30°C in PYG medium [
13].
Cysts or precysts (did not fully showed the 2-distinct cyst walls) of
N. fowleri,
A. castellanii, and
A. polyphaga were induced by cultivating on 3 kinds of encystment media (buffer 1: 120 mM NaCl, 0.03 mM MgCl
2, 1 mM NaHPO
4, 1 mM KH
2 PO
4, 0.03 mM CaCl
2, 0.02 mM FeCl
2, H 6.8; buffer 2 [
11]: 95 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 8 mM MgSO
4, 0.4 mM CaCl
2, 1 mM NaHCO
3, 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 9.0; buffer 3 [
6]: 100 mM KCl, 8 mM MgSO
4, 0.4 mM CaCl
2, 20 mM 2-amino-2-methyl-1,3-propanediol, pH 7.6) (
Table 1). Amoebic trophozoties (approximately 2×10
6 cells) were washed with PBS (pH 7.4) twice, and incubated in 24-well plates with 5 ml of each medium, at 30°C or 37°C. Using an optical microscope (Olympus, Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan), the morphological changes were observed after encystation, and final cysts were re-cultured with fresh Nelson or PYG media, in order to observe the recovered trophozoites.
Total RNA from trophozoites and cysts (or precysts) of
N. fowleri,
A. castellanii, and
A. polyphaga were prepared using an isolation kit Rnasymini kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany); cDNAs were synthesized from 10 μg of total RNA using cDNA Synthesis kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA). RT-PCR was performed using specific primer for
nfa1 and
nf-actin genes for
Naegleria, and
actin and
atg8 genes for
Acanthamoeba [
5,
14,
15]. The reference genes were the
p3 gene (
N. fowleri-specific chromosomal DNA sequence; forward 5′GCTATCGAATGGATTCAAGC and reverse 5′CACTACTCGTGGAAGGCTTA) and
18S rRNA gene [
5]. PCR condition was 95°C for 5 min, 30 cycles at 95°C for 1 min, 50–55°C for 1 min, 72°C for 1 min, and final extension for 10 min at 72°C.
RESULTS
Morphological observation of encysted amoebae
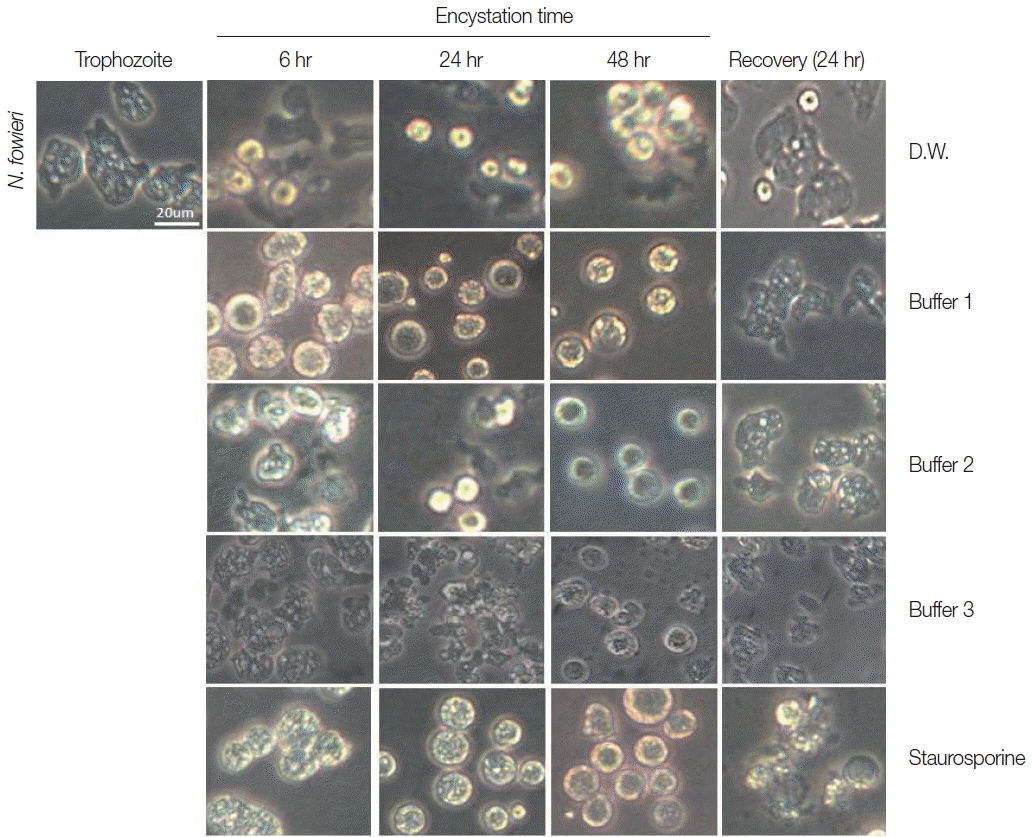
Trophozoites of
N. fowleri cultured with buffer 1 showed the rounding morphological change at 6 hr, and precysts and cysts were observed at 24 hr. After 48 hr cultivation, a large proportion of
N. fowleri trophozoites were encysted (
Fig. 1). On culturing the
N. fowleri trophozoites in buffer 2, the morphological changes (such as rounding), precysts and cysts were induced later than seen in buffer 1 (
Fig. 1). On all occasions, the induced precysts and cysts at 48 hr were recovered into active trophozoites in fresh Nelson’s medium (
Fig. 1). As a control group,
N. fowleri trophozoites cultured in distilled water (DW) did not encyst fully. In addition, when they were incubated with staurosporine, a reagent known to induce cell-death,
N. fowleri trophozoites transformed to their round forms, but live trophozoites could not be recovered in Nelson’s medium (
Fig. 1).
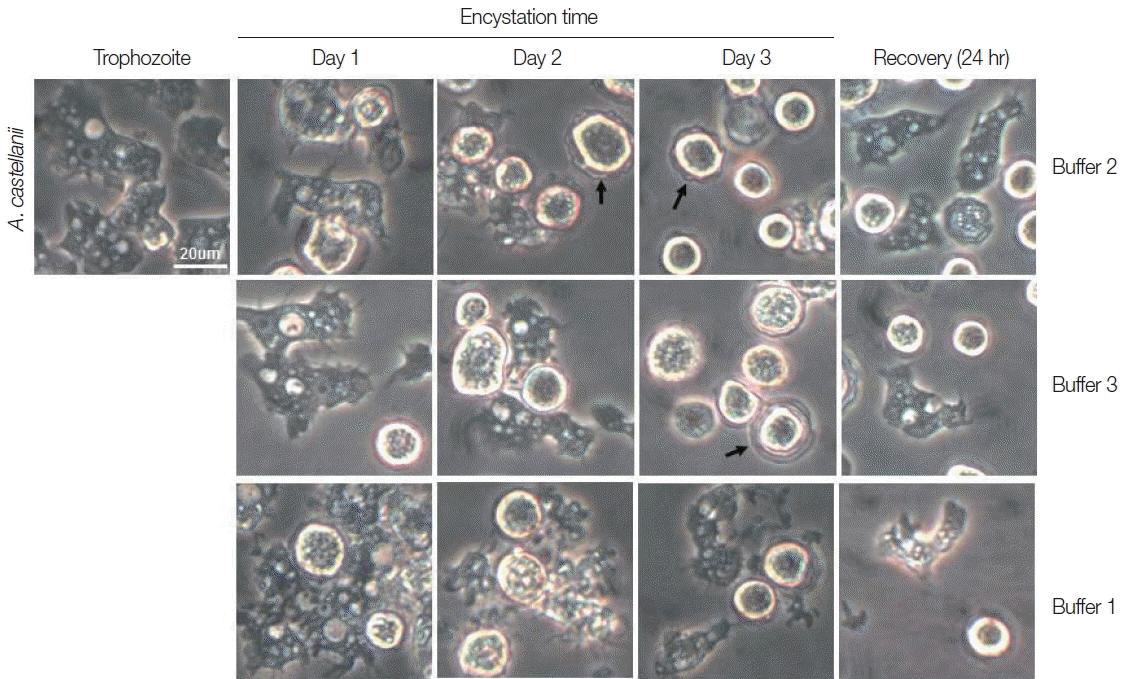
Trophozoites
A. castellanii cultured with buffer 2 and 3 showed rounding at day 1, and precysts and cysts were well observed at day 2. After cultivation for 3 days, a large proportion of
A. castellanii trophozoites were encysted (
Fig. 2). Culturing
A. castellanii trophozoites in buffer 2, the induction of precysts and cysts was better than those of buffer 3 (
Fig. 2). On all occasions, induced precysts and cysts for 3 days recovered into active trophozoites in fresh PYG medium (
Fig. 2). Furthermore,
A. castellanii trophozoites cultured with buffer 1 (shown the well encystation in the case of
N. fowleri) did not encyst fully (
Fig. 2). When encystation was continued for 7 days, similar results were observed, although the number of cysts decreased in accordance with incubation periods (data not shown). In addition, in the case of
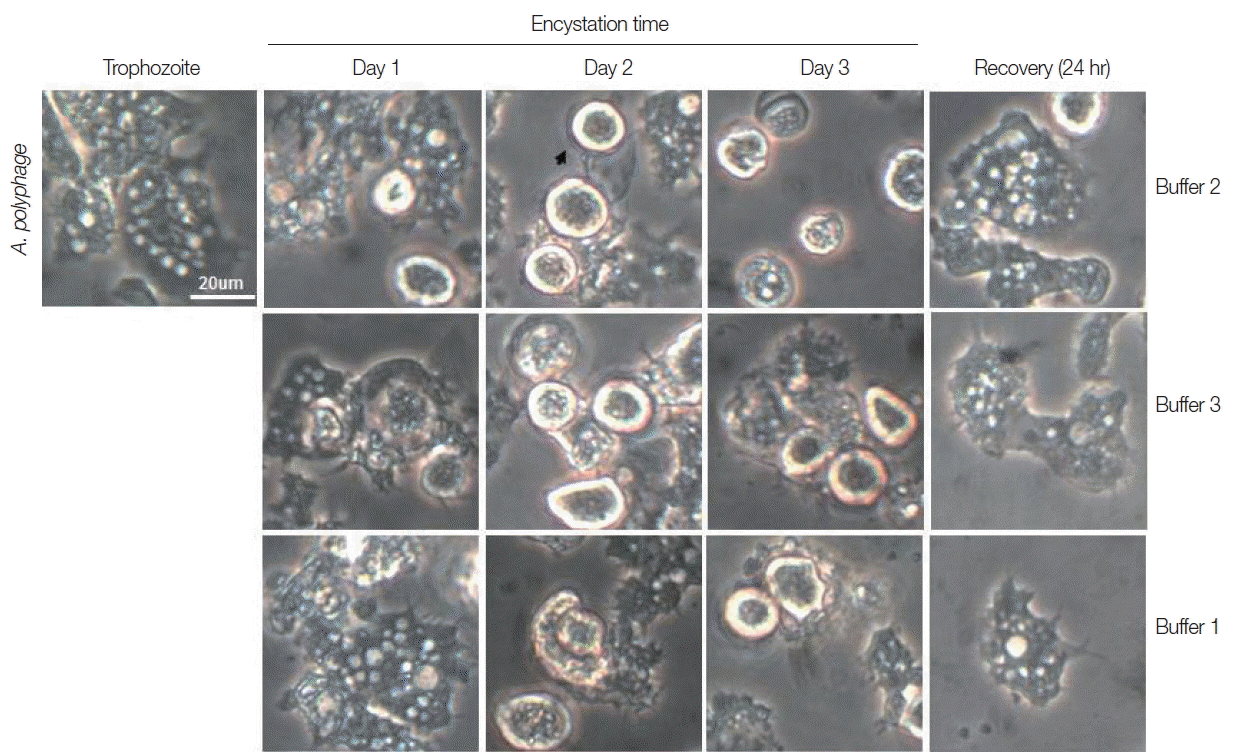
A. polyphaga, the encystation results were similar to those of
A. castellanii (
Fig. 3).
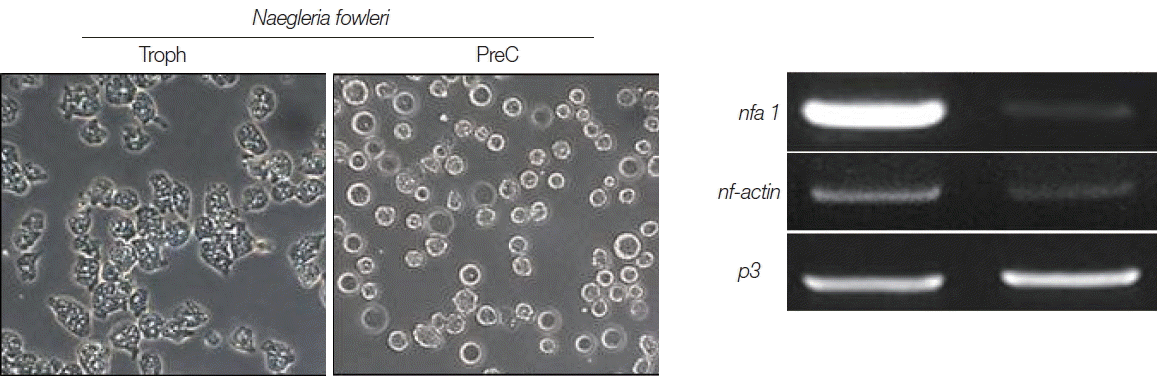
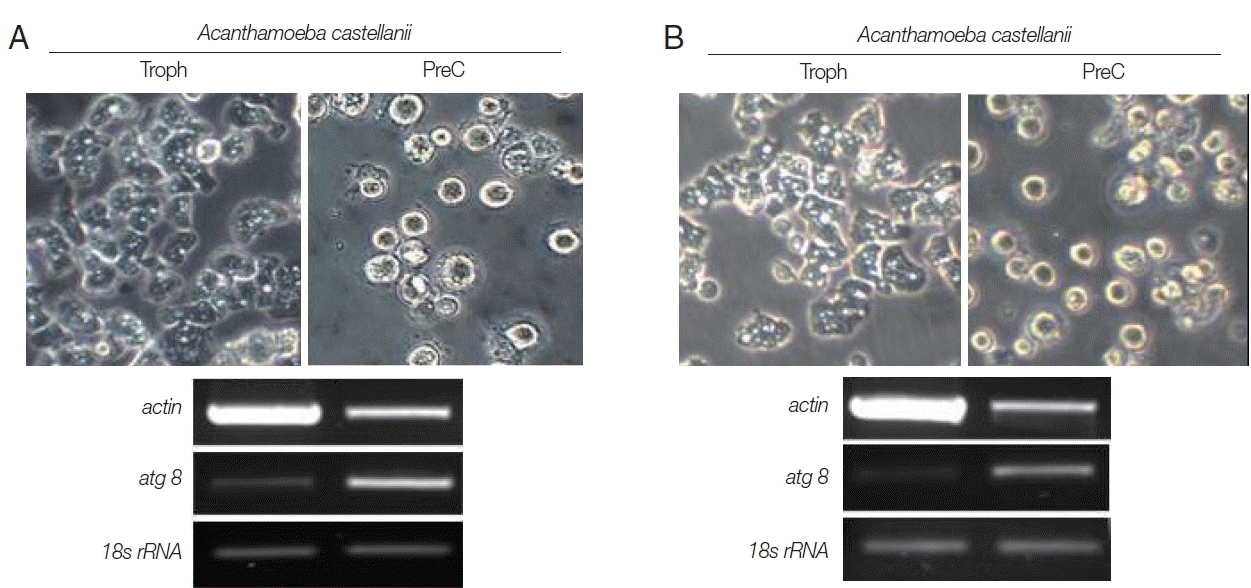
In the results of differential mRNA expression between trophozoites and cysts (precyst) of
N. fowleri, the
nfa1 gene was highly expressed in the trophozoites (
Fig. 4). In addition, the
nf-actin gene on trophozoites was also more expressed than in cysts (
Fig. 4). In the differential mRNA expression of acanthamoebic actin gene, over-expression was observed in trophozoites of
A. castellanii and
A. polyphaga (
Fig. 5). In contrast, the
atg8 gene which is associated with cyst formation in
Acanthamoeba spp. [
11] was expressed more in cysts (
Fig. 5).
DISCUSSION
N. fowleri, known as “brain-eating amoeba”, causes acute PAM in children and young adults with a history of diving in freshwater and recreational activities in amoebae-contaminated water in the hot summer [
2,
16]. In these latter days, death due to PAM is rearing its ugly head as a Neglected Tropical Disease (NTD) in countries of Asia, such as India, Pakistan, Taiwan, Thailand, and Vietnam [
17]. In addition, the AK human case from contact lens wearers has been increasing worldwide [
18].
In recent many studies on free-living amoebae, such as
N. fowleri and
A. castellanii, the encystation of amoebic trophozoite is required to study the pathophysiology, pathogenic mechanisms, immunology, and genomics. For the amoebic encystment of
Acanthamoeba spp., in previous studies, a defined and slightly modified liquid media has been used [
6,
9,
10]. In
N. fowleri encystation, however, the solid non-nutrient agar medium supplemented with heat-inactivated
E. coli has been used, in spite of the possible contamination of
E. coli proteins and smaller numbers of harvested cysts [
4,
19,
20].
In this study, to obtain a large amount of pure
N. fowleri cysts (or precysts), a liquid encystment medium modified from Page’s amoeba saline (named as the encystmemt buffer 1) was applied on
N. fowleri encystation. As the results of
N. fowleri encystation with buffer 1, amoebic cysts were well induced at 48 hr post incubation. And then, the induced cysts at 48 hr were well recovered into active trophozoites in fresh Nelson’s medium. In addition, the above morphological encystation was confirmed by observing the differential mRNA expression of the pseudopodia-specific
nfa1 gene [
14] and the
nf-actin gene [
15] between trophozoites and cysts of
N. fowleri. On the present results, the
nfa1 and
nf-actin gene on trophozoites was also more expressed than in cysts. These results proved the encystation of
N. fowleri trophozoites. Thus, the present method used a liquid encystment medium may replace the previous method of
N. fowleri encystation used a solid non-nutrient agar medium with heat-inactivated
E. coli.
On the morphological findings of
Acanthamoeba encystation, buffer 2 (modified to pH 9.0) was also a more effective agent in this study, which was mainly used for many studies [
6,
8,
9,
11]. In addition, the present results were confirmed by the differential mRNA expression between trophzoites and cysts. The over-expression of actin gene was observed in trophozoites of
A. castellanii and
A. polyphaga. In contrast, the
atg8 gene was expressed more in cysts, as which is associated with cyst formation in
Acanthamoeba spp. [
11]. The above results indicate that buffer 2 is better for the encystation of
A. castellanii and
A. polyphaga trophozoites.
Finally, 2 liquid encystment media, buffer 1 for Naegleria and buffer 2 for Acanthamoeba may be useful for further studies which require axenic and pure amoebic cysts.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We have no conflict of interest related to this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by a Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, the Republic of Korea (no. 2015R1D1A1A01056862).
Fig. 1Morphological changes of N. fowleri trophozoites into precysts (or cysts) cultured with encystation media for 6, 24, and 48 hr. Buffer 1 is an effective medium. Staurosporine induced rounding, but trophozoites were not recovered in Nelson’s medium.
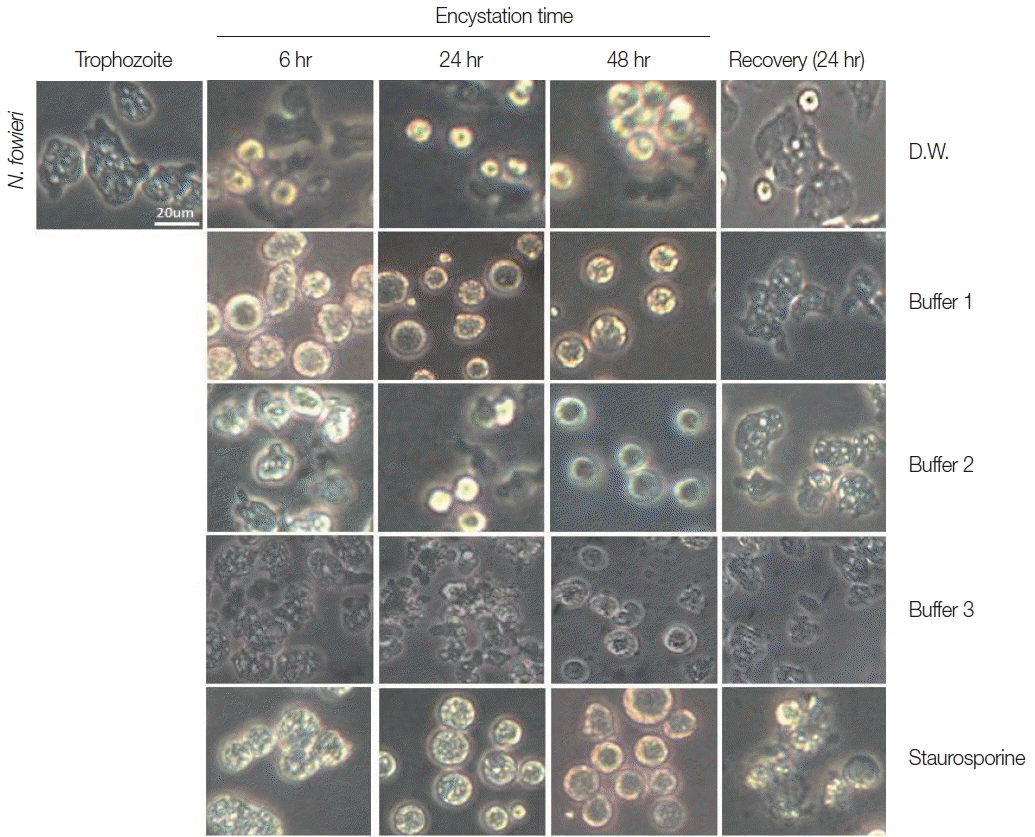
Fig. 2Morphological changes of A. castellanii trophozoites into precysts (or cysts) cultured in encystation media for 1, 2, and 3 days. The effective medium is buffer 2. Cysts recovered to trophozoites in PYG medium. Arrows indicate mature cysts.
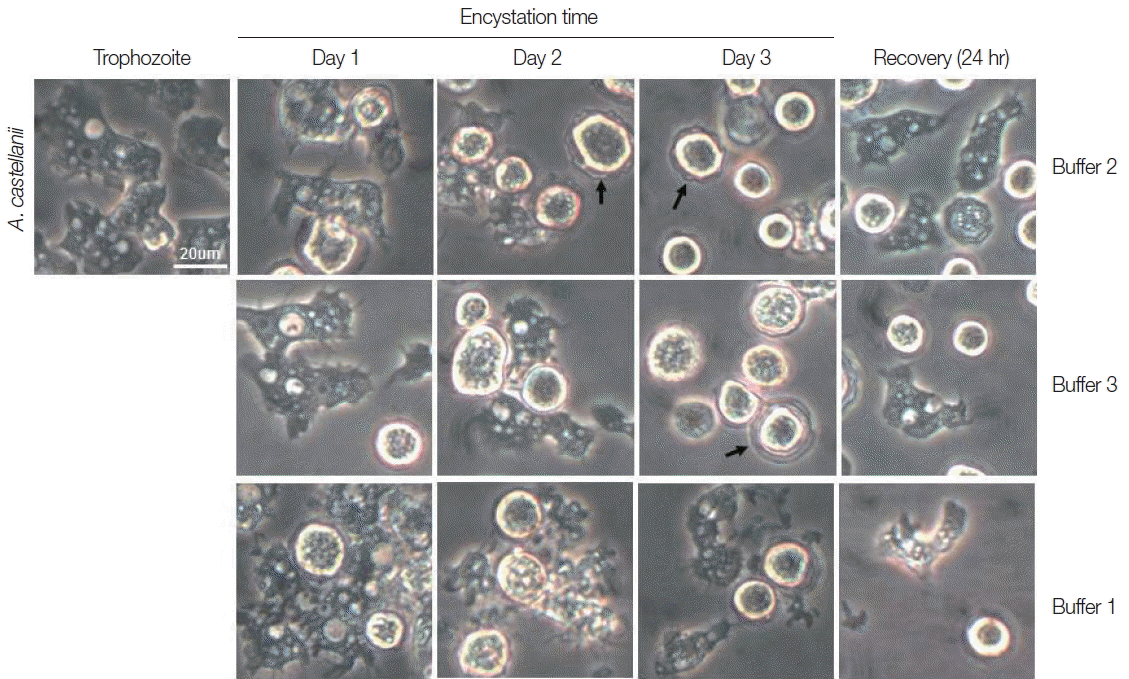
Fig. 3Morphological changes of A. polyphaga trophozoites into precysts (or cysts) cultured in encystation media for 1, 2, and 3 days. Buffer 2 is an effective medium. Cysts recovered to trophozoites in PYG medium.
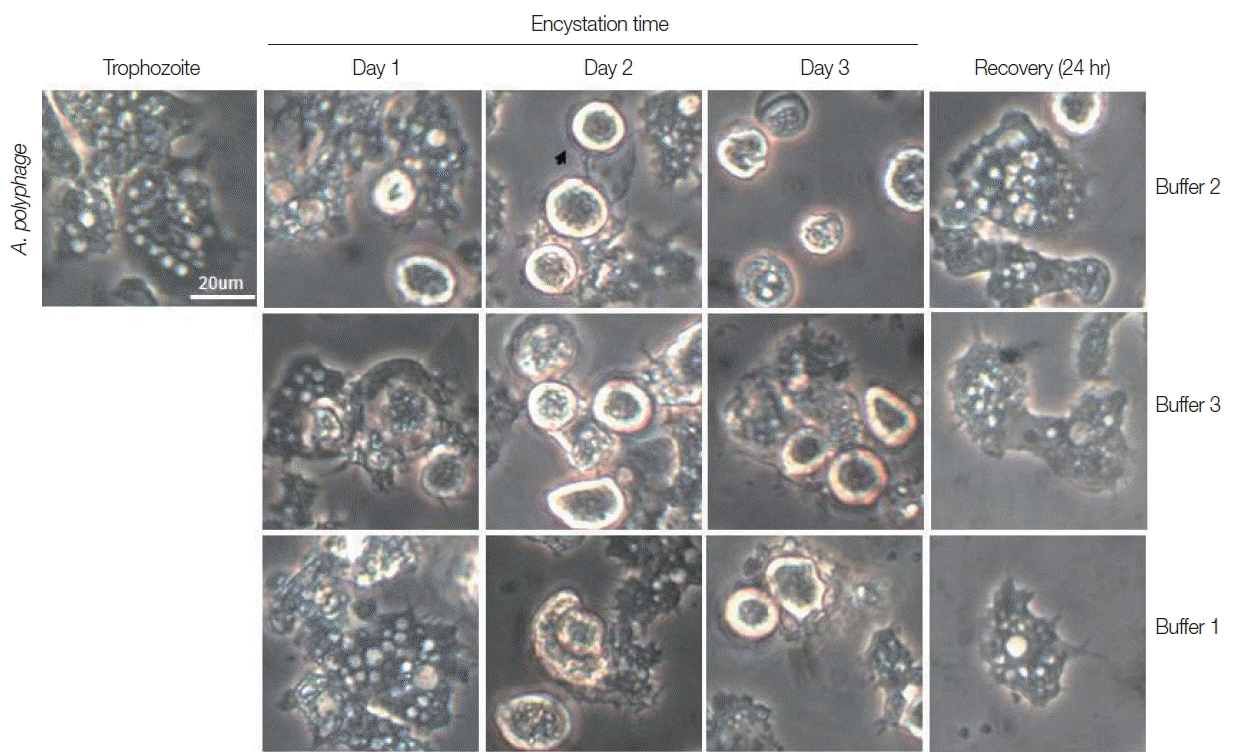
Fig. 4The mRNA expressions of nfa1 and nf-actin genes on N. fowleri trophozoites (Troph), precyts, and cysts (PreC) at 48 hr post cultivation with buffer 1. The p3 mRNA expression is used as the control.
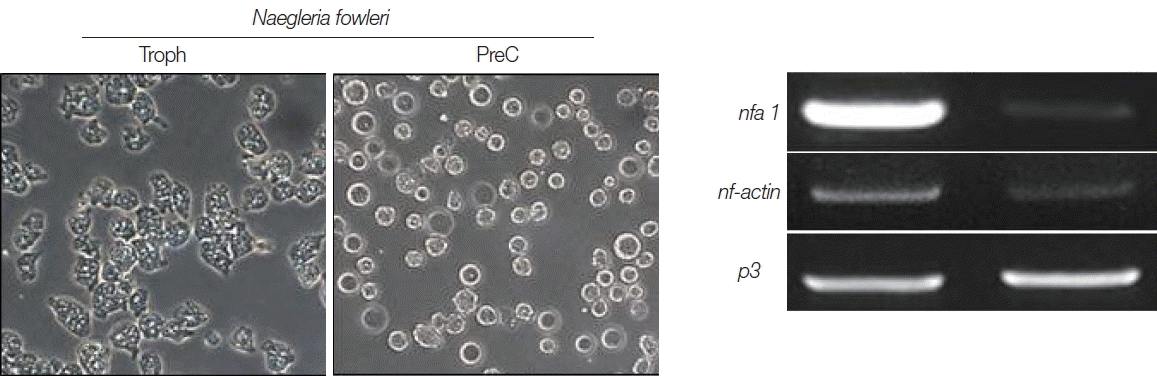
Fig. 5The mRNA expressions of actin and atg8 genes on A. castellanii (A) and A. polyphaga (B) trophozoites, precysts and cysts. The 18S rRNA mRNA expression is used as the control.
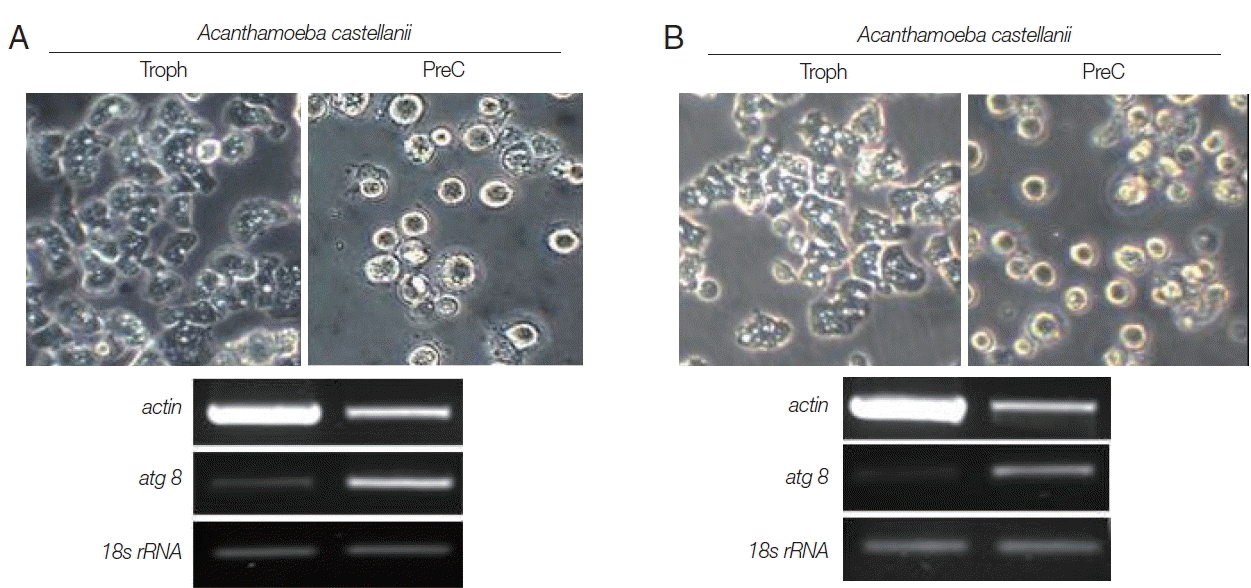
Table 1Compositions of encystation media for Naegleria (buffer 1), Acanthamoeba spp. (buffers 2 and 3), and Page’s amoeba saline
Table 1
|
Buffer 1. Naegleria Encystment media (pH6.8) |
|
120 mM |
NaCI |
|
0.03 mM |
MgCI4
|
|
1 mM |
Na2HPO4
|
|
1 mM |
KH2PO4
|
|
0.03 mM |
CaCI2
|
|
0.02 mM |
FeCI2
|
|
|
Buffer 2. Acanthamoeba Encystment media (pH9.0) |
|
95 mM |
NaCI |
|
5 mM |
KCI |
|
8 mM |
MgSO4
|
|
1 mM |
NaHCO3
|
|
0.4 mM |
CaCI2
|
|
20 mM |
Tris-CI (Ph9.0) |
|
|
Buffer 3. Acanthamoeba Encystment media (pH7.6) |
|
0.1 mM |
KCI |
|
8 mM |
MgSO4
|
|
0.4 mM |
CaCI2
|
|
20 mM |
2-amino-2-methlyl-1, 3-propanediol |
|
|
Page’s amoeba saline (pH6.8–7.9) |
|
2 mM |
NaCI |
|
0.03 mM |
MgSO4
|
|
0.03 mM |
CaCI2
|
|
1 mM |
Na2HPO4
|
|
1 mM |
KH2PO4
|
References
- 1. Ma P, Visvesvara GS, Martinez AJ, Theodore FH, Daggett PM, Sawyer TK. Naegleria and Acanthamoeba infections: review. Rev Infect Dis 1990;12:490-513.
- 2. Schuster FL, Visvesvara GS. Free-living amoebae as opportunistic and non-opportunistic pathogens of humans and animals. Int J Parasitol 2004;34:1001-1027.
- 3. Zhang L, Marciano-Cabral F, Bradley SG. Effects of cyclophosphamide and a metabolite, acrolein, on Naegleria fowleri in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1988;32:962-965.
- 4. Visvesvara GS, Moura H, Schuster FL. Pathogenic and opportunistic free-living amoebae: Acanthamoeba spp., Balamuthia mandrillaris, Naegleria fowleri, and Sappinia diploidea. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2007;50:1-26.
- 5. Moon EK, Chung DI, Hong YC, Kong HH. Autophagy protein 8 mediating autophagosome in encysting Acanthamoeba. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2009;168:43-48.
- 6. Neff RJ RS, Benton WF, Wilborn M. Induction of synchronous encystment (differentiation) in Acanthamoeba sp. Methods Cell Biol 1964;1:55-83.
- 7. Bowers B, Korn ED. The fine structure of Acanthamoeba castellanii (Neff strain). II. Encystment. J Cell Biol 1969;41:786-805.
- 8. Chagla AH, Griffiths AJ. Growth and encystation of Acanthamoeba castellanii. J Gen Microbiol 1974;85:139-145.
- 9. Moon EK, Park HR, Quan FS, Kong HH. Efficacy of Korean multipurpose contact lens disinfecting solutions against Acanthamoeba castellanii. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:697-702.
- 10. Abedkhojasteh H, Niyyati M, Rezaei S, Mohebali M, Farnia S, Kazemi-Rad E, Roozafzoon R, Sianati H, Rezaeian M, Heidari M. Identifying differentially expressed genes in trophozoites and cysts of Acanthamoeba T4 genotype: Implications for developing new treatments for Acanthamoeba keratitis. Eur J Protistol 2015;51:34-41.
- 11. Moon EK, Chung DI, Hong YC, Ahn TI, Kong HH. Acanthamoeba castellanii: gene profile of encystation by ESTs analysis and KOG assignment. Exp Parasitol 2008;119:111-116.
- 12. Willaert E. Isolation and in vitro culture of the amoeba of the genus Naegleria. Ann Soc Belges Med Trop Parasitol Mycol 1971;51:701-708.
- 13. Visvesvara GS, Balamuth W. Comparative studies on related free-living and pathogenic amebae with special reference to Acanthamoeba. J Protozool 1975;22:245-256.
- 14. Shin HJ, Cho MS, Jung SU, Kim HI, Park S, Kim HJ, Im KI. Molecular cloning and characterization of a gene encoding a 13.1 kDa antigenic protein of Naegleria fowleri. J Eukaryot Microbiol 2001;48:713-717.
- 15. Sohn HJ, Kim JH, Shin MH, Song KJ, Shin HJ. The Nf-actin gene is an important factor for food-cup formation and cytotoxicity of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Parasitol Res 2010;106:917-924.
- 16. Kang H, Seong GS, Sohn HJ, Kim JH, Lee SE, Park MY, Lee WJ, Shin HJ. Effective PCR-based detection of Naegleria fowleri from cultured sample and PAM-developed mouse. Eur J Protistol 2015;51:401-408.
- 17. Siddiqui R, Khan NA. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis caused by Naegleria fowleri: an old enemy presenting new challenges. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2014;8:e3017.
- 18. Lorenzo-Morales J, Khan NA, Walochnik J. An update on Acanthamoeba keratitis: diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment. Parasite 2015;22:10.
- 19. Visvesvara GS, De Jonckheere JF, Marciano-Cabral F, Schuster FL. Morphologic and molecular identification of Naegleria dunnebackei n. sp. isolated from a water sample. J Eukaryot Microbiol 2005;52:523-531.
- 20. Chávez-Munguía B, Segovia-Gamboa N, Salazar-Villatoro L, Omaña-Molina M, Espinosa-Cantellano M, Martínez-Palomo A. Naegleria fowleri: enolase is expressed during cyst differentiation. J Eukaryot Microbiol 2011;58:463-468.