Abstract
We described 4 human infection cases of zoonotic fish-tapeworm, Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense, identified with morphological and molecular characters and briefly reviewed Chinese cases in consideration of it as an emerging parasitic disease in China. The scolex and mature and gravid proglottids of some cases were seen, a rosette-shaped uterus was observed in the middle of the mature and gravid proglottids, and the diphyllobothriid eggs were yellowish-brown in color and displayed a small knob or abopercular protuberance on the opposite end of a lid-like opening. The average size of the eggs was recorded as 62–67×42–45 μm. The parasitic materials gathered from 4 human cases were morphologically identified as belonging to the genera Diphyllobothrium and Adenocephalus. The phylogenetic analysis based on the nucleotide sequences of cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene of the etiologic agents confirmed that the 4 cases were D. nihonkaiense infection. The finding of 4 additional D. nihonkaiense cases suggests that D. nihonkaiense might be a major causative species of human diphyllobothriasis in China. A combined morphological and molecular analysis is the main method to confirm D. nihonkaiense infection.
-
Key words: Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense, case report, diphyllobothriasis, phylogenetic analysis, China
INTRODUCTION
Diphyllobothriasis is a fish-borne parasitic zoonosis caused by infection of the adult tapeworm belonging to the genus
Diphyllobothrium [
1]. It has been reported that 14 species are etiologic agents that can cause diphyllobothriasis, including
Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense,
D. latum, and
Adenocephalus pacificus (syn.
D. pacificum) [
1–
3]. Diphyllobothriasis caused by
D. nihonkaiense has been mostly reported in the eastern part of Asia, in particular Japan [
4,
5], South Korea [
6], and the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia [
7]. In Japan, Yamane et al. [
8] established
D. nihonkaiense as a new species in 1986. The infection has been perpetuated among urban people who eat sushi and sashimi. The incidence was particularly high in 2008 [
5].
In Korea,
D. nihonkaiense was first diagnosed in 2009, and there were about 62 cases previously diagnosed as
D. latum which were confirmed to be actually
D. nihonkaiense based on molecular analysis [
6]. As the main infection sources of this tapeworm, salmonid fish, i.e.,
Oncorhynchus masou, O. gorbuscha, O. keta, and
O. nerka, which inhabited in the northern Pacific Ocean, were reported in these countries [
9,
10].
Recently, this tapeworm infections have also been reported in Europe [
11–
13], North America [
14,
15], and New Zealand [
16]. In mainland China, human
D. latum infection was first found in Heilongjiang province in 1927 [
17], and 22 human cases of diphyllobothriasis have been reported between 1927 and 2014 [
18–
22]. There were 14
D. latum cases in total until now, mainly distributed in Heilongjiang province, Beijing, Guangdong province, Tianjin, Fujian province, and Shanghai [
18–
21]. Human
D. nihonkaiense infection was first found in Shanghai in 2008, when it was first morphologically misdiagnosed as
D. latum infection; however, Chen et al. [
22] discovered it as a
D. nihonkaiense human case diagnosed definitively by molecular analysis of expelled proglottids. Total 8 human
D. nihonkaiense cases were reported from 2008 to 2014; 1 case in 2008 [
22], 1 case in 2009 [
22], 3 cases in 2011 [
22], and 3 cases between 2012 and 2014 [
21] (
Table 1).
The main reason for
D. nihonkaiense infection is that the salmon has become an increasingly important commodity globally, and the salmon trade has increased markedly due to rapid advances in international and domestic transport systems. This results in an increase in the occurrence of diphyllobothriasis as an emerging parasitic disease in regions where it previously did not exist. The infection occurs through the consumption of raw or undercooked fish containing the larval forms called plerocercoids. Some species can grow as long as 2–15 m in the human small intestine. Typical features of
D. nihonkaiense, as the same as
D. latum, is the spoon-like scolex with a deep groove and the mature and gravid proglottids having a rosette-shaped uterus [
17]. Complete mitochondrial genomes of
D. nihonkaiense and
D. latum have been demonstrated recently, these genomes can distinguish the 2 species and rendered species diagnosis more reliable [
5]. Clinical manifestations of diphyllobothriasis are generally mild and not serious. Abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, and defecating “inch-sized white worms” have been reported [
23].
The aim of this study is to report 4 human infection cases of zoonotic fish-tapeworm, D. nihonkaiense, identified with morphological and molecular characters and briefly reviewed Chinese cases with a consideration as an emerging parasitic disease in China.
CASE RECORD
The first case was a 43-year-old woman residing in Heilongjiang province, who expelled several fragments of a flat white worm in her feces. The patient stated that she frequently consumed raw or undercooked fish, such as the salmon, especially when she worked in Russia in 2012. She also consumed a lot of raw salmons in July and August in 2013 and 2014, when the salmons migrate from the ocean and swim to the upper reaches of rivers where they spawn. The patient caught the salmon in the river and ate the fish raw. She also had a history of eating other raw freshwater fish. Based on the morphology of the strobila and eggs, the sample was diagnosed as belonging either to Diphyllobothrium or Adenocephalus. On 29 March 2015, the patient orally took Chinese traditional medicine (decoction of betel nut and pumpkin seed) and MgSO4 solution for catharsis. After 4.5 hr, a cestode of about 3 m in length was successfully excreted, though the scolex was missing.
The second case was a 40-year-old man living in Shanghai, who liked eating raw or undercooked salmon and had never traveled abroad. In March 2015, he consumed nearly 1 kg of raw salmon in a Japanese restaurant in Shanghai and passed some alive white proglottids in his feces 2 months later. After ingesting a decoction of betel nut and pumpkin seed, he expelled a 3.2 m long tapeworm, with the scolex morphologically identified as belonging to the genus Diphyllobothrium.
The third case was a 42-year-old Chinese man who spent most of his life living in Canada, where he ate a lot of raw or undercooked salmon and other sea fish. The patient expelled some fragments of a flat white worm in his feces in January 2016 when he came back to Shanghai to visit relatives. Based on the morphology of the strobila and eggs, the sample was diagnosed as belonging either to Diphyllobothrium or Adenocephalus. After he was orally administered with praziquantel, segments of proglottids were expelled from his anus. All proglottids were sent for DNA-PCR analysis.
The fourth case was a previously healthy 36-year-old man residing in Shanghai, who expelled some fragments of a flat white worm in his feces since October 2015. The patient stated that he likes to eat raw or undercooked fish, such as the salmon and trout. Based on the morphology of the strobila and eggs, infection with a diphyllobothriid was strongly suspected. A single dose (20 mg/kg) of praziquantel and 250 ml of citrate magnesium were administered orally. The strobila was preserved in 70% ethanol and sent to our institute for further analysis.
The study was authorized by the ethical committee of Institute of Parasitic Diseases (IPD), Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (China CDC). All participants were informed about the study aims and procedures, following which they were given a written informed consent to participate. Collection of specimens (tapeworm) was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of IPD, China CDC.
The parasitic material gathered was repeatedly washed in physiological saline solution, macroscopically examined and measured, explored by microscopy, and morphologically identified based on morphological characters [
17]. Several proglottids of each tapeworm were preserved in 70% ethanol at 4°C until DNA extraction.
Genomic DNA was extracted from the proglottids excreted by each case using a DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The mitochondrial cytochrome
c oxidase subunit 1 gene (
cox1) was amplified by PCR, according to the method previously described by Yamasaki and Kuramochi [
16]. New primer pairs were constructed as follows: Diphyllo trnW/F (5′-ACAGTGGGTTTAGATGTAAAGACGGC-3′) and Diphyllo trnT/R (5′-AGTATTCTAATTAAACTATAAAGCC-3′).
All PCR products positive for
Diphyllobothrium were sequenced with PCR primers at each locus after being purified using an ABI PRISM® 3730 DNA Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA) and a BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems). The nucleotide sequences obtained in the present study were subjected to a BLAST search (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast), and were analyzed and aligned with each other.
Diphyllobothrium reference sequences were downloaded from GenBank using the program Clustalx 1.83 (
http://www.clustal.org). A neighbor-joining tree was constructed at cox1 loci using the program MEGA 4 (
http://www.megasoftware.net) based on the evolutionary distances calculated using Kimura’s 2-parameter method. The reliability of the tree was assessed by bootstrapping with 500 replicates.
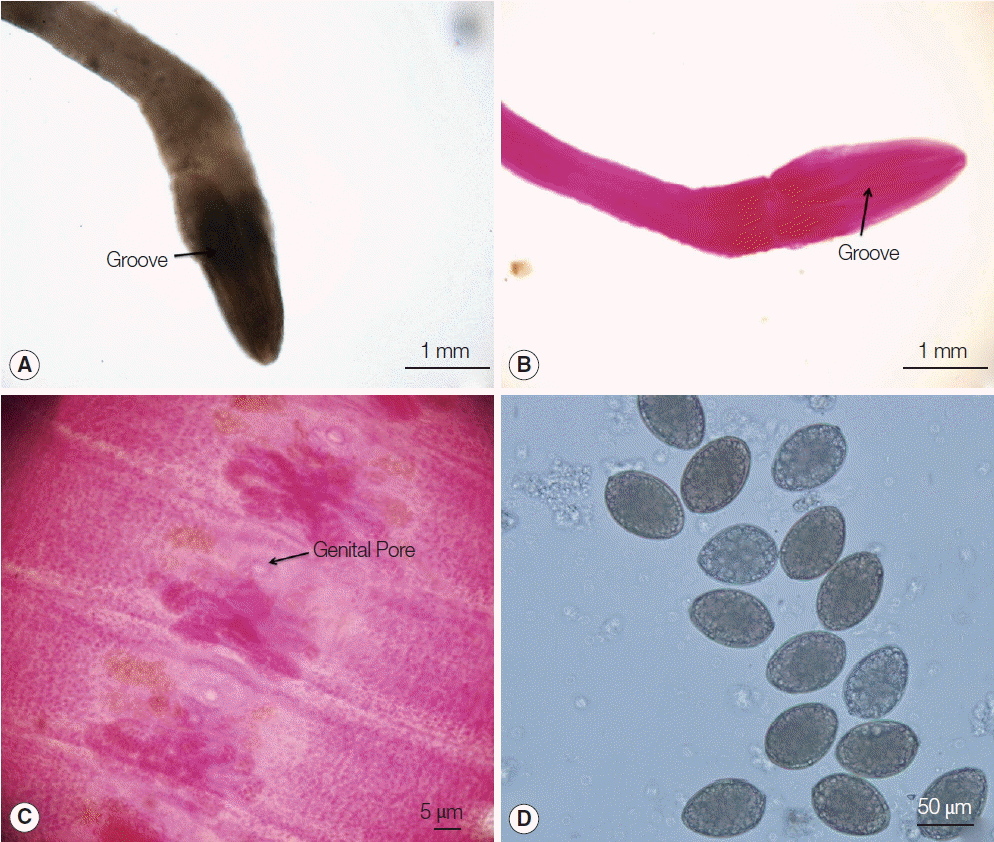
All worms recovered from cases were grossly revealed typical long tapeworm proglottids, and their each segment was wider than long. The tapeworms from the 1st and 2nd cases were 3.0 m and 3.2 m in length, respectively. The scolex of the tapeworm from case 1 was missing, only mature and gravid proglottids were seen. The tapeworm of case 2 was integral, and the scolex and mature and gravid proglottids were seen. From cases 3 and 4, only segments of proglottids were obtained. The tapeworm from case 2 was used for carmine staining and further observation. Using an anatomical lens, it was determined that the scolex from case 2 was spoon-like with a deep groove (
Fig. 1A, B). A rosette-shaped uterus was observed in the middle of the mature and gravid proglottids.
Diphyllobothrium species eggs were also detected (
Fig. 1C). The diphyllobothriid eggs were yellowish-brown in color and displayed a small knob or abopercular protuberance on the opposite end of a lid-like opening. Twenty eggs from each sample were measured using a microscope. The average size of the eggs was recorded as 65×44 μm (case 1), 63×42 μm (case 2), 67×45 μm (case 3), and 62×43 μm (case 4). The eggs from case 4 are shown as an example in
Fig. 1D.
PCR products of cases 1 to 4 were all positive, and all PCR products positive for Diphyllobothrium were sequenced with PCR primers (Diphyllo trnW/F and Diphyllo trnT/R). The lengths of the partial cox1 sequences (pcox1) of the samples were 1,566 bp. Molecular diagnostics confirmed that all parasitic material belonged to the species D. nihonkaiense. The sequences for cases 1 and 2 are available in the DNA Data Bank of Japan, with accession nos. LC070677 and LC070678, respectively. Meanwhile, sequences for cases 3 and 4 are available in GenBank, with accession nos. KU984425 and KU984426, respectively.
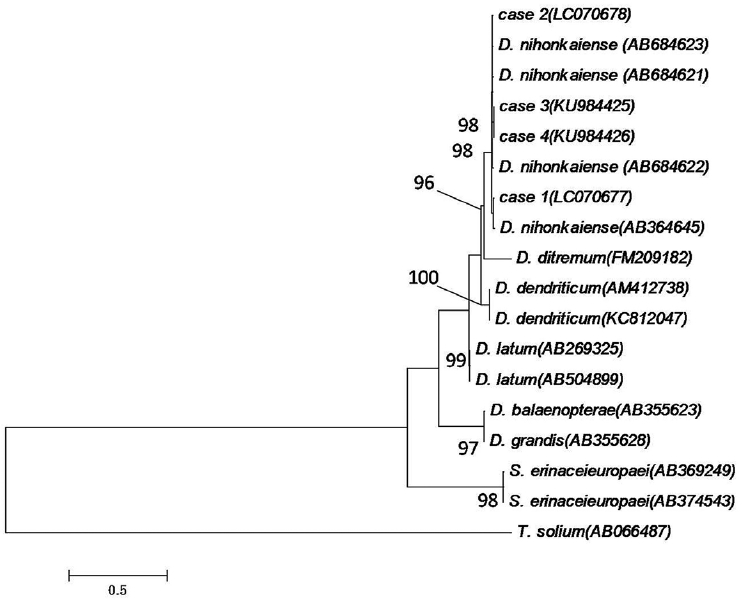
Topologies of
pcox1 sequences inferred by neighbor-joining methods (NJ methods) with different building strategies and/or different distance models were found to be similar (
Fig. 2). The phylogenetic tree consisted of 2 large clades; the first one contained the genus
Diphyllobothrium and the second contained
Spirometra. In the first clade, the 4 patient’s samples were included in the
D. nihonkaiense family with a high bootstrap value (>50%). In the second clade,
Spirometra samples were clustered together. This clustering is in agreement with the results of traditional classifications.
Taenia solium was used as an outgroup (
Table 2).
DISCUSSION
D. latum and
D. nihonkaiense are almost indistinguishable morphologically. As recently reported [
22], the 5 human cases of diphyllobothriasis in China were first diagnosed morphologically as
D. latum infection. However, all tapeworms were confirmed to be
D. nihonkaiense by molecular analysis [
22]. The 4 additional
D. nihonkaiense cases in this study were also confirmed to be
D. nihonkaiense by analysis of cox1 gene. Given the morphological similarities among diphyllobothriid species, molecular analysis is an indispensable method for accurately identifying the correct species, and helpful not only for avoiding diagnostic confusion but also for facilitating the acquisition of reliable epidemiologic and epizootic information.
Adding 4 new cases in this study, total 12 human cases were reported in China in a short span of 8 years from 2008 to 2016; 10 of the 12
D. nihonkaiense cases were local infection, and 2 of them were abroad infection (
Tables 1,
3). For case 1 of this study, the patient stated that she frequently consumed raw or undercooked fish when she worked in Russia from 2012 to 2014. For case 3, the patient ate a lot of raw or undercooked salmon and other sea fish in Canada. The number of
D. nihonkaiense cases is increasing year by year, especially in Shanghai. However, China is not a location where intermediate hosts are commonly distributed, and most of the salmon is imported. United States, Chile, Russia, Norway, and Japan were the top 5 countries that exported salmons to China in 2014 [
24]. The 4 recent cases of
D. nihonkaiense infection reported in Shanghai likely reflect the changes in the raw salmon-eating habits of people and preferences for specialties, such as sushi and sashimi, which are staples of healthy Japanese diets [
15,
16,
22].
In this study, 2 of the patients (cases 1,2) orally took Chinese traditional medicine (decoction of betel nut and pumpkin seed) and MgSO
4 solution for catharsis. Two others (cases 3,4) orally administered a single dose of praziquantel (10 mg/kg). It was similar to the dose used to treat
D. latum infection [
17,
23]. A decoction of betel nut and pumpkin seed has been recommended for the treatment of
D. nihonkaiense and other tapeworm infections in China with a long time using, good effect, and good compliance [
17]. A single dose of praziquantel is also recommended, but for some of the patients, 2 doses are thought to be necessary [
25].
A limitation of this study was the small number of cases evaluated. Moreover, the species of intermediate host of
D. nihonkaiense which the patients had eaten could not be obtained and evaluated. Because it took a long time when the patients were diagnosed and it is difficult to know exactly where the salmon the patients had eaten were from. In conclusion, studies on Pacific salmons as a potential source of infection for
D. nihonkaiense in China should be conducted. More people should be made aware about the harmful effects of eating raw or undercooked fish [
26].
D. nihonkaiense infection may become a new emerging parasitic disease in China.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank all the staff at the National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, and the Department of Parasitology, National Institute of Infectious Diseases of Japan, who involved in this study. This work was supported by the National S & T Major Program (grant no. 2012ZX10004-220) granted to Shao-Hong Chen (SHC), the Parasitic and Tropical Diseases Resource Center Project of the National Science and Technology Basic Conditions Platform Program granted to SHC, and the Research Program on Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases of the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (Kansensho Jitsuyoka-Ippan, no. 15fk0108025h0502) granted to H. Yamasaki.
Fig. 1Morphological features of worms under microscopic examinations. (A) The scolex from case 2. (B) Carmine-stained scolex from case 2. (C) Gravid proglottids stained with acetocarmine from case 2. (D) Eggs detected in fecal samples of case 4.
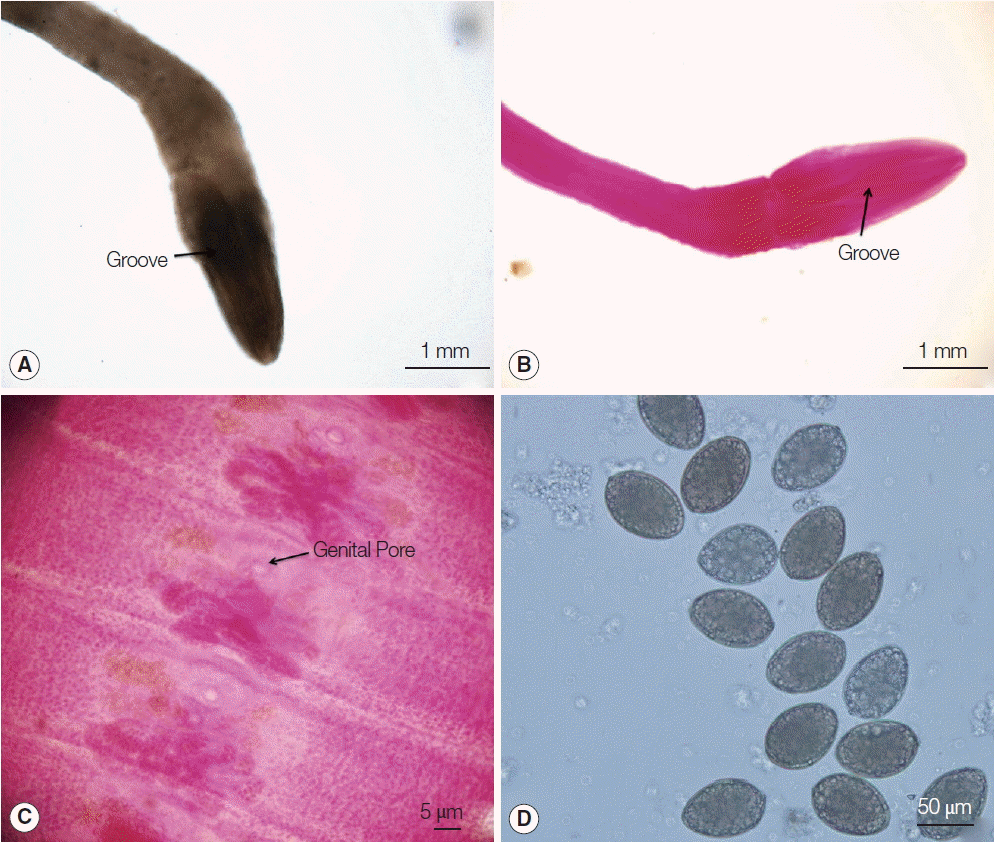
Fig. 2A phylogenetic tree constructed using the maximum likelihood algorithm with HKY+G model on the basis of the complete cox1 sequences of the isolates from the 4 Chinese cases and related Diphyllobothrium species. The numbers of the nodes are bootstrap values (500 replicates). Taenia solium was used as an outgroup. The scale bar indicates the number of base substitutions per site.

Table 1Summary on the human infection cases with D. nihonkaiense in China
Table 1
|
Case no |
Residence |
Year of diagnosis |
Place of eating fish |
Suspected source of infection |
Morphologic and molecular identificaton |
Abroad or local infection |
Reference |
|
1 |
Shanghai/Japan |
2008 |
Shanghai |
raw salmon |
D. nihonkaiense
|
local |
22
|
|
2 |
Heilongjiang |
2009 |
Heilongjiang |
raw fish |
D. nihonkaiense
|
local |
22
|
|
3 |
Shanghai |
2011 |
Shanghai |
raw salmon |
D. nihonkaiense
|
local |
22
|
|
4 |
Shanghai |
2011 |
Shanghai |
raw salmon |
D. nihonkaiense
|
local |
22
|
|
5 |
Shanghai |
2011 |
Shanghai |
raw salmon |
D. nihonkaiense
|
local |
22
|
|
6 |
Heilongjiang |
2012 to 2014 |
Harbin |
raw or undercooked fish |
D. nihonkaiense
|
local |
21
|
|
7 |
Heilongjiang |
2012 to 2014 |
Fuyuan |
raw or undercooked salmon |
D. nihonkaiense
|
not sure |
21
|
|
8 |
Heilongjiang |
2012 to 2014 |
Harbin |
raw fish dishes |
D. nihonkaiense
|
local |
21
|
Table 2Samples of Diphyllobothrium spp., Diplogonoporus spp., Spirometra spp., and Taenia spp. used in the present study, as well as their GenBank accession numbers for sequences of partial mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene (pcox1)
Table 2
|
Sample codes |
Geographic origin |
Host |
Species |
GenBank accession number (pcox1 ) |
|
Case 1 |
Heilongjiang, China |
Homo sapiens
|
Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense
|
LC070677 |
|
Case 2 |
Shanghai, China |
Homo sapiens
|
D. nihonkaiense
|
LC070678 |
|
Case 3 |
Canada |
Homo sapiens
|
D. nihonkaiense
|
KU984425 |
|
Case 4 |
Shanghai, China |
Homo sapiens
|
D. nihonkaiense
|
KU984426 |
|
CHN-005 |
Shanghai, China |
Homo sapiens
|
D. nihonkaiense
|
AB684623 |
|
CHN-002 |
Japan |
Homo sapiens
|
D. nihonkaiense
|
AB684621 |
|
CHN-003 |
Shanghai, China |
Homo sapiens
|
D. nihonkaiense
|
AB684622 |
|
Asahikawa, Japan |
- |
D. nihonkaiense
|
AB364645 |
|
TS02/32 |
Scotland, United Kingdom |
Salvelinus alpinus
|
Diphyllobothrium ditremum
|
FM209182 |
|
- |
Homo sapiens
|
Diphyllobothrium dendriticum
|
AM412738 |
|
CZ49 |
Czech Republic |
Homo sapiens
|
D. dendriticum
|
KC812047 |
|
- |
Homo sapiens
|
Diphyllobothrium latum
|
AB269325 |
|
Santiago, Chile |
Homo sapiens
|
D. latum
|
AB504899 |
|
D3 |
Sanriku-Oki, Japan |
- |
Diphyllobothrium balaenopterae
|
AB355623 |
|
DJ1 |
Tokyo, Japan |
- |
Diplogonoporus grandis
|
AB355628 |
|
Tokyo, Japan |
Elaphe quadrivirgata
|
Spirometra erinaceieuropaei
|
AB369249 |
|
Japan |
Elape quadrivirgata
|
S. erinaceieuropaei
|
AB374543 |
|
Thailand |
-
|
Taenia solium
|
AB066487 |
Table 3Summary of the human infection cases with D. nihonkaiense in China of this study
Table 3
|
Case no |
Residence |
Year of diagnosis |
Place of eating fish |
Suspected source of infection |
Morphologic and molecular identification |
Abroad or local infection |
Reference |
|
Case 1 |
Heilongjiang |
2015 |
Russia |
raw salmon |
D. nihonkaiense
|
abroad |
This study |
|
Case 2 |
Shanghai |
2015 |
Shanghai |
raw salmon |
D. nihonkaiense
|
local |
This study |
|
Case 3 |
Shanghai/Canada |
2016 |
Canada |
raw salmon |
D. nihonkaiense
|
abroad |
This study |
|
Case 4 |
Shanghai |
2016 |
Shanghai |
raw salmon |
D. nihonkaiense
|
local |
This study |
References
- 1. Scholz T, Garcia HH, Kuchta R, Wicht B. Update on the human broad tapeworm (genus Diphyllobothrium), including clinical relevance. Clin Microbiol Rev 2009;22:146-160.
- 2. Šteřiková A, Brabec J, Kuchta R, Jiménez JA, García HH, Scholz T. Is the human-infecting Diphyllobothrium pacificum a valid species or just a South American population of the holarctic fish broad tapeworm, D. latum? Am J Trop Med Hyg 2006;75:307-310.
- 3. Kuchta R, Serrano-Martínez ME, Scholz T. Pacific broad tapeworm Adenocephalus pacificus as a causative agent of globally reemerging diphyllobothriosis. Emerg Infect Dis 2015;21:1697-1703.
- 4. Yamane Y, Shiwaku K. Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense and other marine-origin cestodes. Tokyo, Japan. Prog Med Parasitol Jpn 2003;8:245-254.
- 5. Arizono N, Yamada M, Nakamura-Uchiyama F, Ohnishi K. Diphyllobothriasis associated with eating raw Pacific salmon. Emerg Infect Dis 2009;15:866-870.
- 6. Jeon HK, Kim KH, Huh S, Chai JY, Min DY, Rim HJ, Eom KS. Morphologic and genetic identification of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2009;47:369-375.
- 7. Arizono N, Shedko M, Yamada M, Uchikawa R, Tegoshi T, Takeda K, Hashimoto K. Mitochondrial DNA divergence in populations of the tapeworm Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense and its phylogenetic relationship with Diphyllobothrium klebanovskii. Parasitol Int 2009;58:22-28.
- 8. Yamane Y, Kamo H, Bylund G, Wikgren BJ. Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense sp. nov (Cestoda: Diphyllobothriidae): revised identification of Japanese broad tapeworm. Shimane J Med Sci 1986;10:29-48.
- 9. Fuchizaki U, Ohta H, Sugimoto T. Diphyllobothriasis. Lancet Infect Dis 2003;3:32.
- 10. Yoshida M, Hasegawa H. Takaoka, Miyata, A. A case of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense infection successfully treated by oral administration of gastrografin. Parasitol Int 1999;48:151-155.
- 11. Yera H, Estran C, Delaunay P, Gari-Toussaint M, Dupouy-Camet J, Marty P. Putative Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense acquired from a Pacific salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) eaten in France: genomic identification and case report. Parasitol Int 2006;55:45-49.
- 12. Shimizu H, Kawakatsu H, Shimizu T, Yamada M, Tegoshi T, Uchikawa R, Arizono N. Diphyllobothriasis nihonkaiense: possibly acquired in Switzerland from imported Pacific salmon. Intern Med 2008;47:1359-1362.
- 13. Fang FC, Billman ZP, Wallis CK, Olson JC, Dhanireddy S, Murphy SC. Human Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense infection in Washington State. J Clin Microbiol 2015;53:1355-1357.
- 14. Wicht B, de Marval F, Peduzzi R. Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense (Yamane et al., 1986) in Switzerland: first molecular evidence and case reports. Parasitol Int 2007;56:195-199.
- 15. Wicht B, Scholz T, Peduzzi R, Kuchta R. First record of human infection with the tapeworm Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense in North America. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2008;78:235-238.
- 16. Yamasaki H, Kuramochi T. A case of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense infection possibly linked to salmon consumption in New Zealand. Parasitol Res 2009;105:583-586.
- 17. Wu GL. Human Parasitology. 3rd ed. Beijing, China. Peoples Medical Publishing House; 2013.
- 18. Chen BJ, Li LS, Ling JX, Lin YS, Li YR. A case of human diphyllobothriasis after eating Plecoglossus altivelis. J Trop Dis Parasitol 2005;3:136. (in Chinese).
- 19. Li YH, Wen JS, Shu J, Zhang WZ. A human case caused by Diphyllobothrium latum in Heilongjiang Province. Chinese J Parasitol Parasitic Dis 2009;27:296-302. (in Chinese).
- 20. Guo AJ, Liu K, Gong W, Luo XN, Yan HB, Zhao SB, Hu SN, Jia WZ. Molecular identification of Diphyllobothrium latum and a brief review of diphyllobothriosis in China. Acta Parasitol 2012;57:293-296.
- 21. Zhang W, Che F, Tian S, Shu J, Zhang X. Molecular identification of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense from 3 human cases in Heilongjiang Province with a brief review in China. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:683-688.
- 22. Chen S, Ai L, Zhang Y, Chen J, Zhang W, Li Y, Muto M, Morishima Y, Sugiyama H, Xu X, Zhou X, Yamasaki H. Molecular detection of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense in humans, China. Emerg Infect Dis 2014;20:315-318.
- 23. Li H, Chen SH, Zhang YN, Ai L, Chen JX. A human case report of Diphyllobothrium latum at Shanghai, China. J Anim Vet Adv 2012;11:3073-3075.
- 24. Zhao HJ, Li HQ, Chong Y, Wang LX, Zhou HC, Ou A, Chen W, Huang W, Huo Q, Jiang FJ. Research on quality analysis and regulatory countermeasures of imported salmon in China. J Food Saf Qual 2015;6:3947-3953.
- 25. Park SH, Jeon HK, Kim JB. Four additional cases of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense infection confirmed by analysis of COX1 gene in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:105-108.
- 26. FDA. Fish and fisheries products hazards and controls guide. Washington DC, USA. 1998.