Abstract
A field survey studying intestinal parasites in humans and microbial pathogen contamination at environment was performed in a Laotian rural village to identify potential risks for disease outbreaks. A parasitological investigation was conducted in Ban Lak Sip village, Luang Prabang, Lao PDR involving fecal samples from 305 inhabitants as well as water samples taken from 3 sites of the local stream. Water analysis indicated the presence of several enteric pathogens, i.e., Aeromonas spp., Vibrio spp., E. coli H7, E. coli O157: H7, verocytotoxin-producing E. coli (VTEC), Shigella spp., and enteric adenovirus. The level of microbial pathogens contamination was associated with human activity, with greater levels of contamination found at the downstream site compared to the site at the village and upstream, respectively. Regarding intestinal parasites, the prevalence of helminth and protozoan infections were 68.9% and 27.2%, respectively. Eight helminth taxa were identified in fecal samples, i.e., 2 tapeworm species (Taenia sp. and Hymenolepis diminuta), 1 trematode (Opisthorchis sp.), and 5 nematodes (Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, Strongyloides stercoralis, trichostrongylids, and hookworms). Six species of intestinal protists were identified, i.e., Blastocystis hominis, Cyclospora spp., Endolimax nana, Entamoeba histolytica/E. dispar, Entamoeba coli, and Giardia lamblia. Questionnaires and interviews were also conducted to determine risk factors of infection. These analyses together with a prevailing infection level suggested that most of villagers were exposed to parasites in a similar degree due to limited socio-economic differences and sharing of similar practices. Limited access to effective public health facilities is also a significant contributing factor.
-
Key words: Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, Strongyloides stercoralis, hookworm, Opisthorchis sp., Taenia sp., Blastocystis hominis, Cyclospora sp., Endolimax nana, Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba coli, Giardia lamblia, environment, water, risk factor, Lao PDR
INTRODUCTION
Intestinal parasitic infections are neglected infectious diseases causing public health concerns (i.e., abdominal disorders, retarded growth, and impairment of cognitive skill in young children) and serious economic problems in several subtropical and tropical countries [
1,
2]. These diseases still affect several million people with the prevalence rate in endemic areas ranging from 30–60% [
3], particularly in rural areas of low-income countries, including Lao People’s Democratic Republic (Lao PDR).
Recent studies have explored the prevalence of human parasites such as helminths and protists in the Lao PDR [
4–
6], and an overview of the current situation regarding helminthic infections in different areas of Lao PDR is presented in Eom et al. [
7]. Soil-transmitted helminths (i.e., hookworms,
Ascaris lumbricoides, and
Trichuris trichiura) and fishborne trematodes (i.e.,
Opisthorchis viverrini and minute intestinal flukes) appeared as the dominant helminthiases in Lao PDR [
7–
9]. Soil-transmitted helminths were highly prevalent in populations residing in the northern provinces such as Phongsaly, Luang Prabang, and Vientiane, whereas fishborne trematode infections were dominantly found down to the south of the country, i.e., Savannakhet, Khammouane, Champasak, and Saravane [
7,
8]. Ingestion of the zoonotic tapeworms of raw pork (
Taenia solium) and beef (
Taenia saginata) leading to taeniasis and cysticerosis were thought to be underestimated in Lao PDR as limited numbers of proper surveys of the disease prevalence or incidence have been reported [
10]. However, recent evidences of hyperendemic
T. solium and cysticercosis raised concerns about these diseases, and its impact to public health in Lao PDR. In the Northern Province, i.e., Phongsaly, the seroprevalence rate was extremely high, ranging from 46.7% to 66.7% as opposed to 2.9% to 4.7% prevalence in broader survey from the other provinces [
11–
13]. In addition, apart from those parasites above, some other rare zoonotic helminthiases were also reported in Lao PDR, e.g., capillariasis (
Capillaria philippinensis) from fresh water fish [
14], echinostomiasis (
Echinochasmus japonicus) from fresh water fish and aquatic animals [
15], paragonimiasis (
Paragonimus spp.) from freshwater crab or prawn [
16], trichinellosis (
Trichinella spiralis) from pigs [
5], and trichostrongyliasis (
Trichostrongylus colubriformis) from the livestock [
17,
18].
Unlike helminth infections, information of intestinal protists in the Laotian population is less readily available. However, there have been some reports of intestinal protozoan infections, e.g.,
Blastocystis hominis, Cyclospora sp.,
Endolimax nana, Entamoeba coli, E. histolytica, Giardia intestinalis, and
G. lamblia [
4,
19,
20].
In Lao PDR and across the Southeast Asian region, surveys of helminth and protist co-infections show that they are relatively abundant, as climatic, ecological, and socio-economic conditions are optimal for parasite transmission. None of the previous studies have integrated studies of waterborne environmental pathogens (bacteria and viruses) to give a better understanding of the prevalence of parasites and water-borne pathogens in a specific study site. In addition to helminth and protist infections, particular interest in the present study includes waterborne enteric bacterial and viral agents, such as Shigella spp., Vibrio spp., and adenovirus.
The “One Health” approach has been realized as an important mechanism to achieve improvement of public health, environmental health, and infectious disease control. Here, we applied “One Health” in the local-scale research aiming to develop a better understanding of the degree of waterborne enteric pathogens and human parasitosis in a typical Laotian rural village by using interdisciplinary approach, i.e., medical microbiology and parasitology, public health and medicine, environmental science, and social science. This was achieved by surveying helminths and protists in human fecal samples, as well as testing for the presence of specific enteric pathogens in the sampled water. In addition, the impacts of socio-environmental factors on infection were determined by interviewing the same individuals that were screened for parasites and having them complete questionnaires.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study area
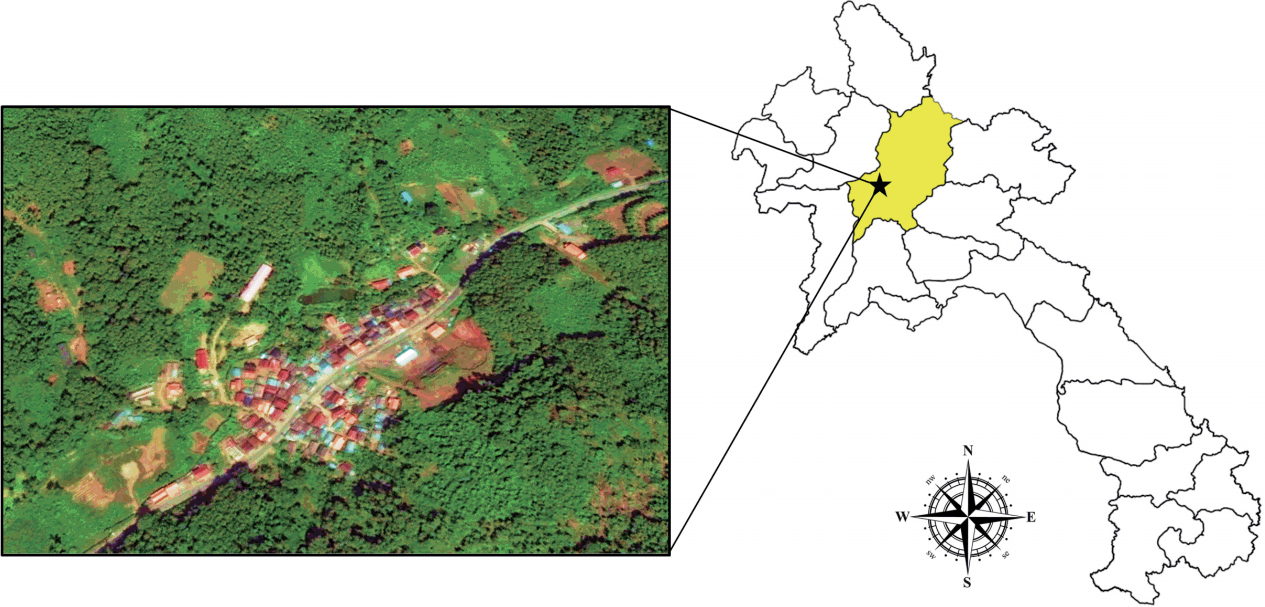
The village of Lak Sip (Luang Prabang district, Luang Prabang Province) is located in northern Lao PDR at 430 m above the sea level and 15 km distance from the Luang Prabang town (
Fig. 1). The village covers an area of about 2 ha and was established in 1962 for the resettlement of Laotian highland communities. The annual rainfall is 1,400 mm and the runoff feeds several streams that run through the village territory, with Houai Xon the main stream traversing through the village. The livelihoods of Ban Lak Sip residents depend on a variety of on-farm activities with upland rice production being the primary agricultural activity in all village households. Most of the population belongs to the Khmu ethnic group. Most houses were of traditional construction, made from wood, and the streets were not paved.
Water sampling was performed at 3 different sites in and near by Ban Lak Sip village with respect to the direction of water flow from the village. The first site was Lak Sip village with the map reference at latitude 19°50′55.615″ and longitude 102°10′4.266″; the second site was upstream of the village (limited human activity) at latitude 19°51′8.781″ and longitude 102°10′7.669″; and the third site was downstream of the village (extensive human activity) at latitude 19°50′54.268″ and longitude 102°8′45.51″. All samplings were completed during the monsoon period in May 2012 because the rainy season is preferred to the drier months due to rising water tables and increased run-off which cause a spike in waterborne pathogens and parasitosis.
At each site, 2 bags of surface water (3 L each) were collected and concentrated using either the tangential flow filtration (TFF) method or the Lifesaver bottle (
http://www.lifesaversystems.com, Lifesaver Systems, Great Britain). For the TFF method, the 3 L water samples were passed through a 100 kDa hollow fiber cartridge using a peristaltic pump to trap both bacteria and viruses. The trapped micro-organisms were then flushed out of the cartridge and collected in 100 ml of water. Similarly, the ultra-filtration membranes encased within the Lifesaver bottle have been shown to be able to trap both bacteria and viruses. Water samples were poured into the bottle and mechanical pumping created the pressure required to force the dirty water through the ultra-filtration cartridge, where micro-organisms were trapped. Then, 100 ml of clean water was poured into the bottle which was then shaken vigorously to dislodge the microorganisms from the cartridge before the water was collected. Water samples collected from Lak Sip village and the upstream site were concentrated using the Lifesaver bottle and the TFF respectively. For the water samples collected from the downstream site, 1 bag (3 L) was concentrated using the TFF and the other was concentrated using the Lifesaver bottle. An aliquot of the concentrated water samples collected from each site was plated on trypticase soy agar (TSA). Viable colonies obtained from the TSA plates were pooled. DNA was extracted from the concentrated raw water or from pooled bacterial colonies using a FastDNA Spin Kit (MP Biomedicals, Solon, Ohio, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The extracted nucleic acids were tested for the presence of enteric pathogens using a commercially available multiplex PCR kit, Seeplex ACE Diarrhea Detection kit (Seegene, Seoul, Korea), according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Pathogens that could be detected by this kit include Salmonella spp. (S. bongori and S. enterica), Shigella spp. (S. flexneri, S. boydii, S. sonnei, and S. dysenteriae), Vibrio spp. (V. cholera, V. parahaemolyticus, and V. vulnificus), Clostridium difficile toxin B, Campylobacter spp. (C. jejuni and C. coli), Clostridium perfringens toxin, Yersinia enterolitica, Aeromonas spp. (A. salmonicida, A. sobria, A. bivalvium, and A. hydrophila), Escherichia coli O157:H7, verocytotoxin-producing E. coli (VTEC), human enteric adenovirus, Group A rotavirus, norovirus GI/GII, and astrovirus.
Human stool collection and intestinal parasite examinations
Human fecal samples were collected every morning in plastic containers (around 5 g) which had been distributed to villagers by the help from local health volunteers and returned to the field laboratory for further examination within the same day. Geographical coordinates of each participant were recorded at the individual households using GPS device Garmin Montana 600 (Garmin International Inc., Olathe, Kansas, USA).
The fecal samples were firstly checked for parasitic infections using the direct smear technique to initially screen for helminth and protozoan infections. Lugol’s iodine was added in simple smears, which helps to stain and produce better visualization of some features for protists identification. Intestinal protist identification was performed by consulting the taxonomic literature [
21,
22]. Subsequently, a concentration method, modified-Katz’s thick smear technique [
23] was followed to identify and quantify helminth eggs or larvae presented in fecal samples. The slides were coated with an equal amount of sieved fecal samples (around 43 mg) through wire-net filter, and then covered with a cellophane strip pre-soaked in the Katz’s solution. The prepared slides were left at room temperature for 30 min allowing fecal contents to dry and clear, then the slides were examined and all helminth eggs were counted in the whole smear under light microscope by experienced parasitologists. Duplication of both modified-Katz’s thick smear and simple smear was performed for each fecal sample. To assess the intensity of helminthic infections, the number of eggs per gram (EPG) of soil-transmitted helminths species (
i.e., Ascaris lumbricoides, hookworm, and
Trichuris trichiura) was calculated following Katz et al. [
23].
The study procedures concerning human sample collection, laboratory investigation, interviewing, and questionnaire were reviewed and approved by National Ethics Committee for Health Research, Lao Ministry of Health (reference no. 51/NECHR). First, the investigator team conducted the meeting with local public health officers, village chief and local health volunteers to inform the details of the research study. Then, community amplifying system was used to spread the research activity in local language in every household. All participants who agreed to join the study were asked to read through the participant information sheet explaining about the objectives, procedures, possible risks, and benefits of the research project. The signed consent/assent forms were consequently obtained from either participant themselves or children’s guardians prior to fecal sample submission and personal information taking through interviewing and questionnaire. All participants infected with intestinal parasites (helminths and protists) were informed of the diagnostic results and subjected for treatment under control by either qualified clinicians from the investigator team or local doctors from Luang Prabang Hospital, Lao PDR.
Interview and questionnaire
All participants providing fecal samples were interviewed and completed a questionnaire to enable the collection of epidemiological data, i.e., sanitary conditions, possession of pet at home, food consumption habits, source of water consumption, and anti-parasitic treatment history. These data were merged with the personal and demographic informations (sex, age, address, educational level, and occupation) extracted from record of local primary health care units (PHCU).
Statistical analysis
Principal Component Analyses (PCA) were performed on (1) individual parasitic infections (helminths and protozoans) and (2) individual questionnaire (socio-economics and habits) of the villagers. These analyses were followed by a Canonical Analysis (CA) representing the correlations among the 2 sets of variables, i.e., socio-economics/habit and parasitic infections. Wilk’s lambda (Wilk’s L) was used to test how well each independent variable contributes to the statistical multivariate model. The scale of Wilk’s L ranges from 0 (full discrimination) to 1 (no discrimination). These analyzes were performed using the packages MASS version 7.3–45 [
24] and CCA version 1–2 embedded in R freeware [
25].
RESULTS
Demographic information of Ban Lak Sip inhabitants
The interviews and informations obtained from the PHCU in the village of Lak Sip allowed data to be obtained from 305 participants who had also been screened for parasitological data. Of these, 159 (52.1%) were males, and data was missing for 2 of the respondents. The average age of the population was 28.8± 19.9 years, reflecting the fact that it was mostly a young population with only a few individuals older than 60 years. In the analysis performed, we considered 4 age classes, i.e., (1) less than 15 years, (2) between 16 to 30 years, (3) between 31 to 45 years, and (4) greater than 45 years. The level of education achieved by most individuals was to the primary/early college level (69.2%), with only 13.4% having achieved a college qualification and 18% of the population being uneducated. Students comprised 29.2% of the respondents, 18.7% were farmers, 20% were dealers or merchants, and 21% were without paid employment. There was a significant association between gender and level of education, with men being formally educated to a higher level than women (chi-square= 10.05,
P < 0.05). The food consumption habits of the villagers of Lak Sip are summarized in
Table 1. In relation to sanitary conditions and preventive measures, 4.9% of the individuals did not use toilets, 10.5% did not systematically wear shoes, and 43.0% of the inhabitants had pets.
Our analysis indicated the presence of enteric pathogens in the water samples taken from the 3 water sampling sites in the vicinity of Lak Sip village as shown in
Table 2. Upon concentrating water samples and culturing on TSA media, we only detected
Aeromonas spp. at the upstream site. However, additional pathogens were found at the Lak Sip village site, including,
Aeromonas spp.,
E. coli H7,
E. coli O157:H7, VTEC, and
Vibrio spp., whereas the downstream site was positive for
Aeromonas spp.,
E. coli H7,
Shigella spp., VTEC,
Vibrio spp., and enteric adenovirus.
The water samples were negative for the other enteric pathogens detectable by the Seeplex ACE Diarrhea Detection kit, i.e., Salmonella spp., Clostridium difficile, C. perfringens, Campylobacter spp., Y. enterolitica, Group A rotavirus, norovirus GI/GII, and astrovirus.
Intestinal parasite infections
The overall prevalence of helminth infections was 68.9% and that of protist infections was 27.2%. Eight helminth species were identified, including 2 tapeworm species (
Taenia sp. and
Hymenolepis diminuta), 1 trematode (
Opisthorchis sp.), and 5 nematodes (
Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, Strongyloides stercoralis, trichostrongylids, and hookworms). The dominant parasite was hookworms which were present in 63.3% of the population. The intensities of soil-transmitted helminths,
A. lumbricoides, T. trichiura, and hookworms were assessed through calculation of the mean number of EPG as 1,132 (min= 23, max= 11,960), 148 (min= 23, max= 2,047), and 691 (min= 23, max= 6,279), respectively. Six species of protists were identified;
Blastocystis hominis, Cyclospora spp.,
Endolimax nana, Entamoeba histolytica/E. dispar, Entamoeba coli, and
Giardia lamblia. Blastocystis hominis was the most prevalent (14.8%). The details are given in
Table 3.
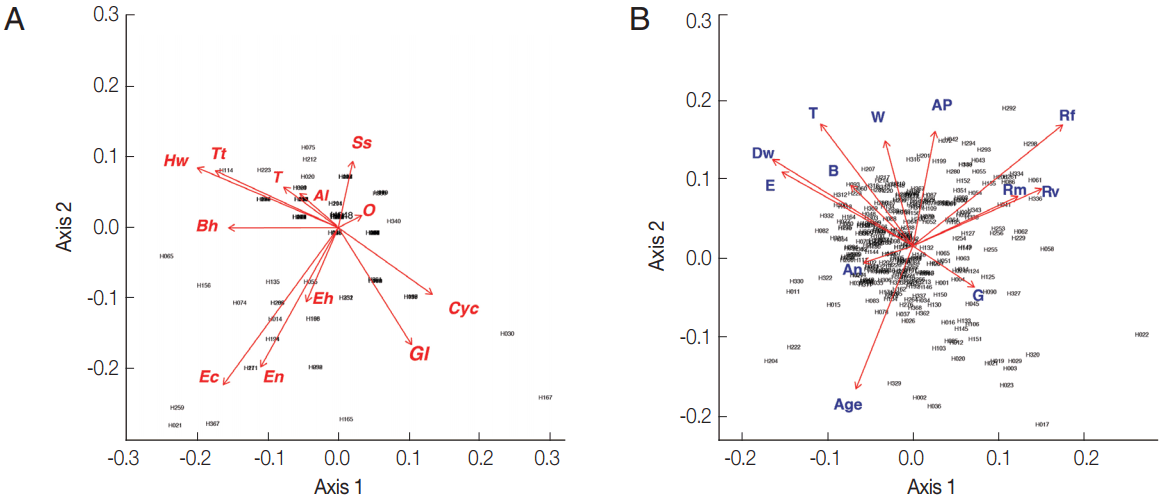
From the PCA results, the villagers of Lak Sip appeared very similar in their level and diversity of infection with intestinal helminths and protists, as well as for their socio-economics and/or habits using questionnaire responses (
Fig. 2). The bip-lot shows no clear clustering pattern (scattered directions of parameters or vector arrows pointing in) for both intestinal parasite infection of individual inhabitants (
Fig. 2A) and distribution of socioeconomic data/attitude among the inhabitants (
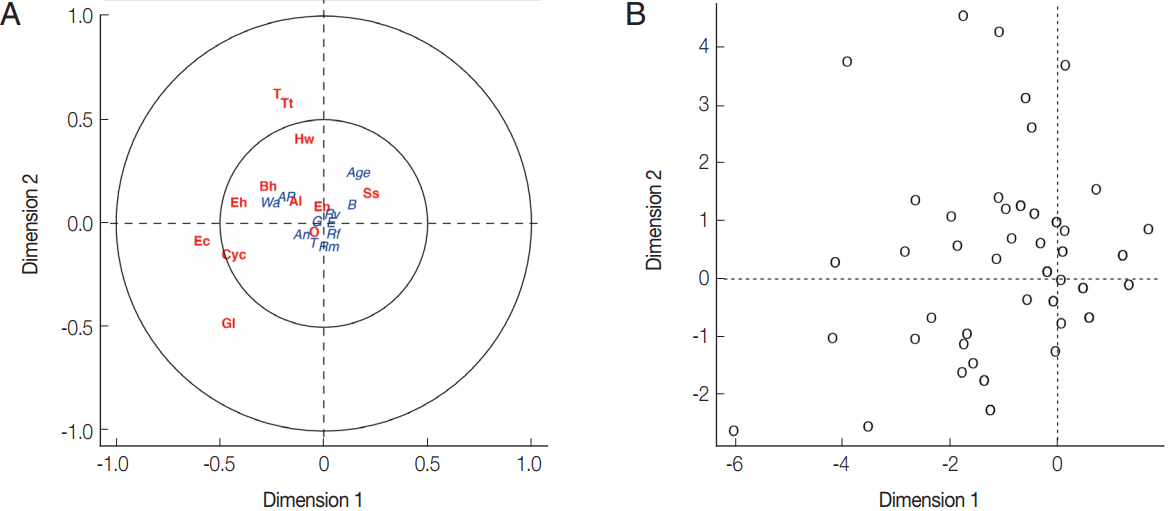
Fig. 2B). Parasite infections showed a weak correlation with socio-economic as only the first canonical dimension being significant (Wilks L= 0.004,
Fig. 3). Since Wilk’s L value is closed to zero revealing association between
S. stercoralis infection with the lack of footwear and the age, i.e., higher infection in medium age classes (16–45 years old) than the younger class (< 15 years) and elderly (> 45 years).
DISCUSSION
The present study conducted surveys of intestinal parasites and pathogenic microbes in clinical samples and the environment, respectively from Lak Sip, Luang Prabang province, Lao PDR. Diversity of intestinal parasites and their infection status in the villagers as well as potential water-borne pathogens found in the area of the village were discussed.
The microbiological and virological survey of water samples showed that they were contaminated with enteric pathogens, with up to 5 pathogens detected simultaneously in some samples. As expected, the monsoon period has a wash out effect, bringing soil and other matrix borne pathogens into the water source. Of notable interest was the correlation between contamination levels and degree of sediments and human activity. At the upstream site where human traffic was low, the water samples were relatively clean and clear, with only
Aeromonas spp. detected. With increased human activity at the Lak Sip village and the downstream site, the levels of sedimentation as well as contamination in the water samples were significantly higher. Pathogens detected at the village included
Vibrio spp.,
E. coli H7,
E. coli O157: H7, and VTEC, which are known to cause severe gastrointestinal disease in the human population. At the downstream site,
Shigella spp. and enteric adenovirus were detected in addition to those pathogens detected at Lak Sip village. It was also observed that the water samples from the latter 2 downstream sites were rich in sediments and flocculated suspended particles which may account for the greater pathogen diversity. The correlation between pathogen types and sediment was reported [
26] as sediments are reservoirs for pathogens. It may be possible that human activities that generate and unsettle sediment gave rise to the higher pathogen counts in the downstream sites.
The presence of such enteric pathogens in the water sources at the Lak Sip village indicated that outbreaks of gastrointestinal diseases with bacterial or virological origins amongst the population could potentially be high. This should be ascertained by bio-surveillance studies conducted on the population in the future. Similarly, water sampling strategy should also take into account concentration of pathogens in sediments or other deposits to obtain a more comprehensive estimate for public health risk.
The most prevalent intestinal parasite found in human feces was hookworms (63.3%), which were also the most prevalent nematode in the Lao PDR study of Eom et al. [
7], see also Niamnuy et al. [
6]. This soil-transmitted helminth has a direct life cycle and the main route of exposure is contact with larvae contaminated soil due to lack of footwear.
Strongyloides stercoralis has a different life cycle but also infects humans by penetration of the skin by larvae when contact is made with the contaminated soil. However, its observed prevalence (4.59%) was much lower than that of hookworms. Other soil-transmitted helminths with significant prevalence were
A. lumbricoides (4.3%) and
T. trichiura (22.0%). Preventive measures should be taken to improve the health of the people against such helminths.
Special mention should be made on the finding of
H. diminuta in human feces in this study as the available information regarding its parasitizing of humans is still limited. The presence of the rat tapeworm
H. diminuta in humans is rare, occurring only in isolated cases [
27] as it is the result of accidental ingestion of infected coprophilic arthropods. For example, a coprological study of more than 6,000 residents across Lao PDR was not able to detect this cestode [
7]. However,
H. diminuta was detected in primary schoolchildren in Laos at the level of 0.04% [
8] and at the level of 2.7% in random population sampling [
4]. The presence of
H. diminuta in rodents was established previously in the same village [
28] so its transmission to humans is unsurprising.
A single individual harbored trichostrongylids, and human trichostrongylosis has recently been reported in Laotians that were found to be infected by
Trichostrongylus colubriformis, identified and confirmed by molecular techniques [
17,
18]. This helminthiasis is contracted by a close contact with farm animals. The prevalence of 4.6% reported by Conlan et al. [
10] was higher than 0.33% found in our study.
It was found that the study participants consumed little raw or undercooked fish (3.0%), partially explaining the low incidence of opisthorchiasis (0.66%) compared with the much higher prevalence found in other rural communities across Lao PDR and Thailand. Apart from opistorchiasis, other fish-borne helminth infections commonly detected in Lao PDR were also not detected in this study [
7]. This could be because our study site is located geographically further away from the areas with reportedly higher incidence [
7]. The detection of taeniid eggs at our study site, 2 species had previously been detected in Lao PDR,
T. solium and
T. saginata with a prevalence of 2.95% is in accordance with an earlier study that found a prevalence of 1.5% [
7]. In an earlier study, 2 taeniid species (
T. solium and
T. saginata) had also been detected in Lao PDR [
11]. As the intermediate hosts of taeniids include pigs and cattle, and infection with taeniid species is associated with consumption of undercooked or raw meat, this suggests evidence that meat forms a major component of the dietary intake of the study population. Efforts should be made to educate the population in this village on the importance of properly cooked meat to safeguard against such tapeworm infections.
The 6 intestinal protists from the present study were mostly identifiable by their morphology and key characteristics (e.g., size, shape, number of nucleus, chromatoid bar, vacuolation, flagella, and cilia), except
E. histolytica/E. dispar as they are morphologically identical. The former one,
E. histolytica is known to cause severe gastrointestinal disorders in humans, whereas the latter species,
E. dispar has been characterized as non-pathogenic amoeba [
29]. Further species diagnoses such as serological and molecular methods are required to discriminate the 2 species.
In terms of disease epidemiology, some of the detected protists, known as agents for diarrheal diseases, were commonly associated with the consumption of contaminated water or food which contained traces of human and/or animal feces. Eighty percent of the population drank bottled water, illustrating that there were other ways in which waterborne parasites can be transmitted. We note that the failure to use appropriate toilet facilities can increase this risk and close contact with pet animals is also a risk factor for low host specific protozoans. Intestinal protozoans were common in Lak Sip village with a considerable diversity that can be compared with similar recent studies in the region, e.g., 4 protist species were found in schoolchildren in Myanmar from 821 analyzed samples [
30], and 3 species in Thailand were found from 236 examined samples [
31]. In addition, there were some other recent studies in rural communities that detected 6 protist species in Northeast Thailand from 253 stool samples [
32] and in Cambodia from 218 stool samples [
33]. In Lao PDR, studies have been limited, although the 4 species
B. hominis, E. coli, G. intestinalis, and
E. nana reported in a previous study [
4] were all recorded in the present study.
The PCA analysis showed a homogeneous distribution of intestinal parasites and risk habits across the population (
Figs. 2,
3), with very few noticeable differences between groups of individuals. These results suggested that a population with well rooted traditional habits, limited socio-economic differences, and lack of access to a public health system result in most of the population being exposed to parasites to a similar degree.
Despite the high intestinal parasitic infections of the inhabitants of Lak Sip village, little information of subclinical or mild abdominal symptoms, e.g., abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation were obtained from interviews. However, a curative treatment was then prescribed by local physicians from Luang Prabang provincial hospital. All patients with positive helminths were delivered treatments for nematodes and/or flatworms according to the helminth egg counts in their stools. Moreover, 4 people with high protist infections were invited for a medical visit at the hospital for further specific treatment.
In conclusion, interdisciplinary research approach (One Health) was implemented here in the study area, including medical and veterinary parasitology [
28], public health and medicine, environmental microbiology, and social science. The present study revealed not only a high diversity of intestinal helminths and protists in Ban Lak Sip inhabitants, but also several pathogenic microbes which were detected in the local river, a natural water source for consumption in the village. Accidental consumption of infective stages of helminths and protists as well as enteric bacteria and viruses from the stream are common risk sources of intestinal infection for Lak Sip inhabitants. Through the analysis of interviews and questionnaires, these parasitic infections highlighted the poor hygienic conditions and the need of local public health improvement. More efforts from local administration are required for prevention strategies to minimize intestinal parasite infection, particularly health education campaigns for villagers, for the improvement of sanitation conditions and consequently the general health of the villagers.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We have no conflict of interest related to this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to thank the leader and people of the village of Lak Sip (Luang Prabang) for their cooperation in this study. We thank the IRD/NAFRI field station and specially Mr. Bounsamay Soulileuth for his precious help for introduction to the community. We would also like to thank Mr. Vongsavanh The-bphachanh, the Governor of Luang Prabang district, Dr. Ni-phone Somphaly, the Deputy Director of the Provincial Health Department, Dr. Bounthiam Siphada, the Director of the Provincial Hospital of Luang Prabang and Ms. Laddavone, a member of the laboratory staff of the Provincial hospital. Also, we would like to acknowledge the fecal examination team: Prof. Wanna Maipanich, Mrs. Somchit Pubampen, Mr. Srisuchart Mongkhonmu, and Mr. Nirundorn Homsuwan from Department of Helminthology, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University for their collaboration in the field. We thank our helpful driver, Mr. Sompote Temchuen for his hard work and dedication for the fieldwork. This study was funded by the French ANR CP&ES, grant ANR 11 CPEL 002 BiodivHealthSEA project (
www.biodivhealthsea.org). A. Ribas was partially supported by 2014-SGR-1241 from the Catalan Government (Spain).
Fig. 1Map showing location and geography of Bann Lak Sip village, Luang Prabang, Lao PDR.
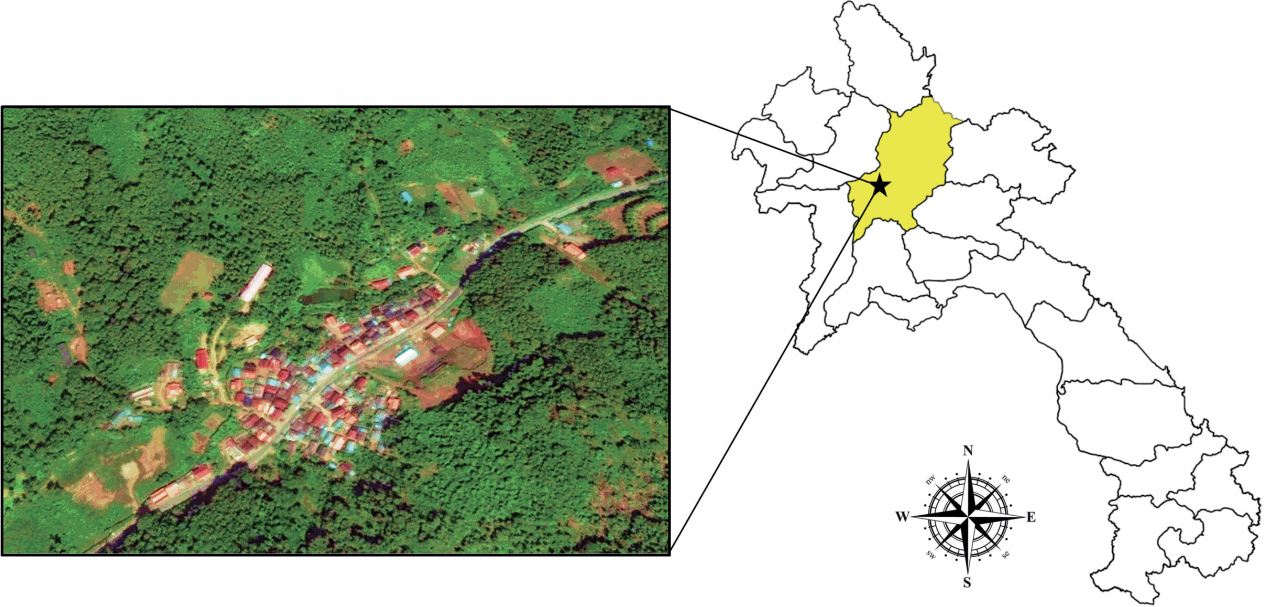
Fig. 2Biplot graphs show distribution of intestinal parasites in Bann Lak Sip villagers and their socioeconomic/attitudes (A) Principal Component Analyses of parasites and their distribution amongst the village inhabitants (the 2 first axes explaining 24% of the variance). (B) Principal Component Analyses of the socioeconomic/attitudes of villagers and their distribution amongst the inhabitants (the 2 first axes explaining 29% of the variance). Al, Ascaris lumbricoides; Hw, Hookworms; O, Opisthorchis sp.; Ss, Strongyloides stercoralis; T, Taenia sp.; Tt, Trichuris trichiura; Bh, Blastocystis hominis; Cyc, Cyclospora spp.; Ec, Entamoeba coli; Eh, Entamoeba hystolytica/E. dispar; En, Endolimax nana; Gl, Giardia lamblia; An, presence of domestic animals; AP, use of anti-parasitic drug; B, use of boots; Dw, type of drinking water; G, gender; E, level of education; Rf, consumption of raw fish; Rm, consumption of raw meat; Rv, consumption of raw vegetable; T, presence of toilet; W, origin of water for consumption.
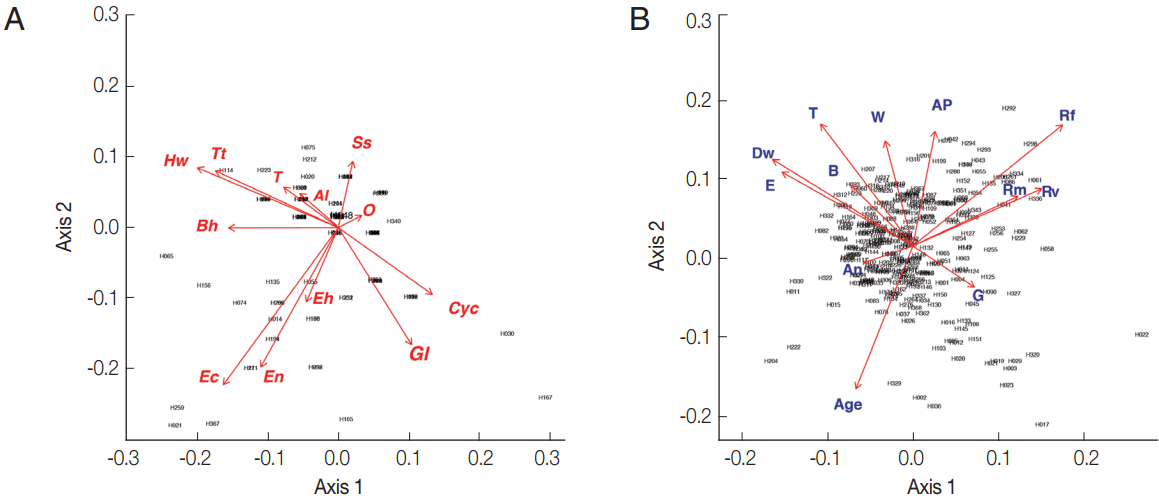
Fig. 3(A) Canonical analysis representation of the correlations between demographic/attitudes and intestinal parasite infection. (B) Canonical representation of the individuals. An, presence of domestic animals; AP, use of anti-parasitic drug; B, use of boots; G, gender; E, level of education; Rf, consumption of raw fish; Rm, consumption of raw meat; Rv, consumption of raw vegetable; T, presence of toilet; Wa, origin of water for consumption; Al, Ascaris lumbricoides; Hw, Hookworms; O, Opisthorchis sp.; Ss, Strongyloides stercoralis; T, Taenia sp.; Tt, Trichuris trichiura; Bh, Blastocystis hominis; Cyc, Cyclospora spp.; Ec, Entamoeba coli; Eh, Entamoeba hystolytica/E. dispar; En, Endolimax nana; Gl, Giardia lamblia.
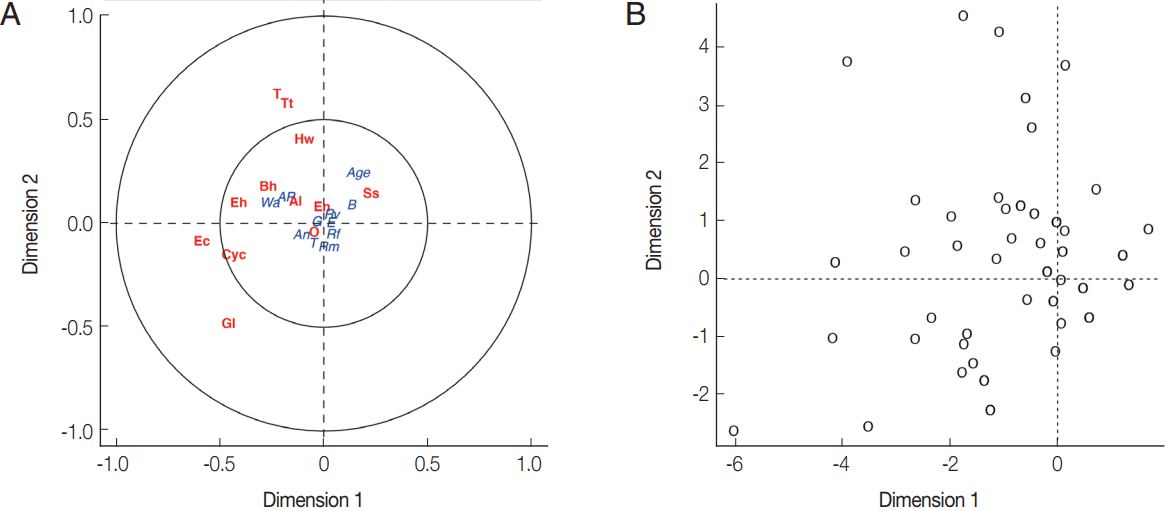
Table 1Description of the food consumption habits of Bann Lak Sip inhabitants
Table 1
|
Food habits (n=305) |
N |
Proportions (%) |
|
Fish consumption |
|
No |
59 |
19.3 |
|
Cooked |
236 |
77.4 |
|
Raw or undercooked |
9 |
3.0 |
|
N/A |
1 |
|
|
|
Fermented fish consumption |
|
No |
74 |
24.3 |
|
Cooked |
205 |
67.2 |
|
Raw or undercooked |
17 |
5.6 |
|
N/A |
9 |
|
|
|
Raw meat |
|
Yes |
79 |
25.9 |
|
No |
226 |
74.1 |
|
N/A |
0 |
|
|
|
Vegetables cooked |
|
Yes |
31 |
|
|
No |
274 |
10.2 |
|
N/A |
0 |
89.8 |
|
|
Source of drinking water |
|
Bottled |
248 |
81.3 |
|
Others (boiled/river) |
56 |
18.7 |
|
N/A |
1 |
|
|
|
Source of water for daily life |
|
River |
4 |
1.3 |
|
Mountain (collected) |
229 |
75.1 |
|
Wells |
72 |
23.6 |
|
N/Aa
|
0 |
|
Table 2Summary of pathogens detected in natural water sources from Lak Sip village, Lao PDR using various PCR assays
Table 2
|
Sampling site |
Sample source |
PCR detection |
Microbial pathogens |
|
Upstream |
Concentrated water |
Seeplex |
Negative |
|
Trypticase soy agar |
Seeplex |
Aeromonas spp. |
|
|
Lak Sip |
Concentrated water |
Seeplex |
Aeromonas spp., E. coli H7, and Vibrio spp. |
|
Trypticase soy agar |
Seeplex |
Aeromonas spp., E. coli H7, E. coli O157:H7, VTEC, and Vibrio spp. |
|
|
Downstream |
Concentrated water |
Seeplex |
Aeromonas spp., E. coli H7, Shigella spp., and enteric adenovirus |
|
Trypticase soy agar |
Seeplex |
Aeromonas spp., E. coli H7, VTEC, and Vibrio spp. |
Table 3Prevalence of helminths and protozoans in fecal samples obtained from 305 inhabitants of Lak Sip village, who participated in parasitological investigations
Table 3
|
Intestinal parasites |
% Prevalence (CI 95%)a
|
|
Helminths |
68.90 (63.7–74.0) |
|
Ascaris lumbricoides
|
4.26 (2.0–6.5) |
|
Hookworms |
63.30 (57.9–68.7) |
|
Hymenolepis diminuta
|
0.33 (−0.3–1.0) |
|
Opisthorchis sp. |
0.66 (−0.3–1.6) |
|
Strongyloides stercoralis
|
4.59 (2.2–6.9) |
|
Taenia sp. |
2.95 (1.1–4.9) |
|
Trichostrongylidae |
0.33 (−0.3–1.0) |
|
Trichuris trichiura
|
21.97 (17.3–26.6) |
|
|
Protozoans |
27.22 (22.2–32.2) |
|
Blastocystis hominis
|
14.80 (10.8–18.7) |
|
Cyclospora spp. |
0.98 (−0.1–2.1) |
|
Endolimax nana
|
2.95 (1.1–4.9) |
|
Entamoeba histolytica/E. dispar
|
2.62 (0.8–4.4) |
|
Entamoeba coli
|
6.56 (3.8–9.3) |
|
Giardia lamblia
|
6.56 (3.8–9.3) |
References
- 1. Hotez PJ, Brindley PJ, Bethony JM, King CH, Pearce EJ, Jacobson J. Helminth infections: the great neglected tropical diseases. J Clin Invest 2008;118:1311-1321.
- 2. Becker SL, Vogt J, Knopp S, Panning M, Warhurst DC, Polman K, Marti H, von Muller L, Yansouni CP, Jacobs J, Bottieau E, Sacko M, Rijal S, Meyanti F, Miles MA, Boelaert M, Lutumba P, van Lieshout L, N’Goran EK, Chappuis F, Utzinger J. Persistent digestive disorders in the tropics: causative infectious pathogens and reference diagnostic tests. BMC Infect Dis 2013;13:37.
- 3. Ammoura AM. Impact of hygienic level on parasite infection. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2010;3:148-149.
- 4. Sayasone S, Mak TK, Vanmany M, Rasphone O, Vounatsou P, Utzinger J, Akkhavong K, Odermatt P. Helminth and intestinal protozoa infections, multiparasitism and risk factors in Champasack Province, Lao People’s Democratic Republic. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2011;5:e1037.
- 5. Holt HR, Inthavong P, Khamlome B, Blaszak K, Keokamphe C, Somoulay V, Phongmany A, Durr PA, Graham K, Allen J, Donnelly B, Blacksell SD, Unger F, Grace D, Alonso S, Gilbert J. Endemicity of zoonotic diseases in pigs and humans in lowland and upland Lao PDR: identification of socio-cultural risk factors. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2016;10:e0003913.
- 6. Niamnuy N, Kaewthamasorn M, Congpuong K, Bounthanh B, Lohsoonthorn V. Prevalence and associated risk factors of intestinal parasites in humans and domestic animals across borders of Thailand and Lao PDR: focus on hookworm and threadworm. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2016;47:901-911.
- 7. Eom KS, Yong TS, Sohn WM, Chai JY, Min DY, Rim HJ, Jeon HK, Banouvong V, Insisiengmay B, Phommasack B. Prevalence of helminthic infections among inhabitants of Lao PDR. Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:51-56.
- 8. Rim HJ, Chai JY, Min DY, Cho SY, Eom KS, Hong SJ, Sohn WM, Yong TS, Deodato G, Standgaard H, Phommasack B, Yun CH, Hoang EH. Prevalence of intestinal parasite infections on a national scale among primary schoolchildren in Laos. Parasitol Res 2003;91:267-272.
- 9. Chai JY, Han ET, Guk SM, Shin EH, Sohn WM, Yong TS, Eom KS, Lee KH, Jeong HG, Ryang YS, Hoang EH, Phommasack B, Insisiengmay B, Lee SH, Rim HJ. High prevalence of liver and intestinal fluke infections among residents of Savannakhet Province in Laos. Korean J Parasitol 2007;45:213-218.
- 10. Conlan J, Khounsy S, Inthavong P, Fenwick S, Blacksell S, Thompson ARC. A review of taeniasis and cysticercosis in the Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Parasitol Int 2008;57:252-255.
- 11. Jeon HK, Yong TS, Sohn WM, Chai JY, Min DY, Yun CH, Rim HJ, Pongvongsa T, Banouvong V, Insisiengmay B, Phommasack B, Eom KS. Current status of human taeniasis in Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Korean J Parasitol 2013;51:259-263.
- 12. Okello AL, Ash A, Keokhamphet C, Hobbs E, Khamlome B, Dorny P, Thomas L, Allen J. Investigating a hyper-endemic focus of Taenia solium in northern Lao PDR. Parasit Vectors 2014;7:134.
- 13. Okello AL, Thomas L, Inthavong P, Ash A, Khamlome B, Keokamphet C, Newberry K, Gauci CG, Gabriël S, Dorny P, Thompson RA, Lightowlers MW, Allen J. Assessing the impact of a joint human-porcine intervention package for Taenia solium control: results of a pilot study from northern Lao PDR. Acta Trop 2016;159:185-191.
- 14. Soukhathammavong P, Sayasone S, Harimanana AN, Akkhavong A, Thammasack S, Phoumindr N, Choumlivong K, Choumlivong K, Keoluangkhot V, Phongmany S, Akkhavong K, Hatz C, Strobel M, Odermatt P. Three cases of intestinal capillariasis in Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2008;79:735-738.
- 15. Sayasone S, Tesana S, Utzinger J, Hatz C, Akkhavong K, Odermatt P. Rare human infection with the trematode Echinochasmus japonicus in Lao PDR. Parasitol Int 2009;58:106-109.
- 16. Odermatt P, Habe S, Manichanh S, Tran DS, Duong V, Zhang W, Phommathet K, Nakamura S, Barennes H, Strobel M, Dreyfuss G. Paragonimiasis and its intermediate hosts in a transmission focus in Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Acta Trop 2007;103:108-115.
- 17. Sato M, Yoonuan T, Sanguankiat S, Nuamtanong S, Pongvongsa T, Phimmayoi I, Phanhanan V, Boupha B, Moji K, Waikagul J. Human Trichostrongylus colubriformis infection in a rural village in Laos. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2011;84:52-54.
- 18. Phosuk I, Intapan PM, Sanpool O, Janwan P, Thanchomnang T, Sawanyawisuth K, Morakote N, Maleewong W. Molecular evidence of Trichostrongylus colubriformis and Trichostrongylus axei infections in humans from Thailand and Lao PDR. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2013;89:376-379.
- 19. Kobayashi J, Vannachone B, Xeutvongsa A, Manivang K, Ogawa S, Sato Y, Pholsena K. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infection among children in two villages in Lao PDR. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 1996;27:562-565.
- 20. Phetsouvanh R, Midorikawa Y, Nakamura S. The seasonal variation in the microbial agents implicated in the etiology of diarrheal diseases among children in Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 1999;30:319-323.
- 21. Chandler AC, Read CP. Introduction to Parasitology. 10th ed. New York, USA. John Wiley and Sons; 1962, pp 37-214.
- 22. Desowitz RS. Ova and Parasites: Medical Parasitology for the Laboratory Technologist. Maryland, USA. Harper and Row; 1980, pp 37-63.
- 23. Katz N, Chaves A, Pelegrino J. A simple device for quantitative stool thick smear technique in schistosomiasis mansoni. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 1972;14:397.
- 24. Venables WN, Ripley BD. Modern applied statistics with S-PLUS. 4th ed. New York, USA. Springer; 2002, p 462.
- 25. Team RC. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2014, R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2016.
- 26. Droppo IG, Liss SN, Williams D, Nelson T, Jaskot C, Trapp B. Dynamic existence of waterborne pathogens within river sediment compartments. Implications for water quality regulatory affairs. Environ Sci Technol 2009;43:1737-1743.
- 27. Patamia I, Cappello E, Castellano-Chiodo D, Greco F, Nigro L, Cacopardo B. A Human case of Hymenolepis diminuta in a child from eastern Sicily. Korean J Parasitol 2010;48:167-169.
- 28. Pakdeenarong N, Siribat P, Chaisiri K, Douangboupha B, Ribas A, Chaval Y, Herbreteau V, Morand S. Helminth communities in murid rodents from southern and northern localities in Lao PDR: The role of habitat and season. J Helminthol 2014;88:302-309.
- 29. Ngui R, Angal L, Fakhrurrazi SA, Lian YLI, Ling LY, Ibrahim J, Mahmud R. Differentiating Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar and Entamoeba moshkovskii using nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in rural communities in Malaysia. Parasit Vectors 2012;5:187.
- 30. Kim MJ, Jung BK, Cho J, Kim DG, Song H, Lee KH, Cho S, Htoon TT, Tin HH, Chai JY. Prevalence of intestinal protozoans among schoolchildren in suburban areas near Yangon, Myanmar. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:345-348.
- 31. Wongstitwilairoong B, Srijan A, Serichantalergs O, Fukuda CD, McDaniel P, Bodhidatta L, Mason CJ. Intestinal parasitic infections among pre-school children in Sangkhlaburi, Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2007;76:345-350.
- 32. Boonjaraspinyo S, Boonmars T, Kaewsamut B, Ekobol N, Laummaunwai P, Aukkanimart R, Wonkchalee N, Juasook A, Sriraj P. A cross-sectional study on intestinal parasitic infections in rural communities, northeast Thailand. Korean J Parasitol 2013;51:727-734.
- 33. Schär F, Inpankaew T, Traub RJ, Khieu V, Dalsgaard A, Chimnoi W, Chhoun C, Sok D, Marti H, Muth S, Odermatt P. The prevalence and diversity of intestinal parasitic infections in humans and domestic animals in a rural Cambodian village. Parasitol Int 2014;63:597-603.