Abstract
A survey was performed to know the infection status of echinostome metacercariae in Cipangopaludina chinensis malleata snails from Korea. Total 75 snails collected in 5 localities, i.e., Imsil-gun, Jeollabuk-do, Hwasun-gun and Shinan-gun (Aphae and Jido), Jeollanam-do, and Jinju-si, Gyeongsangnam-do, were examined for metacercariae by the artificial digestion method. Infection rates of metacercariae were 80.0%, 66.7%, 100%, 60.0%, and 73.3%, and their densities were 39, 32, 183, 19, and 30 per snail infected, respectively. The metacercariae were round, 105–118×105–118 μm in size, with a thin cyst wall, collar spines on the head collar, and excretory granules in 2 canals of excretory tube. Adult flukes were elongated, ventrally curved, and 5,167×939 μm in average size. Head collar distinct, bearing 45 collar spines with 5 end groups on each side. Oral sucker subterminal, pharynx well developed, and esophagus somewhat short. Cirrus sac well developed, with a saccular seminal vesicle, and ventral sucker very large. Ovary elliptical and on the median line of the body. Testes tandem and slightly lobed. Eggs operculated, elliptical, and 90–103×55–60 μm in size. By scanning electron microscopy, the head collar was prominent with 45 collar spines resembling horns of younger stags. Scale-like tegumental spines were densely distributed on the body surface between the head collar and ventral sucker. Conclusively, it has been first confirmed that the life cycle of E. macrorchis is indigenously maintained in Korea, and C. chinensis malleata snails are popularly infected with the metacercariae of this echinostome.
-
Key words: Echinostoma macrorchis, Cipangopaludina chinensis malleata, metacercaria, adult, Korea
INTRODUCTION
Echinostomes (fluke members of the family Echinostomatidae) are medically important because they can cause severe epigastric or abdominal pain accompanied by diarrhea, malnutrition, and fatigue. A total of 20 species belonging to 8 genera, i.e
., Echinostoma, Echinochasmus, Acanthoparyphium, Artyfechinostomum, Episthmium, Himasthla, Hypoderaeum, and
Isthmiophora, are known to infect humans worldwide. Among these 8 genera,
Echinostoma is the type genus and the largest group. More than 6 species, i.e.,
Echinostoma angustitestis, E. cinetorchis, E. echinatum, E. ilocanum, E. macrorchis, and
E. revolutum are known to infect humans [
1,
2].
E. macrorchis was originally described from naturally infected house rats in Japan [
3]. After then, this echinostome has been found in humans, birds, and other rodent species in Japan [
4–
8]. In Taiwan and Lao PDR, the presence of this fluke species was also confirmed by the detection of adults and larval stages [
9–
12].
In the Republic of Korea (= Korea), total 21 echinostome species in 14 genera, i.e.,
Acanthoparyphium marilae, A. tyosenense, Chaunocephalus ferox, Echinochasmus japonicus, E. perfoliatus, Echinoparyphium recurvatum, Echinostoma cinetorchis, E. gotoi, E. miyagawai, E. revolutum, Euparyphium murinum, Himasthla alincia H. kusasigi, H. megacotyle, Isthmiophora hortensis, Nephrostomum ramosum, Patagifer bilobus, Pegosomum bubulcum, Petasiger neocomense, Saakotrema metatestis, and
Stephanoprora sp., have been reported in the literature [
1,
13–
16]. Only 4 of these species, i.e.,
A. tyosenense, E. japonicus, E. cinetorchis, and
I. hortensis, are known to be the causative agents of human echinostomiasis in Korea [
1]. Especially,
I. hortensis has been reported as the dominant species with several endemic foci [
17–
20], and clinical cases which have been sporadically diagnosed by recovery of adult worms in gastroduodenal endoscopy [
21–
25]. Meanwhile, the presence of
E. macrorchis had not been reported in Korea. Therefore, we seriously needed to describe the infection status of metacercariae of this species in snail second intermediate hosts as well as the morphological characteristics of adults recovered from experimental rats to support its taxonomic validity in the faunistic view point.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We collected
Cipangopaludina chinensis malleata snails (
Fig. 1) in irrigation ditches, ponds, and paddies in 5 localities, i.e., Imsil-gun (gun=county), Jeollabuk-do (do=province), Hwasun-gun and Shinan-gun (Aphae-myeon and Jido-myeon) (myeon = township), Jeollanam-do, and Jinju-si (si= city), Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea. They were transferred to our laboratory with ice, and digested with pepsin-HCl solution at 36°C for 2 hr after crushing their shells with a mortar. The digested material was filtered with 1× 1 mm of mesh, and washed with 0.85% saline until the supernatant is clear. The sediment was carefully examined under a stereomicroscope. The echinostome metacercariae were identified by the general morphological features, and they were counted to get hold of infection rates (%) and densities (no. of metacercariae per snail infected) by the surveyed areas. Collected metacercariae by the surveyed areas were morphologically observed and measured under a light microscope equipped with a micrometer (OSM-4, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), and they were orally infected to rats to obtain the adult worms. Adult worms were recovered from the small intestines of rats at 15–30 days after the infection. In animal experiments, the guidelines of animal experiments from Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine were followed.
Recovered adults were fixed with 10% neutral buffered formalin under the cover glass pressure, stained with Semichon’s acetocarmine, and observed under a light microscope. To observe the surface ultrastructure, some of them were washed several times with 0.2 M cacodylate buffer (pH 7.2) and fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde at 4°C. After washing 3 times with the buffer, they were dehydrated through a graded alcohol series (50, 70, 80, 90, 95%, and absolute), dried with hexamethyldisilazane, coated (JFC-1100E ion sputtering device, Tokyo, Japan) with gold, and observed with a scanning electron microscope (Philips XL-30S, Eindhoven, the Netherlands) at a 15 kV accelerating voltage.
To observe morphological characteristics and differential indices by the ages of worms, each of 10 E. macrorchis specimens recovered from experimental rats at 15, 20, 25, and 30 days after infection were analyzed in this study. We basically measured the body length (BL) and width (BW), the size of oral (OS) and ventral suckers (VS), pharynx, esophagus, head collar, cirrus sac, ovary, and 2 testes, and additionally the fore-body length (FBL: from the anterior end to the anterior margin of the ventral sucker), hindbody length (HBL: from the posterior margin of the posterior testis to the posterior end) and uterus length (UL: from the posterior margin of the ventral sucker to the anterior margin of the ovary). Then, we also calculated the ratios of BL/BW, VS/OS, the length/width in ovary and 2 testes, and percentage (%) of FBL/BL, HBL/BL, and UL/BL as the differential indices of this fluke. Measurements and scales are in micrometres (μm).
RESULTS
Infection status with metacercariae in Cipangopaludina chinensis malleata
The metacercariae of
E. macrorchis were detected in 80.0, 66.7, 100, 60.0, and 73.3% of
Cipangopaludina chinensis malleata snails collected from Imsil-gun, Hwasun-gun, Shinan-gun (Aphae and Jido), and Jinju-si, and their densities were 39, 32, 183, 19, and 30 per snail infected, respectively (
Table 1).
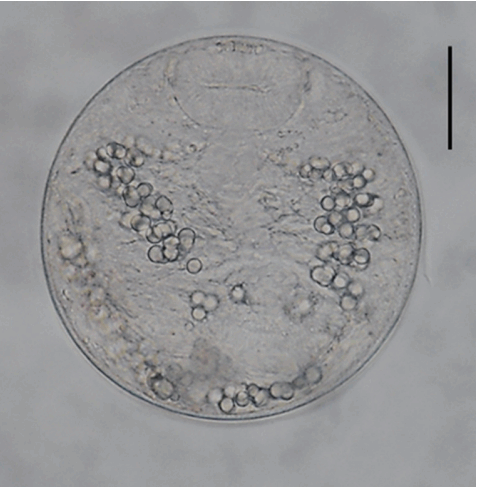
The metacercariae (n= 20) were round, 105–118 (110)× 105–118 (108) in size, with a thin cyst wall, collar spines distributed in the head collar and excretory granules in 2 descending canals of the main excretory tube.
Morphological characteristics of adult worms (Fig. 3)
Total 40 adults recovered from rats experimentally infected with the metacercariae from snails in Imsil-gun, Hwasun-gun, Shinan-gun (Aphae), Jinju-si, were measured and morphologically observed (
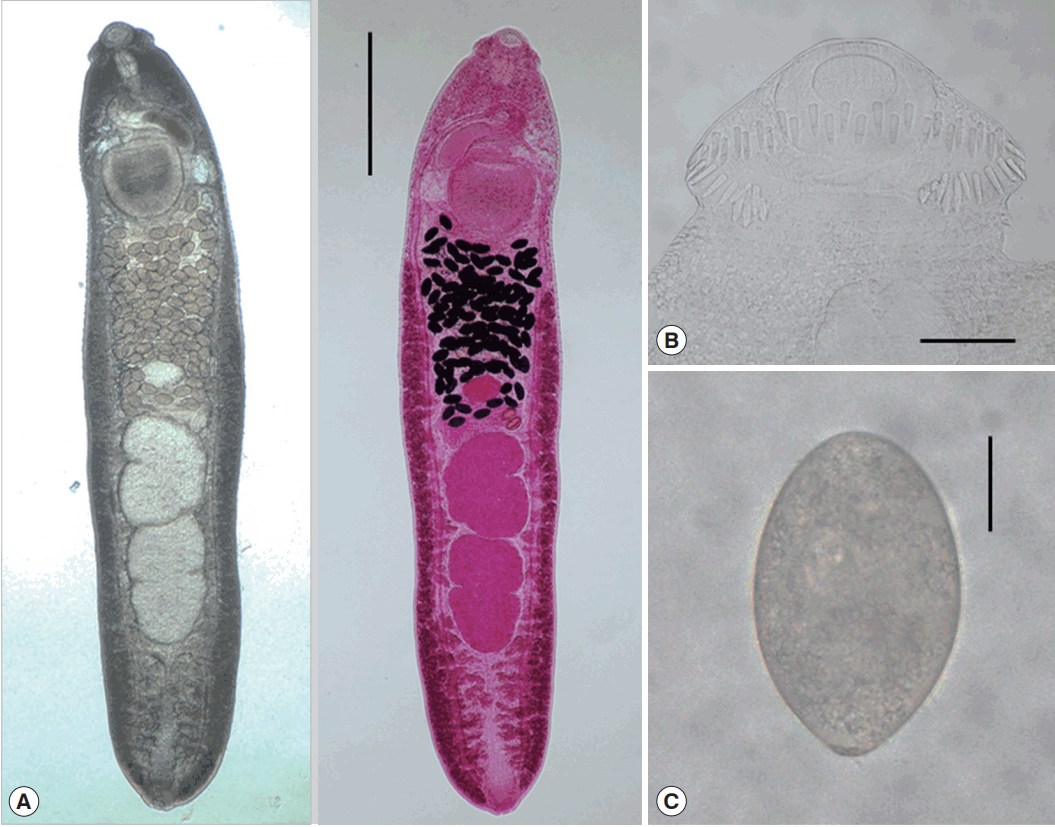
Table 2). They were elongated, ventrally curved, 3,950–6,000 (5,167) long and 700–1,175 (939) wide. Head collar distinct, 300–375 (334) in width, bearing 45 collar spines with 5 end group ones on each side. Oral sucker subterminal, 105–150 (123)× 150–185 (167) in size. Prepharynx very short. Pharynx well developed, 130–165 (150)× 95–130 (115) in size. Esophagus relatively short, 95–175 (135) long. Cirrus sac well developed, with a saccular seminal vesicle, 220–550 (410)× 85–225 (163) in size. Ventral sucker very large, 395–490 (441)× 405–490 (447) in size. Ovary elliptical, 150–290 (227) × 160–335 (250) in size, and on the median line of the body. Testes tandom slightly lobed, 460–990 (701)× 270–630 (427) (anterior testis) and 550–1,080 (821)× 280–550 (401) (posterior testis). Vitelline follicles bilaterally distributed from the anterior 1/3 level of uterine field to the posterior end. Numerous eggs contained in the uterus located between the posterior margin of ventral sucker and ovary. Eggs operculated, elliptical and 93–105 (99)× 53–64 (58) in size. Dimensions of
E. macrorchis by the age of worms are revealed in
Table 3.
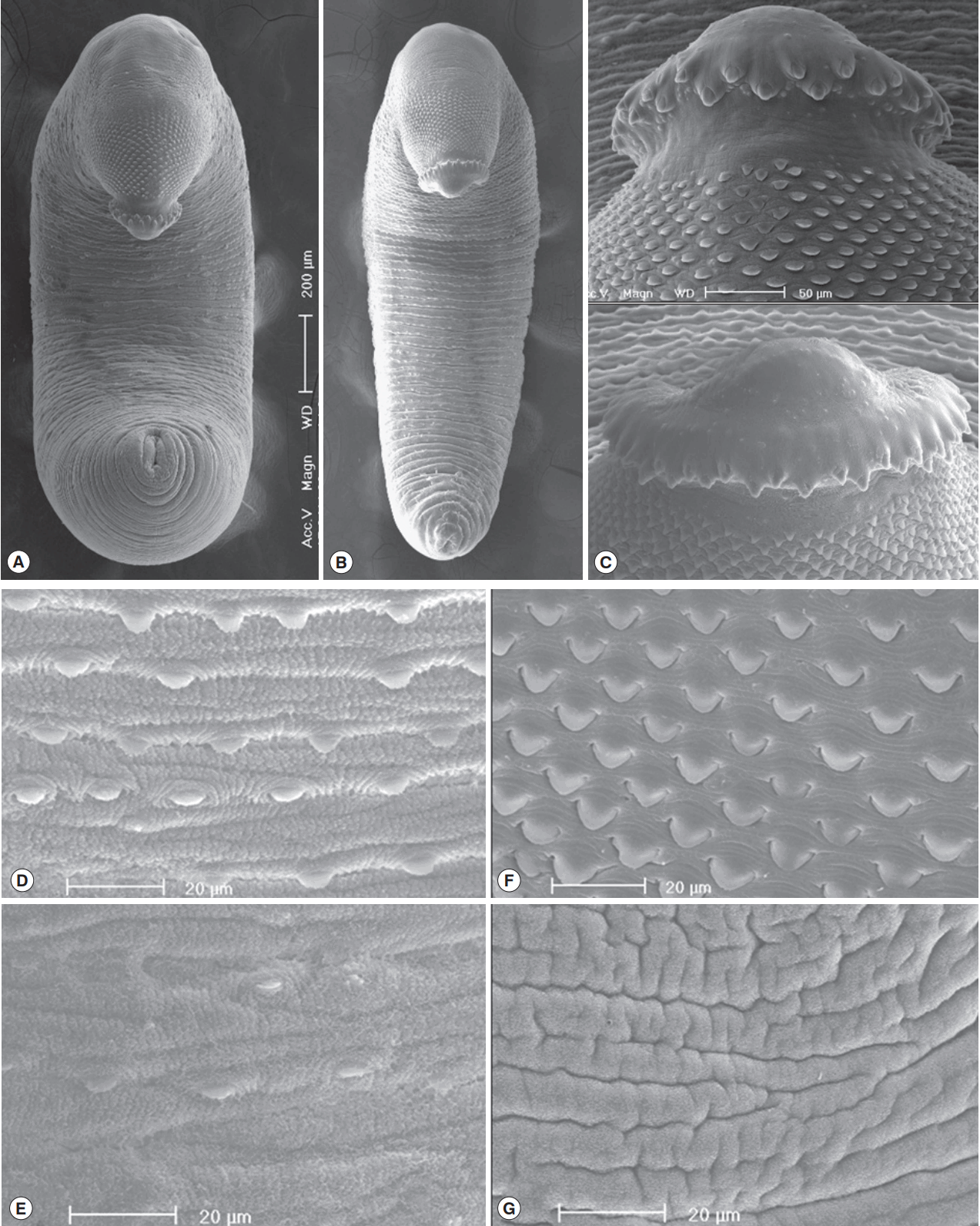
In SEM observations, adult worms were elongated, ventrally curved and had the largest width near the middle portion of the body (
Fig. 4A, B). The head collar was well-developed and prominent bearing total 45 collar spines. A dorsal view of the head collar showed 2 alternating rows of collar spines. Sensory papillae were distributed mainly on the tegument around the 2 suckers and head collar (
Fig. 4C). Scale-like tegumental spines were densely distributed on the body surface between the head collar and ventral sucker level (
Fig. 4F), and their densities decreased posteriorly on the ventral surface (
Fig. 4D, E). However, the dorsal tegument behind the ventral sucker level was devoid of spines (
Fig. 4G).
The ratio of body length (BL) to body width (BW) was 5.30–5.76 (5.56 in average). That of ventral sucker (VS) to oral sucker (OS) was 3.03–3.18 (3.10). The ratio of length (L)/width (W) in the ovary was 0.93–0.97 (0.95), that in the anterior testis was 1.57–1.89 (1.71), and in the posterior testis was 1.88–2.11 (1.99). The percentage of forebody length (FBL) to BL was 11.3–13.4 (12.5), and that of hindbody length (HBL) to BL was 18.9–21.9 (20.6). The percentage of uterine field (U) to BL was 25.4–31.5 (28.2) (
Table 4).
DISCUSSION
By the present study, it has been confirmed for the first time that the life cycle of E. macrorchis is indigenously maintained in Korea. Thus, this echinostome species is added among the list of Korean echinostome fauna.
Various species of molluscs, including
Assiminea, Biomphalaria, Bulinus, Cipangopaludina, Corbicula, Gyraulus, Hippeutis, Lymnaea, Physa, Segmentina, and
Thiara, and amphibians, such as frogs (
Rana spp.) and salamanders (
Hynobius sp.), have been reported as the second intermediate hosts of
E. macrorchis in Japan and Taiwan [
11,
26–
29]. Recently,
Cipangopaludina sp. snails from Vientiane Municipality, Lao PDR, was also confirmed to be the second intermediate host of
E. macrorchis [
12]. In the present study, it was revealed that
C. chinensis malleata are popularly infected with the metacercariae of this echinostome in Korea. Accordingly,
Cipangopaludina spp. snails are regarded as a suitable second intermediate host of
E. macrorchis in Japan, Taiwan, Lao PDR, and Korea. On the other hand, 2 species of freshwater snails, i.e.,
Segmentina hemisphaerula and
Gyraulus chinensis, are known to be the first intermediate host of
E. macrorchis in Japan and Taiwan [
11,
29]. To complete the life history of this echinostome in Korea, studies on the first intermediate hosts should be accomplished in near future.
Adults of
E. macrorchis have been collected naturally in the rodent definitive hosts (
Apodemus spp.,
Microtus montebelli, Mogera spp., and
Rattus spp.), avian host (
Capella gallinago gallinago), and even in humans [
3–
10]. They were also recovered experimentally in rats, mice, and cats infected with the metacercariae [
12,
26,
30–
32]. In the present study, we used albino rats of Sprague-Dawley strain as the experimental definitive host. The recovered worms were well developed in the small intestines of these rats. Therefore, albino rats are considered a suitable experimental animal model for
E. macrorchis infection. In addition, it is seriously needed to trace the presence of human infections and natural definitive hosts through further studies in Korea.
The metacercariae of
E. macrorchis were 105–118 (110)× 105–118 (108) in size in the present study. They were smaller than those from other countries, i.e., Taiwan (122× 118), Lao PDR (121× 120), and Japan (139–159× 99–120). The metacercariae from Taiwan were almost the same in size as those from Lao PDR. Then, the metacercariae from 3 countries were nearly round shape, whereas those from Japan were elliptical in shape [
11,
12,
33]. Whether these differences were originated from the geographical variation and whether they are of taxonomical significance should be analyzed through further studies, including comparative morphological and molecular genetic ones with each isolate from 4 countries.
Total 40 adult worms recovered from the small intestines of rats infected with the metacercariae from 4 surveyed areas were more or less elongated body, and 3.95–6.0 (5.17)× 0.70–1.18 (0.94) mm in size. They had a well-developed head collar with 45 collar spines, including 5 end groups on each side, and their uterine tubules are long with numerous eggs. The ratio of BL/BW was about 5.50. The morphological characteristics of our specimens were almost similar with those of Sohn et al. [
12]: 3,900–6,300 (5,100)× 730–1,050 (900) in size, the ratio of BL/BW about 5.67, and the number of collar spines. However, the size of eggs was more or less larger in our specimens (93–105×53–64) than in Sohn et al. [
12] (88–98×55–61). However, we were able to assign our specimens to
E. macrorchis among the members of
Echinostoma with 43–45 collar spines, i.e.,
E. academica, E. aegyptiaca, E. attenuatum, E. australasianum, E. azerbaidjanicum, E. coromandum, E. coronale, E. dietzi, E. gotoi, E. macrorchis, and
E. phasianina [
34–
40].
On the basis of data from 40 worms, which were recovered from experimental rats at 15, 20, 25, and 30 days after infection in the present study, the following diagnostic features are considered as the differential indices for E. macrorchis. The worm body is long and slender (the ratio of BL/BW: 5.30–5.76); the ventral sucker is larger about 3 times than the oral sucker (the ratio of VS/OS: 3.03–3.18); the ovary is transversely elliptical (the ratio of L/W in the ovary: 0.93–0.97); the anterior testis has a long vertical axis (the ratio of L/W in the anterior testis: 1.57–1.89); the posterior testis has a more longer vertical axis than anterior one (the ratio of L/W in the posterior testis: 1.88–2.11); short forebody (% of FBL/BL: 11.3–13.4); short hindbody (% of HBL/BL: 18.9–21.9); long uterine field (% of UL/BL: 25.4–31.5); the head collar with 45 collar spines, including 5 end groups on each side.
Conclusively, through the present study, the presence of E. macrorchis has been confirmed for the first time in Korea, and it has also been confirmed that C. chinensis malleata snails are popularly infected with the metacercariae of this echinostome as a suitable second intermediate host. Additionally, the morphological characteristics with differential indices derived from numerous age-controlled worm samples were described to support the taxonomic validity of E. macrorchis.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest concerning the work reported in this paper.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Jung-A Kim and Hee-Joo Kim, Department of Parasitology, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea, for their help in collection and examination of the snails, and recovery of adult worms from rats experimentally infected with the metacercariae.
Fig. 1Two Cipangopaludina chinensis malleata snails, the second intermediate host of Echinostoma macrorchis, collected from a pond in Jinju-si, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea.

Fig. 2A metacercariae of Echinostoma macrorchis detected in a snail from Jinju-si, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea. Scale bar=30 μm.
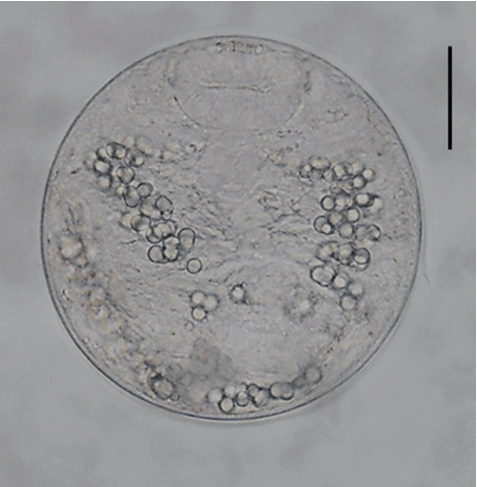
Fig. 3Adult worm of E. macrorchis (ventral view: fresh unstained and dorsal view: Semichon’s acetocarmine stained) recovered from an experimental rat at 18 days after infection (A). Scale bar=1,000 μm. Head collar with 45 collar spines, including 5 end groups on each side (B). Scale bar=100 μm. An egg discharged in the feces of a rat experimentally infected with metacercariae (C). Scale bar=30 μm.
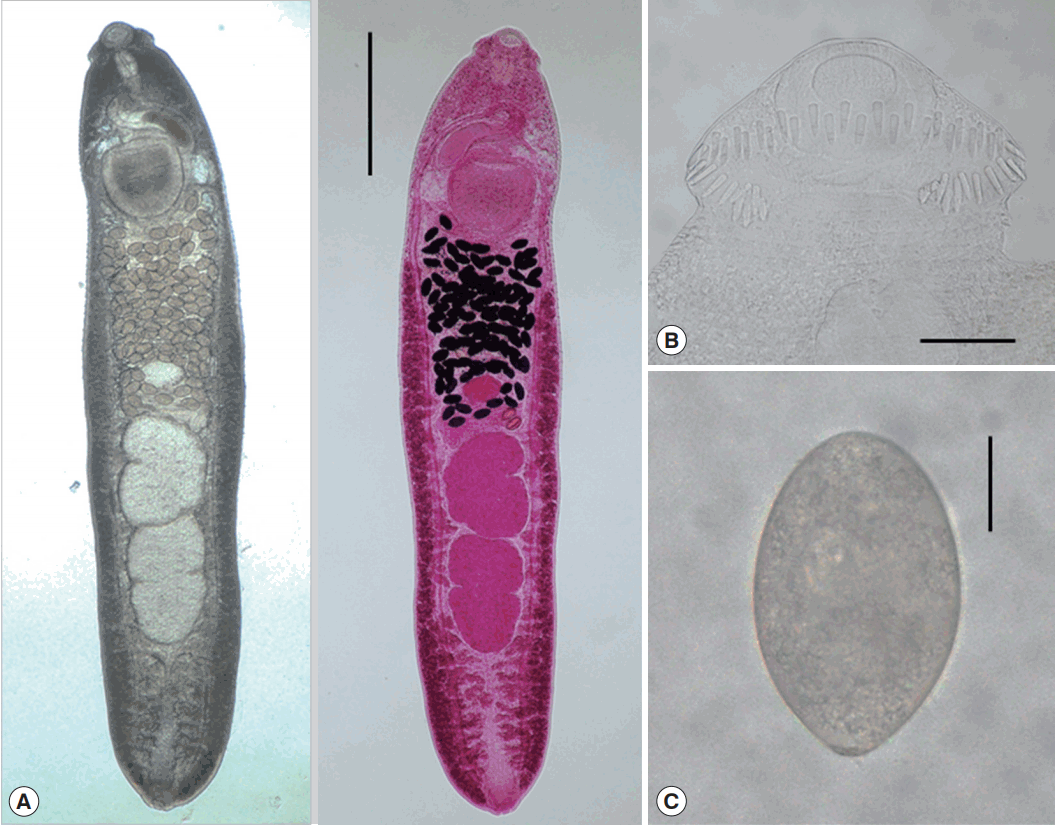
Fig. 4Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) view of E. macrorchis adults. Whole ventral view of the worms originated from Hwasun-gun (A) and Jinju-si (B). Dorsal views of the head collar with collar spines alternatively arranged (C). Tegument with numerous scale-like spines on the ventro-anterior surface, just behind the ventral sucker (D), and dorso-anterior body surface (F), with spines sparsely distributed on the ventro-middle surface (E), and no spines on the dorso-middle body surface (G).
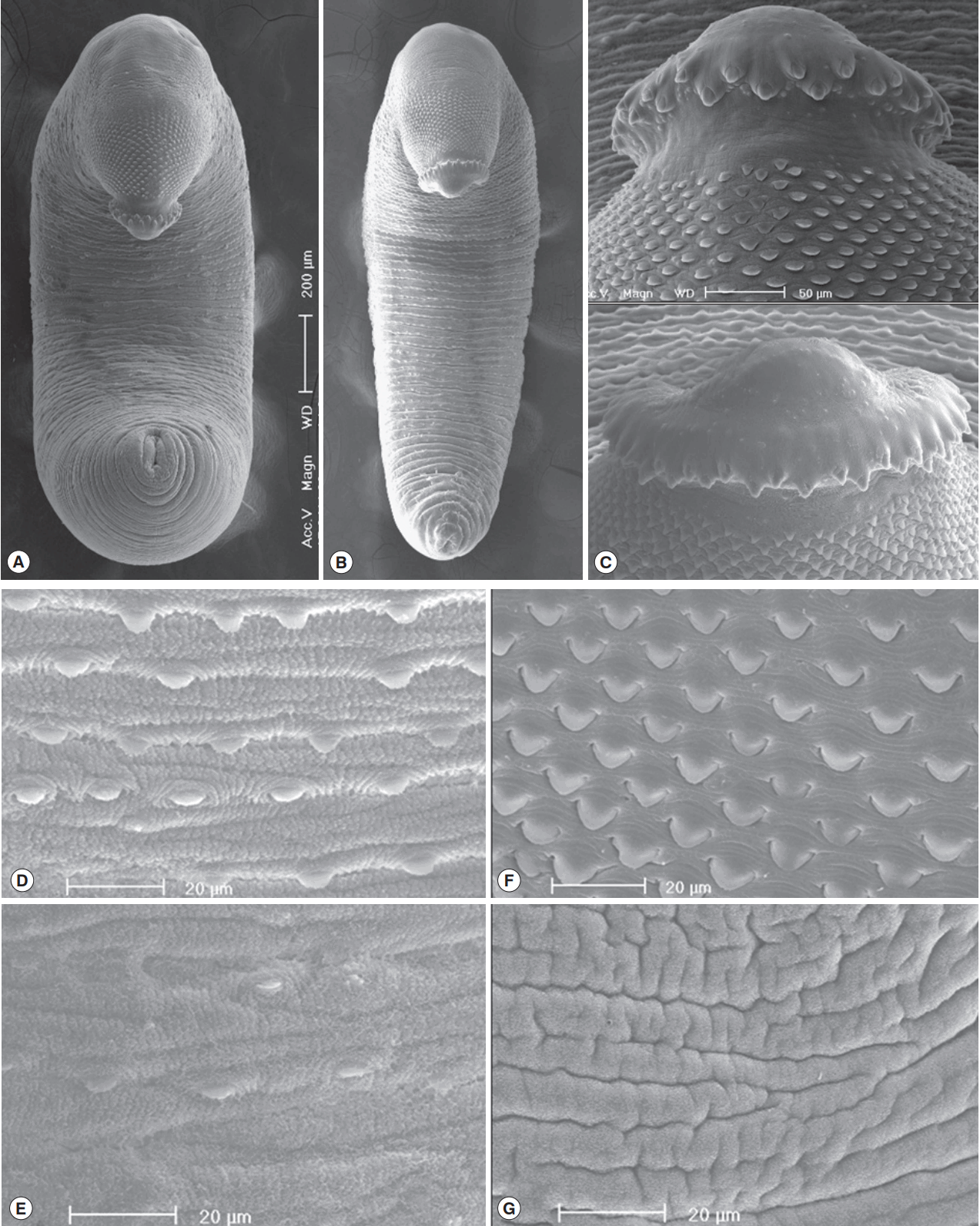
Table 1Infection status of Echinostoma macrorchis metacercariae in Cipangopaludina chinensis malleata collected from 5 localities of Korea
Table 1
|
Locality examined |
No. of snails examined |
No. (%) of snails infected |
No. of metacercariae detected |
|
|
Total |
Range |
Average |
|
Jeollabuk-do |
|
Imsil-gun |
15 |
12 (80.0) |
464 |
8–86 |
39 |
|
|
Jeollanam-do |
|
Hwasun-gun |
15 |
10 (66.0) |
322 |
5–107 |
32 |
|
Shinan-gun (Aphae) |
15 |
15 (100) |
2,741 |
38–412 |
183 |
|
Shinan-gun (Jido) |
15 |
9 (60.0) |
14 |
2–48 |
19 |
|
|
Gyeongsangnam-do |
|
Jinju-si |
15 |
11 (73.3) |
325 |
10–115 |
30 |
Table 2Dimensionsa of Echinostoma macrorchis adults recovered from rats experimentally infected with metacercariae from Cipango-paludina snails from 4 localities of Korea
Table 2
|
Organs |
Imsil-gunb, Jeollabuk-do |
Hwasun-gunc, Jeollanam-do |
Shinan-gund, Jeollanam-do |
Jinju-sie, Gyeongsangnam-do |
Total |
|
Body (L) |
4,075–5,700 (4,718) |
3,950–5,750 (5,178) |
4,550–6,000 (5,363) |
4,850–5,950 (5,408) |
3,950–6,000 (5,167) |
|
(W) |
700–1,175 (818) |
750–1,175 (1,013) |
825–1,000 (948) |
925–1,050 (978) |
700–1,175 (939) |
|
|
Oral sucker (L) |
105–135 (121) |
110–135 (123) |
105–135 (121) |
115–150 (125) |
105–150 (123) |
|
(W) |
150–175 (160) |
150–180 (168) |
160–185 (172) |
155–180 (168) |
150–185 (167) |
|
|
Head crown (W) |
300–355 (321) |
300–355 (333) |
315–375 (343) |
315–355 (337) |
300–375 (334) |
|
Pharynx (L) |
135–150 (142) |
130–165 (154) |
135–160 (151) |
145–165 (154) |
130–165 (150) |
|
(W) |
100–125 (113) |
95–130 (117) |
105–115 (112) |
105–130 (117) |
95–130 (115) |
|
|
Esophagus (L) |
100–160 (135) |
95–150 (131) |
110–160 (136) |
105–175 (139) |
95–175 (135) |
|
Ventral sucker (L) |
395–485 (438) |
400–490 (458) |
410–460 (433) |
425–440 (434) |
395–490 (441) |
|
(W) |
405–455 (433) |
425–490 (455) |
425–485 (455) |
425–470 (445) |
405–490 (447) |
|
|
Cirrus sac (L) |
220–375 (294) |
330–475 (412) |
410–525 (462) |
425–550 (471) |
220–550 (410) |
|
(W) |
85–160 (119) |
140–225 (176) |
155–225 (174) |
150–225 (181) |
85–225 (163) |
|
|
Ovary (L) |
150–250 (188) |
180–275 (223) |
200–275 (231) |
225–290 (264) |
150–290 (227) |
|
(W) |
160–335 (211) |
160–325 (275) |
220–275 (238) |
250–305 (276) |
160–335 (250) |
|
|
Anterior testis (L) |
460–870 (588) |
540–990 (765) |
630–900 (740) |
590–850 (710) |
460–990 (701) |
|
(W) |
270–630 (360) |
320–550 (464) |
400–470 (443) |
390–470 (439) |
270–630 (427) |
|
|
Posterior testis (L) |
550–950 (715) |
640–1,080 (917) |
760–1,000 (826) |
700–900 (826) |
550–1,080 (821) |
|
(W) |
280–550 (332) |
300–480 (431) |
400–450 (419) |
370–460 (422) |
280–550 (401) |
Table 3Dimensions
a of
Echinostoma macrorchis adults recovered from rats experimentally infected with metacercariae from
Cipangopaludina snails of Shinan-gun, Jeollanam-do
Table 3
|
Organs |
15-day-old (n=10) |
20-day-old (n=10) |
25-day-old (n=10) |
30-day-old (n=10) |
|
Body (L) |
4,300–4,775 (4,495) |
4,550–6,000 (5,363) |
4,400–6,325 (5,303) |
5,500–6,800 (6,265) |
|
(W) |
725–950 (848) |
825–1,000 (948) |
850–1,200 (920) |
1,050–1,250 (1,135) |
|
|
Oral sucker (L) |
100–125 (113) |
105–135 (121) |
110–135 (119) |
120–140 (132) |
|
(W) |
140–170 (155) |
160–185 (172) |
155–180 (170) |
155–200 (178) |
|
|
Head crown (W) |
285–325 (311) |
315–375 (343) |
315–360 (348) |
325–400 (354) |
|
Pharynx (L) |
125–150 (141) |
135–160 (151) |
150–160 (154) |
150–175 (160) |
|
(W) |
85–110 (99) |
105–115 (112) |
105–125 (119) |
105–145 (126) |
|
|
Esophagus (L) |
105–160 (129) |
110–160 (136) |
115–160 (131) |
110–160 (134) |
|
Ventral sucker (L) |
380–420 (399) |
410–460 (433) |
435–470 (449) |
455–525 (482) |
|
(W) |
390–440 (412) |
425–485 (455) |
430–500 (470) |
460–515 (494) |
|
|
Cirrus sac (L) |
350–465 (407) |
410–525 (462) |
325–525 (458) |
450–550 (508) |
|
(W) |
130–165 (148) |
155–225 (174) |
150–200 (177) |
175–210 (190) |
|
|
Ovary (L) |
150–225 (199) |
200–275 (231) |
190–325 (232) |
210–325 (273) |
|
(W) |
200–225 (214) |
220–275 (238) |
210–300 (246) |
225–325 (282) |
|
|
Anterior testis (L) |
480–660 (560) |
630–900 (740) |
600–750 (664) |
700–1,060 (893) |
|
(W) |
300–400 (356) |
400–470 (443) |
310–500 (387) |
400–530 (472) |
|
|
Posterior testis (L) |
550–690 (653) |
760–1,000 (826) |
670–970 (748) |
860–1,120 (964) |
|
(W) |
290–390 (347) |
400–450 (419) |
330–500 (378) |
370–500 (456) |
Table 4Differential indices of Echinostoma macrorchis adults recovered from rats experimentally infected with metacercariae from Cipangopaludina snails of Shinan-gun, Jeollanam-do
Table 4
|
Organs |
15-day-old |
20-day-old |
25-day-old |
30-day-old |
Range |
|
Body (L)/(W) |
5.30 |
5.66 |
5.76 |
5.52 |
5.30–5.76 (5.56) |
|
Vental sucker/Oral sucker |
3.03 |
3.03 |
3.18 |
3.15 |
3.03–3.18 (3.10) |
|
Ovary (L)/(W) |
0.93 |
0.97 |
0.94 |
0.97 |
0.93–0.97 (0.95) |
|
Anterior testis (L)/(W) |
1.57 |
1.67 |
1.72 |
1.89 |
1.57–1.89 (1.71) |
|
Posterior testis (L)/(W) |
1.88 |
1.97 |
1.98 |
2.11 |
1.88–2.11 (1.99) |
|
FBL/BLa×100 |
13.40% |
12.70% |
12.50% |
11.30% |
11.3–13.4 (12.5)% |
|
HBL/BLb×100 |
20.40% |
21.90% |
21.00% |
18.90% |
18.9–21.9 (20.6)% |
|
UL/BLc×100 |
27.50% |
25.40% |
28.30% |
31.50% |
25.4–31.5 (28.2)% |
References
- 1. Chai JY. Echinostomes in Humans. In Fried B, Toledo R eds, The Biology of Echinostomes: from the Molecule to the Community. New York, USA. Springer; 2009, pp 147-183.
- 2. Huffman JE, Fried B.
Echinostoma and echinostomiasis. Adv Parasitol 1990;29:215-269.
- 3. Ando R, Ozaki Y. On four new species of trematodes of the family Echinostomatidae. Dobutsugaku Zasshi 1923;35:108-119. (in Japanese).
- 4. Majima M.
Echinostoma macrorchis found in a man. Tokyo Iji Shinshi 1927;2552:2260-2263. (in Japanese).
- 5. Shibue H. Studies on the trematodes of birds in Kyushu. Kurume Igakkai Zasshi 1954;17:178-183. (in Japanese).
- 6. Okabe N, Okabe K. On a human case infected with three species of trematodes. Nippon Iji Shimpo 1972;2531:46-48. (in Japanese).
- 7. Yokohata Y, Abe H, Jiang YP, Kamiya M. Gastrointestinal helminth fauna of Japanese moles, Mogera spp. Jpn J Vet Res 1989;37:1-13.
- 8. Ito M, Itagaki T. Survey on wild rodents for endoparasites in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. J Vet Med Sci 2003;65:1151-1153.
- 9. Fischthal JH, Kuntz RE. Some digenetic trematodes of mammals from Taiwan. Proceed Helminthol Soc Washington 1975;42:149-157.
- 10. Fischthal JH, Kuntz RE. Additional records of digenetic trematodes of mammals from Taiwan. Proceed Helminthol Soc Washington 1981;48:71-79.
- 11. Lo CT.
Echinostoma macrorchis: life history, population dynamics of intramoluscan stages, and the first and second intermediate hosts. J Parasitol 1995;81:569-576.
- 12. Sohn WM, Chai JY, Na BK, Yong TS, Eom KS, Park H, Min DY, Rim HJ.
Echinostoma macrorchis in Lao PDR: Metacercariae in Cipangopaludina snails and adults from experimentally infected animals. Korean J Parasitol 2013;51:191-196.
- 13. Choe S, Lee D, Park H, Oh M, Jeon HK, Lee Y, Na KJ, Kim Y, Lee H, Eom KS. Three echinostome species from wild birds in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:513-520.
- 14. Choe S, Lee D, Park H, Jeon HK, Lee Y, Kim E, Na KJ, Eom KS. Two echinostome species, Pegosomum bubulcum and Nephrostomum ramosum (Digenea: Echinostomatidae), from an Eastern cattle egret, Bubulcus ibis coromandus, in Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:485-496.
- 15. Choe S, Lee D, Park H, Jeon HK, Lee Y, Na KJ, Park SR, Eom KS. A case of chaunocephalosis by Chaunocephalus ferox (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) in an oriental white stork, Ciconia boyciana, in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:659-665.
- 16. Lee YI, Chung OS, Seo M. Recovery of Oswaldotrema nacinovici from whimbrels (Aves) in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:809-812.
- 17. Ryang YS. Studies on Echinostoma spp. in the Chungju Reservoir and upper stream of the Namhan River. Korean J Parasitol 1990;28:221-233. (in Korean).
- 18. Son WY, Huh S, Lee SU, Woo HC, Hong SJ. Intestinal trematode infections in the villagers in Koje-myon, Kochang-gun, Kyongsangnam-do, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1994;32:149-155.
- 19. Ahn YK, Ryang YS. Experimental and epidemiological studies on the life cycle of Echinostoma hortense Asada, 1926 (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). Korean J Parasitol 1986;24:121-136. (in Korean).
- 20. Lee SK, Chung NS, Ko IH, Sohn WM, Hong ST, Chai JY, Lee SH. An epidemiological survey of Echinostoma hortense infection in Chongsong-gun, Kyongbuk province. Korean J Parasitol 1988;26:199-206. (in Korean).
- 21. Chai JY, Hong ST, Lee SH, Lee GC, Min YI. A case of echinostomiasis with ulcerative lesions in the duodenum. Korean J Parasitol 1994;32:201-204.
- 22. Lee OJ, Hong SJ. Gastric echinostomiasis diagnosed by endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2002;55:440-442.
- 23. Cho CM, Tak WY, Kweon YO, Kim SK, Choi YH, Kong HH, Chung DI. A human case of Echinostoma hortense (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) infection diagnosed by gastroduodenal endoscopy in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2003;41:117-120.
- 24. Chang YD, Sohn WM, Ryu JH, Kang SY, Hong SJ. A human infection of Echinostoma hortense in duodenal bulb diagnosed by endoscopy. Korean J Parasitol 2005;43:57-60.
- 25. Park CJ, Kim J. A human case of Echinostoma hortense infection diagnosed by endoscopy in area of southwestern Korea. Korean J Med 2006;71:229-234.
- 26. Takahashi S. The life cycles of Echinostoma cinetorchis and E. macrorchis, particularly on their first and second intermediate hosts. Fukuoka Ika Daigaku Zasshi 1927;20:712-723. (in Japanese).
- 27. Kurisu S. Study on trematodes who take Viviparus as their intermediate host. Seiikai Zasshi 1930;49:65-73. (in Japanese).
- 28. Kurokawa T. Studies on trematodes taking Bulinus (Parafossarulus) striatus (Pilsbry) as their intermediate host and on their metacercariae. Tokyo Iji Shinshi 1935;2937:1795-1800. (in Japanese).
- 29. Yamashita J. Echinostome. Progr Med Parasitol Japan 1964;1:289-313.
- 30. Ochi S. Studies on the life cycle of Echinostoma macrorchis
. Tokyo Joigaku Zasshi 1931;1:12-32. (in Japanese).
- 31. Ando R, Tsuyuki H. Studies on intestinal parasites taking rats as their final host (II) On Echinostoma in Nagoya city and its second intermediate host. Tokyo Iji Shinshi 1923;2340:1487-1499. (in Japanese).
- 32. Ishii N. Studies on rat trematodes. Jikken Igaku Zasshi 1935;19:1122-1128. (in Japanese).
- 33. Komiya Y. Metacercariae in Japan and adjacent territories. Progr Med Parasitol Japan 1965;2:1-328.
- 34. Yamaguti S. Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan. Part. 27. Trematodes of mammals, II. Jpn J Med Sci 1939;1:131-151.
- 35. Yamaguti S. Genus Echinostoma Rud., 1809. In Synopsis of Digenetic Trematodes of Vertebrates. I & II:Tokyo, Japan. Keigaku Publishing Co; 1971, pp 529-533.
- 36. Bashikirova E. Family Echinostomatidae Dietz, 1909. In Skrjabin KI ed, Trematodes of Animals and Man. I:Moscow-Lenin-grad, Russia. Academy of Sciences of the USSR; 1947, pp 246-305 (English translated version).
- 37. Skrjabin KI, Petrov AM, Bashikirova E. Echinostomes of domestic and wild birds in USSR. In Skrjabin KI ed, Trematodes of Animals and Man. I:Moscow-Leningrad, Russia. Academy of Sciences of the USSR; 1947, pp 306-407 (English translated version).
- 38. Skrjabin KI, Bashikirova E. Family Echinostomatidae Dietz, 1909. In Skrjabin KI ed, Trematodes of Animals and Man. XII:Moscow, Russia. Academy of Sciences of the USSR; 1956, pp 53-930.
- 39. Odening K. Trematoda from Indian birds in the Berlin zoological gardens. Z Parasitenkd 1962;21:381-425.
- 40. Kanev I, Fried B, Radev V. Collar spine models in the genus Echinostoma (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). Parasitol Res 2009;105:921-927.