Abstract
Tick saliva is critically important for continuous attachment to the host, blood feeding for days, and transmission of tick-borne pathogens. To characterize the patterns of inflammatory cytokine gene expression during its attachment and blood sucking time, peripheral blood samples of rabbits infested with Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks were collected at different intervals. Blood histamine concentration was evaluated as well as gene encoding IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2, IL-6, IL-4, and IL-10 were compared with non-infested rabbits. Blood histamine concentration of tick-infested rabbits during fast feeding time was significantly higher than that of non-infested rabbits. In both nymph and adult tick infested rabbits, expression of TNF-α and IFN-γ genes were decreased significantly (P<0.05), while expression of IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10 were increased 1.3 to 7 folds in adult infested rabbits with the exception of IL-6 that was significantly (P<0.05) decreased in nymph infested rabbits. IL-2 was not expressed in either nymph or adult infestation. H. longicornis saliva is capable of modulate host responses through a complex correlation with histamine and Th1, Th2 mediated cytokines that suppress the inflammatory responses directed toward inflammatory mediators introduced into the host during tick feeding.
-
Key words: Haemaphysalis longicornis, cytokine, inflammatory cytokine
INTRODUCTION
Tick saliva contains anti-clotting, anti-platelet, vasodilatory, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory components. Cytokines play a very important role in regulating these processes. Tick resistance or susceptibility to hosts is determined by a pattern of response to subsets of CD
4+ T-helper (Th) cells [
1]. Th1 cells produce IL-2, IFN-γ while Th2 cells produce IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-13. These cytokine patterns may direct the immune responses towards different effector mechanisms [
2]. There is very little information regarding the cytokine profiles of
H. longicornis after its infestation of hosts. Cytokines can be measured in serum, plasma, diseased tissues, or in peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) preparations [
3]. The general objectives of these studies were to generate information on changes in plasma histamine and inflammatory cytokine gene expression of IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, and IFN-γ during the attachment and fast feeding stages when rabbits were infested with
H. longicornis nymph and adult ticks. We also tried to determine the effect of time and changes of histamine related inflammatory cytokines on
H. longicornis blood sucking time.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ticks and animals
H. longicornis Jeju strain has been maintained on rabbits and mice for several generations in our laboratory since 2003. To feed, H. longicornis ticks were placed onto the ears of specific pathogen-free (SPF) New Zealand White rabbits (n=10) of 5 months old and weighted 2.5 kg. Approximately 250 nymphs and 200 adults were placed in their respective feeding apparatuses and allowed to feed until full engorgement and spontaneous detachment occurred. Ticks were incubated at 25°C, 85% of relative humidity. All animal studies and protocols met the ethical principles for animal research and were approved by the Chonbuk National University Animal Care and User Committee (CBNU 2015-003).
Blood sampling
Blood samples from rabbits were collected before infestation and at every 24 hr intervals of 0, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120, 144, and 168 hr after infestation from peripheral blood. RNA was extracted from the buffy coat of collected blood using commercial RiboEx (GeneAll, Seoul, Korea).
Primer sequences and one-step real-time PCR
The qPCR primers used to evaluate the expression of genes related to immune responses were TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10 synthesized according to sequences found in the literature. The housekeeping gene GAPDH was used as controls (
Table 1). For each selected gene, optimal amplification conditions (with RNA adjusted for an equal concentration) were selected to achieve a standard efficiency among all selected genes. Relative quantification was performed in triplicate using the SYBR Green qPCR Master MixTaKaRa One Step® Prime scriptTM RT-PCR kit II (Clontech, Palo Alto, California, USA). PCR amplification was carried out using 20 μl reaction mixtures containing 10 pmol of each primer, 12.5 μl of 2X One Step SYBR® RT-PCR Buffer IV, 1 μl PrimeScript
TM, 1 step Enzyme Mix II, 400 ng of template RNA, and 7.5 μl RNase Free dH
2O. The PCRs were performed using the following program: stage 1; reverse transcription; 5 min at 42°C, and then 10 sec at 95°C, stage 2; PCR reaction 40 cycles of 5 sec at 95°C, 30 sec at 60°C, and stage 3; dissociation. IL-6 real-time annealing was set at 55°C.
Expression levels of histamine were measured from plasma according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Histamine EIA ELISA kit; Cat. No. KA Catalog 2589, Abnova Chemicals, Walnut, California, USA). The absorbance of each sample was read using a microplate reader set to 450 nm.
Relative quantification of real-time PCR assay
The data were analyzed using the Livak and Schmittgen equation, where fold change=2
−ΔΔCT. Principles of this method, validation of internal control (GAPDH), and amplification efficiency equality based on amplification of serial dilution of cDNA for each PCR run were determined and performed, as previously described [
2].
RESULTS
In this study, we observed histamine concentration of different feeding stages and 6 inflammatory cytokine gene expressions during its attachment and blood sucking time of nymph and adult H. longicornis. Relative quantification of cytokine gene expression was expressed as a fold-change over a given period for treated vs. untreated samples.
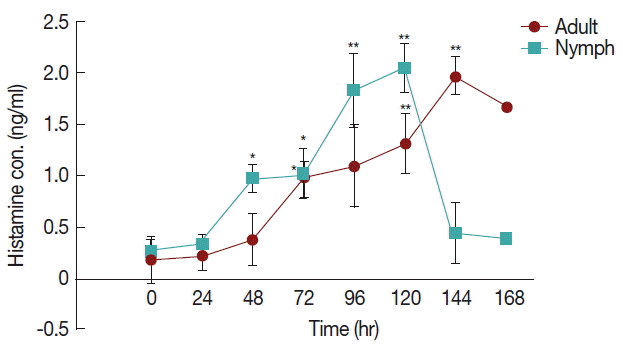
The differences in histamine concentration (
Fig. 1) between the tick attachment time and fast feeding time were significant (
P <0.05). In case of adult tick infested rabbits, the histamine obtained at 24 and 48 hr did not differ at the concentrations of histamine obtained at 72 and 96 hr. Histamine concentration at 120 and 144 hr differed significantly (
P <0.05 and
P <0.01, respectively) from the amount of histamine found in uninfested rabbits. Blood histamine in adult infested rabbits was increased 2.6- to 5.3-folds in comparison to the control in adult-infested rabbits. In nymph-infested rabbits, histamine obtained at 24 hr did not differ at the
P =0.05 level from the histamine level measured in the uninfested group. However, the concentrations of histamine obtained from nymph-infested rabbits at 48, 72 hr and 96, 120 hr differed significantly (
P <0.05 and
P <0.001, respectively) from the amount of histamine found in uninfested rabbits. At 144 hr, the level of histamine sharply reduced to the normal level, and at that time nymph infestation was almost complete. Blood histamine in nymph infested rabbits was increased 2.9 to 5.9-folds in comparison to the control in nymph-infested rabbits.
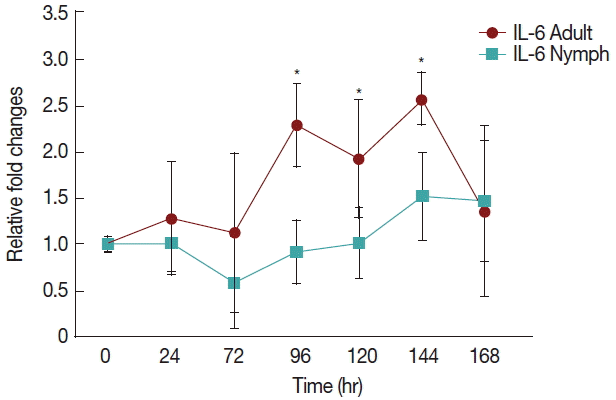
Fig. 2 shows a significant increase (
P <0.05) in IL-6 at 96 hr in rabbits infested with adult (
Fig. 1)
H. longicornis groups compared to the uninfested group. IL-6 also tended to increase during the attachment time of adult infested rabbits but not significantly. IL-6 expression tended to decrease with almost no change in nymph infested rabbits and it did not significantly increase at the last stage of fast feeding compared to controls. The expression of IL-6 was the same for adults and nymphs during fast feeding time but it was reversed during the attachment time in comparison to controls.
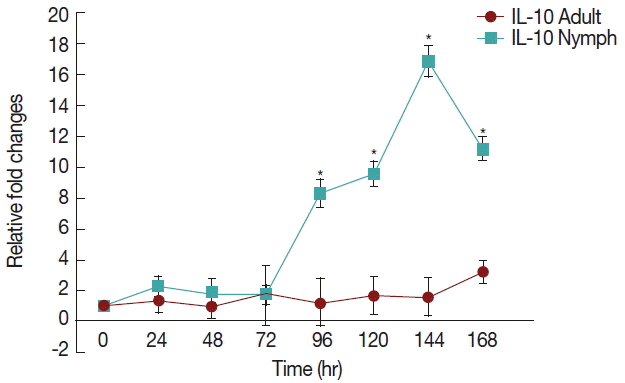
There was a significant increase (
P <0.05) in IL-10 (
Fig. 3) after 72 hr in nymph infested
H. longicornis group compared to the uninfested group. With adult infested rabbits the increases were 1.02 (at 24 hr) to 3.2 times (at 168 hr). With nymph infested rabbits increases ranged from 1.8 (48 hr) to 16.9 (144 hr) times.
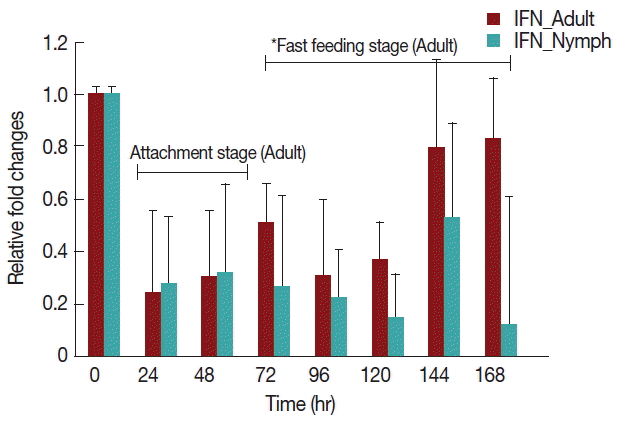
Rabbits infested with
H. longicornis nymphs (
Fig. 4) had decreased IFN-γ production in both the attachment and fast feeding time. When infested with adult
H. Longicornis, the decrease in IFN-γ during attachment was significant (
P <0.05) compared to fast feeding time. With nymph infestation, there was no significant difference between the attachment and fast feeding time.
A significant decrease (
P <0.05) in TNF-α expression (
Fig. 5) after 24 hr in rabbits infested with either nymph or adult
H. longicornis, compared with controls or uninfested groups. TNF-α cytokine expression was also significantly decreased (
P <0.05) in the attachment time of adult-infested rabbits in comparison to the fast feeding time. The expression of TNF-α tended to be lower in rabbits infested with adult
H. longicornis as compared to nymph-infested rabbits (
Fig. 5).
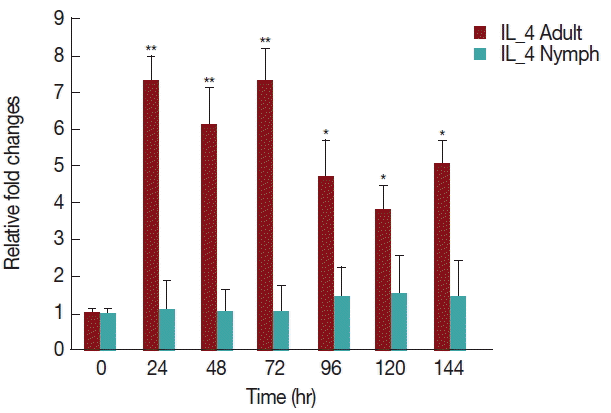
As shown in
Fig. 6, there was a significant increase (
P <0.05) in IL-4 expression after 24 hr of adult
H. longicornis infestation, as compared to controls or uninfested groups. IL-4 cytokine expression was also significantly higher (
P <0.05) in the attachment time of adult-infested rabbits in comparison to that of the fast feeding stage. While there were no significant differences in the mRNA levels of IL-4 cytokine between control and nymph-infested groups at any time points, the expression of IL-4 was higher in adult
H. longicornis-infested rabbits as compared to nymph-infested rabbits.
DISCUSSION
Real time PCR is a powerful tool for studying gene expression in mammalian tissues. Cytokine mRNA quantification is one of the earliest ways this tool was used [
4]. Tick saliva modulates host inflammation to enable successful blood sucking and tick-borne pathogen transmission [
5].
Throughout this study, expression of IL-2 was not detectable both in nymph and adult
H. longicornis infested rabbits. This result suggested that, for IL-2 cytokines, gene expression either is not induced or is induced at later time points. This findings also agreed with Singh and Girschick [
6] who found IL-2 expression 72 hr after
I. ricinus attachment to a previously uninfested host. Some other diseases such as
Anaplasma phagocytophila has very weak expression of IL-2 mRNA when infesting host in vivo model [
7]. In
I. ricinus saliva, an IL-2 binding protein that decreases the availability of IL-2 and affects T-cell proliferation, was described [
4].
Histamine mediated cutaneous inflammation in host defense reaction to tick feeding, as demonstrated by adverse effects on tick attachment, feeding efficiency, and reproductive success when histamine was elevated at a feeding site [
8]. We showed that blood histamine levels were significantly higher (2.6 to 5.3 fold) in the fast feeding time than in the attachment time in adult infested rabbits. Histamine levels in nymph infested rabbits significantly increased during the fast feeding time (2.0 to 4.3 fold) at 120 hr but decreased after that time. An immediate hypersensitivity mechanism was suggested by Rick [
9] upon demonstrating that histamine levels increase in resistant bovine blood. Our data indicated that
H. longicornis must have factors that stop the action or release histamine. Our previous analysis of
H. longicornis saliva showed that it contains lipocalins. The presence of lipocalins in tick saliva is related to control of inflammatory processes and interfere with host hemostatic functions.
IL-10 is the most important anti-inflammatory cytokine, as it is responsible for downregulation of inflammatory reactions [
10]. Our results indicated a significant increse in IL-10 when rabbits were infested with nymph and adult
H. longicornis ticks.
Amblyomma cajennense saliva was found to stimulate increased IL-10 production [
11]. IL-10 is a potent inhibitor of Th1 cytokines, including both IL-2 and IFN-γ [
12]. The current research also found that with enhanched IL-10, there is decrese of IFN-γ (
Fig. 4) in rabbits infested with both nymph and adult
H. longicornis. There is a relationship between the levels of histamine and IL-10. Histamine increased production of IL-10 in whole blood cultures in a dose-dependent manner [
13]. Histamine shifts the Th1/Th2 balance from Th1 to Th2 cytokines, and the effects of histamine on IL-10 secretion is an important factor in this switch.
IL-6 has both anti-inflammatory [
14] and proinflammatory effects. The role of saliva against IL-6 is very complicated. Our results showed that when rabbits were infested with nymphs, there was no increase in IL-6 levels up to last the fast feeding time. Sometimes IL-6 decresed at 48 and 72 hr. When rabbits were infested with adults in both the attachment and fast feeding time IL-6 tended to increase. Tick saliva has both inhibitory and enhancing [
15] effects on IL-6 expression.
Several studies have shown that histamine significantly augmented the production of IL-6 in a dose and time-dependent manner [
16]. The production of IL-6 during the fast feeding time was 1.3 to 2.6 times greater than in the non-infested time, which may be due to the presence of higher histamine concentration in circulating blood. Triggiani et al. [
17] found that histamine increased basal secretion of IL-6 from macrophages in a concentration-dependent fashion. Presumably, histamine increases IL-6 production by increasing its mRNA expression. Our results indicated a clear link between histamine signaling and IL-6 production during the feeding time of
H. longicornis ticks.
We found that IFN-γ decreased in both nymph and adult infested rabbits in comparison to uninfested rabbits (
Fig. 4). The gene expression profile at earlier times of infestation with
H. longicornis nymphs and adults revealed a substantial decrease in proinflammatory cytokines. This early response was dominated by IFN-γ. In vitro experiments suggested that tick saliva inhibits the production of cytokines, IFN-γ, and adhesion molecules [
18].
Tick salivary gland extract inhibits IFN-γ production. Kopecký et al. [
19] found that salivary gland extracts from
Ixodes ricinus ticks inhibited production of IFN-γ by up-regulation of IL-10. These are in agreement with our data, as IL-10 also increases after tick infestation. This is possibly because histamine has an inhibitory effect on IFN-γ expression that depends on the concentration of histamine. Histamine was found to inhibit IFN-γ secretion in a dose-dependent manner in both splenocytes and Th1 cells. In splenocytes, the inhibitory effect was more pronounced than in Th1 cells [
20]. The inhibitory effect of
H. longicornis saliva in IFN-γ mRNA transcription is possibly for the presence of inhibitory peptides which interfere in the cytokines pathway as found in
H. asiaticum that acts through the JNK/SAPK arm of MAPK signaling pathway [
21].
Our data shows that tick attachment has an enhancing effect on the expression of IL-4 in rabbits infested with
H. longicornis nymph and adult ticks (
Fig. 6). It has been previously shown that the salivary secretions of
Aedes aegypti and
Cimex pipiens are able to up-regulate IL-4 and IL-10 production up to 7 days after feeding [
22], and
I. ricinus tick saliva was shown to induce the upregulation of IL-4 [
23]. The most likely cause of these increases is that IL-4 markedly enhances IL-10 gene expression in primary Th2 cells. Our data demonstrated that during the fast feeding time the expression of IL-4 was greater in comparison to that during attachment, a finding that is similar to those of a previous work done in BALB/c mice infested with
I. ricinus nymphs [
24]. Increased expression of IL-4, a marker of differentiation of Th cells into the Th2 subset, has also been reported in a murine model of tick infestation where IL-4 expression was dependent on stimulation of histamine [
25].
TNF-α is a proinflammatory cytokine that has special importance in inflammation [
26]. Tick saliva inhibits the production of TNF-α cytokines and stimulates IL-10 production [
11]. The present study showed that throughout the feeding time of
H. longicornis, TNF-α expression decreased significantly due to the tick salivary secretions, possibly resulting in the inhibition of maturation of dendritic cells. Oliveira et al. [
27] found similar results that
Rhipicephalus sanguineus tick saliva reduced the synthesis of TNF-α.
TNF-α is generally considered to be an inflammatory cytokine while IL-10 usually acts as an immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory cytokine [
28]. The present study showed that when the histamine level is increased in the blood plasma of rabbits it inhibits the release of proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α by stimulating the release of IL-10. A similar finding was also seen by Sirois et al. [
29] when they investigated the effect of histamine pretreatment on the release of TNF-α and IL-10 by alveolar macrophages stimulated with suboptimal concentrations of lipopolysaccharides. Furthermore, several other studies showed that histamine inhibited TNF-α release [
29] and stimulated IL-10 production [
30]. Throughout the study, there was low mRNA expression in nymph than adult infested rabbits.
In our previous study [
31], a glutathione peroxidase was the only protein of this class identified in nymph saliva. This protein has been well characterized for its anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activity in mammals. Probably for this protein in nymph infested rabbits, the inflammatory cytokine genes are less expressed than in adults.
We investigated the extent to which ticks interact with the inflammatory cytokine network by comparing the expression patterns of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediator histamine. Further work needs to be explored on the complexity of these interactions and the role of other notable factors such as chemokines and histamine binding proteins which may be critical for alteration of histamine function. Our results supported a model of tick feeding where the interpretation of cytokines helped to clarify the functional properties of inflammatory cells, both for research and clinical diagnosis.
The present study showed that proinflammatory cytokines are suppressed and anti-inflammatory cytokines are increased during the infestation of H. longicornis nymph and adult ticks, and the patterns of expression differ depending on the life cycle satges of ticks. We found that the secretion of several cytokines involved in inflammatory processes is influenced by histamine, mainly suppressing the host response way that coincides with the inflammation-promoting activities of histamine.
Notes
-
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (no. NRF-2015 R1D1A1A01059607).
Fig. 1Effect of H. longicornis nymph and adult tick infestation and the level of histamine during the attachment and fast feeding stage. Values are means±standard error of mean (SEM) of triplicate determinations from 3 independent experiments.*Significant at P<0.05; **Significant at P<0.001 vs uninfested.
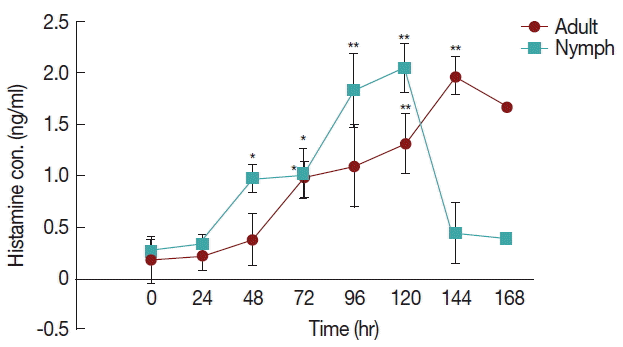
Fig. 2Relative expression of IL-6 cytokines in rabbits when infesteted with adult and nymph H. longicornis. Expression of IL-6 was assessed before the tick infestation (day 0) or after infestation (24 to 168 hr). Expression of IL-6 was measured by real-time quantitative PCR, and changes in cytokine mRNA are expressed relative to the housekeeping gene, GAPDH. Each time point represents the average expression level of 3 value mean and is reported as fold changes±standard error of mean (SEM) as compared to the expression. *Significant at P<0.05 vs uninfested.
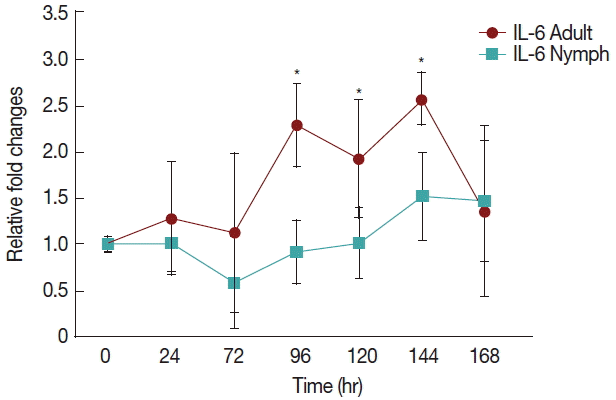
Fig. 3Relative expression of IL-10cytokines in rabbits when infesteted with adult H. longicornis. Expression of IL-10 was assessed before the tick infestation (day 0) or after infestation (24 to 168 hr). Expression of IL-10 was measured by real-time quantitative PCR, and changes in cytokine mRNA are expressed relative to the housekeeping gene, GAPDH. Each time point represents the average expression level of 3 value mean and is reported as fold changes±standard error of the mean (SEM) as compared to the expression. *Significant at P<0.05.
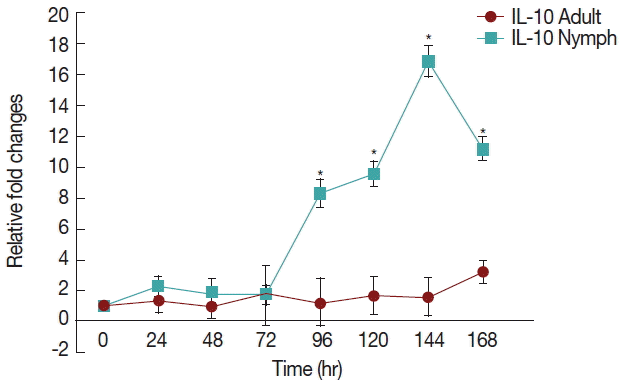
Fig. 4Relative expression of IFN-γ cytokines in rabbits when infesteted with adult H. longicornis. Expression of IFN-γ was assessed before the tick infestation (day 0) or after infestation (24 to 168 hr). Expression of IFN-γ was measured by real-time quantitative PCR, and changes in cytokine mRNA are expressed relative to the housekeeping gene, GAPDH. Each time point represents the average expression level of 3 value mean and is reported as fold changes±standard error of the mean (SEM) as compared to the expression. *Singnificant at P<0.05.
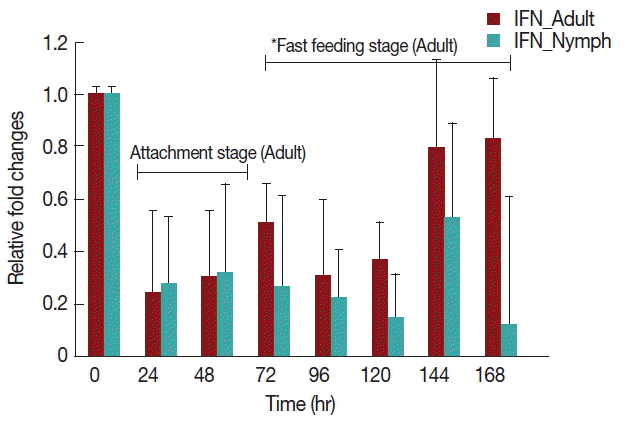
Fig. 5Relative expression of TNF-α cytokines in rabbits infested with adult and nymph H. longicornis. Expression of TNF-α was assessed before tick infestation (day 0) or after infestation (12 to 168 hr). Expression of TNF-α was measured by real-time quantitative PCR, and changes in cytokine mRNA are expressed relative to the housekeeping gene, GAPDH. Each time point represents the average expression level of 3 values and is reported as fold change±standard error of the mean (SEM) as compared to the expression. *Significant at P<0.05.
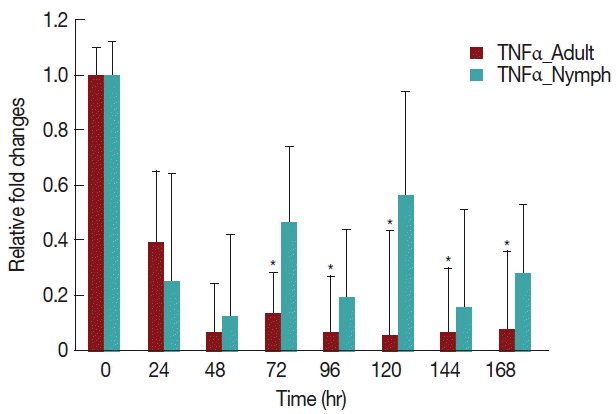
Fig. 6Relative expression of IL-4 cytokine in rabbits infested with adult and nymph H. longicornis. Expression of IL-4 was assessed before tick infestation (day 0) or after infestation (12 to 168 hr). Expression of IL-4 was measured by real-time quantitative PCR, and changes in cytokine mRNA level are expressed relative to the housekeeping gene, GAPDH. Each time point represents the average expression level of 3 values and is reported as fold change±standard error of the mean (SEM) as compared to the expression. *Significant at P<0.05; **Significant at P<0.001 vs uninfested.
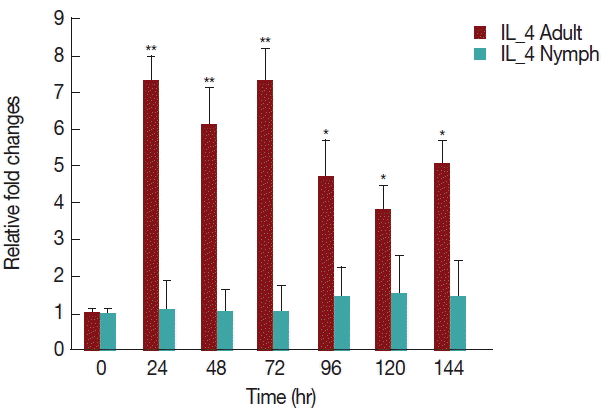
Table 1Oligonucleotides use in real-time PCR
Table 1
|
Cytokine |
Primer |
Reference |
|
GAPDH |
F 5′-CGTTGCTGACAATCTTGAGAGA-3′
R 5′-CGTTGCTGACAATCTTGAGAGA-3′ |
[32] |
|
IL-6 |
F 5′-GAAAACACCAGGGTCAGCAT-3′
R 5′-CAGCCACTGGTTTTTCTGCT-3′ |
[33] |
|
IFNγ |
F 5′-TTCCCAAGGATAGCAGTGGT-3′
R 5′-TGAAGCCAGAAGTCCTCAAAA-3′ |
[32] |
|
IL-2 |
F 5′-TGAAACATCTTCAGTGTCTAGAAG-3′
R 5′-CATTGTAGAATTTCTGAACAGAT-3′ |
[33] |
|
IL-10 |
F 5′-GAGAACCACAGTCCAGCCAT-3′
R 5′-CATGGCTTTGTAGACGCCTT-3′ |
[33] |
|
TNFα |
F 5′-CTCCTACCCGAACAAGGTCA-3′
R 5′-CGGTCACCCTTCTCCAACT-3′ |
[32] |
|
IL-4 |
F 5′-GTCACTCTGCTCTGCCTCCTC-3′
R 5′-GGACTCGACAGGAACCTCTG-3′ |
[33] |
References
- 1. Sher A, Coffman RL. Regulation of immunity to parasites by T cells and T cell-derived cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol 1992;10:385-409.
- 2. Raue U, Slivka D, Jemiolo B, Hollon C, Trappe S. Myogenic gene expression at rest and after a bout of resistance exercise in young (18–30 yr) and old (80–89 yr) women. J Appl Physiol 2006;101:53-59.
- 3. Mosmann TR, Sad S. The expanding universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more. Immunol Today 1996;17:138-146.
- 4. Gillespie RD, Dolan MC, Piesman J, Titus RG. Identification of an IL-2 binding protein in the saliva of the Lyme disease vector tick, Ixodes scapularis
. J Immunol 2001;166:4319-4326.
- 5. Zeidner N, Dreitz M, Belasco D, Fish D. Suppression of acute Ixodes scapularis-induced Borrelia burgdorferi infection using tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-2, and interferon-gamma. J Infect Dis 1996;173:187-195.
- 6. Singh SK, Girschick HJ. Tick-host interactions and their immunological implications in tick-borne diseases. Curr Sci 2003;85:1284-1298.
- 7. Kim HY, Mott J, Zhi N, Tajima T, Rikihisa Y. Cytokine gene expression by peripheral blood leukocytes in horses experimentally infected with Anaplasma phagocytophila
. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2002;9:1079-1084.
- 8. Kemp DH, Bourne A.
Boophilus microplus: the effect of histamine on the attachment of cattle-tick larvaestudies in vivo and in vitro. Parasitology 1980;80:487-496.
- 9. Rick RF. Studies on the reactions of animals to infestation with ticks. VI. Resistance of cattle to infestation with the tick Boophilus microplus (canestrini). Aus J Agri Res 1962;13:532-550.
- 10. Opal SM, DePalo VA. Anti-inflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000;117:1162-1172.
- 11. Carvalho-Costa TM, Mendes MT, da Silva MV, da Costa TA, Tiburcio MG, Anhê AC, Rodrigues V Jr, Oliveira CJ. Immunosuppressive effects of Amblyomma cajennense tick saliva on murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:22.
- 12. Howard M, O’Garra A. Biological properties of interleukin 10. Immunol Today 1992;13:198-200.
- 13. Elenkov IJ, Webster E, Papanicolaou DA, Fleisher TA, Chrousos GP, Wilder RL. Histamine potently suppresses human IL-12 and stimulates IL-10 production via H2 receptors. J Immunol 1998;161:2586-2593.
- 14. Aderka D, Le JM, Vilcek J. IL-6 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor production in cultured human monocytes, U937 cells, and in mice. J Immunol 1989;143:3517-3523.
- 15. Kazimirova M, Štibrániová I. Tick salivary compounds: their role in modulation of host defences and pathogen transmission. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2013;3:43.
- 16. Park IH, Um JY, Cho JS, Lee SH, Lee SH, Lee HM. Histamine promotes the release of interleukin-6 via the H1R/p38 and NF-kappaB pathways in nasal fibroblasts. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 2014;6:567-572.
- 17. Triggiani M, Gentile M, Secondo A, Granata F, Oriente A, Taglialatela M, Annunziato L, Marone G. Histamine induces exocytosis and IL-6 production from human lung macrophages through interaction with H1 receptors. J Immunol 2001;166:4083-4091.
- 18. Brossard M, Wikel SK. Immunology of interactions between ticks and hosts. Med Vet Entomol 1997;11:270-276.
- 19. Kopecký J, Kuthejlová M, Pechová J. Salivary gland extract from Ixodes ricinus ticks inhibits production of interferon-gamma by the upregulation of interleukin-10. Parasite Immunol 1999;21:351-356.
- 20. Osna N, Elliott K, Khan MM. The effects of histamine on interferon gamma production are dependent on the stimulatory signals. Int Immunopharmacol 2001;1:135-145.
- 21. Wu J, Wang Y, Liu H, Yang H, Ma D, Li J, Li D, Lai R, Yu H. Two immunoregulatory peptides with antioxidant activity from tick salivary glands. J Biol Chem 2010;285:16606-16613.
- 22. Zeidner NS, Higgs S, Happ CM, Beaty BJ, Miller BR. Mosquito feeding modulates Th1 and Th2 cytokines in flavivirus susceptible mice: an effect mimicked by injection of sialokinins, but not demonstrated in flavivirus resistant mice. Parasite Immunol 1999;21:35-44.
- 23. Schoeler GB, Manweiler SA, Wikel SK. Cytokine responses of C3H/HeN mice infested with Ixodes scapularis or Ixodes pacificus nymphs. Parasite Immunol 2000;22:31-40.
- 24. Packard KA, Khan MM. Effects of histamine on Th1/Th2 cytokine balance. Int Immunopharmacol 2003;3:909-920.
- 25. Alexander RB, Ponniah S, Hasday J, Hebel JR. Elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines in the semen of patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Urology 1998;52:744-749.
- 26. Oliveira CJ, Carvalho WA, Garcia GR, Gutierrez FR, de Miranda Santos IK, Silva JS, Ferreira BR. Tick saliva induces regulatory dendritic cells: MAP-kinases and Toll-like receptor-2 expression as potential targets. Vet Parasitol 2010;167:288-297.
- 27. Borish L. IL-10: evolving concepts. J Aller Clin Immunol 1998;101:293-297.
- 28. Bissonnette EY. Histamine inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha release by mast cells through H2 and H3 receptors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1996;14:620-626.
- 29. Wang J, Al-Lamki RS, Zhang H, Kirkiles-Smith N, Gaeta ML, Thiru S, Pober JS, Bradley JR. Histamine antagonizes tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling by stimulating TNF receptor shedding from the cell surface and Golgi storage pool. J Biol Chem 2003;278:21751-21760.
- 30. Godornes C, Leader BT, Molini BJ, Centurion-Lara A, Lukehart SA. Quantitation of rabbit cytokine mRNA by real-time RT-PCR. Cytokine 2007;38:1-7.
- 31. Tirloni L, Islam MS, Kim TK, Diedrich JK, Yates JR 3rd, Pinto AF, Mulenga A, You MJ, Da Silva Vaz I Jr. Saliva from nymph and adult females of Haemaphysalis longicornis: a proteomic study. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:338.