Abstract
Due to the critical location and physiological activities of the retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cell, it is constantly subjected to contact with various infectious agents and inflammatory mediators. However, little is known about the signaling events in RPE involved in Toxoplasma gondii infection and development. The aim of the study is to screen the host mRNA transcriptional change of 3 inflammation-related gene categories, PI3K/Akt pathway regulatory components, blood vessel development factors and ROS regulators, to prove that PI3K/Akt or mTOR signaling pathway play an essential role in regulating the selected inflammation-related genes. The selected genes include PH domain and leucine- rich-repeat protein phosphatases (PHLPP), casein kinase2 (CK2), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF), glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL), glutathione S-transferase (GST), and NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1). Using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), we found that T. gondii up-regulates PHLPP2, CK2β, VEGF, GCL, GST, and NQO1 gene expression levels, but down-regulates PHLPP1 and PEDF mRNA transcription levels. PI3K inhibition and mTOR inhibition by specific inhibitors showed that most of these host gene expression patterns were due to activation of PI3K/Akt or mTOR pathways with some exceptional cases. Taken together, our results reveal a new molecular mechanism of these gene expression change dependent on PI3K/Akt or mTOR pathways and highlight more systematical insight of how an intracellular T. gondii can manipulate host genes to avoid host defense.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, reactive oxygen species, PI3K/Akt pathway, mTOR, ARPE-19 cell
INTRODUCTION
Toxoplasma gondii is one of the most widespread zoonotic pathogens in the world that can infect almost any nucleated vertebrate cell. Most of toxoplasmosis patients are asymptomatic in immunocompetent individuals, but ocular lesions may be present in up to 20% of infected patients [
1]. Clinical examination revealed free tachyzoites and cysts in the Retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cell and the retina of
T. gondii-induced retinochoroiditis [
2]. RPE cell is an integral part of the neuroretina in the posterior segment of the eye, which normal functions is phagocytosis and the recycling of components of the outer segments of the rods and cones of the retina during physiological photoreceptor recycling. RPE cell also forms a blood-retinal barrier between the highly vascularized choroid and the retina with a complex architecture of neuronal cells [
3]. Hence, studies of the influences of
T. gondii replication in RPE cells and the responses of the host cells to parasite invasion would be valuable in understanding the immunopathological basis of ocular toxoplasmosis.
Following invasion,
T. gondii resides and replicates within a parasitophorous vacuole (PV) that resists host endosomal acidification and lysosomal fusion. Once the
T. gondii begins growing and dividing within the PV, it must be deprived nutrients such as glucose, lipids and amino acids and nucleotides from the host cell [
4].
T. gondii can secrete multiple effector molecules into host cell, and these effectors are known to interfere with host cell signaling pathways and alter host defenses although the molecular details are unclear [
5]. Previous data demonstrated that
T. gondii can recognized and interfere with host signaling pathways to subvert innate immunity to establish a life-long chronic infection [
6]. One of the initial reactions of host innate immunity is the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in reaction parasites invaders expulsion of parasites [
7]. It has been reported that upon infection with
T. gondii, host phosphatidylinositol3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) pathway was activated, and this activation was required for host cell resistance to apoptosis [
8], and Akt/mTOR activation was also required for
T. gondii to coordinate control of host centrosome position, organelle distribution, and migratory response [
9]. However, most of the mechanisms and pathway involved still not clearly understood.
T. gondii-induced phenotypic changes are characterized by marked changes in gene expression [
10]. There is report that host mRNAs display altered abundance increased 15% relative to uninfected cells after 24 hr post-infection [
11]. The eye is a distinctive immunologic environment that aimed at reducing inflammation, RPE cell is constantly subjected to contact with numerous infectious agents and inflammatory. After parasite infection, change of various host gene expression are observed, which can be deadly or beneficial to the parasite. Since the combination of 3 individual host signals or molecules would determine the fate of infected parasite, identification of the match between specific signal pathway and downstream target gene would be essential for establishing strategy to control infected parasite. Therefore, we categorize selected host genes in 3 categories, signal modulation, vascular formation and ROS regulation, and to determine which are under control of PI3K/Akt or mTOR pathway.
PHLPP has been identified to serve as negative regulator of Akt by dephosphorylation of Akt “Ser-473” directly. Two highly related isoforms in this family, PHLPP1 and PHLPP2, both dephosphorylate the same residue on Akt, however, they differentially terminate Akt signaling by regulating distinct Akt isoforms. PHLPP1 specifically modulates the phosphorylation Akt2, nevertheless PHLPP2 purposely dephosphorylates Akt3 [
12]. A number of studies have clearly demonstrated that PTEN antagonizes PI3K activity and negatively regulates its downstream-target, the serine/threonine kinase Akt [
13]. CK2 is a serine/threonine kinase that consists of 2 catalytic subunits (α, α′) and the regulatory subunit (β) [
14]. Recent report has shown that the CK2 can induce PTEN phosphorylation to inhibit PTEN activity and is also essential to regulate PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [
15].
Choroidal neovascularization (CNV) is a severe complication of ocular toxoplasmosis [
16]. Among the cytokines involved in pathological angiogenesis, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and pigment epithelial derived factor (PEDF) serve as the most potent angiogenic stimulators and angiogenic inhibitors, respectively [
17,
18]. Counterbalancing VEGF angiogenic stimulation and PEDF inhibition is essential to maintain the angiogenic homeostasis.
Recent study provides evidence that
T. gondii can diminish ROS production in the host cell, but the exact mechanism is unclear [
19]. It is well known that a family of proteins called “Phase II genes” can protect against oxidative stress by catalyzing a wide variety of reactions that neutralize reactive oxygen species, toxic electrophiles and carcinogens when they are upregulated [
20]. However, the gene expression levels of selected Phase II enzymes such as: γ-glutamylcysteine ligase and glutathione synthetase, that regulates the key steps in glutathione (GSH) biosynthesis; NQO-1, a reducing agent that plays a crucial role in antioxidant defenses with the cofactor NADH or NADPH were not reported in
T. gondii infection. GSH is a well-studied tri-peptide and has numerous roles in protecting cells from oxidants and maintaining the cellular thiol redox status. The rate-limiting enzyme in the de novo synthesis of GSH is GCL. GCL consists of a catalytic heavy subunit (GCLC) and a modulatory light subunit (GCLM) [
21]. Alpha-class glutathione S-transferases (GSTA) can protect cells against oxidative stress [
22]. GSTA4 enzyme, the alpha subunit that exhibits the highest activity against 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) also efficiently protects against oxidative damage mediated by this cytotoxic product of lipid peroxidation generated by ROS overproduction [
23]. Glutathione S-transferase pi 1 (GSTP1) is a subgroup of GST family, which provides cellular protection against free radical and carcinogenic compounds due to its detoxifying function [
24].
Our results indicate that RPE cell might has a set of genes which can be regulated by T. gondii-induced PI3K/Akt pathway and the sum of individual gene expression change (PI3K-dependent or -independent) will contribute to the PI3K/Akt positive feedback, vascular formation, and ROS down-regulation. Eventually, these gene expression change pattern will be beneficial for T. gondii growth. This study may provide new potential drug targets for the control of RPE-infected T. gondii in case of ocular toxoplasmosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Parasites
Tachyzoites of the virulent Toxoplasma gondii RH strain were used. Parasite were maintained by 3 days passage on human retinal pigment epithelium (ARPE-19 cells) cultured in a 1:1 mixture of Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) with F12 (DMEM/F12) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), and antibiotic-antimycotics (all from Gibco, Grand Island, New York, USA).
Cell culture
ARPE-19 cell line was obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, Virginia, USA) and used at passages 15 to 20 in all experiments. Cultures of ARPE-19 cells were maintained at 37°C, DMEM-F12 medium supplemented with 10% FBS in a humidified at mosphere containing 5% CO2.
Western blot
ARPE-19 cells were cultured in 6-well dishes and infected with RH tachyzoites for 24 hr and then treated for 1 hr with specific PI3-kinase inhibitors LY294002 (LY 0.1, 1, 10 μM), Wortmannin (WM 5, 50, 500 ng/ml), or mTOR inhibitor Rapamycin (Rap 5, 50, 500 ng/ml). The protein samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes and probed with the relevant antibodies. The blots were developed using an enhanced ECL chemi-luminescence detection kit (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK). The primary antibodies used were rabbit anti-phospho-Akt (Thr308), phospho-Akt (Ser473), Akt, phospho-mTOR, mTOR, phospho-p70 S6 kinase and p70 S6 kinase (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, Massachusetts, USA).
Profiling of host gene expression analysis by reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR)
ARPE-19 cells were cultured in 6-well dishes and infected with RH tachyzoites for 24 hr, and then treated for 1 hr with specific PI3-kinase inhibitors LY294002 (LY 10 μM), wortmannin (WM 500 ng/ml), or mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (Rap, 500 ng/ml). Total RNA was exacted using Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, California, USA). The cDNA was synthesized using a Moloney murine leukemia virus cDNA synthesis kit (Enzynomics, Daejeon, Korea) with 2 μg of total RNA. PCR was performed with the Maxime PCR premix kit (Takara Bio, Otsu, Japan). All PCR reactions were performed with a MyCycler instrument (Bio-Rad, Richmond, California, USA) for 25 cycles. The PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 primer sequences for RT-PCR were described by Hirano et al. [
25]. VEGF and PEDF primer sequences for RT-PCR were described previously [
26,
27]. The GCLC, GCLM, GSTP1, GSTA4, and NQO1 primer sequences used were described by Saravanakumar et al. [
28]. Amplified products were electrophoresed in a 2% agarose gel and visualized with ethidium bromide. The relative intensity of bands for each mRNA was related to the intensity of the autoradiogram band of the internal control, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Quantification of mRNA was performed using an imaging densitometer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Otsu, Japan).
After isolation total mRNA with Trizol Reagent, the cDNA was synthesized using the Primer Script RT reagent kit (Takara) with 1 μg of total mRNA. Real-time PCR was performed using the SYBR Premix Ex Taq
TM II (2×) mix (Takara) and specific primer sets (
Table 1) with the Rotor-Gene Q Real Time PCR Systems (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The thermal cycle parameters were 95°C for 10 min and 40 cycles of each for 5 sec at 95°C and 40 sec at 60°C. Ct values for specific genes were corrected by the Ct value for the GAPDH housekeeping gene and expresses as ΔCt. Data represent mean±SD, values of ΔCt.
The unpaired Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis. Three independent experimental data are presented as means ±SD. P-values less than 0.05 are considered significant.
RESULTS
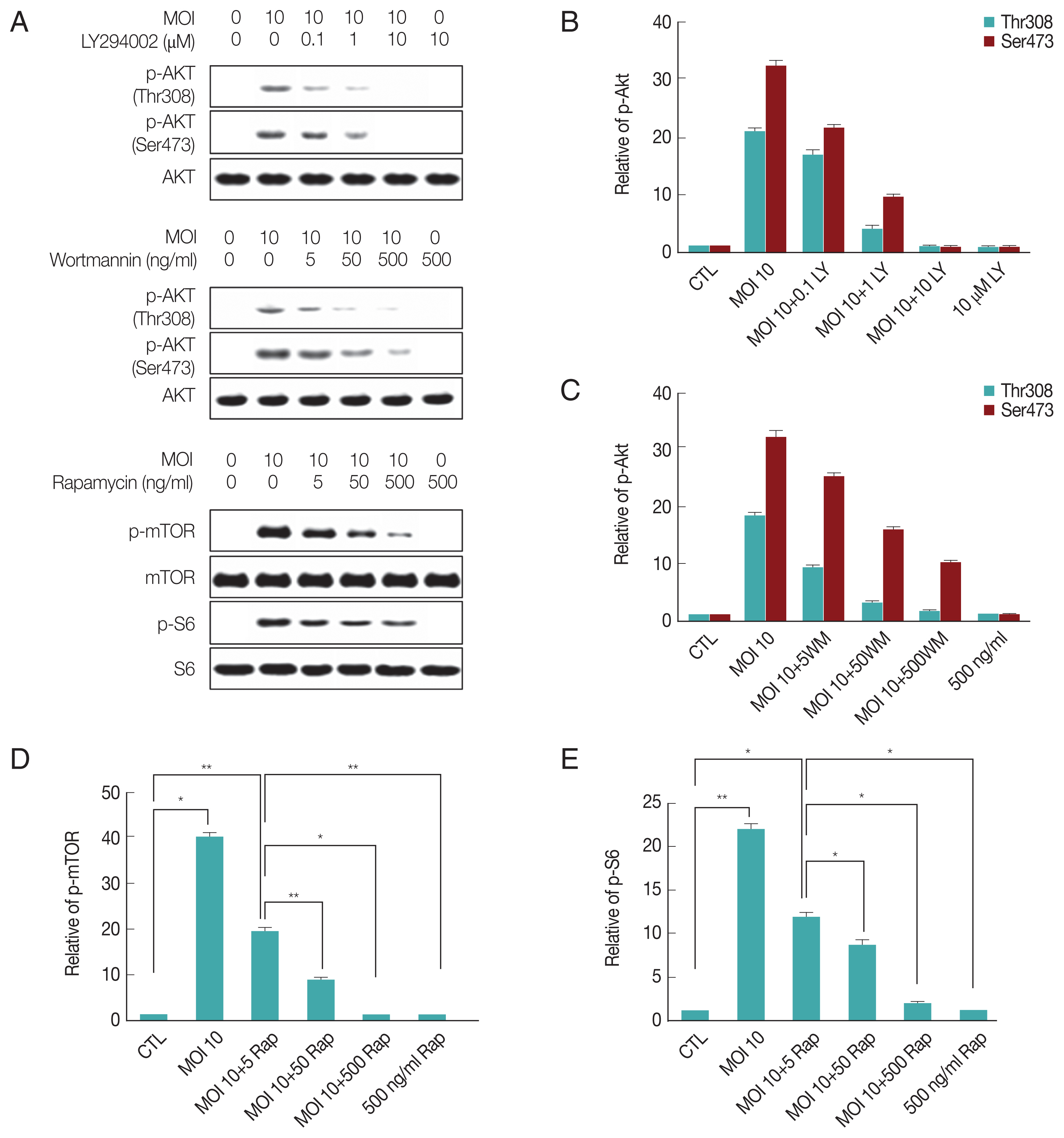
T. gondii induced PI3K/Akt and mTOR/S6 signaling activity
It is well known that
T. gondii trigger PI3-kinase signaling to activate Akt pathway upon infection in vivo and in vitro [
11]. To investigate the impact of
T. gondii-infection on the PI3K/Akt or mTOR pathways, ARPE-19 cells were infected with
T. gondii at multiplicity of infection (MOI) 10 for 24 hr and then treated with specific PI3K inhibitors LY294002 (LY 0.1, 1, 10 μM), wortmannin (WM 5, 50, 500 ng/ml) or mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (Rap 5, 50, 500 ng/ml) for 1 hr and the activity of each signaling protein were measured by western blot. As shown in
Fig. 1A, the phospholation levels of Akt (Thr308), Akt (Ser473), mTOR and S6 were elevated remarkably by
T. gondii infection. However,
T. gondii-induced increased activity Akt and mTOR were markedly attenuated by the LY294002, wortmannin and rapamycin. Furthermore, the densitometric analysis of western blot also confirmed that phosphorylation protein levels of Akt (Thr308), Akt (Ser473), mTOR and S6 were significantly increased by
T. gondii, but LY294002, wortmannin and rapamycin significantly prevented the
T. gondii-induced activity of Akt and mTOR, respectively (
Fig. 1A–E). These observations together suggest that
T. gondii-infection both activates the PI3K/Akt and mTOR pathways.
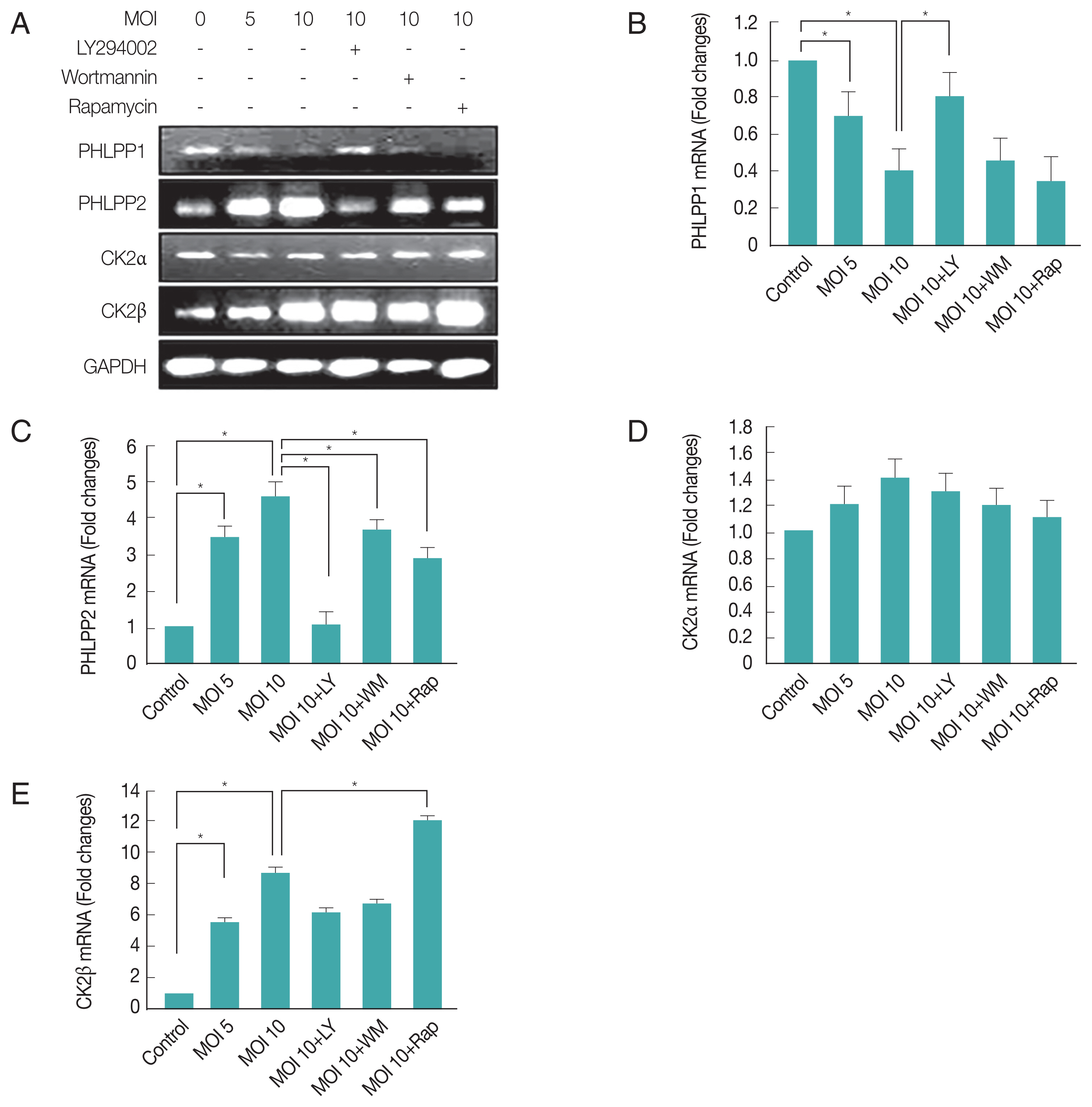
To directly address the consequences of activation of PI3K pathway induced by
T. gondii-infection on modulation of host gene expression, we first analyzed mRNA levels of PHLPP1, PHLPP2, CK2α, and CK2β. RT-PCR results showed that
T. gondii-infection suppressed PHLPP1 mRNA expression. Interestingly, the PI3 kinase inhibitor, LY294002, was able to repress the effect of
T. gondii to reverse the PHLPP1 mRNA level of host cell to normal level, but not wortmannin. The mTOR inhibitor rapamycin also had no effect on
T. gondii-induced PHLPP1 gene expression. Surprisingly, PHLPP2 mRNA expression level was elevated with
T. gondii infection, and all 3 inhibitors restrained the
T. gondii-dependent PHLPP2 mRNA induction.
T. gondii-infection had no effect on CK2α gene expression, but significantly up-regulated CK2β mRNA level. The induction of CK2β in response to
T. gondii infection was partially increased by rapamycin (
Fig. 2A). Similarly,
T. gondii-induced PHLPP1, PHLPP2, CK2α, and CK2β mRNA expression levels and effect of LY294002, wortmannin or rapamycin on these gene expression patterns were also confirmed by qRT-PCR method (
Fig. 2B–E).
These results suggest that PHLPPs are under control of PI3 kinase pathway; however, CK2β expression was insensitive to PI3K inhibitors but was sensitive to rapamaycin which suggests that CK2β might be under control of mTOR. Their sensitivity difference to LY294002, wortmannin or rapamycin implied the presence of micro-regulation system for these enzymes and signaling pathways.
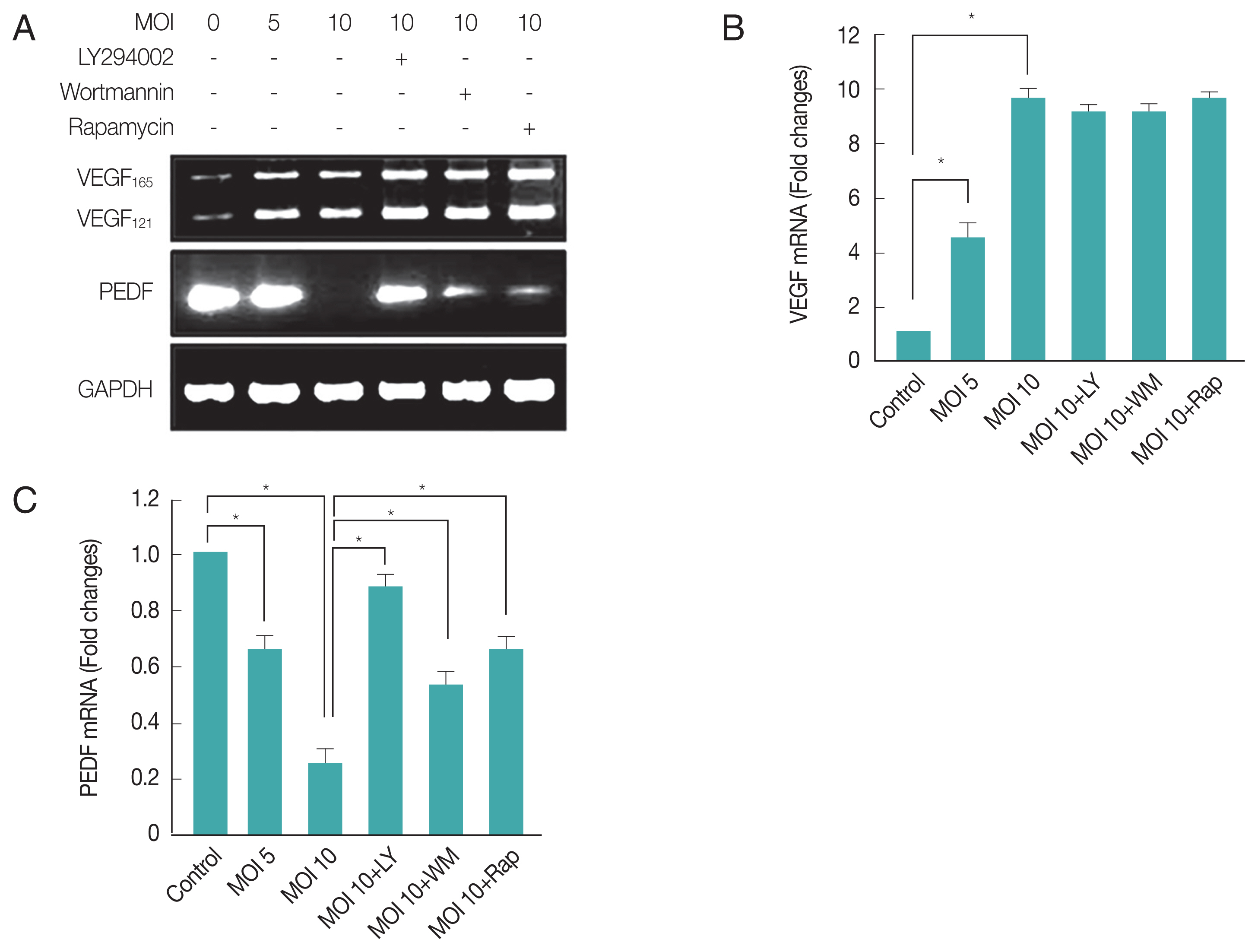
T. gondii infection up-regulated pro-angiogenic VEGF and down-regulated anti-angiogenic PEDF in ARPE-19 cells
Choroidal neovascularization is a severe complication of ocular toxoplasmic retinochoroiditis [
16]. Increased expression of VEGF, in addition to compromise in Bruch’s membrane and inflammation secondary to infection with
T. gondii, may contribute to neovascular disease in ocular toxoplasmosis [
29]. Therefore, we examined whether the
T. gondii infection can change the mRNA expression levels of VEGF and PEDF, well-known factors for neovascularization regulation in PI3K-Akt signaling dependent manner. As shown in
Fig. 3A and 3B,
T. gondii infection increased VEGF mRNA level of host cell in a MOI (parasite burden)-dependent manner, but post-infection treatment of the inhibitors of PI3K or mTOR did not suppress
T. gondii induced VEGF isoform transcription (VEGF
165 and VEGF
121) gene expression. These results suggest that
T. gondii can up-regulate VEGF expression in ARPE-19 cells, but this effect is not under the control of PI3K signaling pathway.
However, PEDF mRNA level was 4–5 times down-regulated by
T. gondii in a MOI (parasite burden)-dependent manner, and treatment of LY294002 was able to restore the reduced PEDF level to basal level. Wortmannin and rapamycin also showed partial suppression of
T. gondii effect on PEDF expression (
Fig. 3A, C). These results suggest
T. gondii induced down-regulation of PEDF expression is dependent on PI3K/Akt and partially on mTOR signaling pathways.
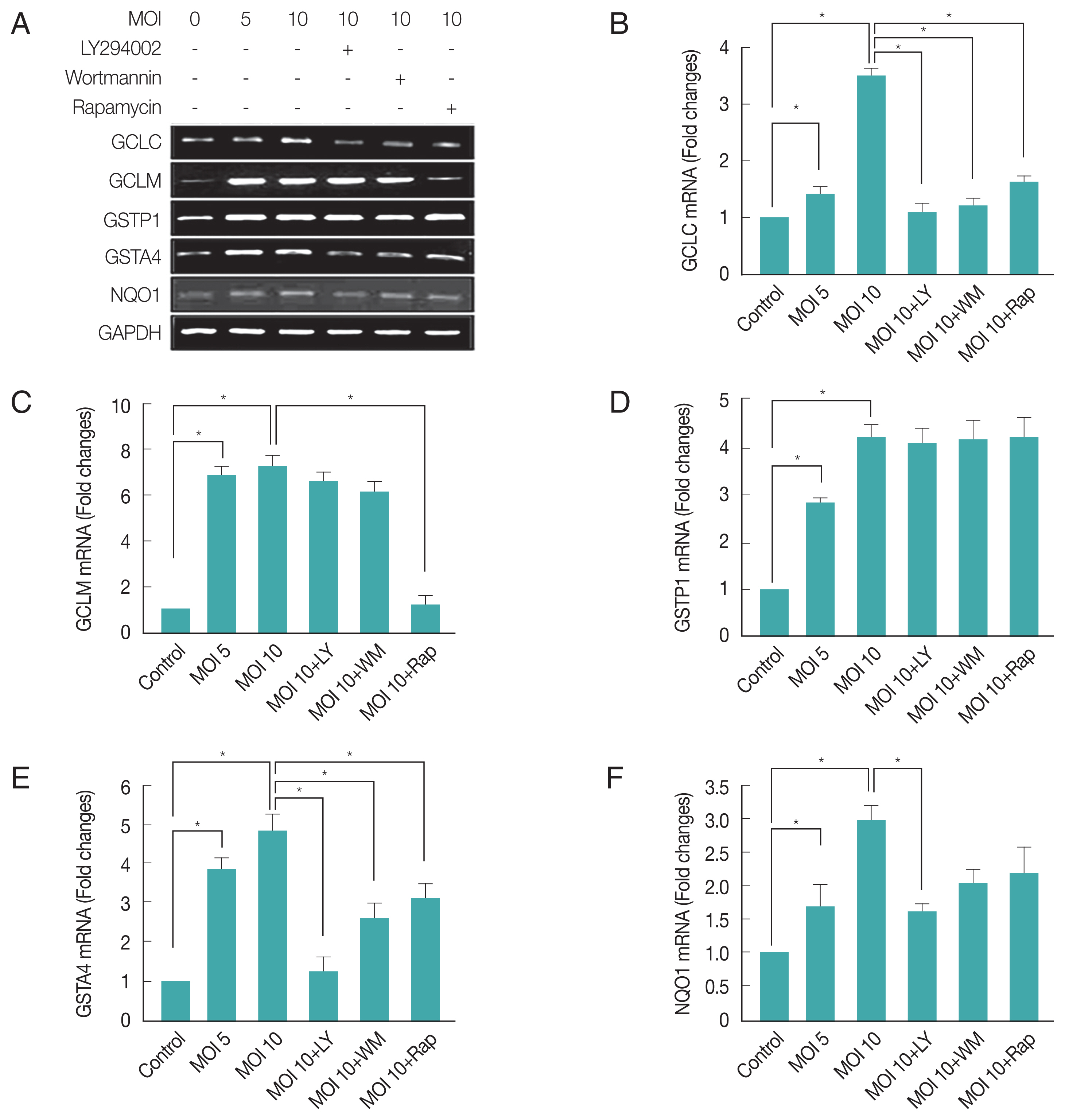
We further investigated
T. gondii modulated Phase II enzymes related gene expression levels via PI3K/Akt or mTOR pathway. As shown in
Fig. 4A and 4B,
T. gondii-infection significantly increased GCLC expression level as compared with uninfected control cell, and treatment of infected cell with LY294002, wortmannin or rapamycin significantly reduced its expression levels based on RT-PCR and qRT-PCR. Surprisingly,
T. gondii-infection dramatically increased GCLM mRNA levels, and treatment of infected cells with LY294002 or wortmannin had no effect on
T. gondii-induced up-regulation of GCLM gene expression, but treatment with rapamycin significantly suppressed
T. gondii-induced GCLM mRNA expression (
Fig. 4A, C). These results show that mTOR but not PI3K was important for
T. gondii to induce GCLM transcription regulation.
Furthermore,
T. gondii-infection significantly induced both GSTP1 and GSTA4 expression in host cells, when
T. gondii-infected cells were treated with PI3K or mTOR inhibitors, these inhibitors had no effect on
T. gondii induced GSTP1 gene expression. In contrast, LY294002, wortmannin or rapamysin remarkably suppressed
T. gondii-induced GSTA4 mRNA transcription to basal level (
Fig. 4D, E). Indicating that GSTP1 expression induced by
T. gondii is insensitive to PI3K or mTOR pathway, but GSTA4 expression is dependent on PI3K and mTOR signaling.
We focused on another oxidoreductase, NQO1, which uses either NADH or NADPH as a reducing cofactor to catalyze the obligate 2-electron reduction of quinones to hydroquinones [
30].
T. gondii-infection significantly increased (about 1.7 folds) NQO1 mRNA expression and LY294002 was significantly inhibited the
T. gondii-induced NQO1 gene expression (
Fig. 4A, F). These results provide strong evidence that
T. gondii may cause Phase II enzyme regulation through the PI3K/Akt pathway.
DISCUSSION
This is the first study to investigate the host PI3 kinase-Akt pathway affiliated genes upon to T. gondii infection in human RPE cell. Since T. gondii is an intracellular parasite, the retina sustains the major damage and primary insult. We found that T. gondii replication is associated with expression level changes of multiple known and novel genes involved in signaling and ROS regulation in ARPE-19 cells on host PI3K/Akt or mTOR pathway activation.
T. gondii have devised strategies to extend the life of infected host cells by targeting key signal transduction pathways such as PI3 kinase-Akt or mTOR pathways [
31,
32]. In vitro experiments revealed that the activation of PKB in host cell infected with
T. gondii was dependent upon the host PI3K and Gi protein-coupled trans-membrane receptors (GiPCR) [
8]. Gene silencing studies reveal that PHLPP1 knockdown or genetic deletion increase Akt phosphorylation at Ser473 which results in significant increase in Akt catalytic activity [
33].
In this study, PHLPP1 mRNA expression was significantly reduced after
T. gondii infection which can contribute to maintain high levels of activated Akt that may prevent host cell death. But for PHLPP2, it is observed that
T. gondii infection induces its gene expression of host cell. This phenomenon could be due to a compensation role of PHLPP2 for the loss of PHLPP1. Indeed, in human cells, it has been reported that knockdown of PHLPP1 resulted in greater expression of PHLPP2, and vice versa [
34]. Treatment with PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, inversed
T. gondii-induced the phosphatases mRNA expression pattern that PHLPP1 increased however PHLPP2 decreased. The
T. gondii-induced reduction of Akt’s negative regulator, PHLPP1, provides a novel mechanism used by
T. gondii to elongate the Akt activation in RPE cells.
It has been reported that CK2 kinase mediates phosphorylation of PTEN, and its phosphorylation inhibits PTEN function [
15]. Gene silencing studies of CK2 indicated that CK2β is essential for cell viability [
35], based on the reports, it was wondered that the main regulated subunit by
T. gondii is CK2β but not CK2α. A very interesting result of the present study is the relationship between CK2β and the PI3K pathway, CK2β showed a significant positive correlation with Akt and a nearly dramatic negative correlation with PTEN immunoexpression [
36].
In the present study, CK2α mRNA level was not sensitive to T. gondii infection, but CK2β mRNA level increased highly in moi-dependent manner. Inhibitor experiment showed that only rapamycin leads to additional up-regulation of CK2β by T. gondii. These results suggest that endogenous PTEN level can be regulated by T. gondii-controlled CK2β level, and mTOR functions as a negative regulating component in CK2β gene expression.
Clinical experiments show that intravitreal anti-VEGF agents therapy plus anti-
T. gondii medicines have potentials to be efficacious in treatment of ocular neovascularization secondary to ocular toxoplasmosis [
29]. Recent studies have identified that PEDF inhibits angiogenesis in the eye and as a therapeutic agent for retinal and choroidal diseases triggered by photoreceptor degenerations and abnormal neovascularization has been explored in animal models and is being evaluated in a clinical trial [
36]. The counterbalance of VEGF and PEDF is supported by the previous demonstrations that either inhibition of the VEGF system or over-expression of PEDF inhibits choroidal neovascularization [
37]. Our experimental results showed that
T. gondii down-regulates PEDF gene expression, and causes the over-expression of VEGF, which will bring the disruption of the balance between VEGF and PEDF. This event might be a valuable target for therapeutic studies about ocular toxoplasmosis.
Inflammatory ROS is believed to play critical roles in various ocular diseases. Several studies have indicated that RPE cells are capable of producing ROS under certain conditions [
38]. It has been reported that proliferation of
T. gondii can diminish oxygen radical production in the macrophage cell in vivo, but most of the mechanisms and pathways involved are not still understood [
19]. Recent studies have shown that the PI3K/Akt pathway is essential in regulating the Nrf2-ARE-dependent protection against oxidative stress in the RPE [
39]. Our results have shown that
T. gondii can induce the expression of the phase II detoxification genes, increase GLC, GST, and NQO1 genes expression, and confirmed that these gene changes were mediated by PI3K/Akt or mTOR pathway. In accordance with our data, it was reported that protein levels of GSTA4 and activity of GST were elevated with the increase of Insulin signaling pathway [
40]. However, it also has been reported that, in Human foreskin fibroblasts,
T. gondii infection reduced GSTA2 levels [
41]. The different reaction between GSTA2 and GSTA4 expression against
T. gondii may imply various considerable factors; different cell context based on intracellular ROS level or nutrition conditions, possible mutual independent gene expression stimulation mechanisms, or even compensation mechanism based on other intracellular GST levels to sustain homeostasis of host cell. Further studies are required to solve the mystery of this observation.
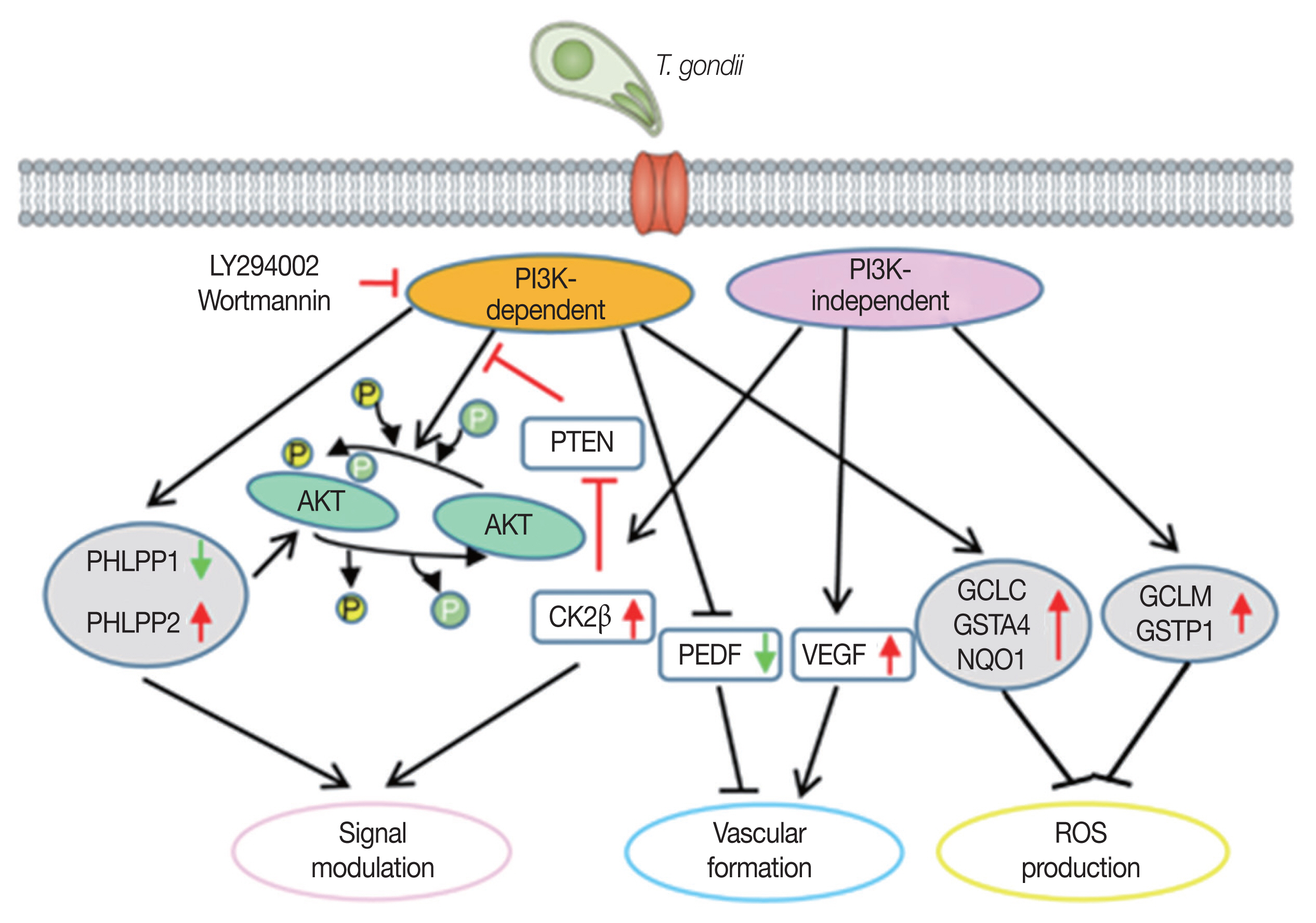
In conclusion, we found that many host genes of ARPE-19 cells involved in Akt signal regulation, vascular formation and ROS suppression can be modulated by
T. gondii-induced PI3K/Akt pathway. Based on their biological functions, we suggest that the compilation of these PI3K/Akt dependent and certain mTOR dependent gene expression change will promote the establishing of host environment which is favorable for infected parasite (
Fig. 5). Characterization of PI3K/Akt or mTOR pathway regulation in response to
T. gondii infection will provide a better understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms of ocular toxoplasmosis and may lead to more innovative methods for developing appropriate therapeutic therapy in correlation with metabolism disease such as diabetes mellitus or age-dependent vision loss.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (NRF-2013R1A1A2062046), the Research Fund of Chungnam National University, the Korea Health Technology Research & Development Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (A100876), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2015HQ033), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81701575).
Fig. 1
T. gondii infection induces PI3K/Akt and mTOR/S6 signaling activity, and the activity was suppressed by PI3K/Akt or mTOR inhibitors. ARPE-19 cells were infected with T. gondii at MOI 10 for 24 hr and then treated with specific PI3K inhibitors LY294002 (LY 0.1, 1, 10 μM), wortmannin (WM 5, 50, 500 ng/ml) or mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (Rap 5, 50, 500 ng/ml) for 1 hr. The activity of each signaling protein levels were measured by western blot (A). Bar plot depicting the phospho-Akt (Thr308)/Total Akt, phospho-Akt (Ser473)/Total Akt, phospho-mTOR/Total mTOR, phospho-S6/Total S6 (B–E) ratios as determined by densitometric analysis of western blot and expressed as fold change compared with control ARPE-19 cells. For all panels, data are presented as the mean±SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with control or MOI 10 of T. gondii-infected groups. All data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments.
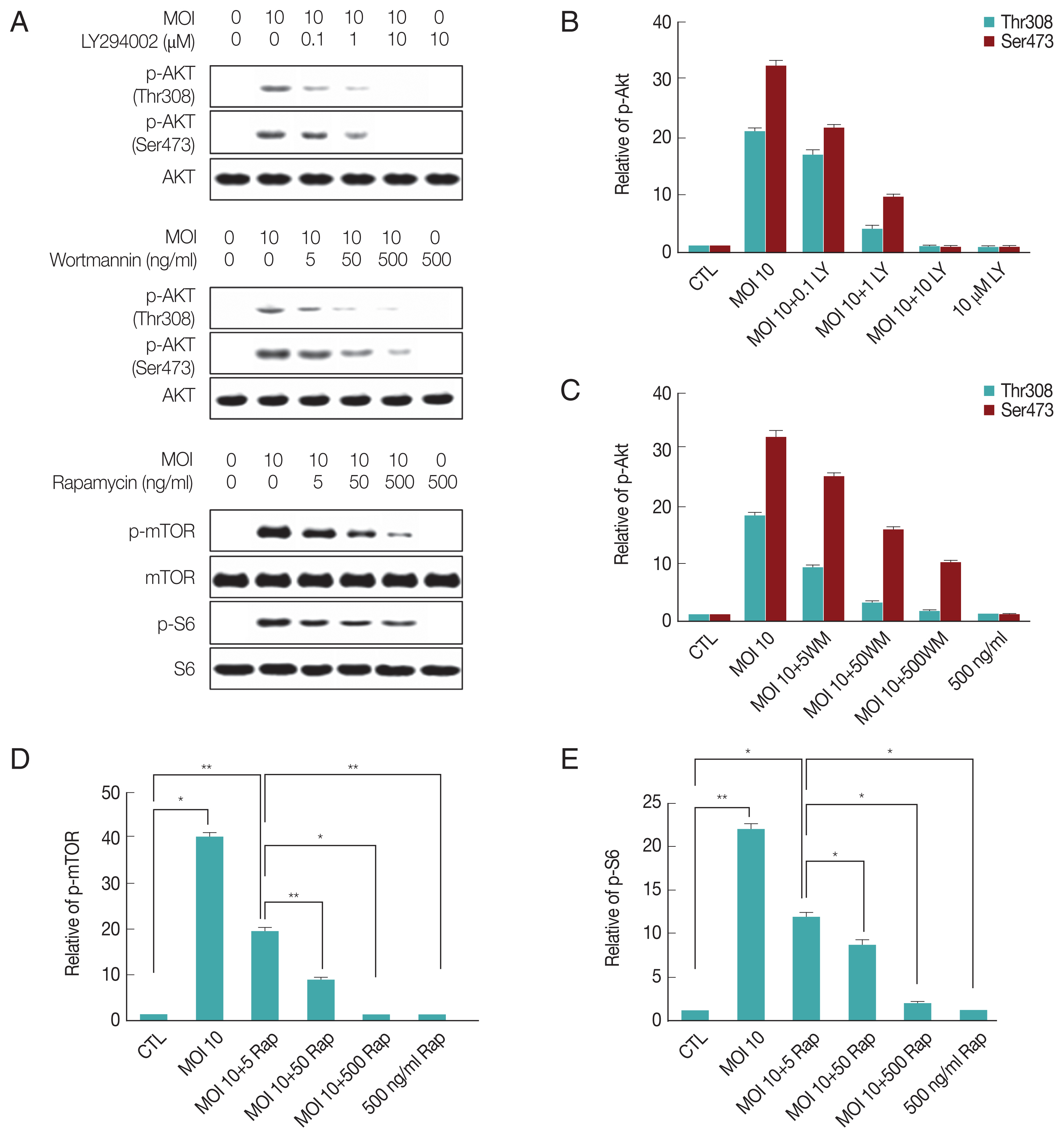
Fig. 2Differential regulations of PHLPP1, PHLPP2, CK2α, and CK2β after infection with T. gondii. ARPE-19 cells were infected with different MOI of T. gondii for 24 hr and then treated for 1 hr with specific PI3K inhibitors LY294002 (LY 10 μM), wortmannin (WM 500 ng/ml) or mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (Rap 500 ng/ml) and gene expression levels were measured by RT-PCR (A) and PHLPP1 (B), PHLPP2 (C), CK2α (D), CK2β (E) expression levels were determined by qRT-PCR. Values represent the Mean±SD of triplicates. *P<0.05 compared with control or MOI 10 of T. gondii-infected groups. All data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments.
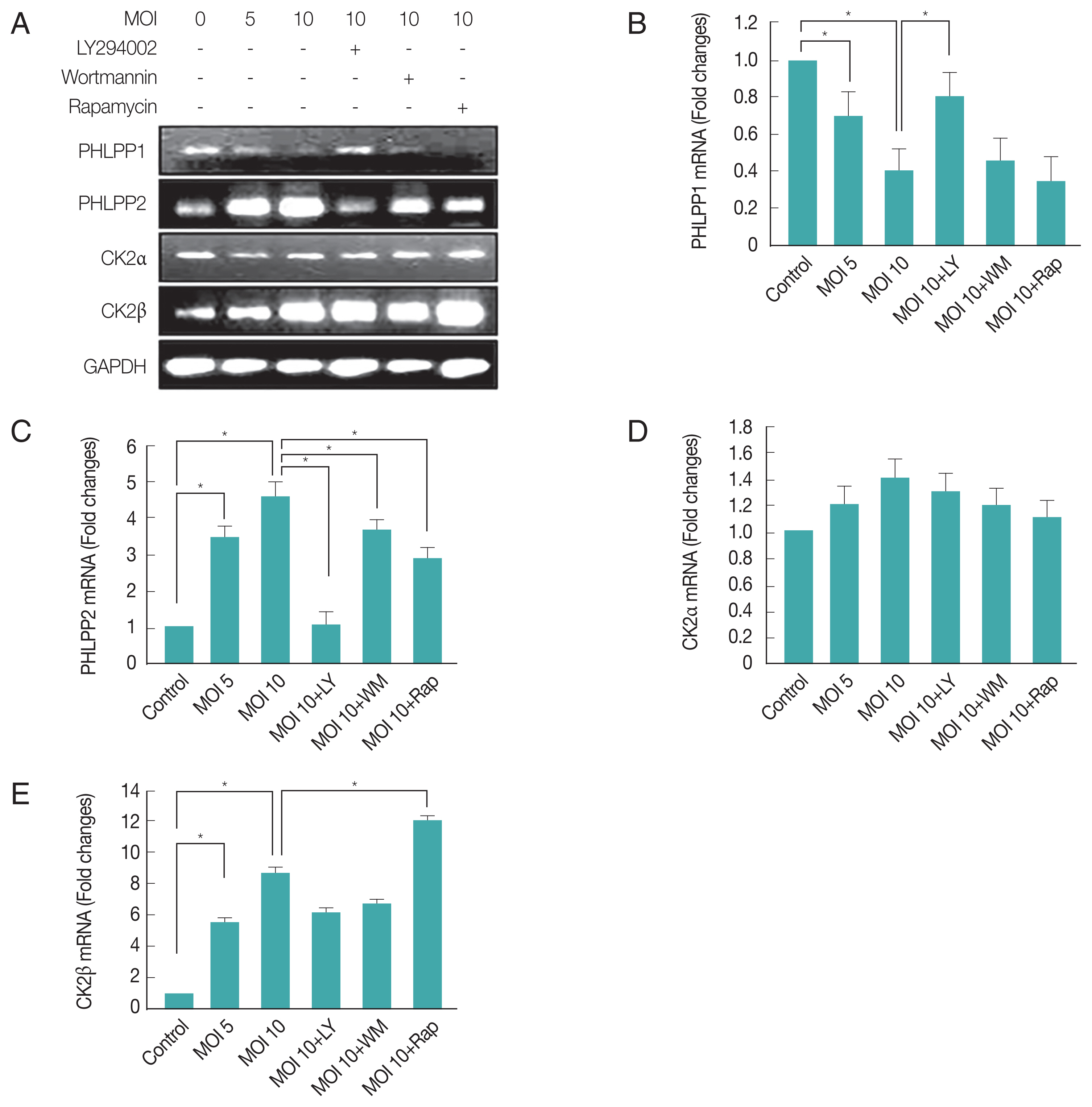
Fig. 3
T. gondii-infection up-regulates VEGF gene expression but down-regulates PEDF gene expression. RT-PCR (A) and qRT-PCR (B, C) were used to measure host cell VEGF and PEDF transcript abundance. Values represent the Mean±SD of triplicates. *P<0.05 compared with control or MOI 10 of T. gondii-infected groups. All data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments.
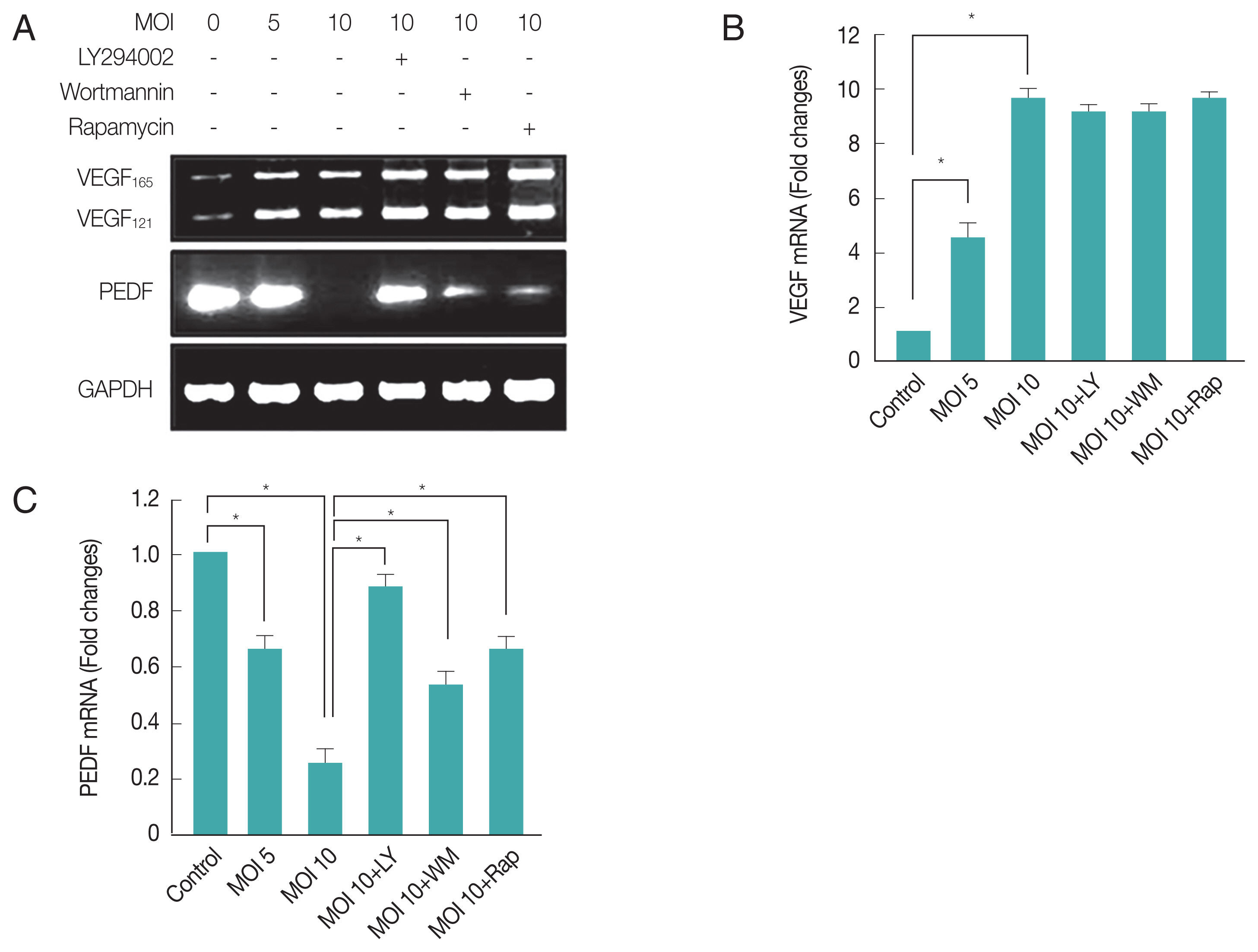
Fig. 4
T. gondii-induced regulation of “Antioxidants and Phase II Enzymes” in ARPE-19 cell. The mRNA levels of both the catalytic (GCLC) and modulatory (GCLM) subunits of GCL as well as 4 other phases 2 detoxification genes, GSTP1, GSTA4, and NQO1 were measured by RT-PCR (A) and qRT-PCR (B, C, D, E, F) after T. gondii infection and inhibitors treatment. Values represent the Mean±SD of triplicates. *P<0.05 compared with control or MOI 10 of T. gondii-infected groups. All data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments.

Fig. 5The model of T. gondii-modulated PI3K/Akt or mTOR pathways on regulating 3 different cellular events to generate parasite-favorable host environment.
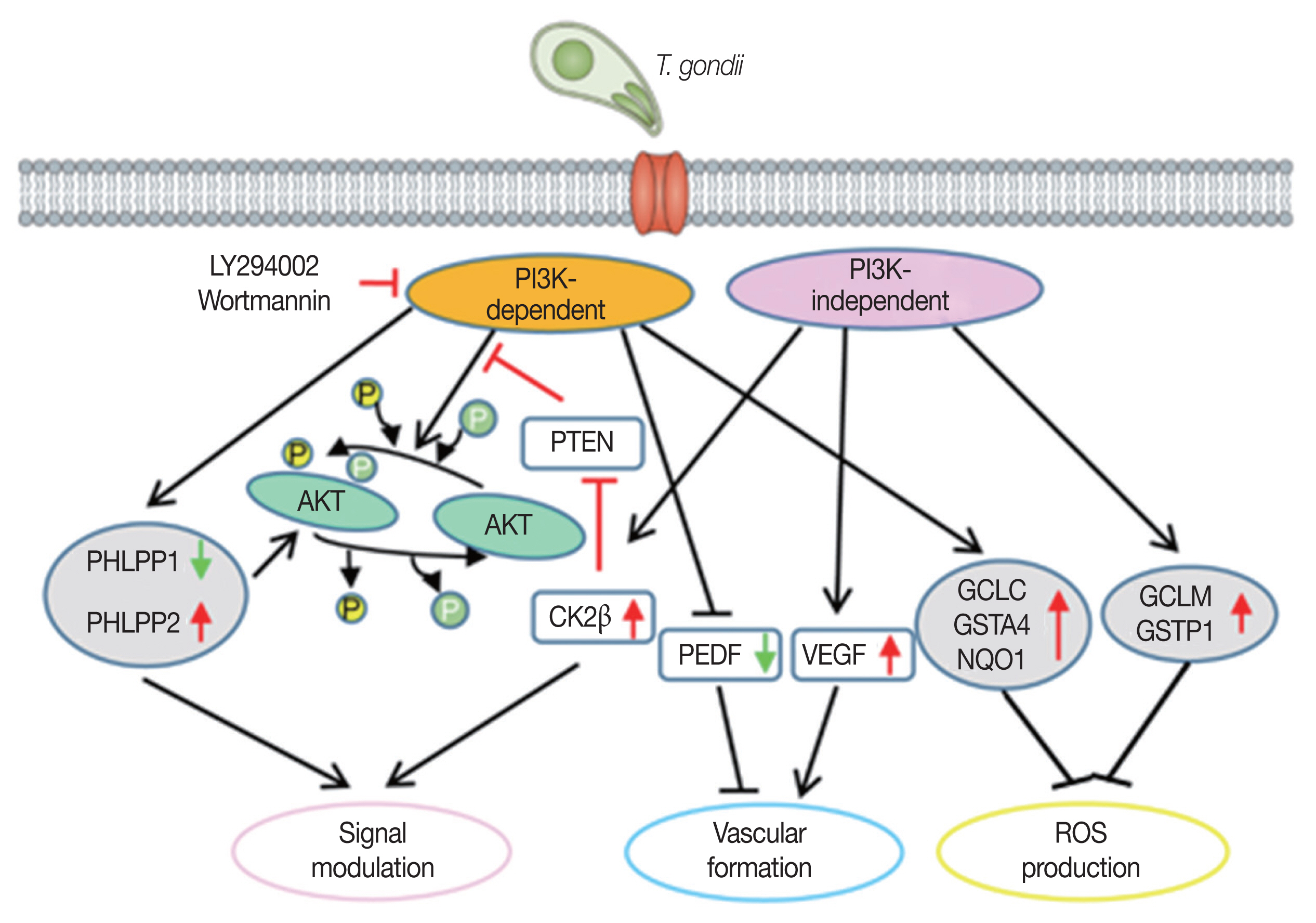
Table 1Primer sequences used for PCR and qRT-PCR in this study
Table 1
|
Gene name |
Primer sequence (5′ to 3′) |
Products size (bp) |
|
|
RT-PCR |
qRT-PCR |
|
PHLPP1 |
F-ACACCGTGATTGCTCACTCC |
F-ACACCGTGATTGCTCACTCC |
156/156 |
|
R-TTCCAGTCAGGTCTAGCTCC |
R-TTCCAGTCAGGTCTAGCTCC |
|
|
|
PHLPP2 |
F-AGGTTCCTGAGCATCTCTTC |
F-AGGTTCCTGAGCATCTCTTC |
128/128 |
|
R-GTTCAGGCCCTTCAGTTGAG |
R-GTTCAGGCCCTTCAGTTGAG |
|
|
|
CK2α |
F-ATTGAATTAGATCCACGTTT |
F-CCCAACATCATCACACTGGC |
346/159 |
|
R-GGTTGGCAGCAGCAATCACT |
R-CCAGGGCCTTCAGAATCTCA |
|
|
|
CK2β |
F-ACTGTGAGAACCAGCCAATG |
F-TCAAGACACCATCACACGGA |
287/187 |
|
R-CTTGAAGTTGCTGGCGGCTT |
R-CTGGGCTCTTGAAGTTGCTG |
|
|
|
VEGF |
F-GAAGTGGTGAAGTTCATGGATGTC |
F-CTGTCTTGGGTGCATTGGAG |
165/121/164 |
|
R-CGATCGTTCTGTATCAGTCTTTCC |
R-ACCAGGGTCTCGATTGGATG |
|
|
|
PEDF |
F-CAGAAGAACCTCAAGAGTGCC |
F-AGAACCTCAAGAGTGCCTCC |
310/176 |
|
R-CTTCATCCAAGTAGAAATCCTC |
R-GAGCTTCCCTTTCATCTGCG |
|
|
|
GCLC |
F-GAGGCTATGTGTCAGACATTGATTGTCG |
F-CAGGTGACATTCCAAGCCTG |
688/120 |
|
R-GTGTACTCCTCTGCAGCGAGCTCCGTG |
R-CGGTAAAAGGGAGATGCAGC |
|
|
|
GCLM |
F-GTCCACGCACAGCGAGGAGCTTCATG |
F-CTGTATCAGTGGGCACAGGT |
542/198 |
|
R-GATCATTGTGAGTCAACAGCTGTATG |
R-GTGCGCTTGAATGTCAGGAA |
|
|
|
GSTP1 |
F-GCTGCGCGGCCCTGCGCATGCTG |
F-GGACTTGCTGCTGATCCATG |
429/145 |
|
R-GCAGGTTGTAGTC AGCGAAGGAG |
R-ATTGATGGGGAGGTTCACGT |
|
|
|
GSTA4 |
F-GGATGAAGTTGGTACACACCCGAAG |
F-CAACAAGTGCCCATGGTTGA |
435/223 |
|
R-GAGGCTTCTTCTTGCTGCCAGGTTCAAG |
R-CTGGGCCATGTTAACCACT |
|
|
|
NQO1 |
F-ATGGTCGGCAGAAGAGCACTGATCG |
F-ACTCTCTGCAAGGGATCCAC |
708/174 |
|
R-TTTTCTAGCTTTGATCTGGTTGTCAGTTGGG |
R-TCTCCAGGCGTTTCTTCCAT |
|
|
|
GAPDH |
F-ACCACAGTCCATGCCATCAC |
F-GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCA |
452/131 |
|
R-TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGT |
R-CCTGGAAGATGGTGATGGGA |
|
References
- 1. Vallochi AL, Nakamura MV, Schlesinger D, Martins MC, Silveira C, Belfort R Jr, Rizzo LV. Ocular toxoplasmosis: more than just what meets the eye. Scand J Immunol 2002;55:324-328.
- 2. Rao NA, Font RL. Toxoplasmic retinochoroiditis: electron-microscopic and immunofluorescence studies of formalin-fixed tissue. Arch Ophthalmol 1977;95:273-277.
- 3. Willermain F, Caspers-Velu L, Nowak B, Stordeur P, Mosselmans R, Salmon I, Velu T, Bruyns C. Retinal pigment epithelial cells phagocytosis of T lymphocytes: possible implication in the immune privilege of the eye. Br J Ophthalmol 2002;86:1417-1421.
- 4. Sibley LD.
Toxoplasma gondii: perfecting an intracellular life style. Traffic 2003;4:581-586.
- 5. Boothroyd JC, Dubremetz JF. Kiss and spit: the dual roles of Toxoplasma rhoptries. Nat Rev Microbiol 2008;6:79-88.
- 6. Zenner L, Foulet A, Caudrelier Y, Darcy F, Gosselin B, Capron A, Cesbron-Delauw MF. Infection with Toxoplasma gondii RH and Prugniaud strains in mice, rats and nude rats: kinetics of infection in blood and tissues related to pathology in acute and chronic infection. Pathol Res Pract 1999;195:475-485.
- 7. Kotze AC, McClure SJ.
Haemonchus contortus utilises catalase in defence against exogenous hydrogen peroxide in vitro. Int J Parasitol 2001;31:1563-1571.
- 8. Kim L, Denkers EY.
Toxoplasma gondii triggers Gi-dependent PI 3-kinase signaling required for inhibition of host cell apoptosis. J Cell Sci 2006;119:2119-2126.
- 9. Wang Y, Weiss LM, Orlofsky A. Coordinate control of host centrosome position, organelle distribution, and migratory response by Toxoplasma gondii via host mTORC2. J BiolChem 2010;285:15611-15618.
- 10. Chaussabel D, Semnani RT, McDowell MA, Sacks D, Sher A, Nutman TB. Unique gene expression profiles of human macrophages and dendritic cells to phylogenetically distinct parasites. Blood 2003;102:672-681.
- 11. Molestina RE, Payne TM, Coppens I, Sinai AP. Activation of NF-kappa B by Toxoplasma gondii correlates with increased expression of antiapoptotic genes and localization of phosphorylated Ikappa B to the parasitophorous vacuole membrane. J Cell Sci 2003;116:4359-4371.
- 12. Brognard J, Scierecki E, Gao T, Newton AC. PHLPP and a second isoform, PHLPP2, differentially attenuate the amplitude of Akt signaling by regulating distinct Akt isoforms. Mol Cell 2007;25:917-931.
- 13. Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL, Brothers GM, Mirtsos C, Sasaki T, Ruland J, Penninger JM, Siderovski DP, Mak TW. Negative regulation of PKB/Akt-dependent cell survival by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell 1998;95:29-39.
- 14. Litchfield DW. Protein kinase CK2: structure, regulation and role in cellular decisions of life and death. Biochem J 2003;369:1-15.
- 15. Miller SJ, Lou DY, Seldin DC, Lane WS, Neel BG. Direct identification of PTEN phosphorylation sites. FEBS Lett 2002;528:145-153.
- 16. Neri P, Mercanti L, Mariotti C, Salvolini S, Giovannini A. Long-term control of choroidal neovascularization in quiescent congenital toxoplasma retinochoroiditis with photodynamic therapy: 4-year results. Int Ophthalmol 2010;30:51-56.
- 17. Wang H, Hartnett ME. Regulation of signaling events involved in the pathophysiology of neovascular AMD. Mol Vis 2016;22:189-202.
- 18. Balaratnasingam C, Dhrami-Gavazi E, McCann JT, Ghadiali Q, Freund KB. Aflibercept: a review of its use in the treatment of choroidal neovascularization due to age-related macular degeneration. Clin Ophthalmol 2015;9:2355-2371.
- 19. Zhou W, Quan JH, Lee YH, Shin DW, Cha GH.
Toxoplasma gondii proliferation require down-regulation of host Nox4 expression via activation of PI3 Kinase/Akt signaling pathway. PLoS One 2013;8:e66306.
- 20. Talalay P. Chemo protection against cancer by induction of phase 2 enzymes. Biofactors 2000;12:5-11.
- 21. Lin YC, Huang GD, Hsieh CW, Wung BS. The glutathionylation of p65 modulates NF-κB activity in 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J-treated endothelial cells. Free Radic Bio Med 2012;52:1844-1853.
- 22. Hayes JD, Strange RC. Potential contribution of the glutathione S-transferase supergene family to resistance to oxidative stress. Free Radic Res 1995;22:193-207.
- 23. Cheng JZ, Singhal SS, Saini M, Singhal J, Piper JT, Van Kuijk FJ, Zimniak P, Awasthi YC, Awasthi S. Effects of mGST A4 transfection on 4-hydroxynonenal-mediated apoptosis and differentiation of K562 human erythroleukemia cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 1999;372:29-36.
- 24. Wang Z, He W, Yang G, Wang J, Wang Z, Nesland JM, Holm R, Suo Z. Decreased expression of GST pi is correlated with a poor prognosis in human esophageal squamous carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2010;10:352.
- 25. Hirano I, Nakamura S, Yokota D, Ono T, Shigeno K, Fujisawa S, Shinjo K, Ohnishi K. Depletion of Pleckstrin homology domain leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatases 1 and 2 by Bcr-Abl promotes chronic myelogenous leukemia cell proliferation through continuous phosphorylation of Akt isoforms. J BiolChem 2009;284:22155-22165.
- 26. Ohta Y, Endo Y, Tanaka M, Shimizu J, Oda M, Hayashi Y, Watanabe Y, Sasaki T. Significance of vascular endothelial growth factor messenger RNA expression in primary lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1996;2:1411-1416.
- 27. Tong JP, Lam DS, Chan WM, Choy KW, Chan KP, Pang CP. Effects of triamcinolone on the expression of VEGF and PEDF in human retinal pigment epithelial and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Vis 2006;12:1490-1495.
- 28. Dhakshinamoorthy S, Porter AG. Nitric oxide-induced transcriptional up-regulation of protective genes by Nrf2 via the antioxidant response element counteracts apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 2004;279:20096-20107.
- 29. Benevento JD, Jager RD, Noble AG, Latkany P, Mieler WF, Sautter M, Meyers S, Mets M, Grassi MA, Rabiah P, Boyer K, Swisher C, McLeod R. Toxoplasmosis-associated neovascular lesions treated successfully with ranibizumab and antiparasitic therapy. Arch Ophthalmol 2008;126:1152-1156.
- 30. Ross D, Kepa JK, Winski SL, Beall HD, Anwar A, Siegel D. NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1): chemoprotection, bioactivation, gene regulation and genetic polymorphisms. Chem Biol Interact 2000;129:77-97.
- 31. Quan JH, Cha GH, Zhou W, Chu JQ, Nishikawa Y, Lee YH. Involvement of PI3 kinase/Akt-dependent Bad phosphorylation in Toxoplasma gondii-mediated inhibition of host cell apoptosis. Exp Parasitol 2013;133:462-471.
- 32. Wang Y, Weiss LM, Orlofsky A. Intracellular parasitism with Toxoplasma gondii stimulates mammalian-target-of-rapamycin-dependent host cell growth despite impaired signaling to S6K1 and 4E-BP1. Cell Microbiol 2009;11:983-1000.
- 33. Miyamoto S, Purcell NH, Smith JM, Gao T, Whittaker R, Huang K, Castillo R, Glembotski CC, Sussman MA, Newton AC, Brown JH. PHLPP-1 negatively regulates Akt activity and survival in the heart. Circ Res 2010;107:476-484.
- 34. Patterson SJ, Han JM, Garcia R, Assi K, Gao T, O’Neill A, Newton AC, Levings MK. Cutting edge: PHLPP regulates the development, function, and molecular signaling pathways of regulatory T cells. J Immunol 2011;186:5533-5537.
- 35. Buchou T, Vernet M, Blond O, Jensen HH, Pointu H, Olsen BB, Cochet C, Issinger OG, Boldyreff B. Disruption of the regulatory beta subunit of protein kinase CK2 in mice leads to a cell-autonomous defect and early embryonic lethality. Mol Cell Biol 2003;23:908-915.
- 36. Pallares J, Llobet D, Santacana M, Eritja N, Velasco A, Cuevas D, Lopez S, Palomar-Asenjo V, Yeramian A, Dolcet X, Matias-Guiu X. CK2beta is expressed in endometrial carcinoma and has a role in apoptosis resistance and cell proliferation. Am J Pathol 2009;174:287-296.
- 37. Rasmussen H, Chu KW, Campochiaro P, Gehlbach PL, Haller JA, Handa JT, Nguyen QD, Sung JU. Clinical protocol. An open-label, phase I, single administration, dose-escalation study of ADGVPEDF.11D (ADPEDF) in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Hum Gene Ther 2001;12:2029-2032.
- 38. Lee H, Chung H, Arnouk H, Lamoke F, Hunt RC, Hrushesky WJ, Wood PA, Lee SH, Jahng WJ. Cleavage of the retinal pigment epithelium-specific protein RPE65 under oxidative stress. Int J Biol Macromol 2010;47:104-108.
- 39. Wang L, Chen Y, Sternberg P, Cai J. Essential roles of the PI3 kinase/Akt pathway in regulating Nrf2-dependent antioxidant functions in the RPE. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008;49:1671-1678.
- 40. Kim SK, Abdelmegeed MA, Novak RF. Identification of the insulin signaling cascade in the regulation of alpha-class glutathione S-transferase expression in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2006;316:1255-1261.
- 41. Nelson MM, Jones AR, Carmen JC, Sinai AP, Burchmore R, Wastling JM. Modulation of the host cell proteome by the Intracellular Apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii
. Infect Immun 2008;76:828-844.