Abstract
Cystic echinococcosis (CE) caused by E. granulosus is a serious helminthic zoonosis in humans, livestock and wildlife. Xinjiang is one of high endemic province for CE in China. A total of 55 sheep and cattle livers containing echinococcal cysts were collected from slaughterhouses in Changji and Yining City, northern region of Xinjiang. PCR was employed for cloning 2 gene fragments, 12S rRNA and CO1 for analysis of phylogenetic diversity of E. granulosus. The results showed that all the samples collected were identified as G1 genotype of E. granulosus. Interestingly, YL5 and CJ75 strains were the older branches compared to those strains from France, Argentina, Australia. CO1 gene fragment showed 20 new genotype haploids and 5 new genotype haplogroups (H1-H5) by the analysis of Network 5.0 software, and the YLY17 strain was identified as the most ancestral haplotype. The major haplotypes, such as CJ75 and YL5 strains, showed identical to the isolates from Middle East. The international and domestic trade of livestock might contribute to the dispersal of different haplotypes for E. granulosus evolution.
-
Key words: Echinococcus granulosus, CO1 gene, cystic echinococcosis, northwest China
INTRODUCTION
Echinococcosis is a worldwide lethal zoonosis caused by adult or larval stages of tapeworms of the genus
Echinococcus [
1]. Transmission of
echinococcosis depends on carnivores as definitive hosts and various animals as intermediate hosts. Human beings and intermediate hosts (
eg. sheep, goat and cattle) will be infected when ingesting eggs of
Echinococcus [
30]. Echinococcosis is highly significant infectious diseases occurring worldwide and caused by metacestodes of
E. granulosus, Which usually form fluid filled hydatids located in liver, lung and other organs [
2]. According to the new molecular phylogeny of the genus
Echinococcus,
E. granulosus is characterized into 10 genotypes, including
E. granulosus sensu stricto (G1-G3),
E. equinus (G4),
E. ortleppi (G5), and
E. canadensis (G6-G10) [
3]. Of which,
E. granulosus sensu stricto composes of genotype G1 (sheep strain), G2 (Tasmanian sheep strain) and G3 (buffalo strain) [
4]. Genotype G1 has the highest host variability, including humans, wild and domestic mammals [
1,
5].
Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR) has a vast territory, complex geographical landscape and climatic conditions. Topographically, XUAR is characterized by a sharp demarcation of mountains and basins [
6]. XUAR is a high incidence area of echinococcosis. The infection rate of echinococcosis in Northern Xinjiang is higher than that of Southern Xinjiang and Eastern Xinjiang. At the same time, the infection rate in Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture (Changji) and Yili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture (Yili) rank the top 2 in XUAR [
33]. Although Changji and Ili regions belong to the northern region of XUAR, but there is obvious difference in the aspect of the geographical environment and climatic conditions, Ili region is located in Ili Valley, the average precipitation is 400–600 mm per year. Changji region is located in Junggar Basin, the average precipitation is 200–300 mm per year [
7]. The different climatic environment provides a good natural conditions for the survival of different kinds of
E. granulosus parasite [
8].
Echinococcosis of human and livestock has highest prevalence rates in western and northwestern China, including XUAR [
9]. In previous work, although genotype G1 is responsible for the majority of human and livestock infections in XUAR, the data on genetic variability and regional genetic differences of genotype G1 are scarce. The aim of this study was to evaluate the genetic variability and phylogeography for
E. granulosus from sheep and cattle collected in Changji and Ili regions, XUAR.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection and DNA extraction
During 2016–2017, a total of 55 livers with CE were collected from sheep (n=45) and cattle (n=10) at the slaughterhouses in Changji City and Yining City, XUAR, northwestern China. Each cystic fluid was extracted into 1.5 ml ependoff tube. The genomic DNA of the supernatants were extracted with TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit and kept at −20°C [
10].
To determine genetic variability and regional differences of
E. granulosus, all samples were examined targeting 12S rRNA and
CO1 genes by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) according to previous descriptions [
11,
12]. Each cycling reaction was provided with double distilled water as negative control and a positive control of the DNA template of
E. granulosus. The PCR products were purified using the TIAN gel Midi Purification Kit (TIANGEN, Beijing, China) and sequenced by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Each amplified product was repeatedly sequenced 3 times. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the maximum likelihood (ML) and neighborjoining algorithms (NJ) with MEGA 6.0 software [
13]. The phylogeography was analyzed by Network 5.0 software [
14].
RESULTS
Fifty-five samples were found to be positive amplification by 12S rRNA gene detection. The sequenced fragments were conserved and presented homology of 100% with
E. granulosus AF288824 (originated from Guangdong Province, China). The 12S rRNA gene sequences in this study were deposited in Gen- Bank (Accession No. MG720014). Targeting
CO1 gene, a 936 bp fragment was amplified from each sample. All the samples were identified as genotype G1 based on the analysis of the partial
CO1 gene by MEGA 6.0 software. The phylogenetic tree revealed that
E. granulosus in XUAR showed genetic diversity. A total of 20 sequences in this study were found and deposited. The inner homology presented 99. 37–100% (
Table 1). Using Gen- Bank/BLAST and DNAman software, we make all
CO1 gene sequences (a total of 287) of
E. granulosus G1 type GenBank has logged before May 1, 2018 for multiple comparisons. Sequence homology is 97.7–100%.
When targeting
CO1 gene,
E. granulosus in hydatid cyst of livers showed genetic diversity. Of which, YL5 strain (originated from Ili region) and CJ75 strain (originated from Changji region) were the older branches compared to worldwide strains including
E. granulosus Japan strain (Accession No. AB033407), France strain (JQ356712), Argentina strain (GU980906), Australia strain (AF297617) and etc (
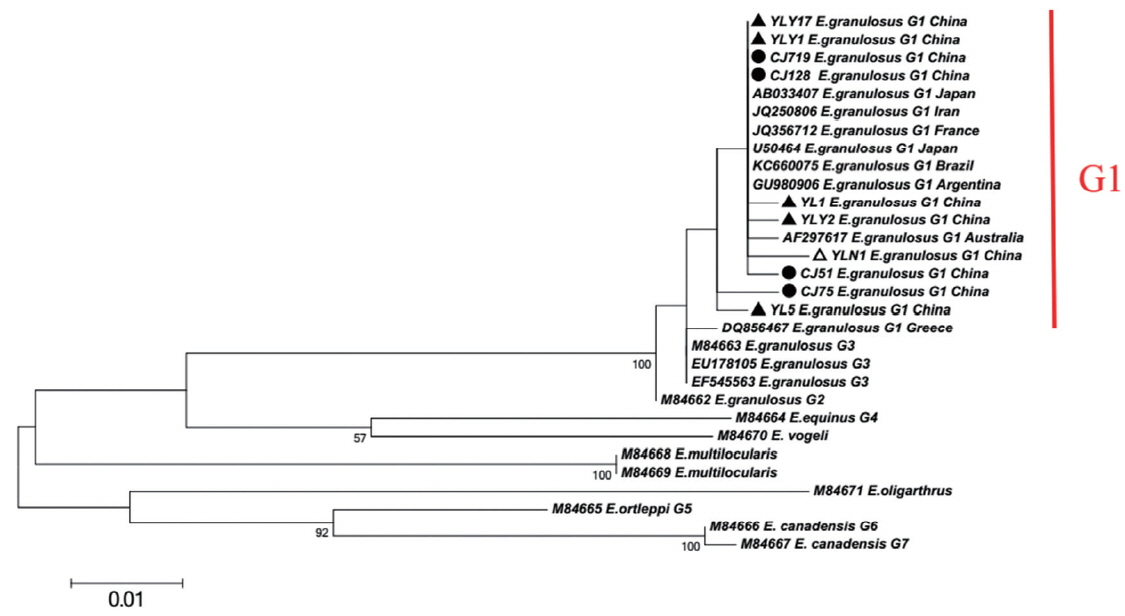
Fig. 1). In addition, the network diagram of geographical population showed the haplotypes in XUAR was particularly complex based on partial
CO1 gene (
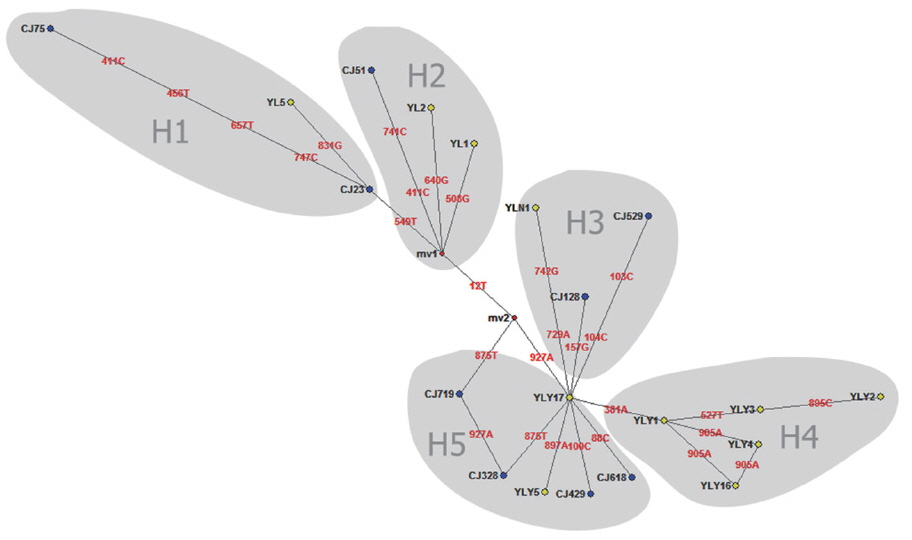
Fig. 2). Twenty haploids, belonging to 5 haplogroups including 3 large haplogroups (H1, H4, H5), and 2 small ones (H2 and H3), were obtained. No major apparent geographic segregation pattern was observed among these haplogroups. YLY17 haplotype (originated from Ili region) was the dominant haplotype. The remains of the haplotypes diverged from YLY17 with the radiation shape, and the genetic distance between haplotypes and central locations ranged from 1 step to 9 step in variety. The sequences in this study were deposited in GenBank (Accession No.: MG333731, MF281535-MF281541 and MG280947-MG280959).
DISCUSSION
To date, a few studies have explored in depth the genetic diversity and the population structure of
E. granulosus [
15–
17]. These studies revealed that the
CO1 gene seemed to be the most appropriate genetic marker for exploring the genetic diversity of
E. granulosus [
31]. In this study, we chose the relatively long sequence of
CO1 (936 bp) and detected a sufficient number of haplotypes to analyze the population genetic structures of sheep and cattle. Our results suggested that
E. granulosus genotype G1 was circulated rather freely in sheep and cattle populations in north XUAR, might due to the mixed breeding pattern of sheep with cattle, leading to sharing similar haplotypes between these 2 intermediate host species (e.g. CJ128, YLN1, and CJ529). In addition, haplotype diversity and nucleic acid diversity were more obvious in Changji and Ili regions. In XUAR, conventional nomads and semi-nomads keep livestock on low-altitude grassland. This breeding pattern, including involvement of pastoral dogs, seem to be essential to maintain the synanthropic cycle of
E. granulosus [
17]. Intermixed feeding model of sheep and cattle in the same meadow is common in endemic areas, XUAR [
18]. From the epidemiological point of view, the pattern of livestock-dog cycle plays an important role in the prevalence of echinococcosis.
XUAR is one of the most important foci of CE in the world [
19]. In previous studies, genotype G1 (sheep strain) was identified as the major source of infection for human CE in XUAR [
6,
20]. As for
CO1 gene can show inter-species and intra-species differences in the genus
Echinococcus, the gene is particularly suitable for the identification of animal parasites and the differentiation of different geographical strains [
5,
21–
23]. In present study, 20 different
CO1 sequences of
E. granulosus genotype G1 were found and accounted for about 2% nucleonic mutation. The sequence changes included conversion, mutation, and deletion, with no insertion. In the previous work, genotype G1 was likely originated from the Middle East (JQ250806) [
24,
25]. Here the major haplotypes (CJ75 and YL5) in Changji and Ili regions showed a 100% homology with the reference haplotype in the Middle East (JQ250806). Furthermore, compared to worldwide strains including
E. granulosus Japan strain (AB033407), France strain (JQ356712), Argentina strain (GU980906), Australia strain (AF297617) and etc, the phylogenetic tree showed YL5 strain (originated from Ili region) and CJ75 (originated from Changji region) were the older branches, which indicated that the ancient strains observed in XUAR were similar to Middle East strains. In addition, due to genetic evolution and international or/and homeland livestock trade, the multiple haplotypes evolved or introduced from foreign location [
32].
Median-joining (MJ) network is proposed as a suitable method for phylogeographical analysis [
26]. MJ network can be used for the evolutionary analysis of various pathogens, including
E. granulosus [
27]. In the previous study, Laurimäe et al. evaluated the genetic variability and phylogeography of G1 in America. The phylogenetic network indicated a long and complex evolutionary history of
E. granulosus G1 in the Americas [
14]. Here, we used the same primers to amplify CE samples from sheep and cattle in Changji and Ili regions, 5 haploids and twenty haplotypes were obtained. The findings indicated haploids and haplotypes showed genetic diversity and complexity of
E. granulosus in XUAR [
28]. In addition, our study revealed many highly divergent haplotypes, e.g. CJ75, YLY2, and CJ529. This phenomenon maybe be related to a long and complex evolutionary history of
E. granulosus. Animal transportation likely contributed to the dispersal of different haplotypes, as showing YL1, YL2, and CJ51 strains in this study (
Fig. 2). These results suggest that E. granulosus in the Northern Xinjiang occurred demographic expansion or bottleneck effects after the introduction of founder haplotype in the Middle East. The population was developed under the geographical isolation.
Despite the improvement in education hygiene and treatment of animal viscera with CE, the unilocular hydatid disease remains a major public health concern in XUAR.
E. granulosus genotype G1 is popular and genetically diverse in north region of XUAR, northwest of China. The intermixed feeding pattern of livestock-shepherd dog cycle contributes to the high prevalence of echinococcosis [
29]. This study recommends: i) increasing regular quarantine of echinococcosis both for livestock and shepherd dog, and timely elimination of the infected individuals from the herd, and ii) avoiding intermixed feeding model of shepherd dogs, cattle, sheep and goats in the same pasture in endemic areas, as possible.
Our study demonstrated that E. granulosus genotype G1 (sheep strain) was popular in north region of XUAR, northwest of China. Based on partial CO1 gene (936 bp), twenty new genotype haploids and 5 new genotype haplogroups (H1-H5) were found by analysis of network 5.0 software, and the YLY17 strain was identified as the most ancestral haplotype. The homeland and international trade of livestock might contribute the dispersal of different haplotypes for local strains of E. granulosus evolution.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported in part by the National key Research & Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018ZX10101002-002-007, 2017YFD0500304 and 2017ZX1034402-002-005), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81560338 and U1503283), and International Scientific and Technological Cooperation in Bingtuan (2016AH001), the natural science foundation from key laboratory of tarim animal husbandry science and technology of Xinjiang production & construction corps (No. HS201608). This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Shihezi University (Approral No. AECSU2016-6).
Fig. 1Maximum-likelihood (ML; 500 bootstrap replicates) and neighbour-joining (NJ; 1,000 bootstrap replicates) phylogenetic tree of the CO1 constructed with MEGA 6.0 software, using the sequences of E. granulosus from Changji (●) and Ili (▲) regions in this study and the sequences available in the GenBank. The sequences from E. multilocularis and E. oligarthrus were used as outgroups. The scale bar represented the inferred substitutions per nucleotide site. The relative support for clades in the tree produced from the ML and NJ analyses were indicated above and below the branches, respectively.
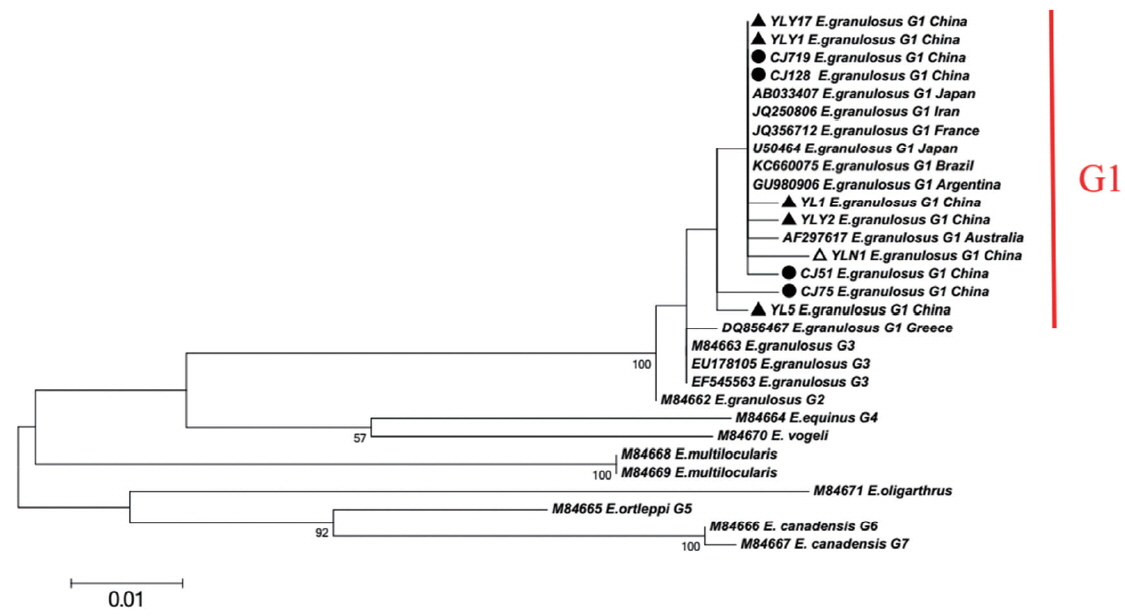
Fig. 2Median joining network for the E. granulosus s. s. genotype G1 samples from Changji and Ili regions, XUAR, China (n=55) based on sequences of 936 bp of mitochondrial DNA (CO1).
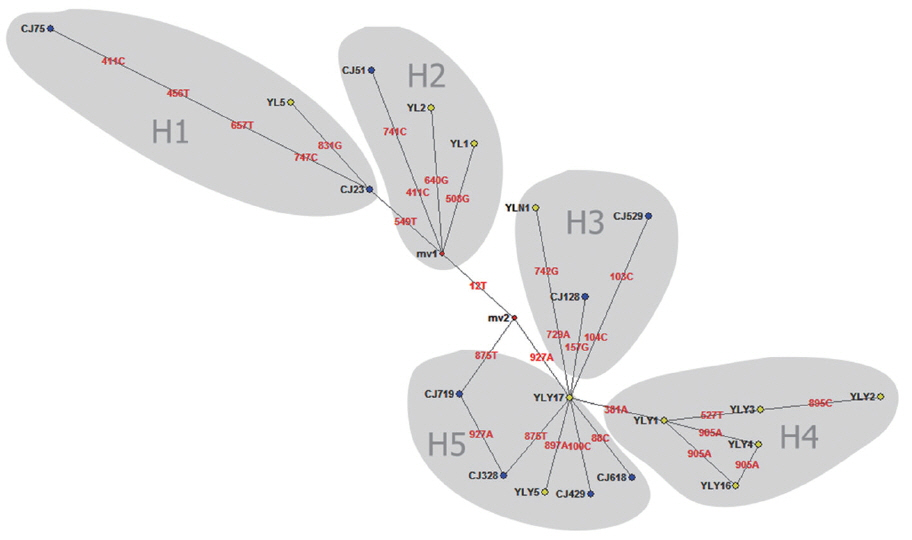
Table 1Substitution in the CO1 gene for the E. granulosus G1 genotype in Changji and Ili regions, XUAR
Table 1
|
G1 haplotype (Standard control) (AF297617) |
Mutation sites |
Sample source |
|
YLN1 (variation) |
594T/C; 729G/A; 742A/G |
cattle |
|
YLY1 (variation) |
381T/A; 594T/C; |
sheep |
|
YLY2 (variation) |
381T/A; 527C/T; 594T/C; 895T/C;900T/A |
sheep |
|
YLY3 (variation) |
381T/A; 527C/T; 594T/C |
sheep |
|
YLY4 (variation) |
381T/A; 594T/C; 905G/A |
sheep |
|
YLY5 (variation) |
594T/C; 897T/A; |
sheep |
|
YLY16 (variation) |
381T/A; 594T/C; 905G/C |
sheep |
|
YLY17 (variation) |
594T/C |
sheep |
|
CJ128 (variation) |
157A/G; 594T/C; |
sheep |
|
CJ328 (variation) |
486T/C; 594T/C; 875A/T |
sheep |
|
CJ429 (variation) |
100T/C; 594T/C; |
sheep |
|
CJ529 (variation) |
103,104GG/CC; 594T/C |
sheep |
|
CJ618 (variation) |
88G/C; 594T/C; 795G/A |
sheep |
|
CJ719 (variation) |
594T/C; 875A/T; 927G/A |
sheep |
|
CJ23 (variation) |
12G/T; 549C/T; 594T/C; 927G/A |
sheep |
|
CJ51 (variation) |
12G/T; 411T/C; 594T/C; 741T/C; 927G/A |
sheep |
|
CJ75 (variation) |
12G/T; 411T/C; 456C/T; 549C/T; 594T/C; 657C/T; 747T/C; 927G/A |
sheep |
|
YL1 (variation) |
12G/T; 508A/G; 594T/C; 927G/A |
sheep |
|
YL2 (variation) |
12G/T; 594T/C; 640A/G;927G/A |
sheep |
|
YL5 (variation) |
12G/T; 432T/C; 549C/T; 594T/C; 831A/G; 927G/A |
sheep |
References
- 1. Eckert J, Gemmell MA, Meslin FX, Meslin , Pawlowski ZS. WHO/OIE manual on echinococcosis in humans and animals: a public health problem of global concern. Paris, France. World Organisation for Animal Health; 2002, pp 1717-1718.
- 2. Omer RA, Dinkel A, Romig T, Mackenstedt U, Elnahas AA, Aradaib IE, Ahmed ME, Elmalik KH, Adam A. A molecular survey of cystic echinococcosis in Sudan. Vet Parasitol 2010;11. 169:340-346.
- 3. Boubaker G, Macchiaroli N, Prada L, Cucher MA, Rosenzvit MC, Ziadinov I, Deplazes P, Saarma U, Babba H, Gottstein B, Spiliotis M. A Multiplex PCR for the Simultaneous Detection and Genotyping of the, Echinococcus granulosus, Complex. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2013;7:e2017.
- 4. Obwaller A, Schneider R, Walochnik J, Gollackner B, Deutz A, Janitschke K, Aspöck H, Auer H.
Echinococcus granulosus strain differentiation based on sequence heterogeneity in mitochondrial genes of cytochrome c oxidase-1 and NADH dehydrogenase- 1. Parasitology 2004;128:569-575.
- 5. Bowles J, Blair D, Mcmanus DP. Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1992;54:165-173.
- 6. Bart JM, Abdukader M, Zhang YL, Lin RY, Wang YH, Nakao M, Ito A, Craig PS, Piarroux R, Vuitton DA, Wen H. Genotyping of human cystic echinococcosis in Xinjiang, PR China. Parasitology 2006;133:571-579.
- 7. Zhao CY, Shi FZ, Sheng Y, Li J, Zhao ZM, Han M, Yimamu Y. Regional differentiation characteristics of precipitation changing with altitude in Xinjiang region in recent 50 years. J Glaciol Geocryol 2011;33:1203-1213.
- 8. People U. Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture Area 2015;11-27.
- 9. Zhang Y, Bart JM, Giraudoux P, Craig P, Vuitton D, Wen H. Morphological and molecular characteristics of Echinococcus multilocularis and Echinococcus granulosus mixed infection in a dog from Xinjiang, China. Vet Parasitol 2006;30. 139:244-248.
- 10. Yu JF, Tan W, Li B, Liu XS, Chang JH, Yang Xiaoye, Wang Rui, Yang Lianru, Li Xiuxia. Gene sequence analysis on CO1 and ND1 of Echinococcus granulosus
. Chin J Zoonoses 2014;30:812-815. (in Chinese).
- 11. Ito A, Nakaya K, Qiu J, Nakao M, Zhen R, Xiao N, Chen X, Giraudoux P, Craig PS. Species identification of human echinococcosis using histopathology and genotyping in northwestern China. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2008;102:585-590.
- 12. Yang J, Jia W, Jing T, Tian G, Cheng X. Analysis of genetic variation of Echinococcus granulosus collected from three provinces in China. Chin J Vet Sci Tech 2004;34:12-16.
- 13. Zhao SS, Li HY, Yin XP, Liu ZQ, Chen CF, Wang YZ. First detection of Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae, in the flea Vermipsylla alakurt, from north-western China. Parasit Vectors 2016;9:325.
- 14. Laurimäe T, Kinkar L, Andresiuk V, Haag KL, Ponce-Gordo F, Acosta-Jamett G, Garate T, Gonzàlez LM, Saarma U. Genetic diversity and phylogeography of highly zoonotic Echinococcus granulosus genotype G1 in the Americas (Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Mexico) based on 8279 bp of mtDNA. Infect Genet Evol 2016;45:290-296.
- 15. Kamenetzky L, Gutierrez AM, Canova SG, Haag KL, Guarnera EA, Parra A, Garcia GE, Rosenzvit MC. Several strains of Echinococcus granulosus infect livestock and humans in Argentina. Infect Genet Evol 2002;2:129-136.
- 16. Badaraco JL, Ayala FJ, Bart JM, Gottstein B, Haag KL. Using mitochondrial and nuclear markers to evaluate the degree of genetic cohesion among Echinococcus populations. Exp Parasitol 2008;119:453-459.
- 17. Nakao M, McManus DP, Schantz PM, Craig PS, Ito A. A molecular phylogeny of the genus Echinococcus inferred from complete mitochondrial genomes. Parasitology 2007;134:713-722.
- 18. Gao P, Huang L, Guo T. A Study of Difficulties in Developing Herbivorous Livestock in Xinjiang. Finance & Economics of Xinjiang 2015.
- 19. Craig P. Epidemiology of echinococcosis in China. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2004;35:158-169.
- 20. Mcmanus DP, Ding Z, Bowles J. A molecular genetic survey indicates the presence of a single, homogeneous strain of Echinococcus granulosus in north-western China. Acta Trop 1994;56:7-14.
- 21. Anderson TJ, Blouin MS, Beech RN. Population biology of parasitic nematodes: applications of genetic markers. Adv Parasitol 1998;41:219-283.
- 22. Pour AA, Hosseini SH, Shayan P. Comparative genotyping of Echinococcus granulosus infecting buffalo in Iran using cox1 gene. Parasitol Res 2011;108:1229-1234.
- 23. Ma J, Wang H, Lin G, Craig PS, Ito A, Cai Z, Zhang T, Han X, Ma X, Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Wang Y. Molecular identification of Echinococcus species from eastern and southern Qinghai, China, based on the mitochondrial cox1 gene. Parasitol Res 2012;111:179-184.
- 24. Yanagida T, Mohammadzadeh T, Kamhawi S, Nakao M, Sadjjadi SM, Hijjawi N, Abdel-Hafez SK, Sako Y, Okamoto M, Ito A. Genetic polymorphisms of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto in the Middle East. Parasitol Int 2012;61:599-603.
- 25. Wang N, Gu XB, Wang T, Yang GY. Genetic Variability of Echinococcus granulosus Determined by the Mitochondrial Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit 1 Gene in the Tibet Plateau of China. Chin J Anim Vet Sci 2015;46:453-460.
- 26. Cai X, Mipam TD. Median-Joining Network Analysis of Phylogeny of Goat Breeds from South China. 2011. 5th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering. Wuhan, China: IEEE; 2011. 1-4.
- 27. Kong S, Sánchez-Pacheco SJ, Murphy RW. On the use of median- joining networks in evolutionary biology. Cladistics 2016;32:691-699.
- 28. Hoehe MR. Haplotypes and the systematic analysis of genetic variation in genes and genomes. Pharmacogenomics 2003;4:547-570.
- 29. Kinkar L, Laurimäe T, Simsek S, Balkaya I, Casulli A, Manfredi MT, Ponce-Gordo F, Varcasia A, Lavikainen A, González LM, Rehbein S, VAN DER Giessen J, Sprong H, Saarma U. High-resolution phylogeography of zoonotic tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto genotype G1 with an emphasis on its distribution in Turkey, Italy and Spain. Parasitology 2016;143:1790-1801.
- 30. Daniel MK, Ponce-Gordo F, Cuesta-Bandera C. Genetic identification and host range of the Spanish strains of Echinococcus granulosus
. Acta Trop 2004;91:87-93.
- 31. Liang R, Chen X, Sun H, Shen Z, Liu J, Wang J, Sun S, Dun W. The feasibility analysis of ovine mtDNA CO1 gene as DNA barcoding in breed identification and phylogenetic. J Yangzhou Univ 2017;38:27-32.
- 32. Nakao M, Li T, Han X, Ma X, Xiao N, Qiu J, Wang H, Yanagida T, Mamuti W, Wen H, Moro PL, Giraudoux P, Craig PS, Ito A. Genetic polymorphisms of Echinococcus tapeworms in China as determined by mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Int J Parasitol 2010;40:379-385.
- 33. Li XJ, Shi BX, Zhao L, Zhang WB, Yan H, Wang GL, Mi XY. The Epidemic and Control Situation of Hydatid Disease in Xinjiang. Grass-Feeding Livestock 2012;4:157.