Abstract
The Alataw Pass, near the Ebinur Lake Wetland (northwest of China) and Taldykorgan (east of Kazakhstan), is a natural habitat for wild rodents. To date, little has been done on the surveillance of Bartonella spp. and Wolbachia spp. from fleas in the region. Here we molecularly detected Bartonella spp. and Wolbachia spp. in wild rodent fleas during January and October of 2016 along the Alataw Pass-Kazakhstan border. A total of 1,706 fleas belonging to 10 species were collected from 6 rodent species. Among the 10 flea species, 4 were found to be positive for Wolbachia, and 5 flea species were positive for Bartonella. Molecular analysis indicated that i) B. rochalimae was firstly identified in Xenopsylla gerbilli minax and X. conforms conforms, ii) B. grahamii was firstly identified in X. gerbilli minax, and iii) B. elizabethae was firstly detected in Coptopsylla lamellifer ardua, Paradoxopsyllus repandus, and Nosopsyllus laeviceps laeviceps. Additionally, 3 Wolbachia endosymbionts were firstly found in X. gerbilli minax, X. conforms conforms, P. repandus, and N. laeviceps laeviceps. BLASTn analysis indicated 3 Bartonella species showed genotypic variation. Phylogenetic analysis revealed 3 Wolbachia endosymbionts were clustered into the non-Siphonaptera Wolbachia group. These findings extend our knowledge of the geographical distribution and carriers of B. rochalimae, B. grahamii, B. elizabethae, and Wolbachia spp. In the future, there is a need for China-Kazakhstan cooperation to strengthen the surveillance of flea-borne pathogens in wildlife.
-
Key words: Bartonella spp., Wolbachia spp., flea, China-Kazakhstan border
Fleas (Insecta: Siphonaptera) are obligate hematophagous insects that infest birds and mammals worldwide. In China, 655 species and subspecies belonging to 10 families and 74 genera have been reported, which corresponds to approximately 25% of the species known worldwide. Some flea species have only been presented in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region and Central Asia, including
Xenopsylla gerbilli minax and
Paradoxopsyllus repandus [
1–
3]. The Alataw Pass, near the Ebinur Lake Wetland and Taldykorgan (east of Kazakhstan), is the second largest land passage in China. Twenty-two flea species have been reported in the region from wild rodents [
4,
5].
Fleas are vectors of several important zoonotic pathogens, including
Yersinia pestis, Rickettsia typhi, R. felis, and
Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae [
1,
5]. Recently,
Bartonella spp. and
Wolbachia spp. lineages have been detected in several flea species [
6]. Further studies indicated that rodent-associated fleas are naturally infected with zoonotic
Bartonella species, including
B. elizabethae, B. rochalimae, B. grahamii, B. henselae, B. clarridgeiae, and
B. koehlerae [
7–
9]. In 1924, Herting and Wolbach found that a
Wolbachia species was found in
Culex pipiens, and therefore, the organism was named as
Wolbachia pipientis.
Wolbachia is a bacterial endosymbiont with a wide distribution and is found in 20–75% of arthropods, including
Ctenocephalides felis felis, X. cheopis, Oropsylla hirsuta, and
Plocopsylla achillea [
10,
11].
In a previous work,
B. henselae, B. clarridgeiae and a new
Bartonella genotype were detected in the Thai-Myanmar border [
12]. Meanwhile,
Bartonella melophagi and
Wolbachia supergroup F from sheep keds (
Melophagus ovinus) in southern Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China [
13]. To the best of our knowledge, little has been done on the surveillace of
Bartonella spp. and
Wolbachia spp. from fleas in this region. Herein we carried out molecular detection of
Bartonella spp. and
Wolbachia spp. in fleas collected from wild rats in the Alataw Pass, northwest of China.
Flea specimens were collected from wild rodents from January to October 2016 along the Chinese Alataw Pass-Kazakhstan border. Briefly, the wild rodents were captured in Sherman traps (H.B. Sherman Traps, Tallahassee, Florida, USA), which were placed at the entrances of occupied burrows [
14]. This study was approved by the Animal Research Ethics Committee of Shihezi University (Approval No. AECSU2013-18). The sampling sites included Hejiaoke Border Station and wetlands around Ebinur Lake, in which the wild rodents were abundant, and there was a potential risk to introduce the flea-borne diseases vectored by wild rodents. Fleas were collected from individual rodents by brushing the animal’s fur [
15]. Each wild rodent was identified to the species level [
16], and capture location was recorded. The fleas were morphologically identified [
3] and stored in 70% ethanol. All flea samples were then grouped into pools ranging from 2 to 15 specimens on the basis of species, and host species, as previously reported [
15,
17]. Before DNA extraction, fleas were washed with purified sterile water for 3 min [
17]. The total genomic DNA of each pool was extracted using the TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit (TIANGEN, Beijing, China).
To ensure absence of contamination, negative control reactions contained double distilled water instead of positive DNA were included in each PCR run [
7]. Each pool was screened for 3 different runs using 3 target genes (citrate synthase [
gltA, 380 bp], 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer [
ITS, 100–300 bp] and riboflavin synthase [
ribC, 588 bp]) to confirm the identification of
Bartonella spp. [
17,
18]. Moreover, 2 primer pairs were used to amplify the 16S rDNA (936 bp) and the outer surface antigen (
wsp, 602 bp) fragment of
Wolbachia spp. in each sample, according to the method of Robertson et al. [
19]. The PCR products were purified using the TIANgel Midi Purification Kit (TIANGEN), cloned into the pBS-T vector, and used for the transformation of One-shot TOP 10 chemically competent
Escherichia coli cells. Three to five positive clones were selected for sequencing by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The resulting sequences were compared with sequences from centralized data bases using BLAST (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/). A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the maximum likelihood (ML) and neighbor joining (NJ) algorithms present in MEGA 6 software [
20].
A total of 1,706 fleas, belonging to 10 species, were collected from 6 rodent species and grouped into 209 flea pools. The average flea index was 11.53 (148/1,706). The detailed data on the hosts, flea pools, and flea species are shown in
Table 1. Among the 10 flea species, 4 were found to be positive for
Wolbachia and 5 flea species were positive for
Bartonella (
Table 2). The negative controls yielded no PCR products, and all positive flea samples were positive for the different target genes.
All the amplicons of the
Bartonella gltA gene were firstly sequenced. After alignment and clustering, the other 2 genetic markers,
Bartonella ITS and
ribC genes, were sequenced in the representative samples. BLAST analysis indicated genetic variations in the 3 species of
Bartonella sp. found in this study on the basis of
gltA,
ITS, and
ribC genes. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that i)
Bartonella sp. AL01, claded into
B. rochalimae, was found in
X. gerbilli minax and
X. conforms conforms; ii)
Bartonella sp. AL02, claded into
B. grahamii, was detected in
X. gerbilli minax; and iii)
Bartonella sp. AL03 and AL04, were both claded into
B. elizabethae. The former was detected in
N. laeviceps laeviceps, and the latter was detected in
Coptopsylla lamellifer ardua and
P. repandus (
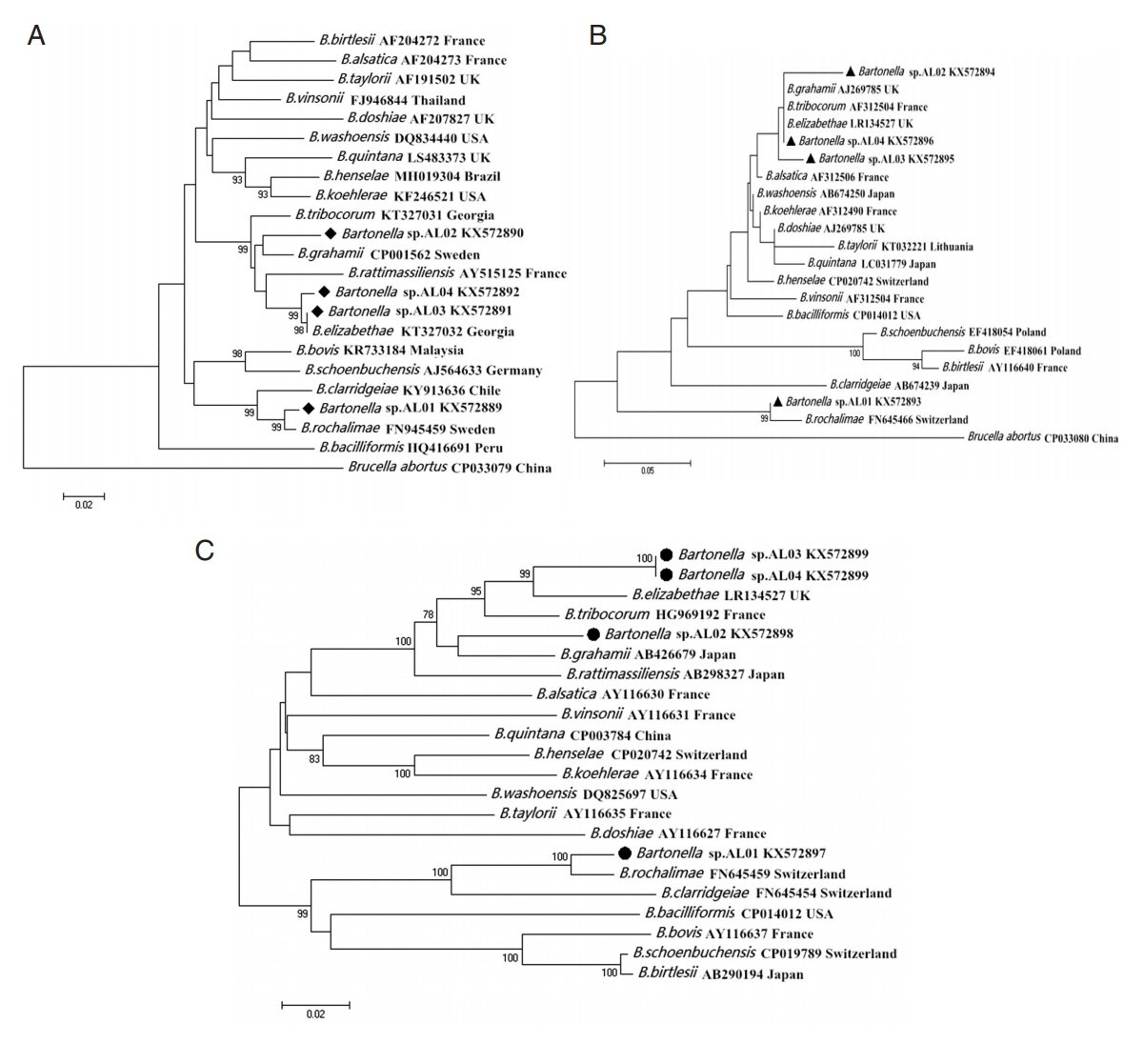
Fig. 1).
The analysis of the
Wolbachia 16S rDNA fragment indicated that
Wolbachia from
Xenopsylla genus (
X. gerbilli minax and
X. conformis conformis),
P. repandus, and
N. laeviceps laeviceps were 99.77% (869/871), 100% (871/871), and 99.54% (867/871) to
Candidatus Wolbachia brouquii (DQ402520),
Wolbachia endosymbiont in
Ectropis grisescens from China tea garden (KT862198), and
Wolbachia endosymbiont in
Agelastica alni (AM180550), respectively. Similarly, the analysis of the
wsp fragment indicated that the degree of identity of
Wolbachia endosymbionts were 98.9% (554/560), 92.5% (520/562), and 95.1% (527/554) to
Wolbachia endosymbiont in
Tribolium confusum (KC305360),
Wolbachia tonolepta hieroglyphica (JF747227), and
Wolbachia endosymbiont in
Cybaeus penedentatus (GQ480746), respectively. Moreover, phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rDNA sequence indicated that 3
Wolbachia endosymbionts in this study were clustered into the non-Siphonaptera
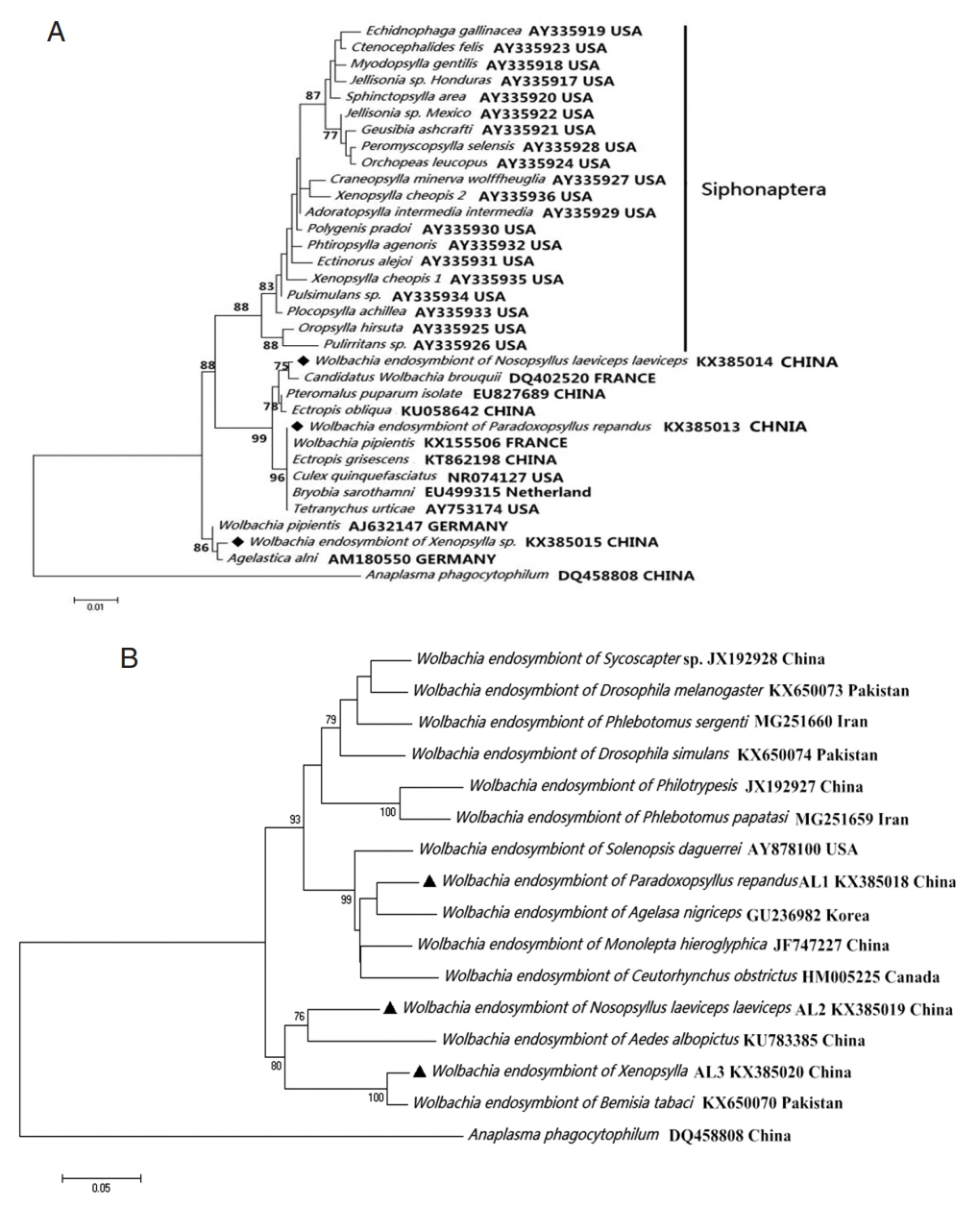
Wolbachia group (
Fig. 2).
The 15 nucleotide sequences from Bartonella (gltA: KX-572889, KX572890, KX572891, and KX572892; ITS: KX-572893, KX572894, KX572895, and KX572896; ribC: KX-572897, KX572898, KX572899, and KX572900) and Wolbachia (16S rDNA: KX385013, KX385014, and KX385015; wsp: KX385018, KX385019 and KX385020) were deposited in the GenBank database.
Bartonella infections occur worldwide and cause severe diseases in humans. Herein, we report the presence of 3 human pathogens of the genus Bartonella (B. rochalimae, B. grahamii, and B. elizabethae). The finding conveys us that X. gerbilli minax, X. conforms conforms and C. lamellifer ardua are novel carriers for these 3 Bartonella species. This information increases our knowledge of the carriers and geographical distribution of Bartonella.
B. rochalimae was recently isolated from the blood of a human patient who presented with fever, rash, and splenomegaly after receiving multiple insect bites in 2007 [
21]. A previous study identified
B. rochalimae in Chile, China, France, Greece, Israel, Peru and United States [
22–
25]. In this study,
B. rochalimae was found in 2 flea species (
X. gerbilli minax and
X. conforms conforms), and this finding is consistent with that of the study of Sofer and Nasereddin, wherein
B. rochalimae was detected in the fleas species
Ctenocephalides sp.,
Xenopsylla sp., and
Pulex sp. [
24,
26].
B. grahamii, primarily isolated from
Clethrionomys glareolus, was involved in a case of neuroretinitis in a human subject in 1999 [
27].
B. grahamii has been found in various countries, including Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, North Korea, Poland, Russia, Slovenia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Thailand, United Kingdom, and United States [
25,
28,
29]. Furthermore, a previous study found that
B. grahamii was transmitted by
Ctenophthalmus nobilis in the United Kingdom [
29]. Of note, in this study, we detected
B. grahamii and
B. rochalimae in
X. gerbilli minax, which is also the vector of
Y. pestis [
4]. Therefore,
X. gerbilli minax bites in humans should be paid more attention.
B. elizabethae, the causative agent of endocarditis [
30], has been detected in Canada, China, France, Israel, Japan, Thailand, Tunisia, United States and Vietnam [
23,
30–
32]. In our study,
B. elizabethae was detected in 3 flea species (
C. lamellifer ardua, P. repandus, and
N. laeviceps laeviceps). Although there is no evidence to prove these flea species are vectors for transmitting bartonellosis, the infestations of these flea species should not be underestimated.
Wolbachia is a bacterial genus that infects several arthropods, including fleas (Siphonaptera), lice (Phthiraptera), and other ectoparasites of mammals and birds.
Wolbachia is a highly diverse genus and has been subdivided into 11 phylogenetic supergroups (A to K) on the basis of a multi-locus sequence typing [
10,
11]. In the present study, 3
Wolbachia endosymbionts were found in
N. laeviceps laeviceps,
Xenopsylla sp., and
P. repandus. This result extends the geographical distribution and number of carrier hosts of
Wolbachia. Additionally, there is an interesting phenomenon that why
Wolbachia-positive flea species and
Bartonella-positive flea species are limited in some several flea species, and highly co-infected in this study. In the future, there should be more efforts to explore it.
The habitats on both sides of the China-Kazakhstan border are similar, without natural geographical barriers, and this allows wild rodents to traverse the border freely. Some of the flea species found in China are also found in Kazakhstan [
5]. However, to the best of our knowledge, few studies have investigated the flea species and their pathogens near China-Kazakhstan border. These results suggest that Kazakhstan should strengthen the investigation of fleas and flea-borne diseases in border regions.
B. rochalimae, B. grahamii, B. elizabethae, and 3 Wolbachia endosymbionts were firstly detected in indigenous flea species near the China-Kazakhstan border. The findings extend our knowledge of the geographical distribution and reservoir hosts of Bartonella spp. and Wolbachia spp., increase the awareness of physicians and public health workers on flea-borne diseases and highlight the importance of flea control in transboundary regions.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported in part by grants from the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection, and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China (2016IK264), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81560338) and the National Key Research & Development Program of China (2018ZX10101002-007). We are grateful to Pro. Sándor Hornok for revising the manuscript.
Fig. 1Maximum likelihood (ML; 1,000 bootstrap replicates) and neighbor joining (NJ; 500 bootstrap replicates) phylogenetic tree of the (A) gltA, (B) ITS, and (C) ribC genes. Bartonella sp. sequences AL01-04 (◆, ▲, ●) obtained in this study.
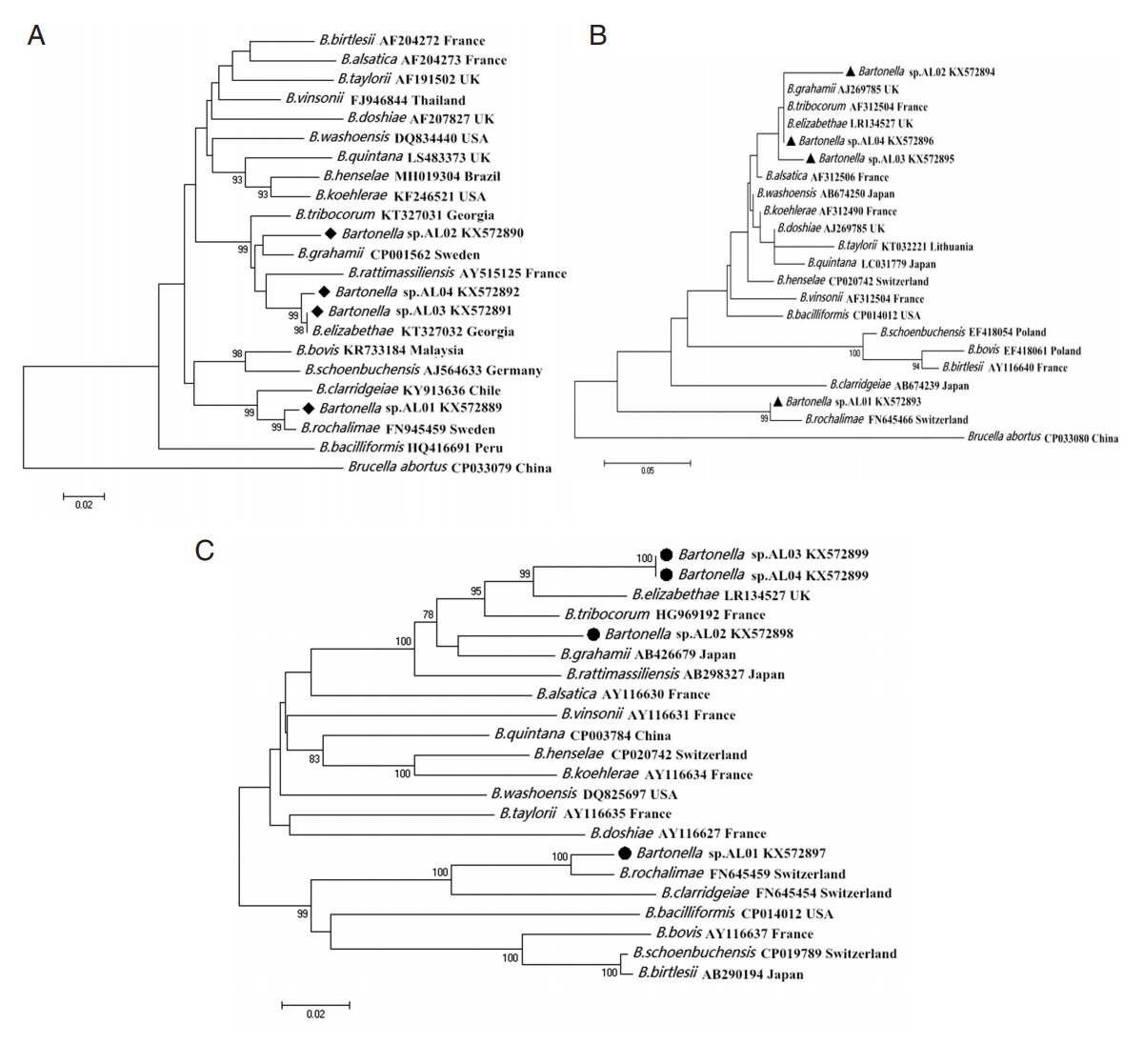
Fig. 2
Wolbachia (◆, ▲) collected from Nosopsyllus laeviceps laeviceps, Xenopsylla sp., Paradoxopsyllus repandus. Phylogemic trees of (A) 16S rRNA and (B) wsp sequences Maximum-likelihood (1,000 bootstrap replicates) and neighbour-joining (500 bootstrap replicates) were applied.
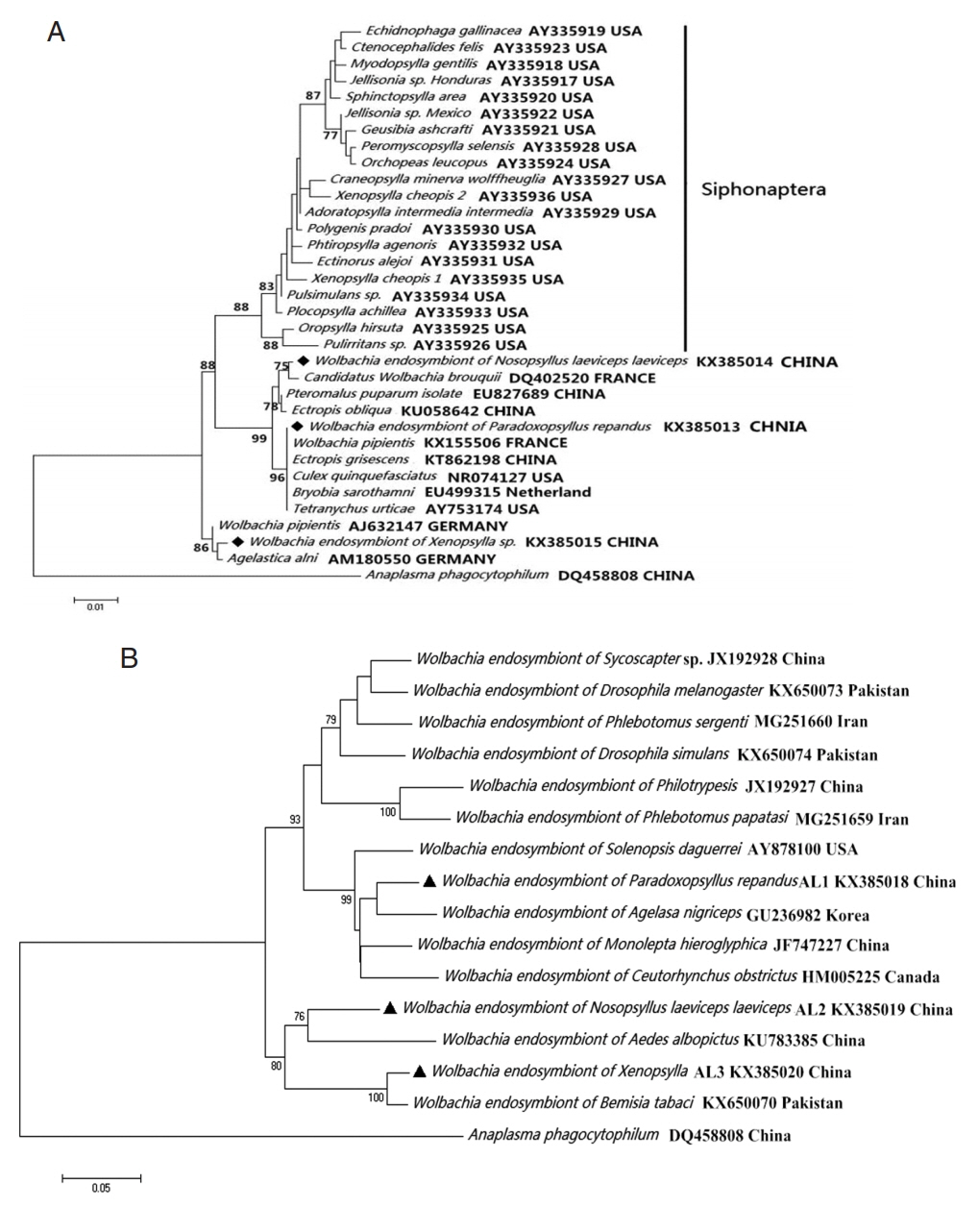
Table 1Information of sampled fleas including captured numbers, flea pools and their hosts
Table 1
|
Flea species |
No. of captured (pool No.) |
Host species (no.) |
|
Echidnopgaga oschanini
|
36 (5) |
Rhombomys opimus (4), Meriones libycus (2) |
|
Xenopsylla conformis conformis
|
41 (4) |
Rhombomys opimus (2), Meriones libycus (5), Meriones tamariscinus (2) |
|
Xenopsylla gerbilli minax
|
1,073 (101) |
Rhombomys opimus (33), Meriones libycus (2), Meriones tamariscinus (2), Meriones meridianus (1) |
|
Coptopsylla Lamellifer ardua
|
36 (11) |
Rhombomys opimus (9) |
|
Ctenophthalmus dolichus dolichus
|
8 (1) |
Meriones tamariscinus (4) |
|
Rhadinopsylla cedestis
|
8 (2) |
Meriones tamariscinus (3) |
|
Leptopsylla nemorosa
|
2 (1) |
Mus musculus Linnaeus (1) |
|
Mesopsylla eucta shikno
|
4 (1) |
Allactaga sibirica (2) |
|
Paradoxopsyllus repandus
|
281 (45) |
Rhombomys opimus (24), Meriones libycus (1), Meriones tamariscinus (1), Meriones meridianus (1) |
|
Nosopsyllus laeviceps laeviceps
|
217 (38) |
Rhombomys opimus (32), Meriones libycus (9), Meriones tamariscinus (3), Meriones meridianus (4) |
|
Total |
1,706 (209) |
Rhombomys opimus (104), Meriones libycus (19), Meriones tamariscinus (16), Meriones meridianus (6), Allactaga sibirica (2), Mus musculus Linnaeus (1) |
Table 2Positivity of flea pools for Bartonella and Wolbachia
Table 2
|
Flea species |
No. of tested flea |
No. of tested flea pool |
No. of Wolbachia spp.-positive pools (MFIR, %) |
No. of Bartonella spp.-positive pools (MFIR, %) |
No. of co-infection (MFIR, %) |
|
Echidnophaga oschanini
|
36 |
5 |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
Xenopsylla gerbilli minax
|
1,073 |
101 |
45 (4.19) |
98 (9.13) |
43 (4.01) |
|
Xenopsylla conformis conformis
|
41 |
4 |
2 (4.88) |
1 (2.44) |
0 (0) |
|
Coptopsylla lamellifer ardua
|
36 |
11 |
0 (0) |
7 (19.44) |
0 (0) |
|
Rhadinopsylla cedestis
|
8 |
2 |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
Ctenophthalmus dolichus dolichus
|
8 |
1 |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
Leptopsylla nemorosa
|
2 |
1 |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
Mesopsylla eucta shikho
|
4 |
1 |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
Paradoxopsyllus repandus
|
281 |
45 |
19 (6.76) |
34 (12.10) |
16 (5.69) |
|
Nosopsyllus laeviceps laeviceps
|
217 |
38 |
9 (4.15) |
29 (13.36) |
7 (3.23) |
|
Total |
1,706 |
209 |
75 (4.40) |
169 (9.91) |
66 (3.87) |
References
- 1. Zhao SS, Li HY, Yin XP, Liu ZQ, Chen CF, Wang YZ. First detection of Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae in the flea Vermipsylla alakurt from north-western China. Parasit Vectors 2016;9:1-5.
- 2. ZipcodeZoo. Siphonaptera; 2011.
http://zipcodezoo.com/
Accessed 3 Jan 2011.
- 3. Liu Q. General account: chapter on morphology and anatomy. In Wu H ed, Fauna Sinica: Insecta. Siphonaptera. Beijing, China. Science Press; 2007, pp 359-361 (in Chinese).
- 4. Yin XP, Peng DX, Li D, Zhang J, Zayer A. Survey and dynamic analysis of flea fauna at alataw port, Xinjiang. Endem Dis Bull 2008;23:33-36. (in Chinese).
- 5. Yin XP, Ye ZH, Ma DH, Jiao W. Risk analysis of imported plague and the control measures at Alataw Port, Xinjiang. International Forum on Sustainable Vector Control 2008;1167-1169. (in Chinese).
- 6. Jones RT, Borchert J, Eisen R, Macmillan K, Boegler K, Gage KL. Flea-associated bacterial communities across an environmental transect in a plague-endemic region of uganda. PLoS One 2015;10:e0141057.
- 7. Rolain JM, Franc M, Davoust B, Raoult D. Molecular detection of Bartonella quintana, B. koehlerae, B. henselae, B. clarridgeiae, Rickettsia felis, and Wolbachia pipientis in cat fleas, France. Emerg Infect Dis 2003;9:338-342.
- 8. Chomel BB, Boulouis HJ, Maruyama S, Breitschwerdt EB.
Bartonella spp. in pets and effect on human health. Emerg Infect Dis 2006;12:389-394.
- 9. Gutiérrez R, Krasnov B, Morick D, Gottlieb Y, Khokhlova IS, Harrus S.
Bartonella infection in rodents and their flea ectoparasites: an overview. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2015;15:27-39.
- 10. Hu YP, Liu XB, Sang SW, Chen B, Liu QY. Application of multilocus sequence typing on Wolbachia genotyping. Chin J Vector Biol Control 2016;27:197-201. (in Chinese).
- 11. Tay ST.
Wolbachia endosymbionts, Rickettsia felis and Bartonella species, in Ctenocephalides felis fleas in a tropical region. J Vector Ecol 2013;38:200-202.
- 12. Parola P, Sanogo OY, Lerdthusnee K, Zeaiter Z, Chauvancy G, Gonzalez JP, Miller RS, Telford SR 3rd, Wongsrichanalai C, Raoult D. Identification of Rickettsia spp. and Bartonella spp. in ffrom the Thai-Myanmar border. Ann NY Acad Sci 2003;990:173-181.
- 13. Liu Y, He B, Li F, Li K, Zhang L, Li X, Zhao L. Molecular identification of Bartonella melophagi and Wolbachia supergroup F from sheep keds in Xinjiang, China. Korean J Parasitol 2018;56:365-370.
- 14. Guo G, Sheng J, Wu X, Wang Y, Guo L, Zhang X, Yao H. Seoul virus in the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus) from Ürümqi, Xinjiang, northwest of China. J Wildl Dis 2016;52:705-708.
- 15. Morick D, Krasnov BR, Khokhlova IS, Shenbrot GI, Kosoy MY, Harrus S.
Bartonella genotypes in fleas (insecta: siphonaptera) collected from rodents in the negev desert, Israel. Appl Environ Microbiol 2010;76:6864-6869.
- 16. Wang SB, Yang GY. Rodent Fauna of Xinjiang. Urumuqi, China. Xinjiang people’s publishing house; 1983, pp 97-150 (In Chinese).
- 17. Li DM, Liu QY, Yu DZ, Zhang LY, Dong XQ. Isolation and molecular identification of Bartonella from fleas and ticks. Chin J Zoonoses 2005;21:1052-1058. (in Chinese).
- 18. Johnson G, Ayers M, Mcclure SC, Richardson SE, Tellier R. Detection and identification of Bartonella species pathogenic for humans by PCR amplification targeting the riboflavin synthase gene (ribC). J Clin Microbiol 2003;41:1069-1072.
- 19. Wiwatanaratanabutr I, Zhang C.
Wolbachia infections in mosquitoes and their predators inhabiting rice field communities in Thailand and China. Acta Trop 2016;159:153-160.
- 20. Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 2013;30:2725-2729.
- 21. Eremeeva ME, Gerns HL, Lydy SL, Goo JS, Ryan ET, Mathew SS, Ferraro MJ, Holden JM, Nicholson WL, Dasch GA, Koehler JE. Bacteremia, fever, and splenomegaly caused by a newly recognized Bartonella species. N Engl J Med 2007;356:2381-2387.
- 22. Pérez-Martínez L, Venzal JM, González-Acuña D, Portillo A, Blanco JR, Oteo JA.
Bartonella rochalimae and other Bartonella spp. in fleas, Chile. Emerg Infect Dis 2009;15:1150-1152.
- 23. Henn JB, Chomel BB, Boulouis HJ, Kasten RW, Murray WJ, Bar-Gal GK, King R, Courreau JF, Baneth G.
Bartonella rochalimae in raccoons, coyotes, and red foxes. Emerg Infect Dis 2009;15:1984-1987.
- 24. Sofer S, Gutiérrez R, Morick D, Mumcuoglu KY, Harrus S. Molecular detection of zoonotic bartonellae (B. henselae, B. elizabethae, and B. rochalimae) in fleas collected from dogs inIsrael. Med Vet Entomol 2015;29:344-348.
- 25. Saisongkorh W, Rolain JM, Suputtamongkol Y, Raoult D. Emerging Bartonella in humans and animals in Asia and Australia. J Med Assoc Thai 2009;92:707-731.
- 26. Nasereddin A, Risheq A, Harrus S, Azmi K, Ereqat S, Baneth G, Salant H, Mumcuoglu KY, Abdeen Z.
Bartonella species in fleas from Palestinian territories: prevalence and genetic diversity. J Vector Ecol 2014;39:261-270.
- 27. Kerkhoff FT, Bergmans AM, Van DZA, Rothova A. Demonstration of Bartonella grahamii DNA in ocular fluids of a patient with neuroretinitis. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37:4034-4038.
- 28. Oksi J, Rantala S, Kilpinen S, Silvennoinen R, Vornanen M, Veikkolainen V, Eerola E, Pulliainen AT. Cat scratch disease caused by Bartonella grahamii in an immunocompromised patient. J Clin Microbiol 2013;51:2781-2784.
- 29. Bown KJ, Bennet M, Begon M. Flea-borne Bartonella grahamii and Bartonella taylorii in bank voles. Emerg Infect Dis 2004;10:684-687.
- 30. Daly JS, Worthington MG, Brenner DJ, Moss CW, Hollis DG, Weyant RS, Steigerwalt AG, Weaver RE, Daneshvar MI, O’Connor SP.
Rochalimea elizabethae sp. nov. isolated from a patient with endocarditis. J Clin Microbiol 1993;31:872-881.
- 31. De Sousa R, Edouard-Fournier P, Santos-Silva M, Amaro F, Bacellar F, Raoult D. Molecular detection of Rickettsia felis, Rickettsia typhi and two genotypes closely related to Bartonella elizabethae
. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2006;75:727-731.
- 32. Ying B, Kosoy MY, Maupin GO, Tsuchiya KR, Gage KL. Genetic and ecologic characteristics of Bartonella communities in rodents in southern china. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2002;66:622-627.