Abstract
Trematode specimens were collected from the intestine of a herring gull, Larus argentatus, which was found in a critical condition on the shore of a small island (Yubu-do, Seocheon-gun, Chungcheongnam-do) located at the western coast of the Korean peninsula. Total 11 specimens of intestinal flukes, including 3 Cryptocotyle lingua (Heterophyidae), 1 Himasthla alincia (Echinostomatidae), 5 Cardiocephaloides medioconiger (Strigeidae), and 2 Diplostomum spathaceum (Diplostomidae), were recovered. C. lingua was morphologically characterized by the presence of a large ventrogenital apparatus and 2 obliquely tandem testes. H. alincia had an elongated body and a head collar equipped with 31 collar spines. C. medioconiger had a bisegmented body and a voluminous copulatory bursa containing the seminal vesicle and ejaculatory duct. D. spathaceum also had a bisegmented body and its vitellaria extended up to the anterior border of the tribocytic organ. It is of note that C. lingua is potentially zoonotic that can occur in birds and humans. Three of them, i.e., C. lingua, C. medioconiger, and D. spathaceum, are new trematode fauna in Korea. Studies on trematode fauna of migratory birds should be continued in Korea.
-
Key words: Cryptocotyle lingua, Himasthla alincia, Cardiocephaloides medioconiger, Diplostomum spathaceum, intestinal fluke
Various species of intestinal flukes infecting avian or mammalian hosts are known to be able to infect also humans [
1]. They are taxonomically diverse and can be classified into the family Heterophyidae (heterophyids), Echinostomatidae (echinostomes), and miscellaneous families, including Diplostomidae (diplostomes) and Strigeidae (strigeids) [
1]. In the Republic of Korea (= Korea), trematode fauna in birds and mammals has not been extensively studied, and studies on this topic are urgently needed.
The herring gull, Larus argentatus, is one of the commonly observed migratory birds along the seashores of Korea during winter season. They are typically found in harbors, on rocky shores, or at river mouths and known to breed in North-East Siberia spanning Chuckchi peninsula and Taymyr peninsula. During the survey of parasites in migratory birds, we discovered adult or juvenile specimens of intestinal flukes, including Cryptocotyle lingua (Creplin, 1825) Fischoeder, 1903, Himasthla alincia Diez, 1909, Cardiocephaloides medioconiger (Dubois et Perez-Vigueras, 1949) Baer, 1969, and Diplostomum spathaceum (Rudolphi, 1819) Olsson, 1876, from the small intestine of a herring gull. In this paper, we described the morphology of each species with discussion on their possibility for human infections.
In November 2010, a herring gull in a critical condition was found on the shore of a small island (Yubu-do, Seocheon, Chungcheongnam-do Province) near the western coast of the Korean peninsula during the routine surveillance of parasitic infections in migratory birds. This island was chosen as one of the eco-tour zones along with several nearby areas since a lot of migratory birds drop by on their way to the breeding or wintering grounds. The herring gull was immediately transferred to our laboratory, and the small intestine was separated. Then, the intestinal segment was opened longitudinally in saline, and the intestinal contents were examined for the presence of parasites. Some trematode specimens were observed, and they were isolated, fixed in 10% neutral formalin, and stained with Semichon’s acetocarmine. Then, their species was identified under light microscopy.
Total 11 adult or juvenile trematode specimens, including 3
C. lingua (Heterophyidae), 1
H. alincia (Echinostomatidae), 5
C. medioconiger (Strigeidae), and 2
D. spathaceum (Diplostomidae), were recovered. Their measurements (
Tables 1–
4) and morphological characteristics were as follows.
Specimens (n=
3) of
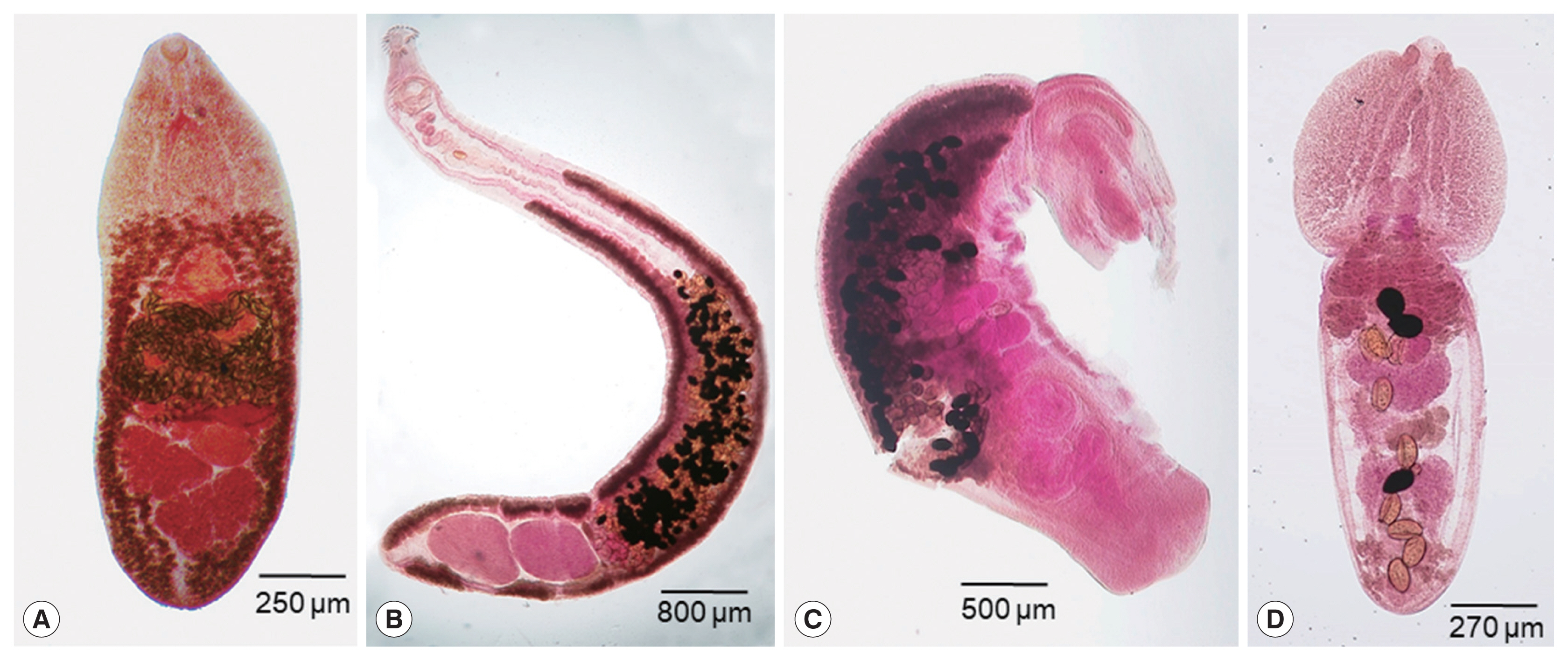
C. lingua (Heterophyidae) were small, leaf-like or tongue-shaped, 1.53–2.03 (av. 1.81) mm in length and 0.58–0.63 (0.59) mm in width (
Table 1;
Fig. 1A). The size of uterine eggs (n=12) was 40–44 (42) μm long and 16–19 (18) μm wide. They were morphologically characterized by having a small ventral sucker imbedded into the large and complex ventrogenital apparatus, 2 obliquely tandem testes, and extensive distribution of vitellaria from the posterior extremity up to far anterior level of the ventrogenital apparatus.
Only 1 adult specimen of
H. alincia (Echinostomatidae) was obtained, which was slender and elongated, 8.75 mm long and 0.93 mm wide (
Table 2;
Fig. 1B). The size of uterine eggs (n=10) was 98–110 (104) μm long and 65–70 (68) μm wide. It characteristically had a prominent head collar equipped with a crown of 31 collar spines (including 4 end group spines on each side). Two tandem testes were located near the terminal portion of the body, and vitellaria were distributed from the posterior extremity up to the posterior level of the cirrus sac.
One adult and 4 juvenile specimens of
C. medioconiger (Strigeidae) were recovered. They were bisegmented, with a pyriform or cordiform forebody (1.25 mm long and 0.65 mm wide) and a cylindrical hindbody (3.50 mm long and 1.10 mm wide), 4.75 mm in total length (
Table 3;
Fig. 1C). The size of uterine eggs (n=10) was 110–118 (115) μm long and 70–78 (74) μm wide. Their forebody was longer than wide, from which freely emerged the lobes of the tribocytic organ. It characteristically had a well-developed voluminous copulatory bursa containing seminal vesicle and ejaculatory duct in the posterior part of the hindbody.
Two adult specimens of
D. spathaceum (Diplostomide) were obtained. They were distinctively bisegmented, with a spoon-shaped forebody (0.68–0.85 mm long and 0.65–0.70 mm wide) equipped with prominent pseudosuckers, the anterior end of which was more or less trilobate, and a long cylindrical hindbody (1.08–1.10 mm long and 0.50–0.52 mm wide), 1.75–2.00 mm in total length (
Table 4;
Fig. 1D). The size of uterine eggs (n=13) was 108–125 (114) μm long and 65–85 (73) μm wide. The size of the ventral sucker was almost equal to that of the oral sucker. They had a sucker-like tribocytic organ, a ventral sucker near or close to the tribocytic organ, vitellaria distribution up to the anterior border of the tribocytic organ, and an ovary far from the junction of the fore- and hindbody.
Foreshore soil and environment along the western coast of the Korean peninsula have provided adequate conditions for migratory birds to drop by, and comprehensive surveys on parasites among these birds, including intestinal flukes, are required. In addition, it should be noted that some of the trematode species infected in migratory birds, for example,
C. lingua is known to have a potential to infect humans also [
1].
C. lingua was originally described in Europe in 1825 from the intestine of birds by Creplin under the name
Distoma lingua [
2]. In 1899, Looss created
Tocotrema as a new genus and designated this species as
Tocotrema lingua [
3]. Subsequently, in 1903, this fluke was renamed as
Cryptocotyle lingua by Fischoeder [
4]. In 1915, Linton [
5] found this fluke in USA but described it under the name
Tocotrema lingua. However, in 1920, Ransom [
4] synonymized the genus
Tocotrema with
Cryptocotyle, and in 1930, Stunkard [
2] finally accepted
C. lingua. It should be noted that human infection with this fluke was reported once in Greenland [
6], and it is listed among the intestinal flukes potentially infecting humans [
1]. The source of infection is various species of fish, including mullets [
1]. In Korea,
Cryptocotyle concava and
Cryptocotyle sp. were reported several times from the small intestines of ducks [
7] and feral cats [
8–
10]. However, no reports have been made on
C. lingua, and this is a new fauna record in Korea. Major morphological differences between
C. lingua and
C. concava include the body shape (slightly elongated vs ovoid, respectively), ventrogenital apparatus or ventrogenital sac (large vs small), and testes (obliquely tandem vs almost side by side) [
9].
H. alincia was originally described from the intestine of an avian species in Brazil [
11] and is now well known to infect birds like gulls, herons, and oystercatchers in North and South Americas [
12,
13]. In Korea, the metacercariae of
H. alincia were discovered in 2003 from a brackish water bivalve species (
Mactra veneriformis) along the western coast [
14]. Several other molluscan species were also found to harbor the metacercariae, and adult flukes were recovered from experimental chicks [
15]. However, no natural infections of birds with
H. alincia had been documented. Therefore, this is the first report of a natural infection of an avian host infected with
H. alincia in Korea. This echinostome has never been reported from humans worldwide; however, it has a potential to infect humans considering that a related species,
Himasthla muehlensi, was reported from a human infection [
1,
16]. It is also of note in Korea that the metacercariae of
Himasthla kusasigi, another related species, were detected in a marine bivalve species,
Meretrix lusoria [
17], and its adult flukes were recovered from dunlin,
Calidris alpina sakhalina [
18]. The major differential points between
H. alincia and
H. kusasigi were the distribution of vitellaria, from the posterior extremity up to the posterior level of the cirrus sac (
H. alincia) vs more anterior distribution beyond the cirrus sac (
H. kusasigi).
H. alincia also differs from a related species
Himasthla limnodromi in the presence of small spines on the cirrus and larger body and egg sizes [
14].
The genus
Cardiocephaloides was created by Sudarikov in 1959 using
C. brandesii as the type [
19,
20]. Prior to this, a related genus
Cardiocephalus was erected by Szidat [
21] in 1928–1929 and assigned
C. longicollis (type),
C. musculosus, C. hillii, and
C. brandesii (n. sp.) in this genus. Another species,
C. medioconiger, was described from birds (
L. argentatus, Larus atricilla, and
Larus delawarensis) in Pennsylvania, USA under the name
Strigea bursigera [
22]. Later, this species was assigned to
Cardiocephalus with a new name
C. medioconiger by Dubois and Pérez-Vigueras in 1949 [
19,
23]. However, it was found that the name
Cardiocephalus was preoccupied as a taxon for an amphibian species by Broilli in 1904 [
23]. Thus, Baer [
24], Dubois [
23], and Dubois and Macko [
25] were of opinion that
C. medioconiger should be assigned under the genus
Cardiocephaloides but not
Cardiocephalus. This opinion was accepted by Niewiadomska [
26] in 2002 and the genus
Cardiocephalus was synonymized with
Cardiocephaloides. In our study, 5 specimens of
C. medioconiger were recovered. Among them, 4 were immature, and only 1 was adult fluke having fully developed sexual organs. In Korea, this is the first report on the presence of this fluke.
C. medioconiger is distinguished from other species of
Cardiocephaloides in that it has a shorter and smaller body but has an enormous copulatory bursa containing the seminal vesicle and ejaculatory duct [
23].
D. spathaceum was originally described from birds in Europe by Rudolphi in 1819 under the name
Distoma spathaceum [
20]. Later, in 1850, it was renamed as
Hemistomum spathaceum by Diesing [
27]. However, the name was changed into
Diplostomum spathaceum by Olsson in 1876 [
20]. Dubois [
23] divided
D. spathaceum into 4 subspecies (
D. spathaceum spathaceum, D. spathaceum huronense, D. spathaceum indistinctum, and
D. spathaceum murrayense). However, Yamaguti [
20] elevated 3 of them (
D. spathaceum, D. huronense, and
D. murrayense) to distinct species and retained only
D. spathaceum indistinctum as a subspecies. After Olsson, more than 50 species had been described in
Diplostomum [
20]. However, only 25 species were considered valid in a taxonomic revision of the genus by Shigin in 1993 [
28]. The most common species in Europe and Asia were 6 in number, including
D. spathaceum (Rudolphi, 1819),
D. pseudospathaceum Niewiadomska, 1984,
D. paracaudum (Iles, 1959),
D. mergi Dubois, 1932,
D. parviventosum Dubois, 1932, and
D. baeri Dubois, 1937 [
29]. Adult flukes of these 6 species can be morphologically discriminated depending on 8 kinds of characters, including the extent of body division, forebody shape, form of holdfast organ, hindbody/forebody ratio, acetabulum/oral sucker ratio, acetabulum to the hold fast organ distance, vitellaria distribution, and ovary position [
29]. Both of our 2 specimens were exactly matched with the characteristics of
D. spathaceum. This is the first report on the presence of
D. spathaceum in an avian species in Korea. The second intermediate host of
D. spathaceum is known to be freshwater, brackish water, or marine fish, and the metacercariae parasitize particularly in their eyes [
20]. The existence of the metacercariae of
Diplostomum sp. were documented several times in freshwater fish in Korea [
30–
32]. However, the species of these
Diplostomum metacercariae in fish should be determined in the near future through animal experimental infection.
In conclusion, this study reported 4 species of intestinal flukes parasitic in a herring gull found in Korea, which included C. lingua, H. alincia, C. medioconiger, and D. spathaceum. Three of them (C. lingua, C. medioconiger, and D. spathaceum) are new trematode fauna in Korea. Considering the adequate conditions of Korean peninsula for migratory birds to drop by, further extensive studies on the infection status of birds with trematode parasites should be performed.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
Fig. 1Intestinal trematodes collected from a herring gull. (A) Cryptocotyle lingua. (B) Himasthla alincia. (C) Cardiocephaloides medioconiger. (D) Diplostomum spathaceum.
Table 1Measurements (μm) of Cryptocotyle lingua (adults) in comparison with a previous report
Table 1
|
Item |
Our specimens (n=3) |
Ransom (1920) [4] |
|
Body (length×width) |
1,530–2,030×580–630 |
550–2,000×200–900 |
|
Oral sucker (diameter) |
50–90 |
66–110 |
|
Prepharynx (length) |
30 |
Smaller than pharynx |
|
Pharynx (length×width) |
65–80×40–55 |
40–80×30–48 |
|
Esophagus (length) |
60–75 |
About 50 |
|
Ventral sucker (diameter) |
70–90 |
55–85 |
|
Genital apparatus (diameter) |
110–115 |
120–250 |
|
Left testis (length×width) |
300–340×175–225 |
120–250×70–130 |
|
Right testis (length×width) |
275–300×175–250 |
120–250×70–130 |
|
Ovary (length×width) |
75–200×75–125 |
140–180×70–120 |
|
Egg (length×width) |
40–44×16–19 |
40–50×18–25 |
Table 2Measurements (μm) of Himasthla alincia (adult) in comparison with a previous report
Table 2
|
Item |
Our specimen (n=1) |
Han et al. (2009) [15] |
|
Body (length×width) |
8,750×930 |
5,400–10,000×340–630 |
|
Head collar (width) |
300 |
300–360 |
|
No. of collar spines |
31 |
31 |
|
No. of corner spines |
4 |
4 |
|
Oral sucker (length×width) |
153×198 |
80–125×75–113 |
|
Pharynx (length×width) |
124×94 |
103–133×80–120 |
|
Esophagus (length) |
248 |
138–200 |
|
Ventral sucker (diameter) |
290×327 |
240–300×200–610 |
|
Anterior testis (length×width) |
650×480 |
290–820×180–340 |
|
Posterior testis (length×width) |
750×550 |
280–850×180–350 |
|
Ovary (length×width) |
200×200 |
63–170×100–168 |
|
Egg (length×width) |
98–110×65–70 |
108–113×65–80 |
Table 3Measurements (μm) of Cardiocephaloides medioconiger (adult) in comparison with a previous report
Table 3
|
Item |
Our specimen (n=1) |
Dubois (1970) [23] |
|
Body (length×width) |
4,750×1,100 |
9,000×1,360–1,400 |
|
Forebody (length×width) |
1,250×650 |
630–1,500×450–1,360 |
|
Hindbody (length×width) |
3,500×1,100 |
2,130–7,500×500–1,400 |
|
Oral sucker (length×width) |
175×90 |
81–179×75–136 |
|
Pharynx (length×width) |
100×200 |
66–183×66–192 |
|
Ventral sucker (diameter) |
150×125 |
104–157×75–138 |
|
Anterior testis (length×width) |
250×600 |
240–560×410–707 |
|
Posterior testis (length×width) |
300×650 |
285–570×500–750 |
|
Ovary (length×width) |
150×250 |
150–278×217–300 |
|
Egg (length×width) |
110–120×70–78 |
96–131×63–78 |
Table 4Measurements (μm) of Diplostomum spathaceum (adults) in comparison with a previous report
Table 4
|
Item |
Our specimens (n=2) |
Dubois (1970) [23] |
|
Total body (length×width) |
1,750–2,000×650–700 |
Up to 4,450 |
|
Forebody (length×width) |
680–850×650–700 |
600–1,800×270–960 |
|
Hindbody (length×width) |
1,080–1,100×500–520 |
520–3,220×210–750 |
|
Oral sucker (length×width) |
60–65×75–100 |
40–100×46–104 |
|
Pharynx (length×width) |
50–52×55–65 |
39–91×25–75 |
|
Ventral sucker (diameter) |
75–85×80–100 |
48–110×48–140 |
|
Tribocytic organ (length×width) |
175–275×125–160 |
125–450×90–390 |
|
Anterior testis (length×width) |
325–350×140–150 |
95–460×130–560 |
|
Posterior testis (length×width) |
300–325×175–225 |
90–485×190–650 |
|
Ovary (length×width) |
100–135×75–100 |
50–205×70–235 |
|
Egg (length×width) |
108–125×65–85 |
84–115×52–76 |
References
- 1. Chai JY. Human Intestinal Fluke From Discovery to Treatment and Control. Dordrecht, The Netherlands. Springer Nature B.V; 2019, pp 1-549.
- 2. Stunkard HW. The life history of Cryptocotyle lingua (Creplin), with notes on the physiology of the metacercariae. J Morphol Physiol 1930;50:143-191.
- 3. Witenberg G. Studies on the trematode-family Heterophyidae. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 1929;23:131-268.
- 4. Ransom BH. Synopsis of the trematode family Heterophyidae with descriptions of a new genus and five new species. Proc US Nat Mus 1920;57:527-573.
- 5. Linton E.
Tocotrema lingua (Creplin): the adult stage of a skin parasite of the cunner and other fishes of the Woods Hole Region. J Parasitol 1915;1:128-134.
- 6. Babbott FL Jr, Frye WW, Gordon JE. Intestinal parasites of man in Arctic Greenland. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1961;10:185-190.
- 7. Eom KS, Rim HJ, Jang DH. A study on the parasitic helminths of domestic duck (Anas platyrhynchos var. domestica Linnaeus) in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1984;22:215-221.
- 8. Sohn WM, Chai JY. Infection status with helminthes in feral cats purchased from a market in Busan, Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2005;43:93-100.
- 9. Chai JY, Bahk YY, Sohn WM. Trematodes recovered in the small intestine of stray cats in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2013;51:99-106.
- 10. Shin SS, Oh DS, Ahn KS, Cho SH, Lee WJ, Na BK, Sohn WM. Zoonotic intestinal trematodes in stray cats (Felis catus) from riverside areas of the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:209-213.
- 11. Dietz E. Die Echinostomatiden der Vogel. Zool Anz 1909;34:180-192.
- 12. Lumsden RD. Four echinostome trematodes from Louisiana birds including the description of a new species. Tulane Stud Zool 1962;9:301-308.
- 13. Diaz JI, Cremonte F.
Himasthla escamosa n. sp. (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) from the kelp gull, Larus dominicanus (Charadriformes: Laridae), on the Patagonian Coast, Argentina. J Parasitol 2004;90:308-314.
- 14. Han ET, Han KY, Chai JY. Tegumental ultrastructure of the juvenile and adult Himasthla alincia (Digenea: Echinostomatidae). Korean J Parasitol 2003;41:17-25.
- 15. Han ET, Whang JD, Chai JY.
Himasthla alincia (Echinostomatidae): metacercariae in brackish water bivalves and their growth and development in experimental animals. J Parasitol 2009;95:1415-1420.
- 16. Vogel H.
Himasthla muehlensi n sp., ein neuer menschlicher Trematode der Familie Echinostomidae. Zbl Bakt Parasitol (I Abt Org) 1933;127:385-391. (in German)..
- 17. Kim YG, Chun SK. Studies on a trematode parasite in bivalves. IV. On the metacercaria of Himasthla kusasigi Yamaguti, 1939 (Trematoda) found in the clam, Meretrix lusori Roding. Bull Korean Fisher Soc 1984;17:61-67. (in Korean)..
- 18. Chu JP, Cho YJ, Yoo JC, Park SG.
Himasthla kusasigi (Trematoda, Echinostomatidae) recovered from the intestinal of the dunlin, Calidris aplina sakhalina, in Korea. Korean J Syst Zool 2000;16:125-131.
- 19. Sudarikov VE. Order Strigeidida (La Rue, 1926) Sudarikov, 1959. In Skrjabin KI ed, Trematodes of Animals and Man. Moscow, Russia. 1959, 16:pp 217-631 (in Russian).
- 20. Yamaguti S. Synopsis of Digenetic Trematodes of Vertebrates. I:Tokyo, Japan. Keigaku Publishing Co; 1971, pp 1-1074.
- 21. Szidat L. Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Gattung Strigea (Abildg.). Z Parasitenkd 1929;1:688-764. (in German)..
- 22. Linton E. Notes on trematode parasites of birds. Proc US Nat Mus 1928;73:1-36.
- 23. Dubois G. Synopsis des Strigeidae et des Diplostomatidae (Trematoda). Mém Soc Neuchâtel Sci Natur 1970;10:259-727.
- 24. Baer JG. Un Trématode parasite du Comoran Phalacrocorax bougainvilleii (Less.) des íles Guañape, Pérou. Parasitol Sbaronik 1969;24:7-15.
- 25. Dubois G, Macko JK. Contribution á l’étude des Strigeata La Rue, 1926 (Trematoda: Strigeida) de Cuba. Ann Parasitol (Paris) 1972;47:51-75. (in French)..
- 26. Niewiadomska K. Family strigeidae railliet, 1919. In Gibson DI, Jones A, Bray RA eds, Keys to the Trematoda. 1:London, UK. Natural History Museum; 2002, pp 231-241.
- 27. La Rue GR. Studies on the trematode family Strigeidae (Holostomidae). No. II. Taxonomy. Trans Am Microscop Soc 1926;45:11-19.
- 28. Georgieva S, Soldanova M, Perez-del-Olmo A, Dangel DR, Sitko J, Sures B, Kostadinova A. Molecular prospecting for European Diplostomum (Digenea: Diplostomidae) reveals cryptic diversity. Int J Parasitol 2013;43:57-72.
- 29. Niewiadomska K, Laskowski Z. Systematic relationships among six species of Diplostomum Nordmann, 1832 (Digenea) based on morphological and molecular data. Acta Parasitol 2002;47:20-28.
- 30. Nam HS, Sohn WM. Infection status with trematode metacercariae in pond smelts, Hypomesus olidus
. Korean J Parasitol 2000;38:37-39.
- 31. Cho SH, Sohn WM, Shin SS, Song HJ, Choi TG, Oh CM, Kong Y, Kim TS. Infection status of pond smelts, Hypomesus olidus, and other freshwater fishes with trematode metacercariae in 6 large lakes. Korean J Parasitol 2006;44:243-246.
- 32. Sohn WM, Na BK, Cho SH, Lee SW, Choi SB, Seok WS. Trematode metacercariae in freshwater fish from water systems of Hantangang and Imjingang in Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:289-298.