Abstract
The pathogenic mechanism of granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE) and amebic keratitis (AK) by Acanthamoeba has yet to be clarified. Protease has been recognized to play an important role in the pathogenesis of GAE and AK. In the present study, we have compared specific activity and cytopathic effects (CPE) of purified 33 kDa serine proteinases from Acanthamoeba strains with different degree of virulence (A. healyi OC-3A, A. lugdunensis KA/E2, and A. castellanii Neff). Trophozoites of the 3 strains revealed different degrees of CPE on human corneal epithelial (HCE) cells. The effect was remarkably reduced by adding phenylmethylsulfonylfluoride (PMSF), a serine proteinase inhibitor. This result indicated that PMSF-susceptible proteinase is the main component causing cytopathy to HCE cells by Acanthamoeba. The purified 33 kDa serine proteinase showed strong activity toward HCE cells and extracellular matrix proteins. The purified proteinase from OC-3A, the most virulent strain, demonstrated the highest enzyme activity compared to KA/E2, an ocular isolate, and Neff, a soil isolate. Polyclonal antibodies against the purified 33 kDa serine proteinase inhibit almost completely the proteolytic activity of culture supernatant of Acanthamoeba. In line with these results, the 33 kDa serine proteinase is suggested to play an important role in pathogenesis and to be the main component of virulence factor of Acanthamoeba.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba, amebic encephalitis, amebic keratitis, serine proteinase, cytopathic effects
INTRODUCTION
Members of the genus
Acanthamoeba, one of amphizoic amoebae, are ubiquitous in nature and are found in diverse habitats including soil, water, air-conditioning units, contact lenses, and lens cases (
Marciano-Cabral and Cabral, 2003;
Schuster and Visvesvara, 2004). In recent years,
Acanthamoeba spp. became a public health issue as causative agent of amebic keratitis (AK) and granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE) (
Alfieri et al., 2000;
Marciano-Cabral et al., 2000). GAE associated with individuals suffering from underlying diseases progressed chronically and usually ended with fatal results (
Marciano-Cabral and Cabral, 2003). AK, relatively more common than GAE, affects young and healthy individuals particularly contact lens wearers.
Although studies to define pathogenic mechanisms have been conducted, the mechanisms by which
Acanthamoeba give rise to human diseases remain poorly understood. It is generally recognized that pathogenesis of
Acanthamoeba infections is a multi-step process involving adhesion to host cells, degradation and invasion into host tissues in both cases of GAE and AK. Amoeba may access to the central nervous system to cause GAE by hematogenous spread from a primary site in the lungs or skin. In the case of AK, amoeba from environment may attach to the injured surface of cornea and invade the stroma. Up to date, proteinases and adhesion molecules such as laminin binding protein and mannose binding protein have been investigated to understand the pathogenic mechanisms of
Acanthamoeba (
Hong et al., 2000;
Garate et al., 2004;
Hong et al., 2004).
As in various protozoan parasites, proteases secreted by
Acanthamoeba are regarded as an important factor in the pathogenesis (
Mckerrow et al., 1993). Serine proteases have been the most extensively investigated but most were focused on keratitis. Leher et al. (
1998) reported that mannose treatment induced
Acanthamoeba trophozoites to release cytopathic factors and lyse corneal epithelial cells in vitro. The cytopathic activity was completely inhibited by a serine protease inhibitor. In contrast, Cao et al. (
1998) showed that inhibition of amoeba binding to corneal epithelial cells with exogenous mannose resulted in loss of cytopathogenicity of
Acanthamoeba on host cells. Khan (
2003) suggested that serine proteases play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of
Acanthamoeba keratitis, because a serine protease inhibitor abolished cytotoxicity of
Acanthamoeba conditioned medium on corneal epithelial cells. However, effects of purified enzymes of
Acanthamoeba on cytopathy have seldom been studied.
Previously, a secretory 33 kDa serine protease of
A. healyi OC-3A isolated from the brain of a GAE patient was purified and characterized (
Kong et al., 2000). The serine protease revealed strikingly potent proteolytic activity against mammalian extracellular matrix proteins including types I and IV collagen and other serum proteins. Hong et al. (
2000) isolated a cDNA encoding a 33 kDa serine protease (AhSUB), and identified the protease to be a member of subtilase superfamily. Northern blot analysis revealed that AhSUB was expressed at higher levels in the high-virulent strain than low- or avirulent strains. Recently, we confirmed the secretion of a 33 kDa serine protease from ocular and environmental isolates of
Acanthamoeba (
Kim et al., 2003).
In the present study, the authors have compared specific activity and cytopathic effect of purified 33 kDa serine proteases from Acanthamoeba strains with different degree of virulence (A. healyi OC-3A, A. lugdunensis KA/E2, A. castellanii Neff) and proposed the protease as a virulence factor for Acanthamoeba infections.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Culture of amoebae
Three strains of
Acanthamoeba with different origin were used in this study.
Acanthamoeba healyi OC-3A (ATCC #30866) isolated from the brain of a GAE patient (
Moura et al., 1992) and
A. castellanii Neff strain (ATCC #30010) isolated from soil were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, Maryland, USA). Corneal isolate
A. lugdunensis KA/E2 was originated from the infected cornea of a Korean AK patient (
Yu et al., 2004). They were cultured axenically in PYG medium at 25°C.
HCE cells for cytopathy assay were kindly provided by the Department of Biochemistry, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. Cells were cultured in DMEM/F12, 15% fetal bovine serum, 5 µg/ml insulin and 10 ng/ml human EGF at 37°C under 5% CO2 condition. Monolayered HCE cells in 96-well culture plates were coincubated with 2 × 105 trophozoites of one of the 3 strains of Acanthamoeba, i.e., OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff, for 24 hr at 37°C under 5% CO2. Phenylmethylsulfonylfluoride (PMSF) (0.1 mM), one of the serine proteinase inhibitors, was added to each well with same c conditions to estimate the effects of serine proteinase on cytopathy by Acanthamoeba trophozoites. CPE was assessed visually after Giemsa staining and measurement of optical density (OD) at 590 nm with 0.1 ml of cells solubilized in 0.4 ml of 5% sodium dodecyl sulfate in phosphate buffered saline. Percent CPE was calculated according to the following formula: % CPE = 100-[(OD of experimental well-OD of amoeba alone)/OD control cells alone] × 100. Assay was performed in triplicate. CPE by purified subtilases was determined by the same way. One, 2 or 10 µg purified enzymes of 3 Acanthamoeba strains were incubated with monolayer of HCE cells for 24 hr at 37°C under 5% CO2.
Purification of subtilase
Purification of 33 kDa serine proteases from culture media of 3 strains were performed as described in previous papers (
Kong et al., 2000;
Kim et al., 2003). The amoeba culture supernatant was precipitated with 65% ammonium sulfate and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 15 min. The pellet was dissolved in 50 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.2) and dialyzed against the same buffer at 4°C for 30 hr. The dialyzed solution was then applied to a CM-Sepharose column (3.0 × 17 cm) equilibrated with 50 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.2), and eluted with a 0.1 M NaCl gradient at a rate of 0.5 ml/min, with 5 ml of fraction volume. Each fraction was tested for enzymatic activity. The active fractions were pooled and dialyzed against 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.8). The dialyzed solution was concentrated using a freeze dryer (Bondiro, Ilshine, Korea). The concentrated solution was loaded onto a Sephacryl S-200 column (HiPrep 1.6/60, Amersham, Uppsala, Sweden) and fractionated at a rate of 0.5 ml/min into 2.5 ml fraction volumes. Pooled active fractions were applied to a mono Q-anion-exchange column (Mono Q HR 5/5, Amersham, Uppsala, Sweden) and eluted with a 0-0.35 M NaCl gradient in 50 mM Tris (pH 8.0). Fractions showing proteinase activity were retained for further characterization.
The proteinase activity was assayed against casein. A mixture of 500 µl of 0.6% casein (Sigma Co., Steinheim, Germany) in 50 mM Tris (pH 8.0) and 100 µl of enzyme was incubated for 2 hr at 40°C. The reaction was stopped by adding 500 µl of 0.4 M trichloroacetic acid and incubating at 40°C for 10 min. After centrifugation, 200 µl of supernatant was mixed with 1 ml of 0.4 M sodium carbonate and 200 µl of Folin-Ciocateu reagent (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA) and incubated at 40°C for 20 min. The amount of degradation was determined from the absorbance at 660 nm. One unit of enzyme activity was defined as the amount of enzyme necessary to elaborate 1 µl of tyrosine from casein in 1 ml of reaction volume per min. Bradford dye-binding procedure (Bradford, 1976) was used to determine the protein concentration except during chromatography where absorbance was monitored at 280 nm.
Optimum conditions (pH and temperature)
The pH optimum was monitored over the pH range 5.5-10.0 using casein as a substrate. The buffer formulations used were 50 mM sodium acetate buffer at pH 5.5-6.0, 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer at pH 6.0-8.0 and 50 mM Tris-HCl at pH 8.0-10.0. The optimal temperature was also monitored by incubation at temperature ranging from 4°C to 65°C.
Inhibitor and activator sensitivity
Various effectors, namely PMSF (1.0 mM), diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP, 1.0 mM), L-transepoxysuccinyl-leucylamide (4-guanidino) butane (E-64, 10 µg/ml and 50 µg/ml), dithio-threitol (DTT, 1.0 mM), pepstatin A (1.0 µg/ml), EDTA (1.0 mM and 10.0 mM), 1,10-phenanthroline (1.0 mM) were preincubated with the purified enzyme for 20 min at 37°C. Substrate was added and the proteolytic activity was assayed. All proteinase inhibitors and activators were purchased from Boehringer Mannheim Biochemicals (Mannheim, Germany).
Gelatin dot zymogram
Five hundred micrograms of purified serine proteinases in 500 ml volume of three Acanthamoeba strains were loaded on the hole of 3 mm diameter on an 10% acrylamid gel copolymerized with 0.1% gelatin without SDS. The gel was incubated in 37°C for 24 hr. The inhibitory effect of PMSF was tested with the proteinase sample preincubated with 0.1 mM PMSF for 30 min at room temperature. After reaction, the gel was stained with Commassie blue and destained several times with 40% methanol and 10% acetic acid. The proteolytic activity of the enzyme from 3 strains was compared with the size of visualized clear zone where gelatin was degraded by the enzyme.
Substrate specificity
The substrate specificity of purified subtilases was analyzed with mammalian extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, i.e., type I and IV collagens, fibronectin, and laminin. Five hundred micrograms of each substrate, dissolved in 0.1 M sodium acetate buffer (collagens) or 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4 (fibronectin and laminin), at a concentration of 1 mg/ml, was mixed with 1 µg of the enzyme and incubated at 37°C. Twenty-five microliter aliquots were withdrawn from the reaction mixture after 10 min, 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, 4 hr, and 6 hr and electrophoresed in a 4-20% gradient acrylamide gel. After electrophoresis, the gels were stained with 0.1% Coomassie blue.
Inhibition of proteinase activity by antibody against 33 kDa serine proteinase
Inhibiton of proteinase activity of culture supernatant by antibody against 33 kDa serine proteinase was analysed. Antibody produced as previously described by Hong et al. (
2004) was preincubated with culture supernatant which was obtained by incubation 3.0 × 10
6 trophozoites of three
Acanthamoeba strains for 18 hr in 1.5 ml medium. Two microliters of supernatnat of three strains were preincubated with two microliter of 20 fold diluted antibody at 37°C for 20 min. The mixture of each strain was loaded on 3 mm diameter-hole of 10% acrylamide gel copolymerized with 0.1% gelatin without SDS. After incubation at 37°C for 24 hr, the gel was stained with Commassie blue. The inhibition of proteinase activity of culture supernatant was analyzed by comparing the size of clear zone around the hole where gelatin was degraded.
RESULTS
CPE of Acanthamoeba trophozoites
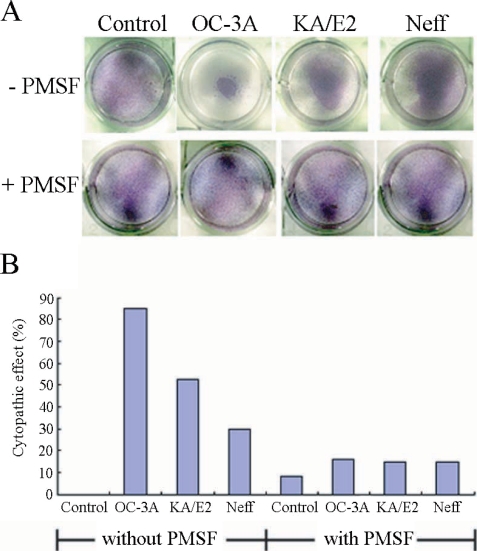
Fig. 1 shows the CPE on HCE cells by trophozoites of
Acanthamoeba 3 strains, OC-3A, KA/E2, and Neff. Calculated CPE on HCE cells were 85% by OC-3A, 53% by KA/E2 and 30% by Neff strain. HCE cells remained almost intact in 0.1 mM PMSF treated culture plates. The CPE of trophozoites of the 3 strains on HCE cells were reduced remarkably to 16%, 15% and 15%, by adding 0.1 mM PMSF to the coculture media.
Purification and specific activity of serine proteinases
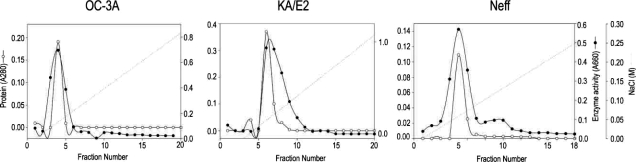
The purification steps to separate the 33 kDa proteolytic enzyme from the culture supernatant of
Acanthamoeba 3 strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff are summarized in
Table 1 and
Fig. 2. Ammonium sulfate precipitated culture supernatant of three strains was applied on the CM sepharose column. Pooled fractions showing proteolytic activity were applied on Gel filtration column for further purification. Pooled fractions with proteolytic activity were applied on anion exchange column. One protein peak was matched with proteolytic activity peak (
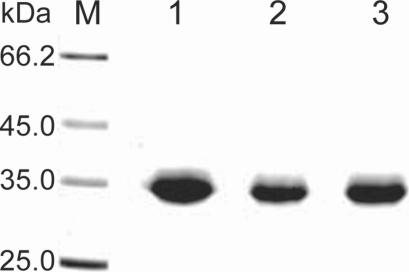
Fig. 2). Purified proteinase of the 3 strains was electrophoresed on a SDS-PAGE gel and determined as a single protein band (
Fig. 3). The final amount of purified serine proteinase from 1 L of collected culture media was 0.04 mg for OC-3A, 0.03 mg for KA/E2 and 0.02 mg for Neff strain. The specific activity for 1 mg of purified proteinase was highest in OC-3A with 1145.0 units, followed by KA/E2 with 817.4 units, and Neff with 704.6 units.
The purified proteinase of all 3 strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff, maintained enzymatic activity with wide range of pH 5.5-10.0, and showed maximum activity at pH 8.5, 8.5, and 8.0 respectively. The purified enzyme of OC-3A strain retained enzymatic activity over pH 9 at which that of the other 2 strains lost their activities rapidly. The optimal temperatures for the proteinases were 60°C for OC-3A and 55°C for KA/E2 and Neff. The purified enzyme of OC-3A strain showed more stable activity than that of KA/E2 and Neff at high pH and high temperature.
Effect of inhibitors and activators
As shown in
Table 2, the enzyme activities of purified proteinase of OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff were almost completely inhibited by serine proteinase inhibitors, PMSF and DFP. The other inhibitors or activators for cysteine, aspartic, or metallo classes had no effect on the enzyme activity.
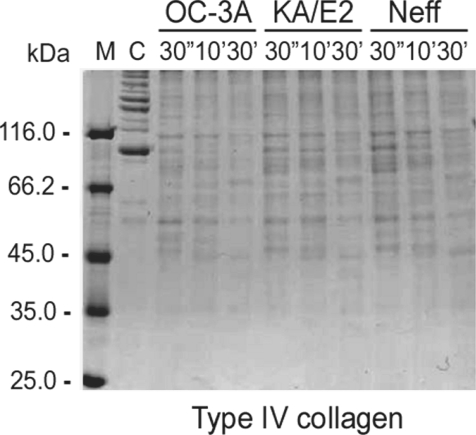
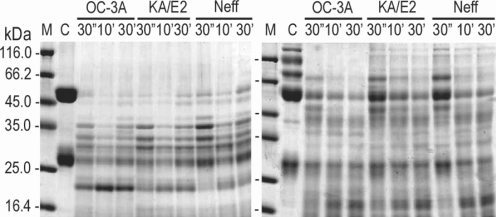
The purified enzyme of 3 strains degraded type IV collagen, the main components of extracellular matrix (
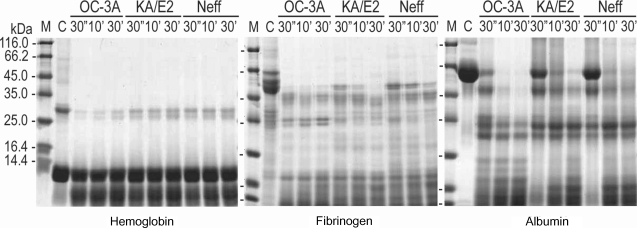
Fig. 4) as well as type I collagen and fibronectin (data not shown). Alpha and beta subunits of type IV collagen were fragmented into small pieces within a min. The purified enzymes also degraded host serum proteins such as fibrinogen, hemoglobin, and albumin (
Fig. 5). The enzyme of OC-3A strain degraded all subunits of fibrinogen within a minute. However, gamma subunit of fibrinogen was not completely digested by the enzyme of KA/E2 and Neff strain. The enzymes of KA/E2 and Neff strains needed longer time to degrade albumin than that of OC-3A.
In the case of immunoglobulins, the enzyme of OC-3A showed strongest activity against human IgG and IgA (
Fig. 6). The light chain of IgG was more resistant to the enzymes than that of heavy chain. IgA was hardly degraded by the purified enzymes of the three strains compared to the other substrates. The enzymes of KA/E2 and Neff strains needed longer time to degrade any substrate than that of OC-3A.
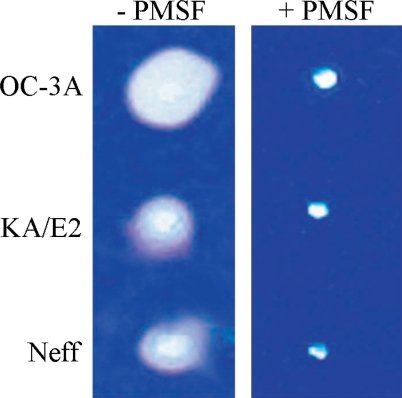
Coomassie Blue stained acryl amide gel copolymerized with gelatin showed clear zones around 3 holes where purified enzyme was loaded. The enzyme of OC-3A strain showed the biggest clear zone while that of KA/E2 and Neff strain revealed quite similar results. PMSF-treated purified enzyme made little or no clear zone around the hole in all cases (
Fig. 7).
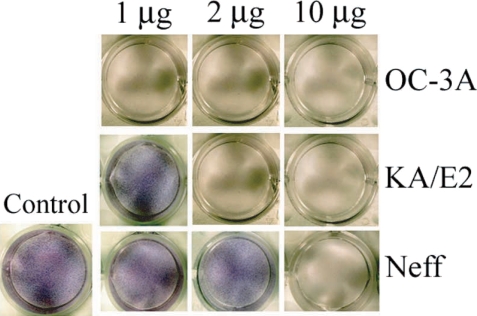
When the purified serine proteinases of the 3 strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff, were added to the HCE cell monolayer, 1
µg of the enzyme of OC-3A strain was enough to lyse target cells (
Fig. 8). In the case of KA/E2, HCE cells were almost completely lysed with 2
µg of the purified enzyme. HCE cells were completely lysed upon the addition of 10
µg of any purified enzyme from the 3 strains.
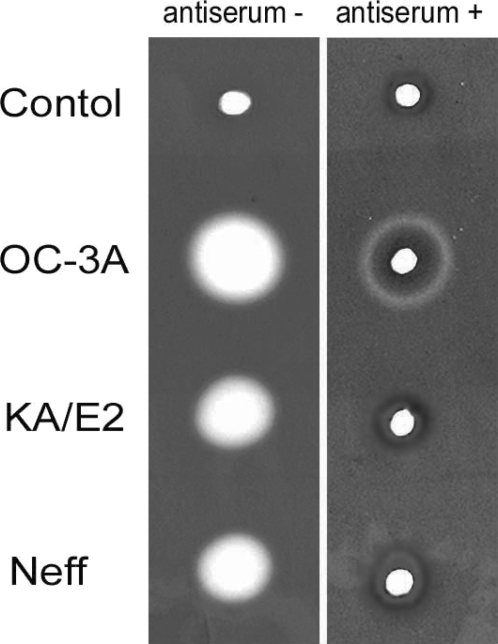
Anti-serum of immunizing SD rats with the purified recombinant 33 kDa serine proteinase inhibited almost completely the proteinase activity of culture supernatant in three strains. Two microliter of 20 fold diluted anti-serum was enough to diminish proteinase activity of same amount of culture supernatant. In the case of
A. healyi OC-3A strain, partial clear zone was observed around the hole (
Fig. 9).
DISCUSSION
The mechanisms associated with the pathogenesis of
Acanthamoeba infections are believed to be highly complex and mechanisms and virulence factors have yet to be clarified. Kahn (
2003) classified the pathogenetic mechanisms into contact-dependent and contact-independent ones. Contact-dependent mechanism includes adhesion, apoptosis, and phagocytosis, while extracellular proteases belong to contact-independent one. In this study, contact-dependent mechanisms such as adhesion and phagocytosis proved minor factors for the cytopathy against corneal epithelial cells because 0.1 mM PMSF, one of the serine proteinase inhibitor, reduced the CPE of
Acanthamoeba trophozoites remarkably. PMSF of 0.1 mM concentration may not be recognized to affect significantly the contact-dependent cytopathic mechanisms. Furthermore, by adding 0.1 mM PMSF, the CPE of 3
Acanthamoeba strains with different degree of virulence came to be equal level. This indicates that the difference in virulence and cytopathy have may originated mainly from PMSF susceptible serine proteinases as suggested by previous studies (
Leher et al., 1998;
Alfrei et al.,2000;
Kong et al., 2000;
Kim et al., 2003).
Many serine proteinases with different molecular size had been reported in
Acanthamoeba (
Mitra et al.,1995;
Cho et al., 2000;
Kong et al., 2000;
Na et al., 2001;
Hurt et al., 2003). Among them, Kong et al. (
2000) proposed that a 33 kDa serine proteinase from culture supernatant may play a critical role in pathogenesis of GAE by
A. healyi because of the strong activity of the enzyme against main components of extracellular matrix and serum proteins. Hong et al. (
2000) isolated a cDNA encoding 33 kDa serine proteinase from an
A. healyi cDNA library and reported that the proteinase belonged to the subtilisin family. Furthermore, the gene was expressed at higher level in highly-virulent strain (OC-3A) than the low-virulent (KA/E2) or environmental isolate (KA/S8). This study revealed that the specific activity of purified 33 kDa serine proteinase from a high virulent strain (OC-3A) was 1.5 times more potent than those from a low virulent (KA/E2) and an environmental isolate (Neff). The origin of difference in specific activity remains unclear and may be a subject for further study.
The cytopathy of purified serine proteinase was profoundly different from strain to strain. Only 1 µg of the proteinase from OC-3A was enough for complete lysis of corneal epithelial cells after 24 hr whereas 10 µg of the enzyme from Neff and 2 µg from KA/E2 were needed. This result coincides with the ability of Acanthamoeba trophozoite to produce CPE. Trophozoites of OC-3A strain showed the strongest cytopathy to HCE cell, followed by KA/E2, and lastly Neff strain exhibiting the weakest cytopathy. The correlation of cytopathy by the purified proteinase and trophozoites indicated that the proteinase activity is the main factor for cytopathy in Acanthamoeba infection.
The proteolytic effects of the enzymes against various ECM and serum protein were not strikingly different. The purified proteinases showed potent proteolytic activity especially against type I and IV collagens, the main component of corneal stroma and basement membrane respectively. This indicates that the proteinase may play a key role in corneal tissue destruction in AK and spread of amoeba in GAE. Immunoglobulins were found relatively resistant compared with ECM proteins. However, Immunoglobulin alone can hardly be regarded as effective defence mechanism against Acanthamoeba infection. As a matter of fact, healthy persons who secrete anti-acanthamoebic IgA in their tears can be victims of AK.
Although present study revealed that cytopathy of HCE cells by
Acanthamoeba is dependent mainly on the secretory proteinase, pathogenesis of AK and GAE may need other factors and mechanisms in addition to the cytopathy. There has been reported the coordination of contact-dependent mechanism and contact-independent mechanism. Adhesion of
Acanthamoeba to corneal epithelial cells by mannose-binding protein resulted in increased secretion of proteases (
Cao et al., 1998;
Hurt et al., 2003;
Khan, 2003). The relation between those two components for pathogenesis and the mediating pathway would be the subject for further research.
Due to reports on the important role of proteinases in the pathogenesis of
Acanthamoeba infection, the possibility of proteinase as a target for development of therapeutic agent was considered by investigators (
Khan, 2003). Considering the result of this study, treatment with proteinase inhibitors for the serine proteinase as eye drop could be a promising way to delay the pathogenesis of keratitis by
Acanthamoeba. Up to date, it usually takes long time to cure and results in bad outcome in AK because of absence of specific drug for
Acanthamoeba. Therefore, prevention of lysis of corneal epithelial cells and degradation of stromal collagens by proteinase inhibitors may delay the process of AK.
In conclusion, PMSF susceptible proteinase activity was revealed as the main component to cause cytopathy in HCE cells by Acanthamoeba. The purified 33 kDa serine proteinase showed strong activity toward HCE cell and extracellular matrix proteins. Among the 3 Acanthamoeba strains, the most virulent strain, OC-3A exbihited the highest level of enzyme activity in comparison with KA/E2, ocular isolate, and Neff strain, a soil isolate.
Notes
-
This work was supported by a Korea Research Foundation grant (KRF-2001-042-F00031).
References
Fig. 1A. Light microscopic pictures of Giemsa stained human corneal cells after coculture with trophozoites of the 3 strains of Acanthamoeba, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff, with or without serine proteinase inhibitor, PMSF. B. Bar graph showing calculated cytopathic effects of the 3 strains.

Fig. 2Anion exchange column chromatograms of proteinase purification from the culture supernatant of Acanthamoeba strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff.

Fig. 3SDS-PAGE of the purified enzyme of the 3 strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff in a 4-20% gradient acrylamide gel. A single protein band stained with Coomassie blue is observed with a size of approximately 33 kDa in 3 strains. Lane: M, standard size marker; 1, OC-3A; 2, KA/E2; 3, Neff strain.

Fig. 4Proteolytic activity of the purified 33 kDa serine proteinase of Acanthamoeba strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff against extracellular matrix proteins. M, standard size marker; C, reaction mixture without enzyme; Reaction mixtures for each strain were incubated for 30'', 10', 30'.
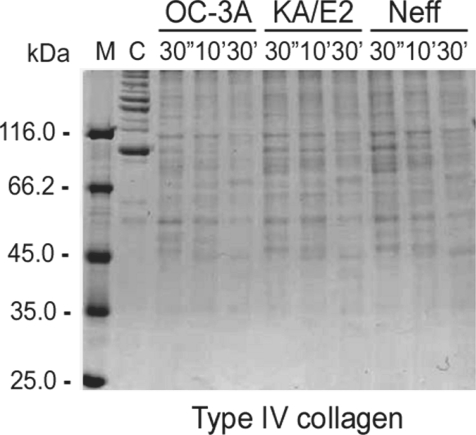
Fig. 5Proteolytic activity of the purified 33 kDa serine proteinase of Acanthamoeba strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff against host serum proteins. M, standard marker; C, reaction mixture without enzyme; Reaction mixtures for each strain were incubated for 30'', 10', 30'.
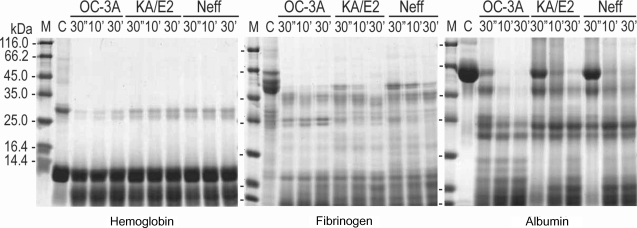
Fig. 6Proteolytic activity of the purified 33 kDa serine proteinase of Acanthamoeba strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff against immunoglobulins. M, standard marker; C, reaction mixture without enzyme; Reaction mixtures for each strain were incubated for 30'', 10', 30'.

Fig. 7Gelatin zymogram of the purified enzyme of Acanthamoeba strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff. Acrylamide gel copolymerized with gelatin was stained with Commassie blue after incubation with the purified serine proteinase loaded in the hole of the gel.

Fig. 8Cytopathic effects of the purified 33 kDa enzymes of Acanthamoeba strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff on HCE cell. Cytopathy was determined by staining the culture plate with Giemsa after incubation with the purified enzyme.
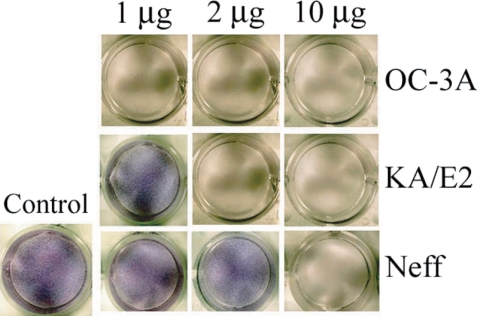
Fig. 9Gelatin zymogram of culture supernatant of Acanthamoeba strains, OC-3A, KA/E2 and Neff. Acrylamide gel copolymerized with gelatin was stained with Commassie blue after incubation with anti-serum against purified 33 kDa serine proteinase or without anti-serum.
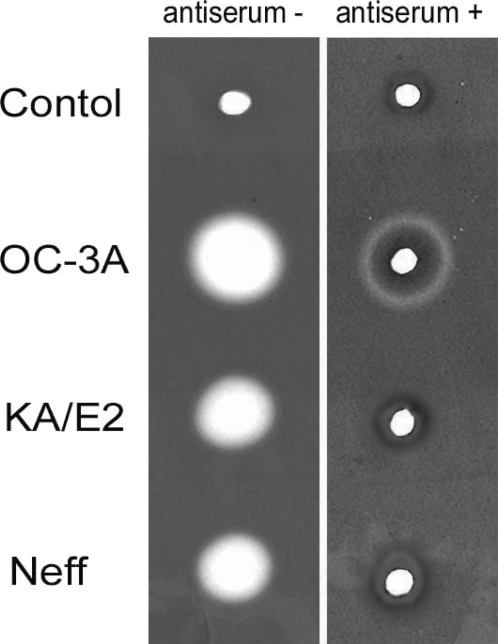
Table 1.Purification steps of 33 kDa serine proteinase from culture supernatant of 3 strains of Acanthamoeba, OC-3A, KA-E2 and Neff
Table 1.
|
Step |
Total protein (mg)
|
Total activity (nmol/min)
|
Specific activity (nmol/min/mg)
|
Purification (fold)
|
Yield (%)
|
|
OC-3A |
KA/E2 |
Neff |
OC-3A |
KA/E2 |
Neff |
OC-3A |
KA/E2 |
Neff |
OC-3A |
KA/E2 |
Neff |
OC-3A |
KA/E2 |
Neff |
|
Culture supernatant |
135.0 |
156.3 |
246.1 |
1836.3 |
813.0 |
516.7 |
13.6 |
5.2 |
2.1 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
Amonium sulfate percipitation |
25.3 |
28.0 |
30.0 |
1120.7 |
770 |
426.0 |
44.3 |
27.5 |
14.2 |
3.3 |
5.3 |
6.8 |
61.0 |
94.7 |
82.4 |
|
CM-Sepharose |
8.0 |
3.7 |
6.5 |
763.0 |
243.1 |
226.9 |
95.5 |
66.6 |
34.9 |
7.0 |
12.8 |
16.8 |
41.6 |
29.9 |
43.9 |
|
Sephacryl S-200 |
0.4 |
0.3 |
0.4 |
364.5 |
142.6 |
120.6 |
1041.4 |
570.3 |
335.0 |
76.6 |
109.7 |
159.5 |
19.8 |
17.5 |
23.3 |
|
Q-anion exchange |
0.04 |
0.03 |
0.02 |
45.8 |
26.1 |
10.6 |
1145.0 |
814.4 |
704.6 |
84.2 |
156.6 |
335.5 |
2.5 |
3.2 |
2.0 |
Table 2.Effects of proteinase inhibitors and activators on the activity of the purified enzymes of 3 strains of Acanthamoeba
Table 2.
|
Inhibitor/Activitor |
Final concentration |
Activity as percentage of control
|
|
OC-3A |
KA/E2 |
Neff |
|
Control (none) |
|
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
Serine Class |
|
|
|
|
|
PMSF |
1.0 mM |
6.1 |
6.9 |
7.3 |
|
DFP |
1.0 mM |
15.3 |
15.9 |
16.7 |
|
Cystein Class |
|
|
|
|
|
E-64 |
10.0 μg/ml |
115.8 |
96.7 |
93.3 |
|
DTT |
1.0 mM |
111.9 |
85.8 |
102.0 |
|
Aspartic Class |
|
|
|
|
|
Pepstatin A |
1.0 μg/ml |
107.9 |
97.4 |
96.7 |
|
Metallo Class |
|
|
|
|
|
EDTA |
1.0 mM |
102.6 |
108.3 |
90.3 |
|
1,10-Phenanthroline |
1.0 mM |
91.8 |
107.2 |
93.3 |