Abstract
Leishmaniasis is a prevalent cause of death and animal morbidity in underdeveloped countries of endemic area. However, there is few vaccine and effective drugs. Antimicrobial peptides are involved in the innate immune response in many organisms and are being developed as novel drugs against parasitic infections. In the present study, we synthesized a 5-amino acid peptide REDLK, which mutated the C-terminus of Pseudomonas exotoxin, to identify its effect on the Leishmania tarentolae. Promastigotes were incubated with different concentration of REDLK peptide, and the viability of parasite was assessed using MTT and Trypan blue dye. Morphologic damage of Leishmania was analyzed by light and electron microscopy. Cellular apoptosis was observed using the annexin V-FITC/PI apoptosis detection kit, mitochondrial membrane potential assay kit and flow cytometry. Our results showed that Leishmania tarentolae was susceptible to REDLK in a dose-dependent manner, disrupt the surface membrane integrity and caused parasite apoptosis. In our study, we demonstrated the leishmanicidal activity of an antimicrobial peptide REDLK from Pseudomonas aeruginosa against Leishmania tarentolae in vitro and present a foundation for further research of anti-leishmanial drugs.
-
Key words: Leishmania tarentolae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, leishmaniasis, antimicrobial peptide, REDLK
Leishmaniasis is a vector-borne disease caused by protozoan parasites, genus
Leishmania [
1]. There are over 2 million new cases of leishmaniasis per year, with approximately 400 million people at risk worldwide. It is also one of the most prevalent causes of death and animal morbidity in endemic area of underdeveloped countries [
2,
3]. Leishmaniasis has different clinical manifestations, including cutaneous, mucocutaneous, diffuse cutaneous, viscera and post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis [
4,
5]. No effective vaccine against leishmaniasis is available and treatments drugs including pentavalent antimonials, amphoteric B, miltefosine and paromomycin, priced, have toxic side effects. Moreover, drug resistance to current treatments has been emerging [
6,
7]. Therefore, there is an urgent need for developing a safe, effective, and affordable drugs or vaccine to treat with leishmaniasis.
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are generally considered as positively charged small peptides, comprising about 12–50 amino acids. They have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions, which make them soluble in aqueous environments, facilitating their interaction with biological membranes [
8,
9]. The therapeutic potential of AMPs, produced by a wide variety of organisms ranging from bacteria to animals, is enhanced owing to the ability of these compounds to rapidly kill a large number of micro-organisms [
10]. Previous studies were detected various types of AMPs with different structures, including defensin, cecropins, magainins, and cathelicidins. Many AMPs present broad activities against pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites [
11]. The confirmed mechanisms of AMPs include the disruption of microbial cellular membranes, modulation of the innate and adaptive immunity [
12].
Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE) is a protein toxin that consists of 3 functional domains, including the receptor binding domain I, the translocation domain II, and the enzymatic domain III. The receptor binding domain can be genetically modified to create an immunotoxin by replacing the binding domain with antibodies specific for various cancers, leading to the killing of target cells by inhibition of protein synthesis via ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 and induction of apoptosis. Additionally, PE has certain toxicity to prokaryotic cells due to the slow growth of
Escherichia coli expressing the recombinant immunotoxin [
13,
14]. Mutation analysis of the C-terminus of PE has demonstrated that the last amino acids (positions 609–613) in REDLK are crucial to its cytotoxic activity but unrelated to the ADP-ribosylation activity [
15]. Therefore, we were prompted to synthesize the short peptide REDLK, a 5-amino acid peptide composed of arginine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, leucine and lysine, to evaluate its bioactivities as an AMP.
In this study, we used non-pathogenic Leishmania tarentolae (L. tarentolae), a parasite isolated from the gecko Tarentolae annularis, as an in vitro model for evaluation of the specific leishmanicidal activity of REDLK. Anti-microbial peptide, REDLK derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a promising candidate as a novel antimicrobial peptide REDLK against Leishmania tarentolae and lay a foundation for further research on studying anti-leishmanial drugs.
The UC strain of
Leishmania tarentolae (ATCC PRA-229, USA) promastigote conserved by our laboratory was cultured in BHI medium supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin and 5 μg/ml hemin (Sigma, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) at 26°C. GFP-transfected
Leishmania tarentolae was constructed using
Leishmania expression vector pLEXSY-neo2 (Jena Bioscience, Thuringia, Germany), as previously described [
16]. The GFP expression cassette was integrated into the chromosomal ssu locus of
Leishmania tarentolae via homologous recombination. GFP can be stably expressed in promastigote.
REDLK is a 5-amino acid peptide (REDLK, mass: 659.36 Da). It was synthesized using standard Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis strategy on a Symphony XTM Multiplex Synthesizer (Rainin, Woburn, Massachusetts, USA). Fmoc was used for the Nα protecting group and acid-labile tert-butyl-based groups were used for side chain protection. Both auxiliary nucleophile and in situ coupling reagent were used to facilitate the peptide bond formation [
17]. Then, REDLK was purified by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) and confirmed by mass spectroscopy (
Supplementary Fig. S1) and amino acid analysis. Purified peptides were lyophilized and re-suspended in sterile PBS at a concentration of 1 mg/ml and stored at 4°C until use.
The viability of REDLK-treated
Leishmania tarentolae was assessed using 3-(4, 5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT; Sigma–Aldrich, St. Louis, Missouri, USA), as previously described [
18]. Briefly, promastigotes were seeded at 3×10
6 cells per well into a 96-well flat-bottom microtiter plate and exposed to 12.5 μg/ml, 25 μg/ml, and 50 μg/ml REDLK at 26°C for 72 hr. PBS was used as the control. The plate was centrifuged at 3,500 rpm for 15 min, re-suspended in 100 μl fresh medium, and treated with 10 μL of 5 mg/ml MTT at 26°C for 4 hr. Each group was repeated 3 times. Absorbance was read at 570 nm to determine the amount of formazan production, which correlates with relative cell viability. Values were normalized by the untreated control. Cell viability (%)=A
570 nm of treated cells/ A
570 nm of control×100.
Parasites were seeded into a 96-well flat-bottom microtiter plate at 5×106/well in the presence of 12.5 μg/ml, 25 μg/ml, 50 μg/ml REDLK or PBS as a control. Reactions were performed in triplicate wells per concentration. After 72 hr, viable parasite counts were determined using a hemocytometer following trypan blue dye.
L. tarentolae promastigotes were treated with different concentrations (12.5 μg/ml, 25 μg/ml, and 50 μg/ml) of REDLK or PBS at 26°C for 72 hr. For light microscopy, 10 μl of each sample was loaded onto a glass slide, fixed with methanol, and stained with Giemsa for 2 hr. For electron microscopy, the ultrathin sections were prepared as previously described [
19] and observed using a transmission electron microscope (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan).
After
L. tarentolae promastigotes were treated with different concentrations of REDLK, the apoptotic cells were identified using the Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis Detection Kit (KeyGen, Nanjing, China) and a mitochondrial membrane potential assay kit (JC-1) (Beyotime, Jiangsu, China), according to the manufacturer’s protocols [
20]. JC-1, a lipophilic dye, which forms aggregates in mitochondrial matrix and emits red fluorescence at 585 nm in normal cells. However, when mitochondrial membrane potential collapses, JC-1 de-aggregates as monomers and emits green fluorescence at 514 nm. Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone (CCCP), which can cause quick mitochondrial membrane depolarization, was used as the positive control [
21].
L. tarentolae promastigotes were cultured in BHI media with 12.5 μg/ml, 25 μg/ml, and 50 μg/ml REDLK or PBS for 72 hr. The cells were stained with JC-1 dye. Flow cytometry analysis was performed in a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (BD Bioscience, San Jose, California, USA), and the data were analyzed using BD CellQuest Pro software.
Differences between the experimental group and control group were determined using a Student’s t test. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for multiple group comparisons. P-values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
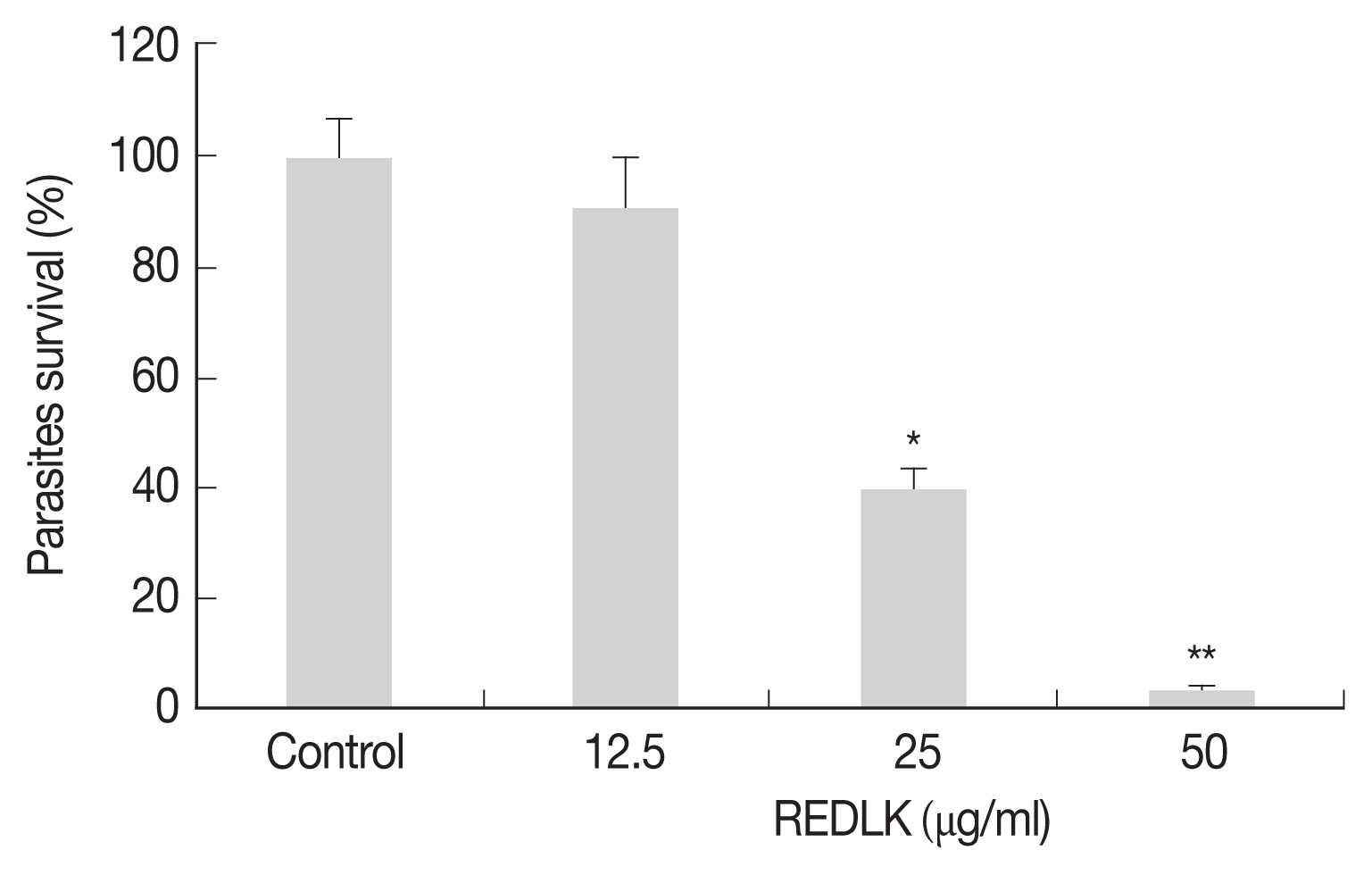
The cell viability was determined by Trypan blue dye test and measuring the reduction of substrate MTT. REDLK inhibited the growth of
Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes by 3.2%, 39.5%, and 90.7% at the concentrations of 12.5 μg/ml, 25 μg/ml, and 50 μg/ml, respectively after 72 hr treatment (
Fig. 1). MTT viability assay also produced similar results (
Supplementary Fig. S2).
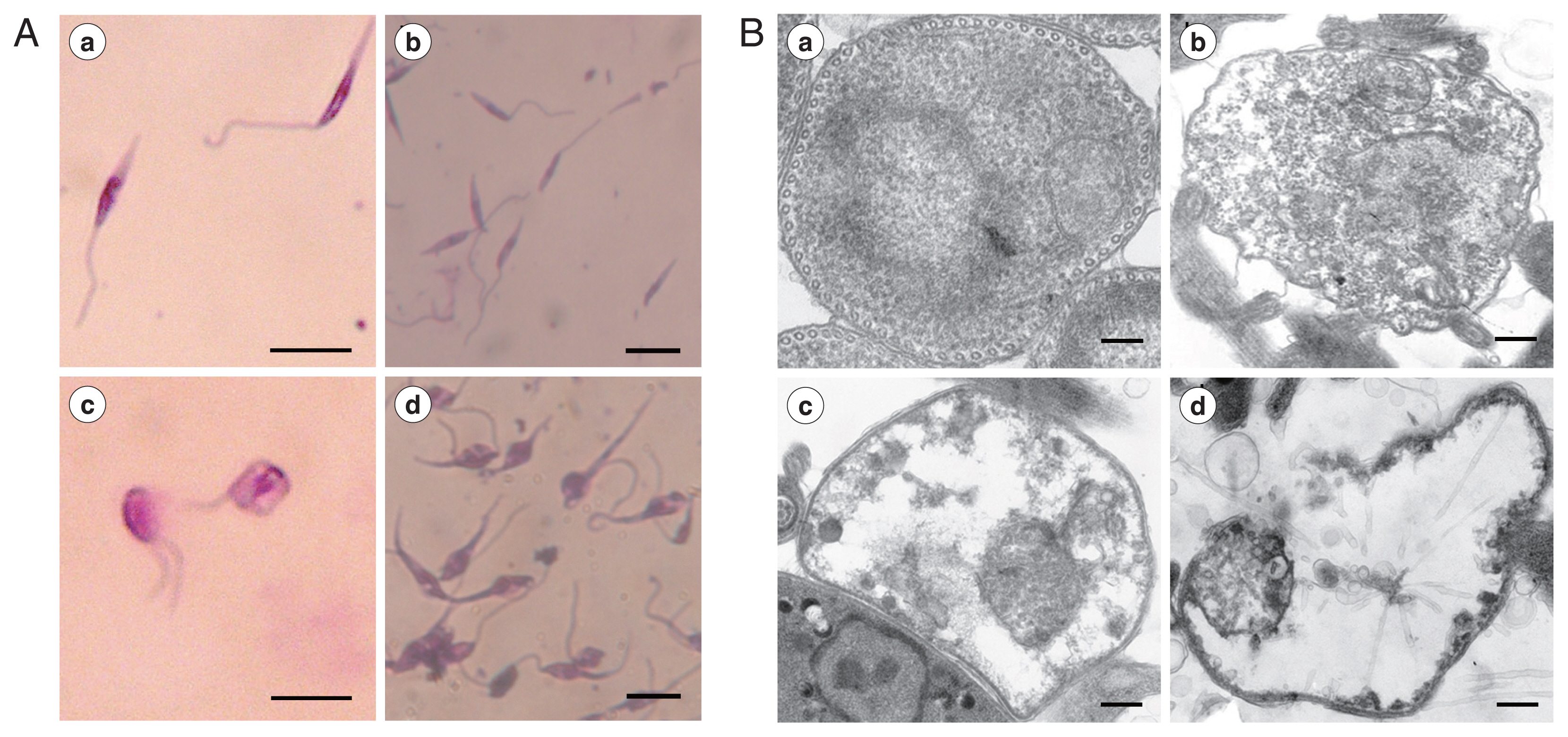
Microscopic observation showed that REDLK can cause dramatic changes in the structural integrity of the parasite. Untreated promastigotes presented thin, elongated cells with a unipolar flagellum and a clearly visible nucleus and kinetoplast (
Fig. 2Aa, b). However, REDLK-treated promastigotes exhibited rounding and swelling of cell bodies, with clear disruption of the cellular membrane accompanied by release of cytoplasmic contents into the medium. After 72 hr of exposure, nearly all of the treated promastigotes had lost their elongated form and appeared in various states of disintegration. High levels of amorphous staining were likely due to release by cellular material (
Fig. 2Ac, d).
Transmission electron microscopy of AMP-treated parasites revealed cytoplasm blebbing, a severe disruption of the membrane structure and near complete loss of electron dense cytoplasmatic components (
Fig. 2B).
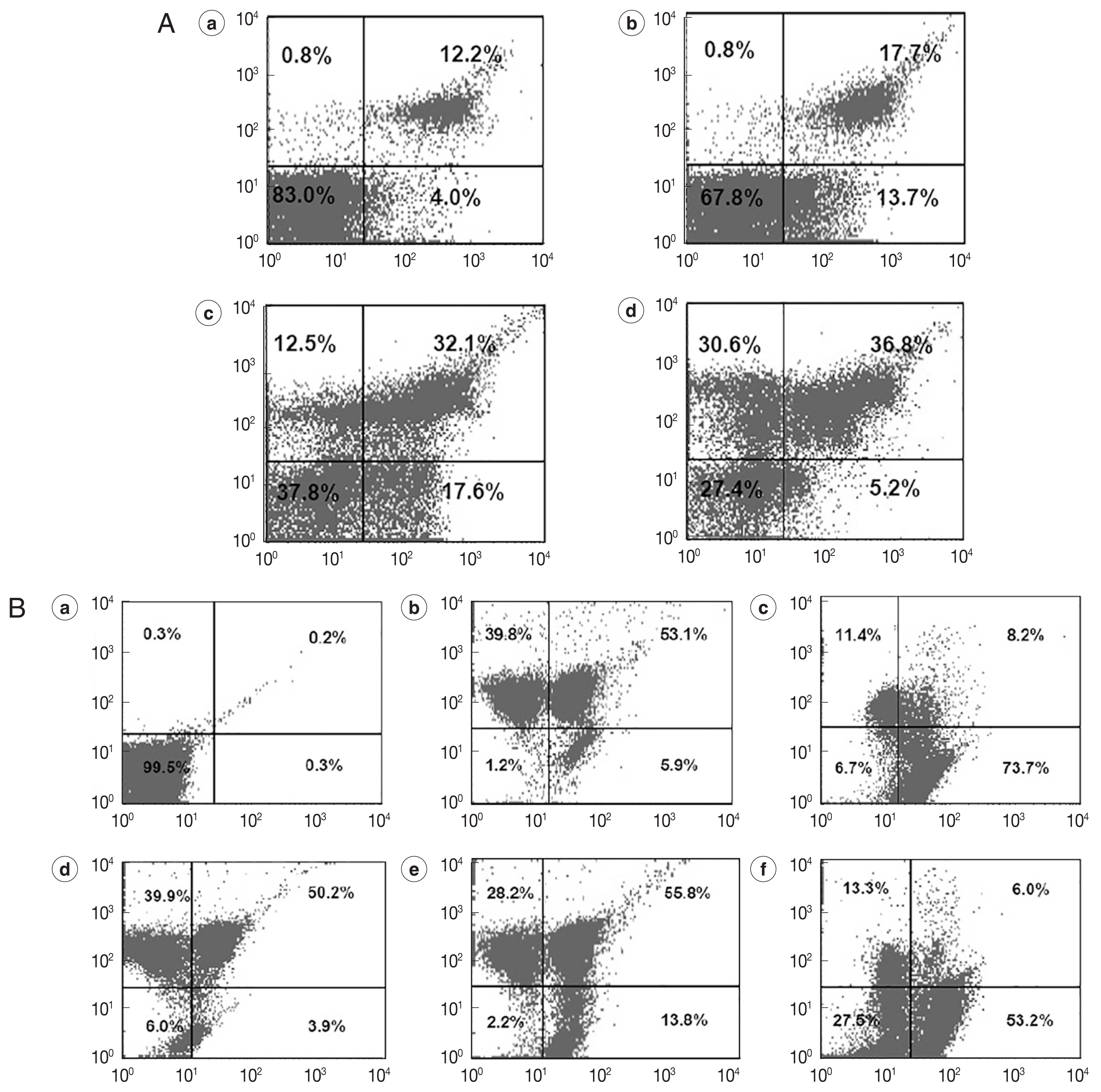
We co-stained REDLK-treated promastigotes with Annexin V-FITC, which is a Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding protein with an affinity for PS, and propidium iodide (PI). PI can permeate the protozoa and bind to cellular DNA only if a loss of plasma membrane integrity occurs at the same time as necrosis or late-stage apoptosis.
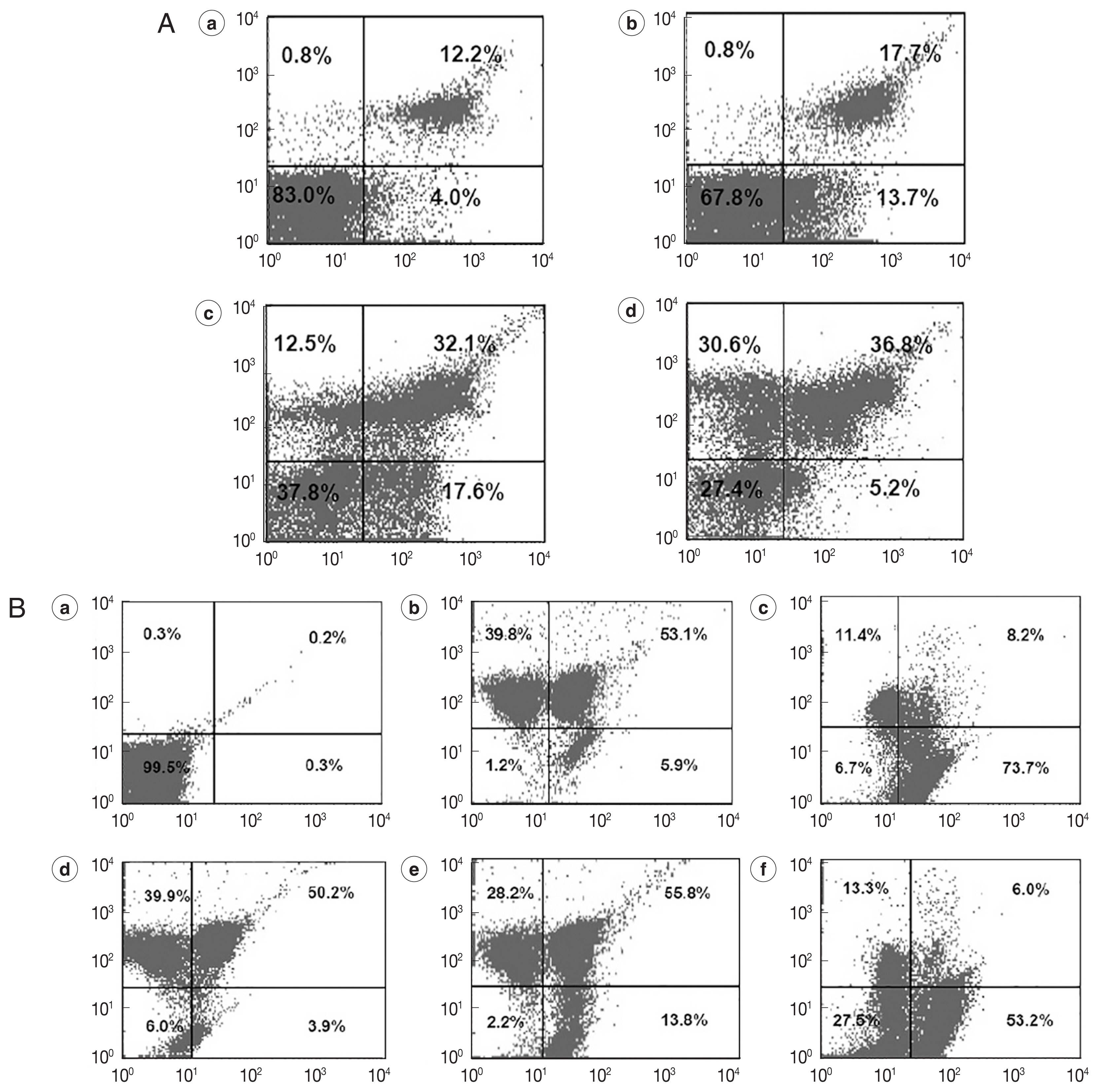
On flow cytometer, the number of parasites staining positive for PI, but negative for Annexin V (upper left quadrant), was significantly increased following exposure to 25 μg/ml and 50 μg/ml REDLK, compared to 12.5 μg/ml REDLK (
Fig. 3A), showing that the peptide induced late-stage apoptosis or necrosis of the parasite is dose-dependent. The peptide also induced early-stage apoptosis (lower right quadrant). However, when exposure to REDLK was increased to 50 μg/ml, the number of parasites during early-stage apoptosis was decreased as parasites transitioned from early-stage apoptosis to late-stage apoptosis (
Fig. 3A). These results demonstrate that REDLK has distinct effects on promastigotes in terms of membrane permeability and PS accessibility.
The loss of mitochondrial membrane potential is a key indicator for the initiation of programmed cell death. After exposure to different concentrations of REDLK, JC-1-stained parasites led to a decrease in red fluorescence intensity (upper left quadrant) and increase in green fluorescence intensity (lower right quadrant), compared to untreated parasites. These results suggest that REDLK can induce a loss of membrane electrochemical gradient in the mitochondria (
Fig. 3B).
Protozoan parasites of
Leishmania parasites belong to the genus
Leishmania and family Trypanosomatidae. They have a single flagellum and a characteristic mitochondrial DNA-containing organelle. Infected female
Phlebotomus sp., sandflies bites vertebate host and could spread
Leishmania parasites to vertebrate hosts by bites. The promastigote flagellar form is found in the gut of the sandfly vector [
22,
23].
Leishmania tarentolae is a suitable model for the screening of potential anti-leishmanial drugs in vitro, based on the following considerations: (i) More than 90% of the
Leishmania tarentolae genes are shared with the other pathogenic
Leishmania species [
24]; (ii)
Leishmania tarentolae do not induce clinical symptoms of leishmaniasis in mammalian animals and is therefore safe for humans. Importantly,
Leishmania tarentolae present similar sensitivity to pentavalent antimony, amphotericin B, miltefosine and paromomycin as other
Leishmania species that are pathogenic in humans [
6,
25]. The availability of non-pathogenic species,
L. tarentolae provides us with a resource to do the preliminary in vitro evaluation of novel anti-leishmanial drugs.
AMPs are novel therapeutic agents that range from 12 to 50 amino acids in length. As potent, broad spectrum antibiotics in all living organisms, AMPs permeabilized membranes and modulation of the host immune responses [
26]. In addition, several amphibian AMPs, such as magainin, temporin, dermaseptin, bombinin, and cecropin-melittin hybrid peptide, mammalian AMPs, including histatin-5, BMAP-28 and CM11, DRS 01 possess significant anti-leishmanial activity against intracellular amastigotes and extracellular promastigotes [
27–
29]. The REDLK peptide could inhibit the growth of promastigote by 3.2%, 39.5%, and 90.7% at the concentrations of 12.5 μg/ml, 25 μg/ml, and 50 μg/ml, respectively. In previous report, we observed
leishmanicidal effect of KDEL that extracted from
Pseudomonad exotoxin. The growth inhibition effect of REDLK displayed significantly remarkable than that of KDEL peptide, which shares 10.4% and 33.3% growth inhibition at the concentrations of 25 μg/ml and 50 μg/ml, respectively [
30].
REDLK presented potent leishmanicidal activity against
Leishmania tarentolae in a dose-dependent manner. In all
Leishmania species, the surface of promastigotes is surrounded by glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins and metalloproteinase GP63. GP63 knockout mutants are more susceptible to some types of AMPs and undergoes cellular apoptosis more readily than wild-type parasites [
31,
32]. GP63 is inhibited in
Leishmania tarentolae, which decreases the prevention ability of the peptide activity.
There are at least 2 major mechanisms responsible for AMP-mediated antimicrobial effects, including apoptotic and non-apoptotic mechanisms [
33]. In this study, the number of parasites positive for PI, but negative for Annexin V, was significantly increased following exposure to 25 μg/ml and 50 μg/ml REDLK, compared to 12.5 μg/ml, suggesting that late-stage apoptosis of parasites induced by REDLK is dose-dependent. REDLK can cause significant disruption of membrane integrity in
Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes and ultimately result in osmotic instability, vacuolar swelling, loss of cytosolic contents, and eventual cell death. REDLK-treated parasites presented positive for PI, but negative for Annexin V, which resembled typical early apoptotic stage in which PS exposure occurred, but the membrane was not permeable. The early apoptosis in promastigotes was also confirmed by depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potentials.
In the present study, we demonstrated the leishmanicidal activity of a short peptide REDLK from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. REDLK induced apoptosis of L. tarentolate promastigote and resulted in parasite death.
In summary, we evaluated the synthetic 5-amino acid peptide REDLK derived from from Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a novel anti-leishmanial agent against Leishmania tarentolae. The action mechanisms of the peptide against Leishmania tarentolae involve disruption of surface membrane integrity and cellular apoptosis. Our results provide the basis for further research on studying anti-leishmanial drugs.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No conflict of interest exists in this work, and the manuscript was approved by all authors for publication. The work described is original research has not been published previously.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was, partly, supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 31672288, 31302076, 31001057), National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (grant number 2012ZX09103301-021), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2014M552636), and the technological innovation and entrepreneurship projects of people returned oversea in Jilin province of China (2012).
The authors thank Professor Xiaohuan Zou Institute of Military Veterinary, Academy of Military Medical Sciences for providing technical supports of transmission electron microscope.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Table S2.
Assessment of REDLK-mediated Leishmania tarentolae using MTT. Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes were incubated with different concentrations of REDLK at 26°C for 72 hr. The promastigotes were determined using MTT and absorbance was read at 570 nm. Each bar represents the mean of 4 replicates; Error bar represents standard error of the mean.
Fig. 1REDLK-mediated killing effect on Leishmania tarentolae. Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes were incubated with different concentrations of REDLK at 26°C for 72 hr. The promastigotes were counted using a hemocytometer after trypan blue dye. The promastigotes were susceptible to REDLK in a dose-dependent manner. Each column represents a mean of 4 replicates. Error bar represents mean±SE. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
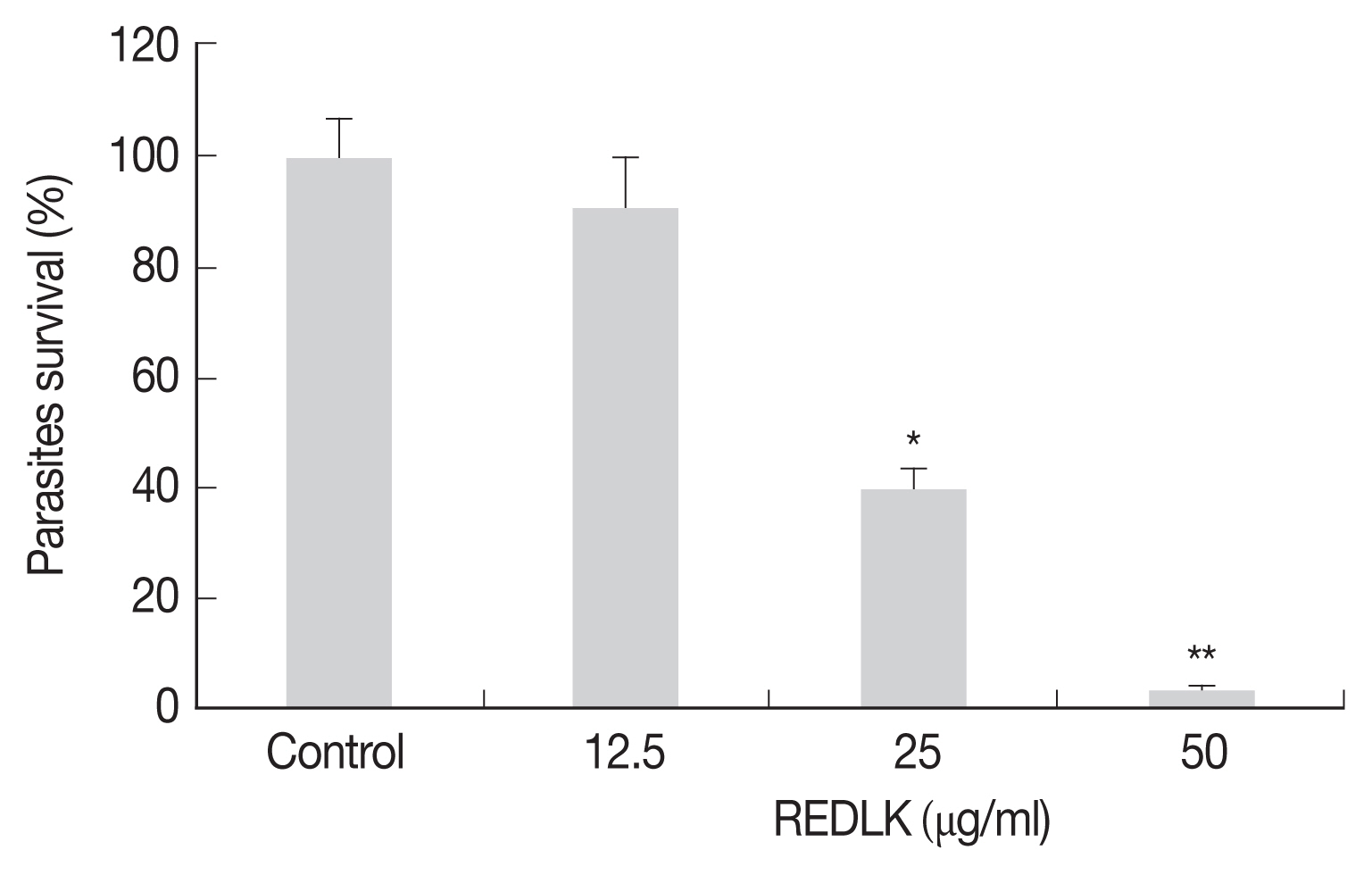
Fig. 2Morphologic changes of Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes induced with REDLK. (A) Optical microsgraphs of REDLK-treated Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes. Untreated (a, b) or REDLK-treated (c, d) Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes were Giemsa-stained after 72 hr exposure to 50 μg/ml peptide REDLK. Scale bar=10 μm. (B) Transmission electron micrographs of REDLK-treated Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes. Parasites were cultured in media with PBS (a), 12.5 μg/ml (b), 25 μg/ml (c), or 50 μg/ml (d) REDLK for 72 hr. Membrane disruption, cytoplasm blebbing, and membrane breakages and depletion of electron-dense cytoplasmic material are observed. Scale bar=1 μm.
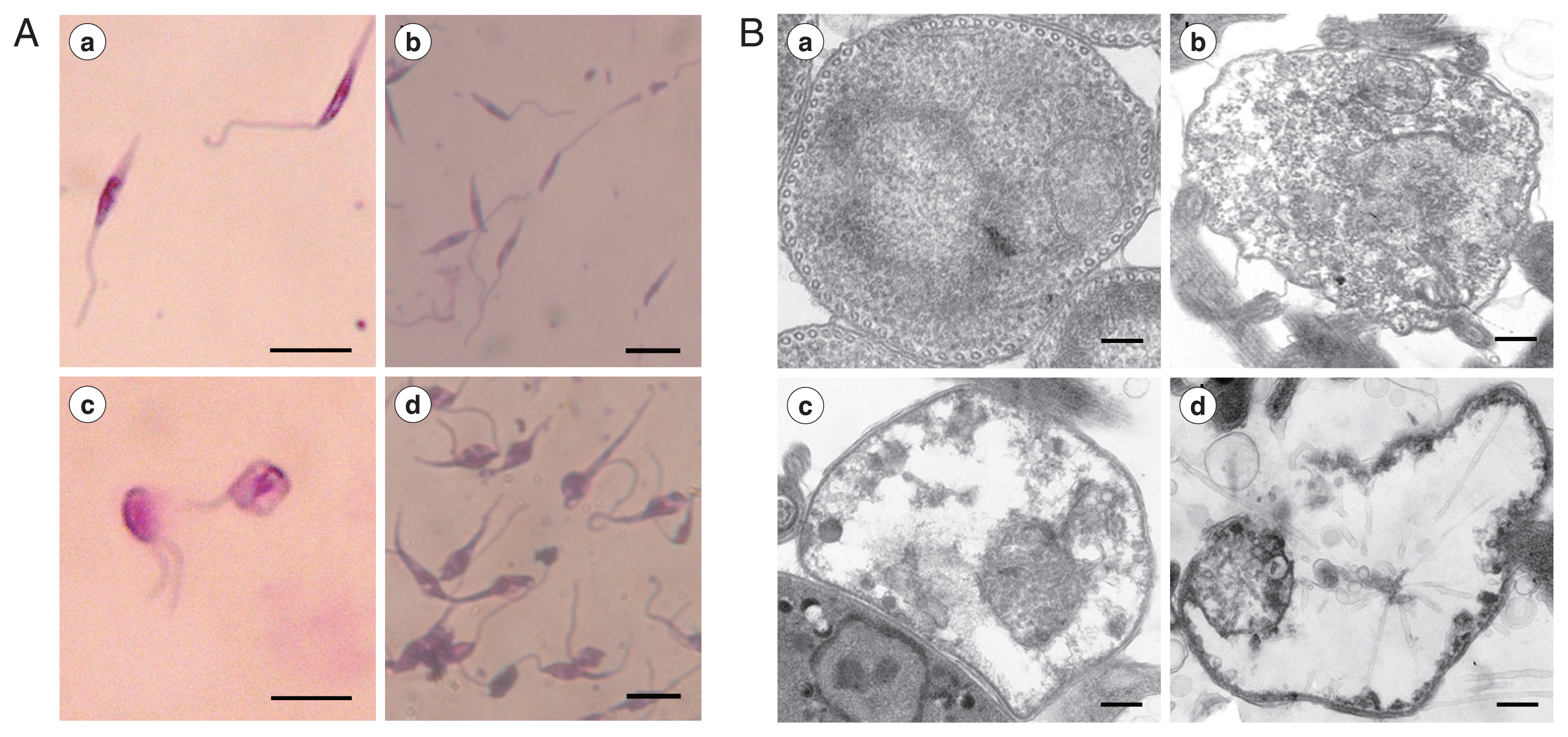
Fig. 3Cellular apoptosis of REDLK-treated Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes. (A) Cellular membrane permeability and phosphatidylserine exposure induced by REDLK in Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes. Parasites were cultured in media with PBS (a), 12.5 μg/ml (b), 25 μg/ml (c), or 50 μg/ml (d) REDLK for 72 hr. The cells were stained with Annexin V-FITC and PI and analyzed by flow cytometer. The results are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. (B) Depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane induced by REDLK. (a) Untreated promastigotes not stained with JC-1. (b) Untreated promastigotes stained with JC-1. (c) CCCP-treated promastigotes stained with JC-1. (d, e, and f) Promastigotes were treated with 12.5 μg/ml, 25 μg/ml, and 50 μg/ml REDLK and stained with Annexin V-FITC and PI. The results are representative of at least 3 independent experiments.
References
- 1. Desjeux P. Leishmaniasis: current situation and new perspectives. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 2014;27:305-318.
- 2. Castillo-Ureta H, Zazueta-Moreno JM, Rendón-Maldonado JG, Torres-Avendaño JI, López-Moreno HS, Olimón-Andalón V, Salomón-Soto VM, Pérez-Sánchez FP, Torres-Montoya EH. First report of autochthonous canine leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania (L.) mexicana in Sinaloa, Mexico. Acta Trop 2018;190:253-256.
- 3. Çizmeci Z, Karakuşb M, Karabelac SN, Erdoğand B, Güleça N. Leishmaniasis in Istanbul: A new epidemiological data about refugee leishmaniasis. Acta Trop 2019;195:23-27.
- 4. Aronson NE, Joya CA. Cutaneous leishmaniasis updates in diagnosis and management. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2019;33:101-117.
- 5. Griensven J, Diro E. Visceral leishmaniasis: recent advances in diagnostics and treatment regimens. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2019;33:79-99.
- 6. Kapil S, Singh PK, Silakari O. An update on small molecule strategies targeting leisghmaniasis. Eur J Med Chem 2018;157:339-367.
- 7. Marty P, Rosenthal E. Treatment of visceral leishmaniasis: a review of current treatment practices. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2002;3:1101-1108.
- 8. AlMatar M, Makky EA, Yakıcı G, Var I, Kayar B, Köksal F. Antimicrobial peptides as an alternative to anti-tuberculosis drugs. Pharmacol Res 2017;128:288-305.
- 9. Ebenhan T, Gheysens O, Kruger HG, Zeevaart JR, Sathekge MM. Antimicrobial peptides: their role as infection-selective tracers for molecular imaging. Biomed Res Int 2014;867381.
- 10. Lynn MA, Kindrachuk J, Marr AK, Jenssen H, Pante N, Elliott MR, Napper E, Hancock RR, Master WRM. Effect of BMAP-28 antimicrobial peptides on Leishmania major promastigote and amastigote growth: role of leishmanolysin in parasite survival. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2011;5:e1141.
- 11. Aguilar-Diaz H, Canizalez-Roman A, Nepomuceno-Mejia T, Gallardo-Vera F, Hornelas-Orozco Y, Nazmi K, Bolscher JG, Carrero JC, Leon-Sicairos C, Leon-Sicairos N. Parasiticidal effect of synthetic bovine lactoferrin peptides on the enteric parasite Giardia intestinalis. Biochem Cell Biol 2017;95:82-90.
- 12. Cederlund A, Gudmundsson GH, Agerberth B. Antimicrobial peptides important in innate immunity. FEBS J 2011;278:3942-3951.
- 13. Müller F, Cunningham T, Beers R, Bera TK, Wayne AS, Pastan I. Domain II of Pseudomonas exotoxin is critical for efficacy of bolus doses in a xenograft model of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Toxins 2018;10:E210.
- 14. Qaiser H, Aslam F, Iftikhar S, Farooq A. Construction and recombinant expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa truncated exotoxin A in Escherichia coli
. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2018;64:64-69.
- 15. Chaudhary VK, Jinno Y, Gallo MG, FitzGerald D, Pastan I. Mutagenesis of Pseudomonas exotoxin in identification of sequences responsible for the animal toxicity. J Biol Chem 1990;265:16306-16310.
- 16. Bolhassani A, Taheri T, Taslimi Y, Zamanilui S, Zahedifard F, Seyed N, Torkashvand F, Vaziri B, Rafati S. Fluorescent Leishmania species: development of stable GFP expression and its application for in vitro and in vivo studies. Exp Parasitol 2011;127:637-645.
- 17. Hansen PR, Oddo A. Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis. Methods Mol Biol 2015;1348:33-50.
- 18. Kiderlen AF, Kaye PM. A modified colorimetric assay of macrophage activation for intracellular cytotoxicity against Leishmania parasites. J Immunol Methods 1990;127:11-18.
- 19. McGwire BS, Olson CL, Tack BF, Engman DM. Killing of African trypanosomes by antimicrobial peptides. J Infect Dis 2003;188:146-152.
- 20. Zhang X, Liu X, Shang HF, Xu Y, Qian MZ. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 induces endothelial cell apoptosis in vitro through a p53-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2011;43:787-795.
- 21. Tang CL, Liang J, Qian JF, Jin LP, Du MR, Li MQ, Li DJ. Opposing role of JNK-p38 kinase and ERK1/2 in hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage of human trophoblast-like JEG-3 cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:959-968.
- 22. Sacks DL, Perkins PV. Identification of an infective stage of Leishmania promastigotes. Science 1984;223:1417-1419.
- 23. de Sousa APS, de Oliveira SSC, d’Avila-Levy CM, Dos Santos ALS, Branquinha MH. Susceptibility of promastigotes and intracellular amastigotes from distinct Leishmania species to the calpain inhibitor MDL28170. Parasitol Res 2018;117:2085-2094.
- 24. Raymond F, Boisvert S, Roy G, Ritt JF, Légaré D, Isnard A, Stanke M, Olivier M, Tremblay MJ, Papadopoulou B, Ouellette M, Corbeil J. Genome sequencing of the lizard parasite Leishmania tarentolae reveals loss of genes associated to the intracellular stage of human pathogenic species. Nucleic Acids Res 2012;40:1131-1147.
- 25. Taylor VM, Munoz DL, Cedeno DL, Velez ID, Jones MA, Robledo SM.
Leishmania tarentolae: utility as an in vitro model for screening of antileishmanial agents. Exp Parasitol 2010;126:471-475.
- 26. Lohner K, Blondelle SE. Molecular mechanisms of membrane perturbation by antimicrobial peptides and the use of biophysical studies in the design of novel peptide antibiotics. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 2005;8:241-256.
- 27. Eaton P, Bittencourt CR BSc, Silva VC, VérasMSc LMC, Costa CHN, Feio MJ, Leite JRSA. Anti-leishmanial activity of the antimicrobial peptide DRS 01 observed in Leishmania infantum (syn. Leishmania chagasi) cells. Nanomedicine 2014;10:483-490.
- 28. khalili S, Ebrahimzade E, Mohebali M, Shayan P, Mohammadi-Yeganeh S, Moghaddam MM, Elikaee S, Akhoundi B, Sharifi-Yazdi MK. Investigation of the antimicrobial activity of a short cationic peptide against promastigote and amastigote forms of Leishmania major (MHRO/IR/75/ER): an in vitro study. Exp Parasitol 2019;196:48-54.
- 29. Torrent M, Pulido D, Rivas L, Andreu D. Antimicrobial peptide action on parasites. Curr Drug Targets 2012;13:1138-1147.
- 30. Lili C, Weina J, Songgao C, Panpan Z, Juan L, Hang D, Yanbing G, Quan L, Pengtao G. In vitro leishmanicidal activity of antimicrobial peptide KDEL against Leishmania tarentolae
. Acta Bioch Bioph Sin 2019;51:1286-1292.
- 31. Hassani K, Shio MT, Martel C, Faubert D, Olivier M. Absence of metalloprotease GP63 alters the protein content of Leishmania exosomes. PLoS One 2014;9:e95007.
- 32. Parashar S, Mukhopadhyay A. GTPase Sar1 regulates the trafficking and secretion of the virulence factor gp63 in Leishmania
. J Biol Chem 2017;292:12111-12125.
- 33. Risso A, Braidot E, Sordano MC. BMAP-28, an antibiotic peptide of innate immunity, induces cell death through opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Mol Cell Biol 2002;22:1926-1935.
- 34. Arayan LT, Kim HB, Reyes AWB, Huy NTX, Hong IH, Lee K, Yeom J, Park Y, Kim S. The immunomodulatory effect of antimicrobial peptide HPA3P restricts Brucella abortus 544 infection in BALB/c mice. Vet Microbiol 2018;225:17-24.
- 35. Bowdish DM, Davidson DJ, Scott MG, Hancock RE. Immunomodulatory activities of small host defense peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005;49:1727-1732.