Abstract
Blastocystis has recently been recognized as the most common eukaryotic microbe of the human gut. We investigated the prevalence of Blastocystis and their subtypes in diarrheal and non-diarrheal groups and the associated clinical parameters. A total of 324 stool samples were obtained from 196 diarrheal and 128 non-diarrheal subjects. Blastocystis subtypes were determined by sequencing the small subunit ribosomal DNA (SSU rRNA) gene. Demographic, clinical and laboratory data were collected and analyzed by diarrhea and Blastocystis status. The overall rate of Blastocystis positivity was 9.0% (29/324) but was significantly higher in the non-diarrheal group (18.0% vs. 3.1%, P<0.0001). Of the 6 Blastocystis-positive diarrheal patients, 3 (50.0%), none (0.0%), 2 (33.3%), and 1 (16.7%) were infected with subtypes ST1, ST2, ST3, and multiple subtypes, respectively. Of the 23 Blastocystis-positive non-diarrheal patients, 4 (17.4%), 1 (4.3%), and 18 (78.3%) were infected with subtypes ST1, ST2, and ST3, respectively. Blastocystis was less common in the diarrheal than the non-diarrheal group (odds ratio, 0.144; 95% confidence interval, 0.057–0.365, P<0.001). Of the 3 subtypes, ST3 was more frequently observed in the non-diarrheal than diarrheal group (78.3% vs. 33.3%, P=0.0341). Collectively, Blastocystis was found in both the diarrheal and non-diarrheal groups and ST3 was the most common subtype in Korea.
-
Key words: Blastocystis, subtype, diarrhea, Korea
Blastocystis has recently been recognized as the most prevalent eukaryotic microbe in the human gut [
1], occurring worldwide in both healthy and symptomatic humans and other animals.
Blastocystis is thought to be transmitted via the fecal–oral route and in cyst form [
2]. Recently, PCR-based approaches using feces directly or after culture of fecal specimens have been widely used to diagnose
Blastocystis infection [
3]. Based on small subunit ribosomal DNA (SSU rRNA) gene analysis, this genus comprises at least 17 subtypes (STs) [
4]. In human, ST1–ST4 probably account for more than 90% of carriage; the other subtypes are ST5–ST9 [
5]. Although
Blastocystis is of great scientific interest, neither its biology nor pathophysiology has been well-explored. Since no direct evidence indicates that
Blastocystis causes diarrhea, this point also remains controversial. Only 3 Korean studies on
Blastocystis have been published [
6–
8], all in animals. Here, we investigated the prevalence of
Blastocystis and its subtypes, and the associated clinical parameters, in diarrheal and asymptomatic Korean groups.
A total of 324 stool samples were obtained from 196 diarrheal and 128 non-diarrheal subjects who underwent general checkups at Chonnam National University Hospital and Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, from February 2016 to October 2018. Fecal samples were collected in accordance with the guidelines of, and with the approval of, the Institutional Review Board of Chonnam National University Hospital (approval no. IRB CNUH-2015-052). We recorded age, sex, white blood cell count (WBC,×10
3/μl), and differential counts, red blood cell count (RBC,×10
6/μl), hemoglobin (Hgb, g/dl), platelet count (PLT), total protein (g/dl), albumin (g/dl), alkaline phosphatase (U/L), AST (U/L), ALT (U/L), BUN (mg/dl), creatinine (mg/dl), lactate dehydrogenase (U/L), CRP (mg/dl), and stool occult blood test data. If necessary, stool culture or multiplex PCR panel evaluation was scheduled to determine pathogens causative of diarrhea. Laboratory findings and stool culture data were analyzed by diarrhea and
Blastocystis status. DNA was extracted using the Cica Geneus® DNA Prep Kit (Kanto Chemical, Tokyo, Japan) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Blastocystis was detected based on the SSU rRNA gene using the Blast-505–532 (5′–GGA GGT AGT GAC AAT AAA TC–3′) and Blast-998–1017 (5′–TGC TTT CGC ACT TGT TCA TC–3′) primers [
9]. Each tube contained 8.5 μl PCR primer solution (1 μl each of Blast-505–532 and Blast-998–1017 (each 25 pmol)), 36.5 μl distilled water, and 5 μl template DNA. All PCR amplifications were performed using the TaKaRa PCR Thermal Cycler Dice Gradient (TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan). Initial denaturation at 94°C for 3 min was followed by 30 cycles of 59°C for 30 sec and 72°C for 60 sec, and a final extension at 72°C for 5 min. The PCR products were analyzed by 1.5% (w/v) agarose gel electrophoresis with ethidium bromide staining and then sent to Macrogen (Seoul, Korea) for direct DNA sequencing. Phylogenetic analysis was performed by reference to database
Blastocystis SSU rRNA genes, and a phylogenetic tree was constructed using Geneious Prime (Biomatters Ltd, Auckland, New Zealand). Phylogenetic inferences were derived using a pair-group method featuring arithmetic average clustering with 1,000 bootstrap replications. Student’s t-test was used to compare continuous variables (age and laboratory parameters). The chi-squared or Fisher’s exact test was employed to determine the distributions of categorical variables (sex and the statuses of stool occult blood, diarrhea, and
Blastocystis). The likelihood-ratio chi-squared test was employed to calculate odds ratios (ORs) for
Blastocystis positivity by subtype. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS ver. 25.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA). A
P-value <0.05 was considered to indicate significance.
Of the 324 samples, 29 (9.0%) including 6 diarrheal and 23 non-diarrheal samples were positive for
Blastocystis, with a significant difference between the 2 groups (
P<0.001) (
Table 1). Thus,
Blastocystis may not necessarily cause diarrhea.
Blastocystis has previously been found in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients [
10–
12]. It has been suggested that intra-subtype variation at the SSU rRNA gene level might affect the presenting symptoms of patients with identical
Blastocystis subtypes [
13]. We found subtypes ST1, ST2, ST3, and multiple infections in 3 (50.0%), 0 (0.0%), 2 (33.3%), and 1 (16.7%) patient in the diarrheal group and in 4 (17.4%), 1 (4.3%), 18 (78.3%), and 0 (0.0%) patient the non-diarrheal group. Of the 3 subtypes, ST3 was more common in the non-diarrheal group (78.3 vs. 33.3%,
P=0.0341). ST1 seemed to be frequently found in diarrheal group compared to non-diarrheal group, but no statistical significance (diarrheal group vs. non-diarrheal group, 3/6 vs. 4/23,
P=0.0964). Further study may be necessary to determine potential correlation of certain subtypes and symptoms. We did not detect ST4, in agreement with previous studies suggesting that this ST was rare in Asia and the Middle East [
14,
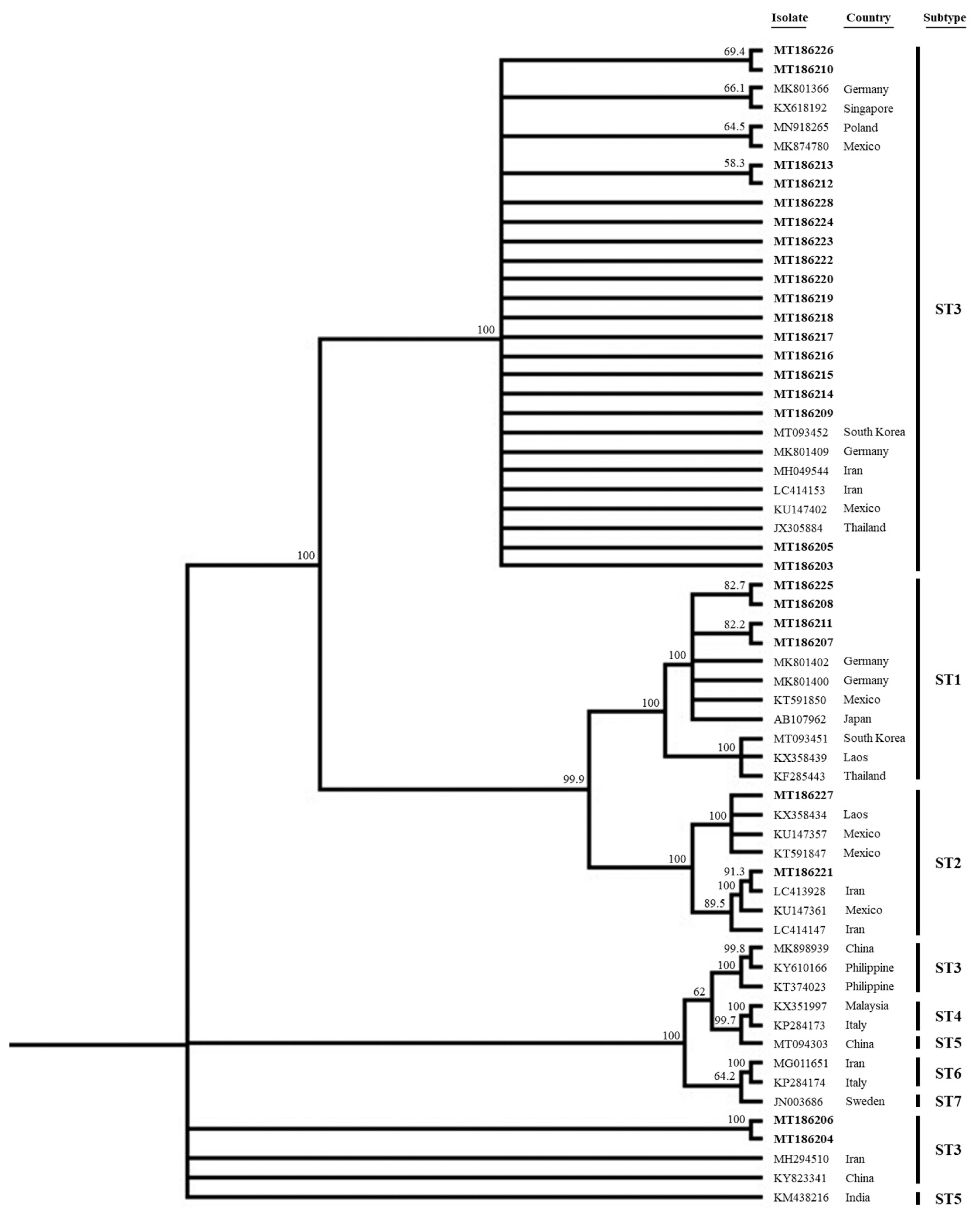
15]. When we analyzed the distribution of STs, a total of 26 sequenced samples (GenBank accession no. MT186203-MT186218 enrolled in this study) were closely related to the sequences of each known human STs (
Fig. 1). All but 2 ST3 sequences clustered together with sequences from the other countries such as Germany (MK801366, MK801409), Singapore (KX618192), Poland (MN918265), Mexico (MK874780, KU147402), South Korea (MT093452), Iran (MH049544, LC414153) and Thailand (JX305884), respectively. Notably, 2 ST3 sequences (MT186204, MT186206) from the diarrheal group were somewhat distant from the others; ST3 thus exhibited intra-genetic variation. All sequences lay distant from those of ST4 (KX351997, KP284173), ST5 (MT094303, KM438216), ST6 (MG011651, KP284174), and ST7 (JN003686), respectively. We also analyzed several laboratory parameters by
Blastocystis presence or symptoms. The white and red blood cell counts, hemoglobin level, percentages of lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils, and the levels of total protein, albumin, BUN, lactate dehydrogenase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, and C-reactive protein, and the rate of positive results on stool occult blood tests differed significantly between the diarrheal and non-diarrheal groups. However, only the creatinine level differed significantly between the
Blastocystis-positive and -negative groups (3.6 vs. 1.1 mg/dl,
P=0.001) (
Table 2). Of the 196 diarrheal patients, 54 exhibited other causative pathogens (
Clostroides difficile with or without other pathogens (23),
Campylobacter spp. with or without other pathogens (15),
Salmonella spp. (9),
Citrobacter freundii (1),
Cryptosporidium spp. (1),
Enterococcus faecalis (1), ETEC LT/ST, STEC stx1/sb2 (1), Norovirus GI/GII (1),
Giardia spp. (1) and
Shigella spp. (1)). Of the 29
Blastocystis-positive patients, all but 2 (one with
Campylobacter sp. and one with
Giardia sp.) were negative for other possibly causative pathogens. Overall, our data support the suggestion that
Blastocystis may not be pathogenic.
This is the first report of Blastocystis infections in Koreans. Blastocystis was found in both the diarrheal and non-diarrheal groups, but the subtype prevalence differed between the groups. Any role played by Blastocystis in human health and disease should be explored further.
Fig. 1Phylogenetic tree of 26 sequences of Blastocystis SSU rRNA gene compared to database Blastocystis SSU rRNA genes. All of sequences of this study were enrolled to GenBank database (GenBank accession no. MT186203-MT186218), which were indicated in bold.

Table 1Characteristic of laboratory findings according to the diarrheal symptoms
Table 1
|
Clinical parametersa
|
Laboratory characteristics of |
P-value |
|
Diarrheal group (n=196) |
Healthy control (n=128) |
|
Age (yr) |
60.8±17.78 |
62.6±11.37 |
0.318 |
|
WBC count (×103/μl) |
9±5.61 |
5.6±1.43 |
<0.001 |
|
RBC count (×106/μl) |
3.6±0.66 |
4.8±0.43 |
<0.001 |
|
Hemoglobin (g/dl) |
10.9±2.22 |
14.1±1.33 |
<0.001 |
|
Platelet count (×103/μl) |
219.6±136.82 |
252.3±54.3 |
0.13 |
|
Lymphocytes (%) |
15.8±11.27 |
34.9±8.01 |
<0.001 |
|
Monocytes (%) |
9.3±7.54 |
6.8±2.18 |
0.034 |
|
Neutrophils, (%) |
73.1±14.94 |
66.1±73.8 |
0.224 |
|
Eosinophils (%) |
1.9±2.21 |
2.8±2.69 |
0.015 |
|
Basophils (%) |
0.4±0.38 |
0.7±0.27 |
<0.001 |
|
Total protein (g/dL) |
6±0.99 |
7.5±0.48 |
<0.001 |
|
Albumin (g/dL) |
3.3±0.75 |
4.4±0.3 |
<0.001 |
|
ALP (U/L) |
114.4±134.06 |
75.7±22.59 |
0.058 |
|
AST (U/L) |
36.1±38.3 |
29±12.01 |
0.067 |
|
ALT (U/L) |
28.4±29.73 |
27.7±18.33 |
0.829 |
|
Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) |
1.2±2.11 |
0.8±0.33 |
0.348 |
|
BUN (mg/dl) |
17.6±14.35 |
12.1±4.89 |
0.011 |
|
Creatinine (mg/dl) |
1.2±3.36 |
1.3±3.51 |
0.812 |
|
Lactate dehydrogenase (U/L) |
618.9±450.65 |
141.5±94.76 |
<0.001 |
|
r-GTP (IU/L) |
109±147.21 |
31.5±28.56 |
<0.001 |
|
CRP (mg/dl) |
7.8±7.69 |
0.1±0.13 |
<0.001 |
|
Sex (male) |
116/196 (59.2) |
54/128 (42.2) |
0.003 |
|
Presence of abdominal pain No. (%) |
92/196 (46.9) |
4/128 (3.1) |
<0.001 |
|
Positive for stool occult blood No. (%) |
9/23 (39.1) |
0/86 (0.0) |
<0.001 |
|
Positive for Blastocystis, No. (%) |
6/196 (3.1) |
23/128 (18.0) |
<0.001 |
|
Blastocystis subtype No. (%) |
|
ST1 |
3/6 (50.0) |
4/23 (17.4) |
0.0964 |
|
ST2 |
0/6 (0.0) |
1/23 (4.3) |
|
|
ST3 |
2/6 (33.3) |
18/23 (78.3) |
0.0341 |
|
Multi band |
1/6 (16.7) |
0/23 (0.0) |
|
Table 2Characteristic of laboratory findings according to the presence of Blastocystis
Table 2
|
Clinical parametersa
|
Laboratory characteristics |
P-value |
|
Blastocystis-negative (n=295) |
Blastocystis-positive (n=29) |
|
Age (yr) |
61.4±15.94 |
62.6±11.48 |
0.692 |
|
WBC count (×103/μl) |
8.5±5.29 |
6.5±4.75 |
0.234 |
|
RBC count (×106/μl) |
3.8±0.76 |
4.1±0.9 |
0.301 |
|
Hemoglobin (g/dl) |
11.9±2.48 |
12.7±2.2 |
0.147 |
|
Platelet count (×103/μl) |
226.6±128.34 |
197.7±82.64 |
0.482 |
|
Lymphocytes (%) |
19.1±13.11 |
23.9±11.13 |
0.254 |
|
Monocytes (%) |
8.8±6.99 |
8.9±5.8 |
0.965 |
|
Neutrophils (%) |
72.1±34.9 |
64.4±13.94 |
0.488 |
|
Eosinophils (%) |
2±2.35 |
2.2±2.1 |
0.808 |
|
Basophils (%) |
0.4±0.39 |
0.5±0.38 |
0.495 |
|
Total protein (g/dl) |
6.3±1.09 |
6.5±1.07 |
0.606 |
|
Albumin (g/dl) |
3.5±0.82 |
3.9±0.56 |
0.083 |
|
ALP (U/L) |
107.5±121.95 |
64.9±14.12 |
0.357 |
|
AST (U/L) |
34.3±32.85 |
24.8±7.42 |
0.177 |
|
ALT (U/L) |
28.5±27.09 |
23.5±10.74 |
0.387 |
|
Total Bilirubin (mg/dl) |
1.1±1.93 |
0.7±0.2 |
0.515 |
|
BUN (mg/dl) |
16.7±13.25 |
13±12.89 |
0.299 |
|
Creatinine (mg/dl) |
1.1±2.82 |
3.6±7.37 |
0.001 |
|
Lactate dehydrogenase (U/L) |
499.6±446.27 |
225.9±199.58 |
0.109 |
|
r-GTP (IU/L) |
70.8±112.65 |
25.6±17.51 |
0.137 |
|
CRP (mg/dl) |
6.8±7.69 |
5.5±5.94 |
0.613 |
|
Sex male No. (%) |
159/295 (53.9) |
11/29 (37.9%) |
0.12 |
|
Presence of abdominal pain No. (%) |
93/295 (31.5) |
3/29 (10.3%) |
0.018 |
|
Positive for stool occult blood No. (%) |
9/95 (9.5) |
0/14 (0.0%) |
0.601 |
|
Positive for Diarrhea No. (%) |
190/295 (64.4) |
6/29 (20.7%) |
< 0.001 |
|
Other pathogens No. (%) |
52/295 (17.6)b
|
2/29 (6.9%)c
|
|
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and the writing of the paper.
AKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was partially supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2019R1C1C1004605; NRF-2019M3E5D1A02067953) and by the Research Grant from Korea Association of Health Promotion (2017-02; 2019-01). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Wawrzyniak I, Poirier P, Viscogliosi E, Dionigia M, Texier C, Delbac F, Alaoui HE.
Blastocystis, an unrecognized parasite: an overview of pathogenesis and diagnosis. Ther Adv Infect Dis 2013;1:167-178.
- 2. Lepczyńska M, Białkowska J, Dzika E, Piskorz-Ogórek K, Korycińska J.
Blastocystis: how do specific diets and human gut microbiota affect its development and pathogenicity? Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2017;36:1531-1540.
- 3. Stensvold CR.
Blastocystis: Genetic diversity and molecular methods for diagnosis and epidemiology. Trop Parasitol 2013;3:26-34.
- 4. Alfellani MA, Taner-Mulla D, Jacob AS, Imeede CA, Yoshikawa H, Stensvold CR, Clark CG. Genetic diversity of Blastocystis in livestock and zoo animals. Protist 2013;164:497-509.
- 5. Alfellani MA, Stensvold CR, Vidal-Lapiedra A, Onuoha ES, Fagbenro-Beyioku AF, Clark CG. Variable geographic distribution of Blastocystis subtypes and its potential implications. Acta Trop 2013;126:11-18.
- 6. Lee H, Lee SH, Seo MG, Kim HY, Kim JW, Lee YR, Kim JH, Kwon OD, Kwak D. Occurrence and genetic diversity of Blastocystis in Korean cattle. Vet Parasitol 2018;258:70-73.
- 7. Paik S, Jung BY, Lee H, Hwang MH, Han JE, Rhee MH, Kim TH, Kwon OD, Kwak D. Molecular Detection and Subtyping of Blastocystis in Korean Pigs. Korean J Parasitol 2019;57:525-529.
- 8. Lee H, Seo MG, Oem JK, Kim YS, Lee SY, Kim J, Jeong H, Jheong WH, Kim Y, Lee WJ, Kwon OD, Kwak D. Molecular Detection and Subtyping of Blastocystis Detected in Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) in South Korea. J Wildl Dis 2020.
- 9. Ramírez JD, Sánchez LV, Bautista DC, Corredor AF, Flórez AC, Stensvold CR.
Blastocystis subtypes detected in humans and animals from Colombia. Infect Genet Evol 2014;22:223-228.
- 10. Alinaghizade A, Mirjalali H, Mohebali M, Stensvold CR, Rezaeian M. Inter- and intra-subtype variation of Blastocystis subtypes isolated from diarrheic and non-diarrheic patients in Iran. Infect Genet Evol 2017;50:77-82.
- 11. Elwakil HS, Talaat RM. Genetic analysis of Blastocystis hominis isolated from symptomatic and asymptomatic human hosts in Egypt. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 2009;39:99-109.
- 12. Moosavi A, Haghighi A, Mojarad EN, Zayeri F, Alebouyeh M, Khazan H, Kazemi B, Zali MR. Genetic variability of Blastocystis sp. isolated from symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals in Iran. Parasitol Res 2012;111:2311-2315.
- 13. Tan KS, Mirza H, Teo JD, Wu B, Macary PA. Current views on the clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp. Curr Infect Dis Rep 2010;12:28-35.
- 14. Domínguez-Márquez MV, Guna R, Muñoz C, Gómez-Muñoz MT, Borrás R. High prevalence of subtype 4 among isolates of Blastocystis hominis from symptomatic patients of a health district of Valencia (Spain). Parasitol Res 2009;105:949-955.
- 15. Alinaghizade A, Mirjalali H, Mohebali M, Stensvold CR, Rezaeian M. Inter- and intra-subtype variation of Blastocystis subtypes isolated from diarrheic and non-diarrheic patients in Iran. Infect Genet Evol 2017;50:77-82.