Abstract
Strongyloidiasis is caused by Strongyloides stercoralis and is one of the most neglected tropical diseases in tropical and subtropical regions. Although several strongyloidiasis cases have been reported in Korea, genetic analysis of Korean isolates is still incomplete. In this study, a parasite was isolated from a 61-year-old man diagnosed with strongyloidiasis during the treatment of lymphoma on his retroperitoneal lymph node. Diffuse symmetric wall thickening from the ascending to descending colon and a nematode-infected intestine was observed following microscopic examination. Genomic DNA was isolated from a patient tissue block, and S. stercoralis was identified by PCR and sequencing (18S rDNA). In order to determine phylogenetic location of a Korean isolate (named KS1), we analyzed cox1 gene (500-bp) and compared it with that from 47 previous S. stercoralis isolates (28 human isolates and 19 canid isolates) from Asian countries. Our results showed that phylogenetic tree could clearly be divided into 5 different groups according to hosts and regions. KS1 was most closely related with the Chinese isolates in terms of genetic distance.
-
Key words: Strongyloides stercoralis, Strongyloidiasis, Phylogenetic
Strongyloidiasis is caused by
Strongyloides stercoralis and is one of the most neglected tropical diseases in tropical and subtropical regions [
1]. Although most patients present as asymptomatic, fatal disseminated strongyloidiasis can arise in immunocompromised patients (immunosuppressive therapy, high-dose steroid therapy, and others) [
2,
3].
Strongyloides can cause general gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, and respiratory symptoms such as cough, dyspnea, and asthma [
2,
3]. Hyperinfection or disseminated strongyloidiasis can affect several organs, leading to fatal outcomes [
4–
8].
Recently, molecular phylogeny approaches based on the mitochondria and genome markers in
S. stercoralis were used to understand microevolution and the phylo-geographical gene flow of
S. stercoralis haplotypes among various endemic areas of the world [
9–
12]. Nagayasu et al. [
10] suggested that 2 distinct genetic lineages of
S. stercoralis, referred to as Clade I and Clade II, were detected after 571 isolates were genetically analyzed. Clade I can be found in isolates from humans and dogs in different countries, but the Clade II can be found only in isolates from dogs [
10]. Spotin et al. [
9] also reported that most isolates from several southeast Asian and east Asian countries can be divided into 2 lineages. They used the cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (
cox1), which is a well-known evolutionary mitogenome marker, as a genetic marker for accurate determination of the taxonomic status and phylogeny of infection-causing helminths [
9].
In Korea,
S. trongyloides stercoralis infection has been sporadically reported, with most cases being described in patients with immunodeficiency or during steroid chemotherapy [
4,
5,
13,
14]. However, no reports exist on genetic analysis of the Korean isolates. In this study, we report an additional disseminated strongyloidiasis case in a Korean patient and compare the genetic characteristics of this Korean isolate with those of previously reported
S. stercoralis isolates from Asia using
cox1 gene sequencing and multi-align methods.
A 61-year-old Korean man who was living at Yangsan-si, Kyungsangnam-do and previously diagnosed as having retroperitoneal non-Hodgkin lymphoma stage IV, was admitted to the emergency room at the Pusan National University Hospital with gastric discomfort, complaints of dyspnea, and fever on October 25, 2019. He was under chemotherapy to treat the retroperitoneal lymphoma. After esophagogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy analysis, reflux esophagitis was identified as Los Angeles Classification-C and Mallory-Weiss syndrome; further, colitis that may have been caused by infection was detected (
Fig. 1). A follow up-abdominal CT performed on November 4 showed diffuse symmetric wall thickening of the colon from the ascending to descending areas, which might have been caused by infectious colitis. Finally, parasite nematode infections were detected through the previously obtained biopsy specimens from the colon and duodenum (
Fig. 1). However, the patient had died of bacterial septic shock on November 15, 2019.
As the general method for stool examination failed to detect filariform larvae, PCR was performed on DNA samples extracted from a formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded gastric tissue block, to identify
S. stercoralis. The study was approved by institutional review board of the Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital (IRB No. 05-2020-249). The specific primers and PCR conditions used to identify the
S. stercoralis 18S rRNA gene have been previously described: 5′-ATC GTG TCG GTG GAT CAT TC-3′ and 5′-CTA TTA GCG CCA TTT GCA TTC-3′ [
15,
16]. In order to establish the source of the parasite from a foreign country during international travel by the patient, we performed
cox1 gene sequencing and compared the genetic variations with genes from 49 previously reported isolates from foreign countries.
cox1 gene amplification was performed with the primers 5′-TGG TTT GGG TAC TAG TTG-3′ and 5′-GAT GAG CTC AAA CTA CAC A-3′, and PCR conditions were optimized based on a previous report [
17]. DNA sequencing was performed using the same primers by Cosmo Genetech (Seoul, Korea). The 47
cox1 reference sequences from
S. stercoralis and 2 from S. planiceps and Enterobius vermicularis (used as outgroup) were obtained from GenBank (
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucgss). Nucleotide sequences were grouped according to host species [29 human isolates and 19 canid isolates] and regions from where they were isolated [east Asia (Japan, China, and South Korea), southeast Asia (Thailand, Myanmar, Laos, and Cambodia)]. Isolate and reference sequences were used for multiple alignment, and phylogenetic distances were calculated using MEGA, (v. 10.1.8, MEGA software). Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA.
In this study, we identified
S. stercoralis infection from an advanced stage lymphoma patient using histopathologic data and molecular studies. Histopathologic examination revealed abundant inflammatory cells, epithelial cells, and numerous larval nematodes. The larvae were elongated and slender and measured approximately 201 to 280 μm in length and 8 to 14 μm in width (
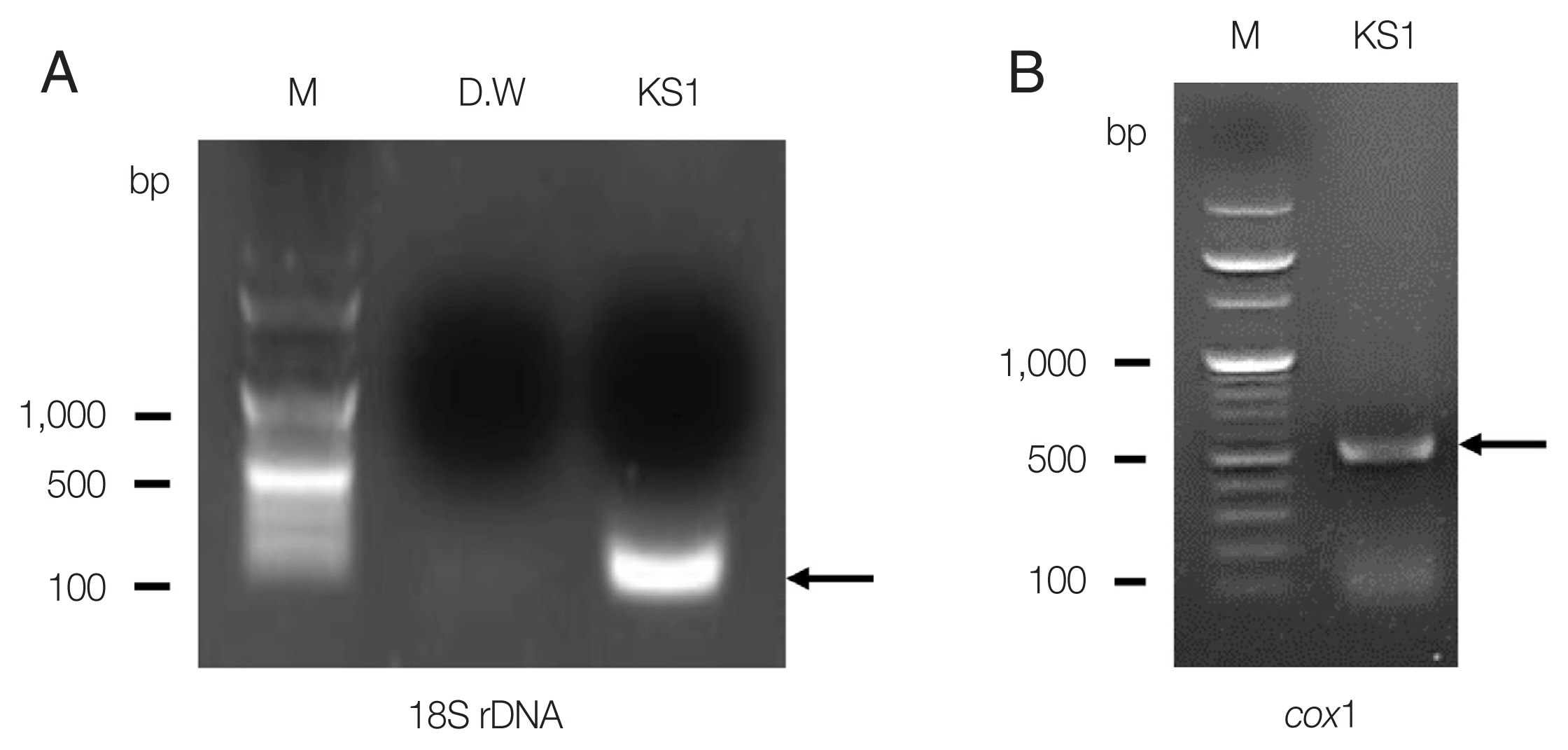
Fig. 1). After 18S rDNA PCR analysis, we obtained a positive band that was amplified to a length of 114 bp for the targeted
S. stercoralis gene; the PCR products were confirmed by sequencing analysis (
Fig. 2A). For comparison with the other isolates reported from foreign countries, we additionally performed
cox1 gene sequencing.
S. stercoralis isolate (KS1) from the Korean patient was compared with 47 isolates (28 human isolates and 19 canid isolates) previously reported from foreign countries, using
cox1 gene phylogenetic analysis. After PCR amplification, we obtained a target band approximately 509 bp in length for
cox1 (
Fig. 2B).
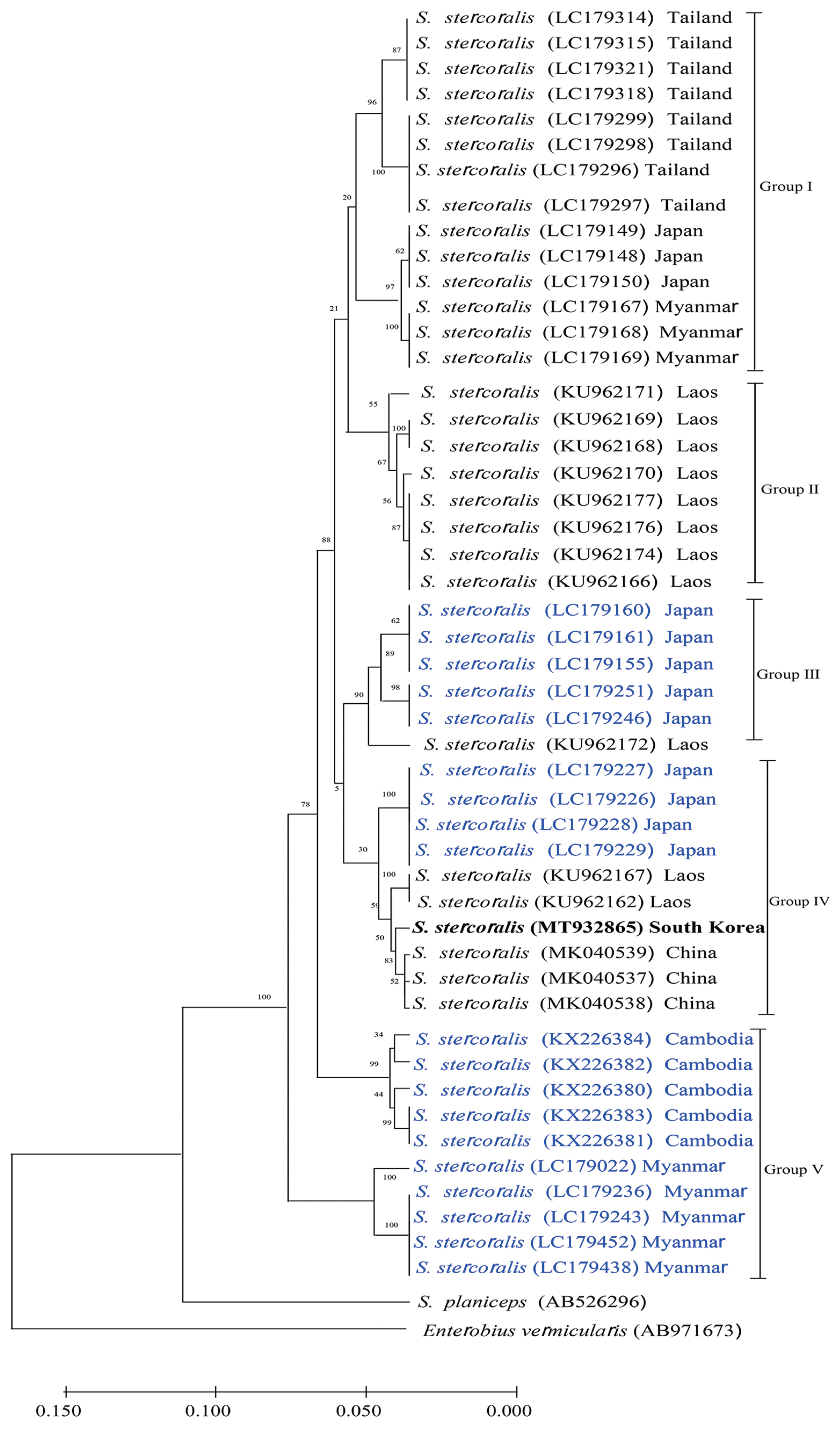
Fig. 3 shows that the phylogenetic tree could clearly be divided into 5 different groups according to hosts and regions. KS1 (GenBank No. MT932865) was the most closely related with the Chinese isolates in terms of genetic distance (Group IV). Japanese isolates were divided into 3 different groups; the genetic distances between KS1 and the Japanese groups were longer than those between KS1 and the Chinese isolates.
Analysis of a recent strongyloidiasis case report in Korea uncovered a generally complex medical history, such as, consuming or injecting steroid drugs or chronic wasting diseases. The immune function in all patients appeared to be significantly lowered [
6,
13,
14,
18]. As the patient’s immune function continues to decline, the infection becomes increasingly severe (hyperinfection or disseminated strongyloidiasis). One of the best methods for the diagnosis of
Strongyloides infection is the detection of larva via stool examination. Rhabditoid (L1) and filariform (L3) are 2 common types of
S. stercoralis larvae, and their sizes and morphological features are different. Filariform larvae are of a greater size and have a longer esophagus than rhabditoid larvae and have a unique tail with a notched appearance [
2,
18]. In this study, we measured the length of the larva (201–280 μm length), but we could not observe notched tails from the histopathologic results. It was very difficult to accurately observe the size and shape of the parasite while reviewing pathological tissue slides.
We sought to determine the genetic origin of the
S. stercoralis KS1 isolate to evaluate whether it was imported from a foreign country or originated in Korea. In order to address this issue, we carried out phylogenetic studies via
cox1 gene-sequencing analysis on other isolates from foreign countries.
Fig. 3 shows that all the isolates are classified into 5 groups. There is no regional specificity between countries from East Asia and those from Southern-East Asia. KS1 was grouped in the canid isolates from Japan named Group IV (
Fig. 3). Strongyloidiasis could be a zoonotic infection; phylogenetic analysis revealed that humans and dogs from the same community share an
S. stercoralis strain, suggesting a potential role for dogs in the transmission of this parasite [
1,
19]. Spotin et al. (2019) [
9] analyzed the genetic variability of
S. stercoralis using meta-analysis methods, and they identified 4 distinct geographical haplotypes from 106 human isolates and 48 canid isolates. Their haplotype network data showed that haplogroup IV originated from Cambodian dogs and had not zoonotically adapted to infect humans. Nagayasu et al. (2017) [
10] also suggested that
S. stercoralis has 2 distinct lineages globally, and one group of parasites was isolated from both humans and dogs in different countries (Clade I), while another group of parasites was found exclusively in dogs, indicating that this group had not adapted to infect humans (Clade II).
In this study, a limitation associated with the interpretation of the phylogenetic results was that only one Korean isolate was used for analysis. Unfortunately, we could not find any genetic information regarding S. stercoralis Korean isolates (except KS1) in the GenBank system. Although we do not have adequate information, results suggested that strongyloidiasis in South Korea was more likely to be a zoonotic infection; evidence from phylogenetic analysis revealed that humans and dogs from the same community share an S. stercoralis strain, suggesting a potential role for dogs in the transmission of this parasite.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Fig. 1Esophagogastroduodenoscopic views and histology of the biopsied gastroesophageal junction and pyloric antrum tissue demonstrating nematode infection. Reflux esophagitis and Mallory-Weiss syndrome were found, and the erosions extended to the submucosal level (Los Angeles Classification-C). Gastroesophageal junction (A). Pyloric antrum (B). Multiple eggs and larvae of S. stercoralis were detected in the tissue (C–F).
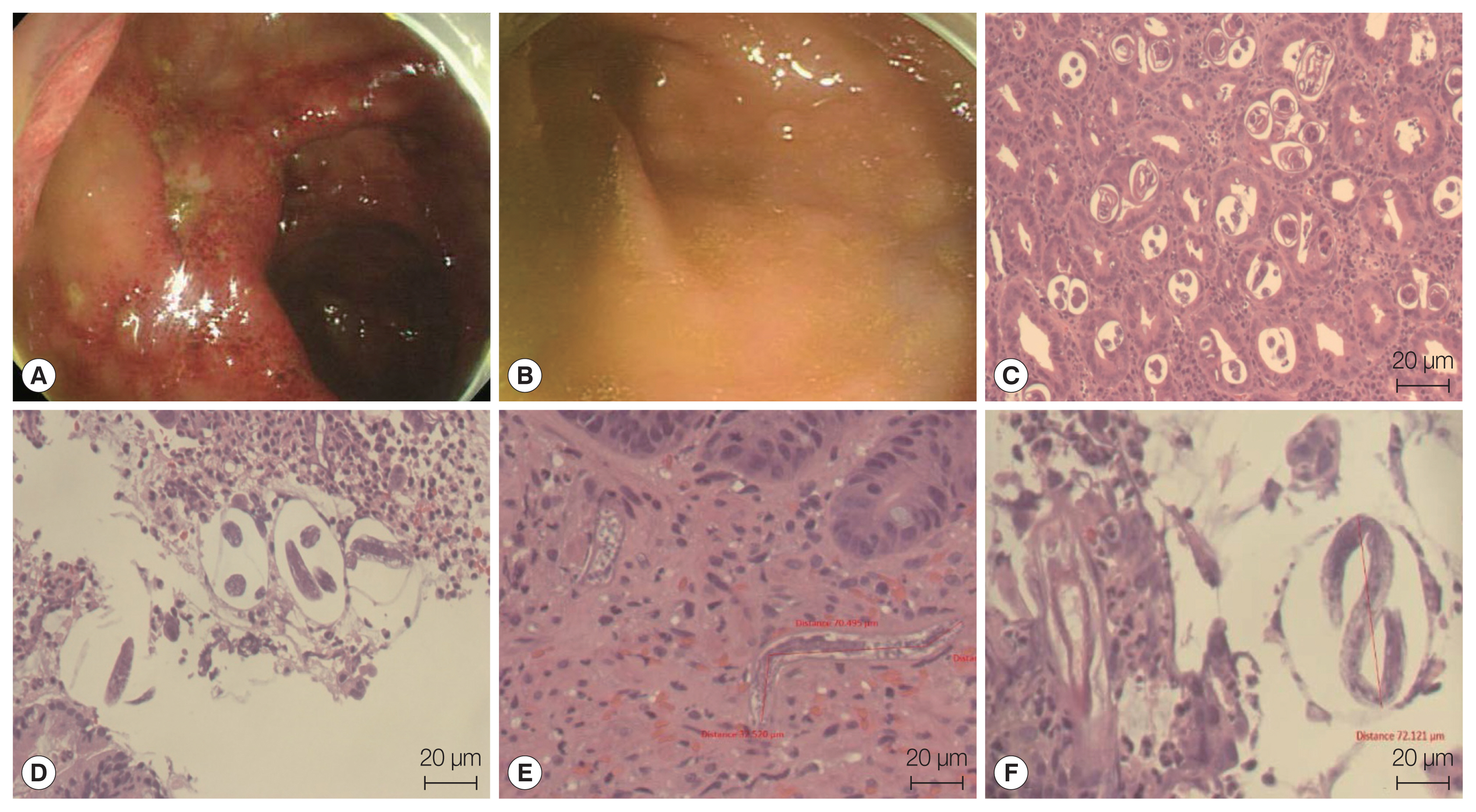
Fig. 2Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products of S. stercoralis KS1. (A) 18S rDNA partial PCR product (arrow, 114 bp). (B) cox1 partial PCR product (arrow, 509 bp; M, 1-kb ladder).
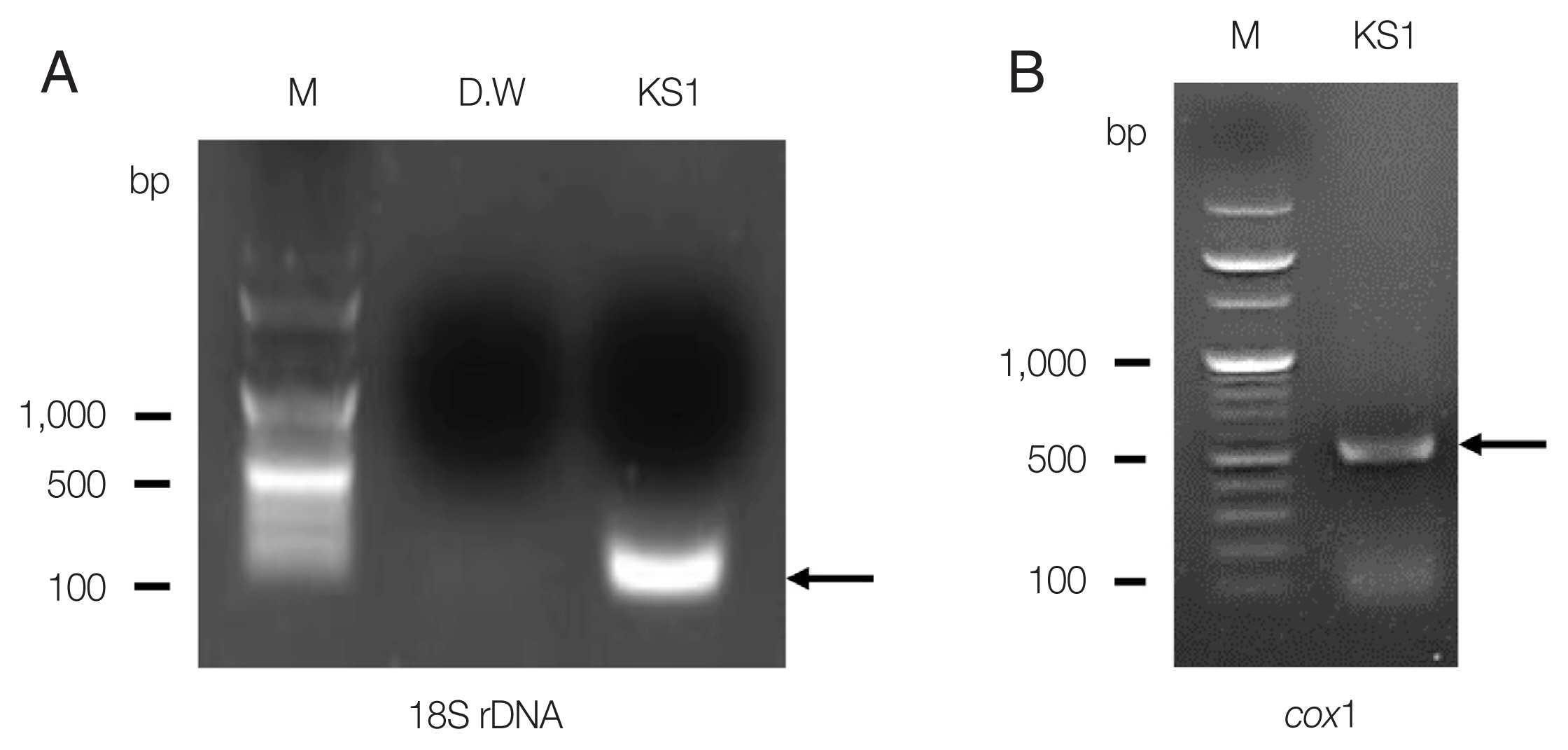
Fig. 3Phylogenetic tree of Strongyloides stercoralis isolates generated using cox1 partial gene sequences. Genetic relationship among S. stercoralis KS1 (MT932865, bolded) were inferred based on phylogenetic analysis using their cox1 sequences along with 47 corresponding reference sequences. A phylogenetic tree was constructed by neighbor-joining method using MEGA (v. 10.1.8). Reference sequences are named by their GenBank accession numbers (Black string, human isolate; Blue string, dog isolate).

References
- 1. Krolewiecki A, Nutman TB. Strongyloidiasis: a Neglected Tropical Disease. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2019;33:135-151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2018.10.006
- 2. Grove DI. Human strongyloidiasis. Adv Parasitol 1996;38:251-309. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60036-6
- 3. Beknazarova M, Whiley H, Ross K. Strongyloidiasis: a disease of socioeconomic disadvantage. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2016;13:517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13050517
- 4. Seo AN, Goo YK, Chung DI, Hong Y, Kwon O, Bae HI. Comorbid gastric adenocarcinoma and gastric and duodenal Strongyloides stercoralis infection: a case report. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:95-99. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2015.53.1.95
- 5. Ra H, Chung JW, Chung DH, Kim JH, Kim YJ, Kim KO, Kwon KA, Park DK. Strongyloidiasis Presenting as Yellowish Nodules in Colonoscopy of an Immunocompetent Patient. Clin Endosc 2019;52:80-82. https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2018.078
- 6. Hakeem I, Moritz C, Khan F, Garrett E, Narayanan M. Strongyloidiasis hyperinfection after renal transplant presenting as diffuse alveolar hemorrhage with respiratory failure. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2019;32:413-416. https://doi.org/10.1080/08998280.2019.1596440
- 7. Ronan SG, Reddy RL, Manaligod JR, Alexander J, Fu T. Disseminated strongyloidiasis presenting as purpura. J Am Acad Dermatol 1989;21:1123-1125. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70311-x
- 8. Waters M, Krajden S, Kim C, Elsobky R, Lychacz B, Cheung M, Crowther M, Keystone J. Case report: two cases of strongyloidiasis presenting with thrombotic events. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2019;101:418-421. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.19-0347
- 9. Spotin A, Mahami-Oskouei M, Nami S. Assessment of the global paradigms of genetic variability in Strongyloides stercoralis infrapopulations determined by mitochondrial DNA sequences. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 2019;67:101354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cimid.2019.101354
- 10. Nagayasu E, Aung MPPTHH, Hortiwakul T, Hino A, Tanaka T, Higashiarakawa M, Olia A, Taniguchi T, Win SMT, Ohashi I, Odongo-Aginya EI, Aye KM, Mon M, Win KK, Ota K, Torisu Y, Panthuwong S, Kimura E, Palacpac NMQ, Kikuchi T, Hirata T, Torisu S, Hisaeda H, Horii T, Fujita J, Htike WW, Maruyama H. A possible origin population of pathogenic intestinal nematodes, Strongyloides stercoralis, unveiled by molecular phylogeny. Sci Rep 2017;7:4844. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05049-x
- 11. Ko PP, Suzuki K, Canales-Ramos M, Aung M, Htike WW, Yoshida A, Montes M, Morishita K, Gotuzzo E, Maruyama H, Nagayasu E. Phylogenetic relationships of Strongyloides species in carnivore hosts. Parasitol Int 2020;78:102151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2020.102151
- 12. Barratt JLN, Lane M, Talundzic E, Richins T, Robertson G, Formenti F, Pritt B, Verocai G, Nascimento de Souza J, Mato Soares N, Traub R, Buonfrate D, Bradbury RS. A global genotyping survey of Strongyloides stercoralis and Strongyloides fuelleborni using deep amplicon sequencing. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2019;13:e0007609. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0007609
- 13. Kim EJ. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome With Alveolar Hemorrhage due to Strongyloidiasis Hyperinfection in an Older Patient. Ann Geriatr Med Res 2018;22:200-203. https://doi.org/10.}4235/agmr.18.0041
- 14. Won EJ, Jeon J, Koh YI, Ryang DW. Strongyloidiasis in a diabetic patient accompanied by gastrointestinal stromal tumor: cause of eosinophilia unresponsive to steroid therapy. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:223-226. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2015.53.2.223
- 15. Sitta RB, Malta FM, Pinho JR, Chieffi PP, Gryschek RC, Paula FM. Conventional PCR for molecular diagnosis of human strongyloidiasis. Parasitology 2014;141:716-721. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182013002035
- 16. Moghaddassani H, Mirhendi H, Hosseini M, Rokni M, Mowlavi G, Kia E. Molecular Diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection by PCR Detection of Specific DNA in Human Stool Samples. Iran J Parasitol 2011;6:23-30.
- 17. Sharifdini M, Mirhendi H, Ashrafi K, Hosseini M, Mohebali M, Khodadadi H, Kia EB. Comparison of Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction with Parasitological Methods for Detection of Strongyloides stercoralis in Human Fecal Samples. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2015;93:1285-1291. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.15-0309
- 18. Kim J, Joo HS, Ko HM, Na MS, Hwang SH, Im JC. A case of fatal hyperinfective strongyloidiasis with discovery of autoinfective filariform larvae in sputum. Korean J Parasitol 2005;43:51-55. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2005.43.2.51
- 19. Jaleta TG, Zhou S, Bemm FM, Schar F, Khieu V, Muth S, Odermatt P, Lok JB, Streit A. Different but overlapping populations of Strongyloides stercoralis in dogs and humans-Dogs as a possible source for zoonotic strongyloidiasis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017;11:e0005752. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0005752
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- Comparison of different PCR amplification targets for molecular diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis
F. Marquet, N. Mora, R.N. Incani, J. Jesus, N. Méndez, R. Mujica, H. Trosel, E. Ferrer
Journal of Helminthology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Seropositivity Rates of Strongyloides stercoralis Antibody in the Southeastern Region of Republic of Korea: A Single-Center Retrospective Study
Taehwa Kim, Seungjin Lim
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2022; 60(3): 181. CrossRef