Abstract
Life cycle stages, including daughter sporocysts, cercariae, and metacercariae, of Parvatrema duboisi (Dollfus, 1923) Bartoli, 1974 (Digenea: Gymnophallidae) have been found in the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum from Aphae-do (Island), Shinan-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea. The daughter sporocysts were elongated sac-like and 307–570 (av. 395) μm long and 101–213 (av. 157) μm wide. Most of the daughter sporocysts contained 15–20 furcocercous cercariae each. The cercariae measured 112–146 (av. 134) μm in total length and 35–46 (av. 40) μm in width, with 69–92 (av. 85) μm long body and 39–54 (av. 49) μm long tail. The metacercariae were 210–250 (av. 231) μm in length and 170–195 (av. 185) μm in width, and characterized by having a large oral sucker, genital pore some distance anterior to the ventral sucker, no ventral pit, and 1 compact or slightly lobed vitellarium, strongly suggesting P. duboisi. The metacercariae were experimentally infected to ICR mice, and adults were recovered at day 7 post-infection. The adult flukes were morphologically similar to the metacercariae except in the presence of up to 20 eggs in the uterus. The daughter sporocysts and metacercariae were molecularly (ITS1–5.8S rDNA-ITS2) analyzed to confirm the species, and the results showed 99.8–99.9% identity with P. duboisi reported from Kyushu, Japan and Gochang, Korea. These results confirmed the presence of various life cycle stages of P. duboisi in the Manila clam, R. philippinarum, playing the role of the first as well as the second intermediate host, on Aphae-do (Island), Shinan-gun, Korea.
-
Key words: Parvatrema duboisi, gymnophallid, sporocyst, cercaria, metacercaria, Manila clam, Aphae-do (Island), Korea
Five genera are acknowledged in the family Gymnophallidae Odhner, 1905, which include
Gymnophalloides Fujita, 1925 (syn.
Lacunovermis Ching, 1965),
Parvatrema Cable, 1953 (syn.
Meiogymnophallus Ching, 1965),
Gymnophallus Odhner, 1900 (syn.
Paragymnophallus Ching, 1973),
Pseudogymnophallus Hoberg, 1981, and
Bartolius Cremonte, 2001 [
1,
2]. Adult gymnophallids generally infect the intestine, gall-bladder, and bursa Fabricii of avian hosts, including shore birds and diving ducks [
1]. However, they rarely occur also in mammals in 2 species of
Gymnophalloides;
G. seoi in humans and cats [
3,
4] and
G. heardi in rats [
5]. The species of
Parvatrema,
Gymnophallus,
Pseudogymnophallus, and
Bartolius have so far been found exclusively in avian hosts [
1]. However, their zoonotic capability remains to be further determined.
In the Republic of Korea (=Korea), the existence of several gymnophallid species has been documented. They include
G. seoi [
3,
6],
Parvatrema macrostomus (syn.
Gymnophallus macrostoma Yamaguti, 1939) [
2,
7],
Parvatrema duboisi (Dollfus, 1923) Bartoli, 1974 (syn.
Parvatrema timondavidi Bartoli, 1964) [
2,
8],
Parvatrema chaii Sohn et al., 2007 [
9],
Parvatrema homoeotecnum James, 1964 [
10], and
Parvatrema sinonovaculae n. comb. (syn.
Meiogymnophallus sinonovaculae Chai et al., 2007) [
11].
The presence of
P. duboisi metacercariae in Korea was first reported by Yu et al. [
8] who detected these metacercariae in the Manila clam,
Ruditapes philippinarum (syn.
Tapes philippinarum) purchased from a fishery market in Seoul and obtained adult flukes after experimental infection to ICR mice. The locality origin of the Manila clam was unknown at that time [
8] but later it was suggested to have been Gochang-gun, Jeollabuk-do (Province) [
2]. Sohn et al. [
12,
13] found metacercariae of
Parvatrema spp., including
P. duboisi, in Manila clam collected from various localities of southern and southwestern parts of Korea. In addition, Chung et al. [
10] collected adult flukes of
P. duboisi from the intestine of great knots
Calidris tenuirostris caught from a western coastal area, i.e., Gunsan-si (‘si’ is City), Jeollabuk-do. In Gochang-gun (‘gun’ is County), where the Manila clam is abundantly produced, the gymnophallid metacercariae detected were morphologically and molecularly confirmed to be
P. duboisi [
2]. However, on Aphae-do (Island), Shinan-gun, Korea, where a high endemicity of human
G. seoi infection was reported [
3,
14], no information has been available regarding the presence of other gymnophallid species. In the present study, we found the existence of various life cycle stages (daughter sporocysts, cercariae, and metacercariae) of
P. duboisi on Aphae-do (Island). Brief morphologies of these larval stages are described here.
The Manila clam, R. philippinarum, was collected from 3 estuary areas, i.e., Shinjang-3-ri (‘ri’ is village), Daecheon-ri, and Jang-gam-ri, of Aphae-do (Island), Shinan-gun, Jeollanam-do from 2001 through 2020. After the shell of the clam was removed, the animal part was cut into several pieces using a pair of scissors or briefly (a few seconds) ground in an electronic mixer with 0.85% saline. The mixture was washed several times with saline, and then the sediment was examined for daughter sporocysts, cercariae, and metacercariae of gymnophallids using a stereomicroscope. Some specimens were fixed in 70–80% ethanol for molecular studies, and others were fixed in 10% formalin for morphological studies.
The adult flukes were recovered from experimentally infected ICR mice with metacercariae at day 7 post-infection. The animal experiment was performed according to the guidelines of the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments at Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. The adult flukes collected from the small intestine of mice were fixed with 10% formalin and stained with Semichon’s acetocarmine.
Molecular studies were performed on daughter sporocysts (containing cercariae) and metacercariae. Genomic DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Blood and Tissue kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region (ITS1, 5.8S rRNA, ITS2) was amplified using the standard PCR protocol with eukaryotic universal primers, 18d (5′-cacaccgcccgtcgctactaccgattg-3′) and 28cc (5′-actcgccgttactgagggaatcctggttag-3′) [
15]. The amplified product was processed for initial denaturation at 94°C for 5 min, 35 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 65°C for 30 sec, and extension at 72°C for 1.3 min, followed by a final elongation at 72°C for 5 min. The PCR product was purified and directly sequenced by Macrogen Inc. (Seoul, Korea). The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the maximum-likelihood method based on Tamura-Nei model of nucleotide substitution with 1,000 bootstrap replications with our samples and other gymnophallid species available in GenBank. The tree was viewed by MEGA v6 program.
Based on morphological (
Figs. 1,
2) and molecular data (
Fig. 3), the larval gymnophallids found in the Manila clam from 3 localities of Aphae-do (Island) were confirmed to be
P. duboisi. The brief morphologies of daughter sporocysts, cercariae, metacercariae, and adults (experimental) were as follows:
The daughter sporocysts (
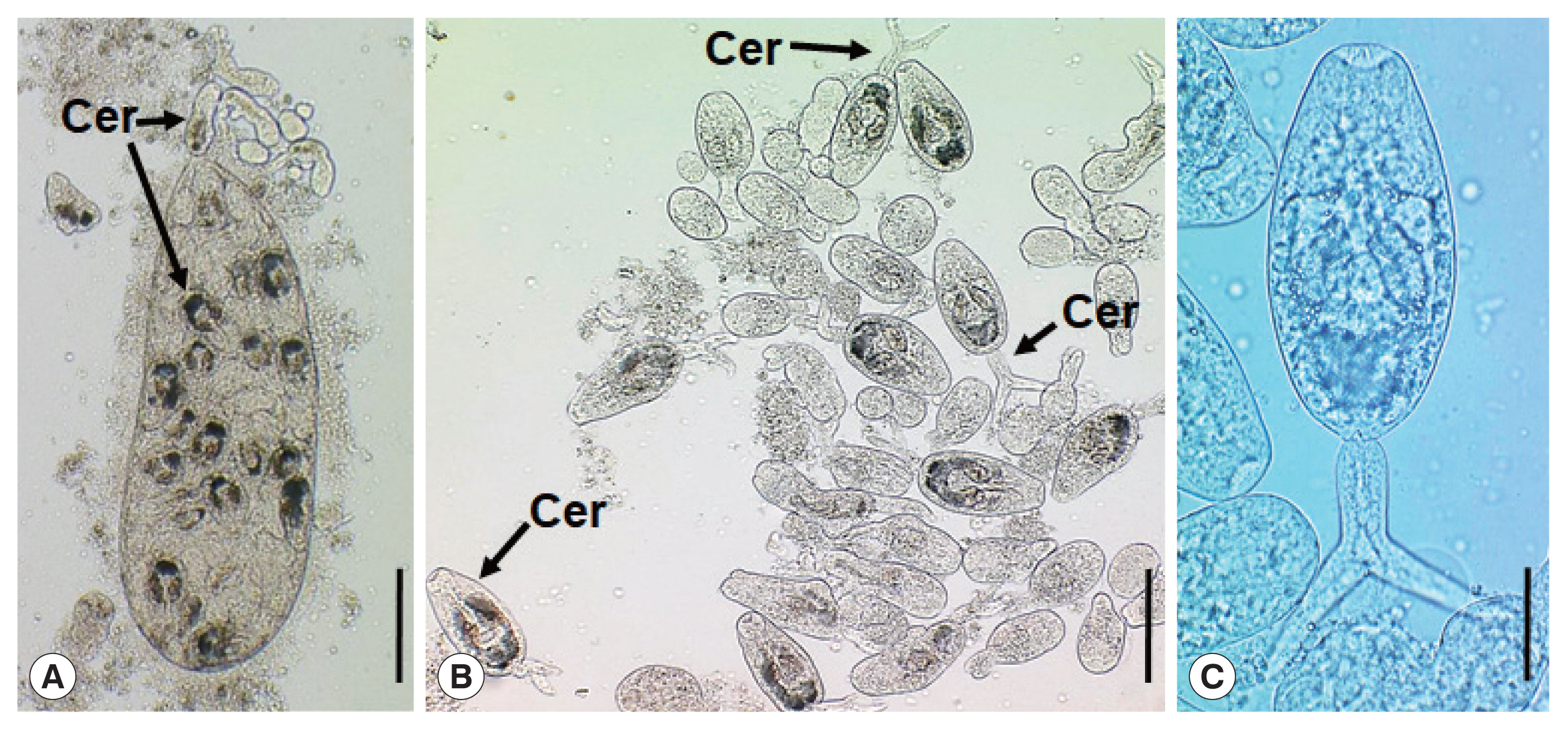
Fig. 1A) were elongated sac-like having a birth pore at the anterior end, enveloped with a thin wall, but without a pharynx-like structure and a primitive gut, and 307–570 (av. 395) μm long and 101–213 (av. 157) μm wide (n=10). Most of them contained 15–20 cercariae and seemed to be the second or third generation daughter sporocysts, i.e., ripe daughter sporocysts.
The cercariae (
Fig. 1B, C) were furcocercous (dichotoma) type with moderately long tail (furcae slightly longer than the tail stem) which measured 112–146 (av. 134) μm in total length and 35–46 (av. 40) μm in width; body 69–92 (av. 85) μm long and tail 39–54 (av. 49) μm long (n=10). The cercarial body showed a subterminal oral sucker, small ventral sucker, pharynx, short slightly inflated ceca, and U-, V-, or butterfly-shaped excretory bladder.
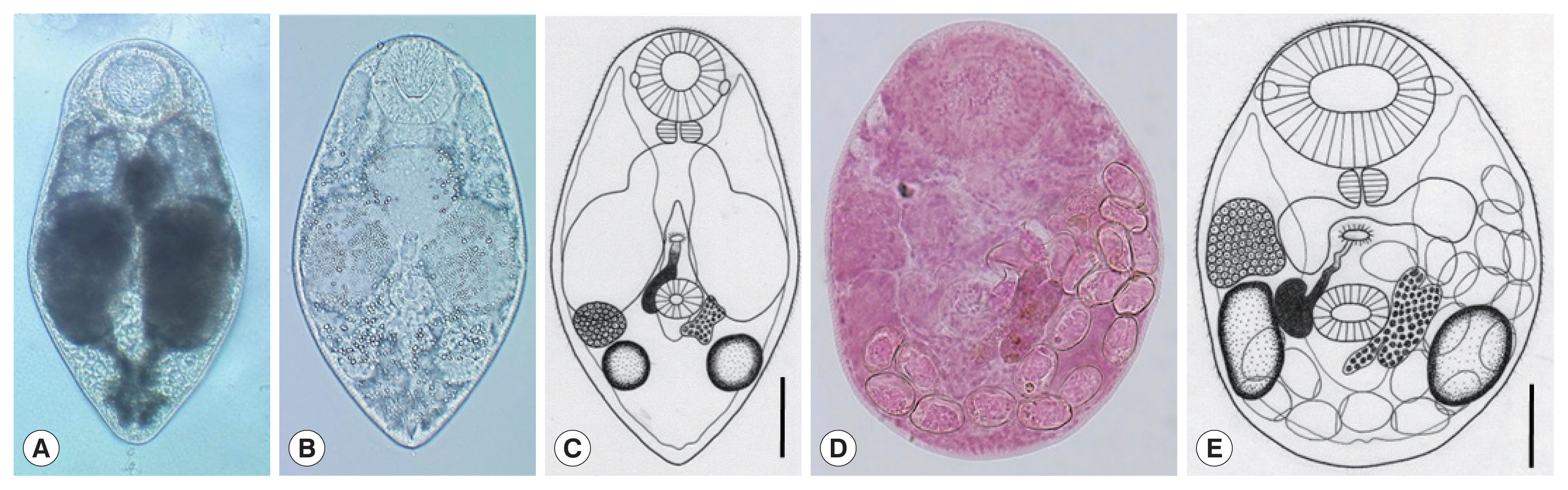
The metacercariae (n=10) were 231 (210–250) μm long and 185 (170–195) μm wide (
Fig. 2A–C). They had a well-developed oral sucker with 2 small lateral projections on the lip, a small muscular pharynx, no pre-pharynx, 2 inflated oval ceca, a small round ventral sucker, 2 testes laterally located, an ovary in front of the right testis, a uniparpite seminal vesicle, and 1 compact or slightly lobed vitellarium at the left or postero-sinistral side of the ventral sucker. They had a genital pore, a wide slit-like opening, located some distance anterior to the ventral sucker but no ventral pit was present. The excretory bladder was U- or V-shaped with 2 arms reaching to the level of the oral sucker.
The adult flukes (n=10) were 225 (180–239) μm long and 170 (150–198) μm wide (
Fig. 2D, E). They had a large oral sucker with 2 small lateral projections on the lip. The pharynx was well developed. The ventral sucker was small, round in shape, and located in the posterior field of the body. Two slightly elliptical testes were located laterally to the ventral sucker. One compact vitellarium was seen on the sinistral side of the ventral sucker, and a seminal vesicle on its dextral side. The ovary was at some distance anterior to the right testis. The genital pore was well developed, anterior to the ventral sucker, and connected to the seminal vesicle. The uterus was filled with a small number (≤20) of eggs; the egg size was 24 (22–27) μm long and 14 (12–20) μm wide.
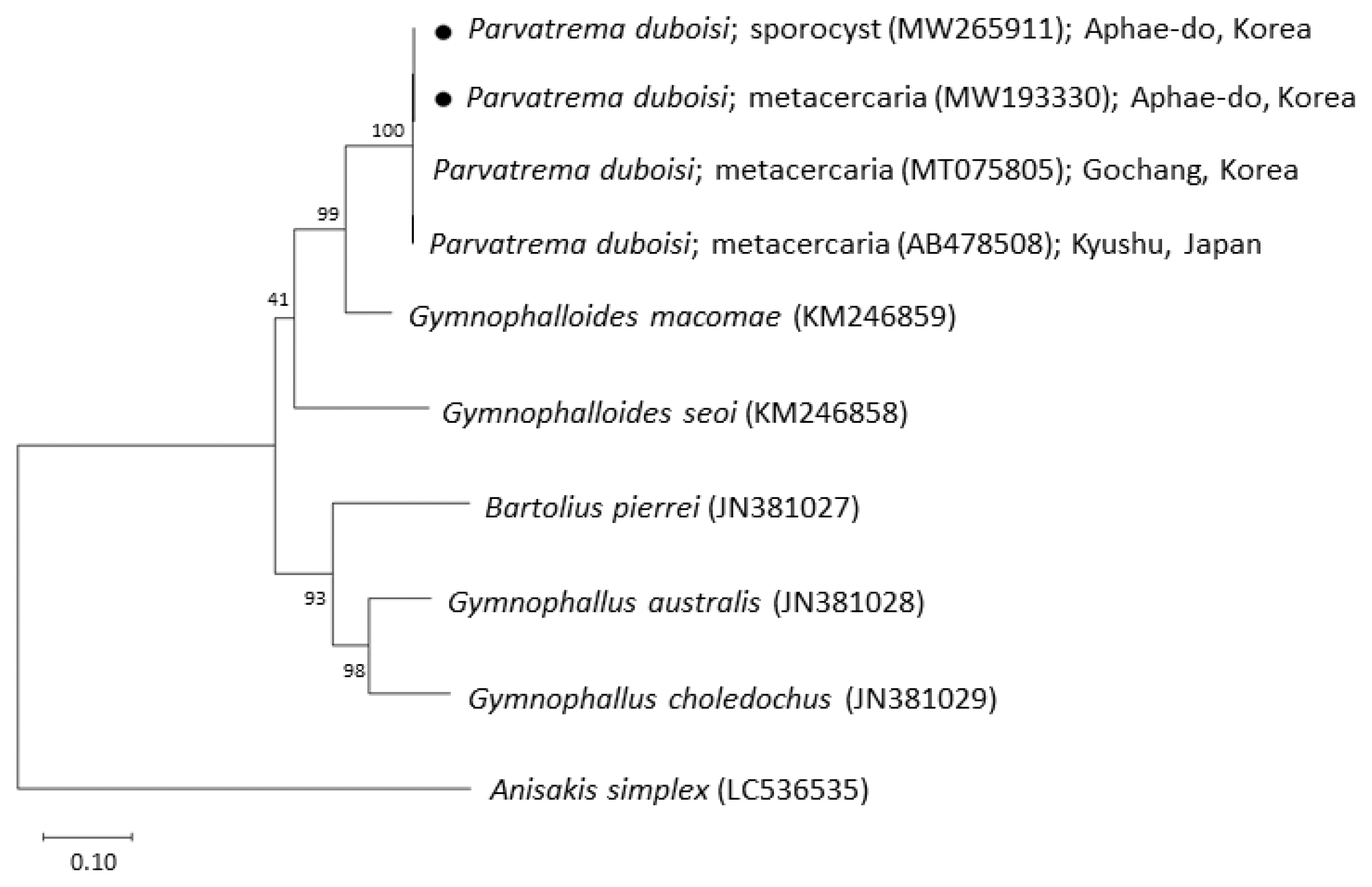
The sequences of the ITS region of our specimens (sporocyst, GenBank no. MW265911; metacercaria, no. MW193330) revealed only 1 nucleotide substitution (1,192 of 1,193 sites or 99.9% were identical) from the known sequences of
P. duboisi in Gochang, Korea (no. MT075805) [
2] and 2 nucleotide substitutions (1,266 of 1,268 sites or 99.8% were identical) from
P. duboisi in Kyushu, Japan (no. AB478508) [
15] (
Table 1). Meanwhile, our samples showed a sequence homology of only 77.1% in comparison with
G. seoi. The phylogenetic tree (
Fig. 3) showed that our samples were distant from
Gymnophalloides macomae n. comb. Scholz, 2002 [syn.
Lacunovermis macomae (Lebour, 1908) Loos-Frank, 1970],
Bartolius pierrei,
Gymnophallus australis, and
G. choledochus (
Table 1;
Fig. 3).
In the family Gymnophallidae, Ching [
16] created 2 genera,
Lacunovermis (wide genital pore, ventral pit present) and
Meiogymnophallus (small genital pore, no ventral pit). However, Yamaguti [
17] and Scholz [
1] synonymized
Lacunovermis with
Gymnophalloides which has a small genital pore and a well-developed ventral pit, because the size of the genital pore could not be a significant character to differentiate the 2 genera. In addition,
Meiogymnophallus was synonymized with
Parvatrema by Scholz [
1] because the difference between the 2 genera given by Ching [
16,
18] was only the size of the genital pore, small in the former and wide in the latter.
Paragymnophallus was created by Ching [
19] to accept those gymnophallids that have a wide genital pore at a distance anterior to the ventral sucker. However, this genus was synonymized with
Gymnophallus by Scholz [
1].
Our specimens were morphologically assigned to
Parvatrema because they had an oral sucker with 2 lateral projections and U- or V-shaped excretory bladder, lacking a ventral pit [
1]. In the genus
Parvatrema, 24 species are currently known [
2]. Among them, 7 species that have a single compact mass of vitellarium were comparable with our specimens [
2]. They included
P. borinqueñae,
P. bushi,
P. chaii,
P. donacis,
P. duboisi,
P. polymesoda, and
P. rebunense. The differential points between
P. duboisi and 7 other
Parvatrema species were previously described by Chang et al. [
2].
In molecular analysis by sequencing of the ITS region, the homology of our specimens (sporocysts and metacercariae) with
P. duboisi reported from Korea (Gochang) and Japan (Kyushu) was 99.8–99.9%, while the homology with
Gymnophalloides spp. (
G. macomae and
G. seoi) was 77.1–85.6%. On the other hand,
Gymnophallus spp. (
G. australis and
G. choledochus) and
Bartolius sp. (
B. pierrei) were far from our specimens, with only 72.4–74.6% homology with our specimens. These results agreed to Cremonte et al. [
20] that
Parvatrema and
Gymnophalloides are phylogenetically closer to each other than to the other genera of the family Gymnophallidae (
Gymnophallus and
Bartolius) and possibly also
Pseudogymnophallus (no molecular data have been provided in GenBank).
P. duboisi was first described by Dollfus [
21] in 1923 under the name
Gymnophallus duboisi with the metacercariae obtained from the marine mussel
Mytilus galloprovincialis in France. Later (1963–1965), Bartoli [
22,
23] described a new species (
Parvatrema timondavidi) based on metacercariae from the same species of mussels collected from the Gulf of Marseille, France. However, in 1974, Bartoli [
24] found that the gymnophallid species described by himself as
P. timondavidi was identical with those of
G. duboisi and renamed it as
Parvatrema duboisi as a new combination. The natural definitive host included tufted ducks
Aythya fuligula, and experimental hosts were chickens and ducks [
24]. Meanwhile, in 1944, Ogata [
25] obtained gymnophallid metacercariae from the Manila clam and adults from an experimental rat in Japan and diagnosed them as
Gymnophallus bursicola which was reported by Odhner in 1900. Later, however, Endo and Hoshino [
26] found that these metacercariae and adults obtained from experimental mice should be assigned to
P. timondavidi. Subsequently, Shimura et al. [
27] settled the name of this parasite as
P. duboisi. Now the geographical distribution of
P. duboisi has been extended from France [
21–
24] to Japan [
15,
25–
27], Korea [
2,
8,
10,
12,
13], Ukraine [
28], and Turkey [
29].
The second intermediate host of
P. duboisi had been repeatedly confirmed to be marine bivalves or clams, including
M. galloprovincialis [
24,
28,
29],
Brachydontes minimus [
24],
Venus gallina [
24], and the Manila clam
R. philippinarum [
2,
8,
10,
12,
13,
15,
25–
27]. However, its first intermediate host and the developmental (larval) stages of parasites were only recently discovered by Yanagida et al. [
15]. The Manila clams collected from Ariake Sea, Japan were confirmed to be the first as well as the second intermediate host harboring the sporocysts, cercariae, and metacercariae [
15], to which the present study from Aphae-do (Island), Korea agreed well. Yanagida et al. [
15] also suggested that there may be another snail or clam species acting as the first intermediate host. However, morphological details and measurements of the sporocysts and cercariae were not given by Yanagida et al. [
15], and the present study is the first in which the measurements of these larval stages have been provided.
In conclusion, the present study confirmed the presence of the life cycle stages of P. duboisi, including the sporocysts, cercariae, and metacercariae, in the Manila clam caught from 3 estuary areas of Aphae-do (Island), Korea. The Manila clams were found to take the dual role of the first as well as the second intermediate host. The possibility of human infections with this gymnophallid remains to be determined.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank the staff of Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Korea Association of Health Promotion, Seoul, Korea who helped this study.
Fig. 1
Parvatrema duboisi daughter sporocyst (A), ruptured daughter sporocyst (B), and cercaria (C) from a Manila clam, Ruditapes philippinarum collected from Aphae-do (Island), Korea. The sporocyst (A) contains about 19 cercariae (Cer), which are freely liberated (B). A cercaria (C) showing its oral and ventral suckers, ceca, and excretory bladder. Scale bars=120 μm (A), 80 μm (B), and 25 μm (C).
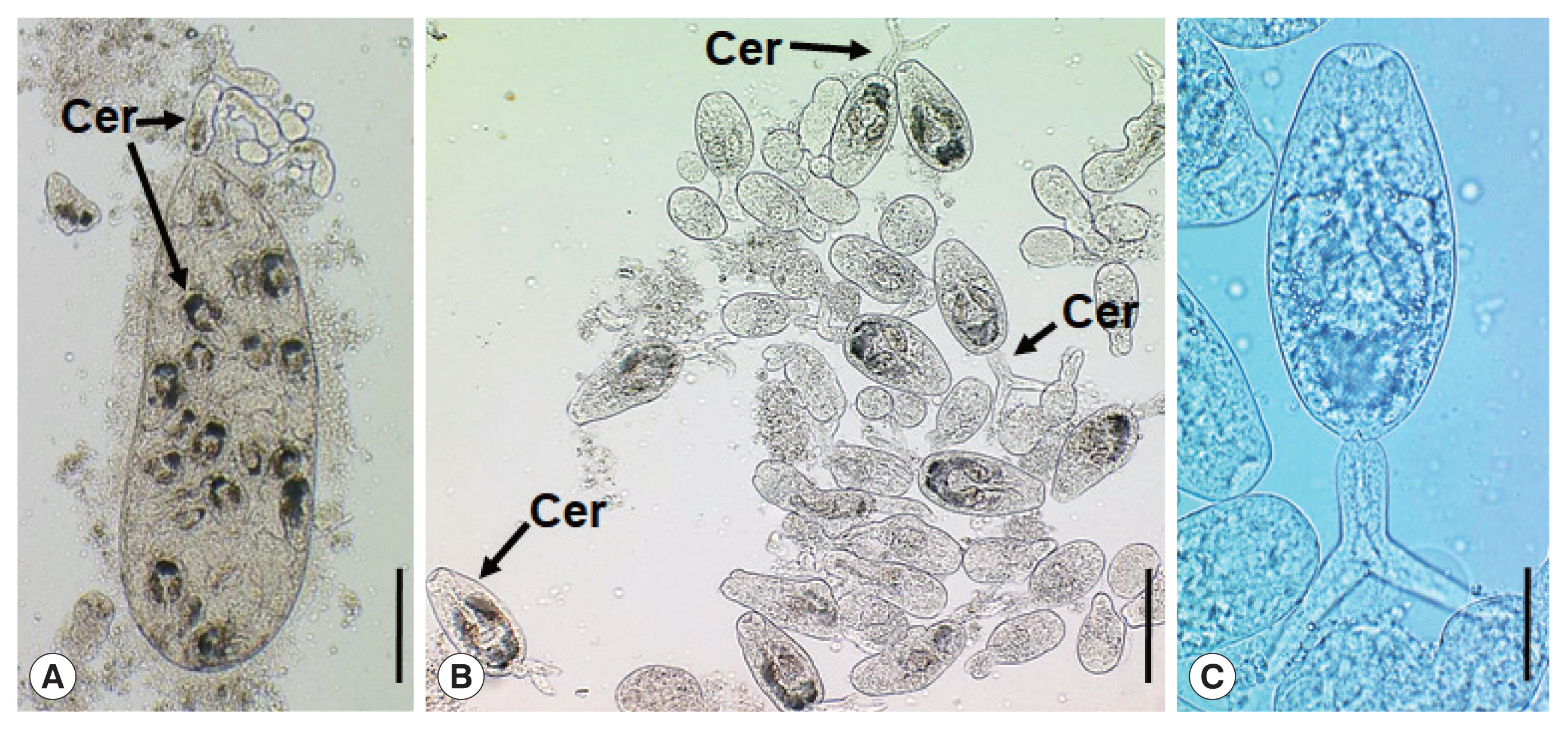
Fig. 2
Parvatrema duboisi metacercariae (A–C) from a Manila clam,
Ruditapes philippinarum collected from Aphae-do (Island), Korea and adult (D, E) recovered from experimental mice. In some metacercariae (A), dark substances were seen within the inflated ceca, whereas in others (B), such substances were only scanty in amount. Line drawing of a metacercaria (C) showing the oral sucker with lateral projections, pharynx, ceca, ventral sucker, seminal vesicle, genital pore, vitellarium, ovary, 2 testes, and excretory vesicle. An adult fluke (D) recovered from an experimental mouse at day 7 post-infection. The seminal vesicle is well developed and the uterus with eggs is seen. Line drawing (E) of the adult fluke in
Fig. 2D which shows the oral sucker, pharynx, ceca, ventral sucker, genital pore, seminal vesicle, ovary, 2 testes, vitellarium, and eggs. Scale bars=40 μm (C) and 45 μm (E).
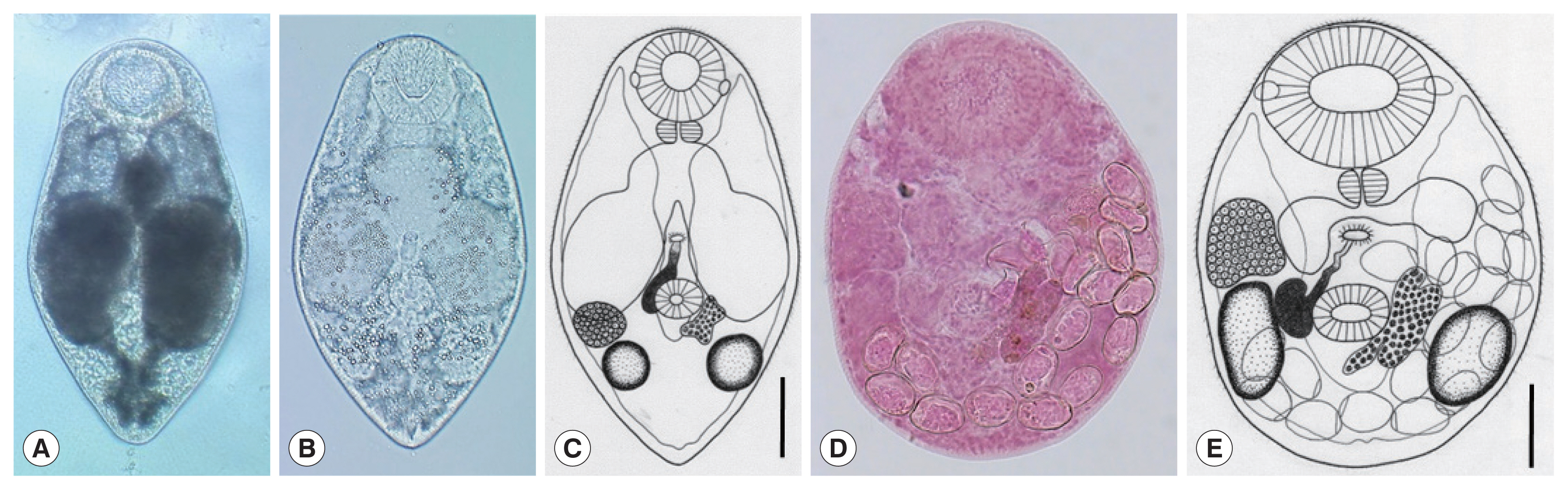
Fig. 3Phylogenetic tree of ITS region showing the relationships between Parvatrema duboisi from this study (sporocyst and metacercaria) with members of the family Gymnophallidae available in GenBank analyzed by the maximum-likelihood method. GenBank accession numbers are indicated for reference species. Scale bar indicate the number of nucleotide substitutions per site. ●, our specimens.
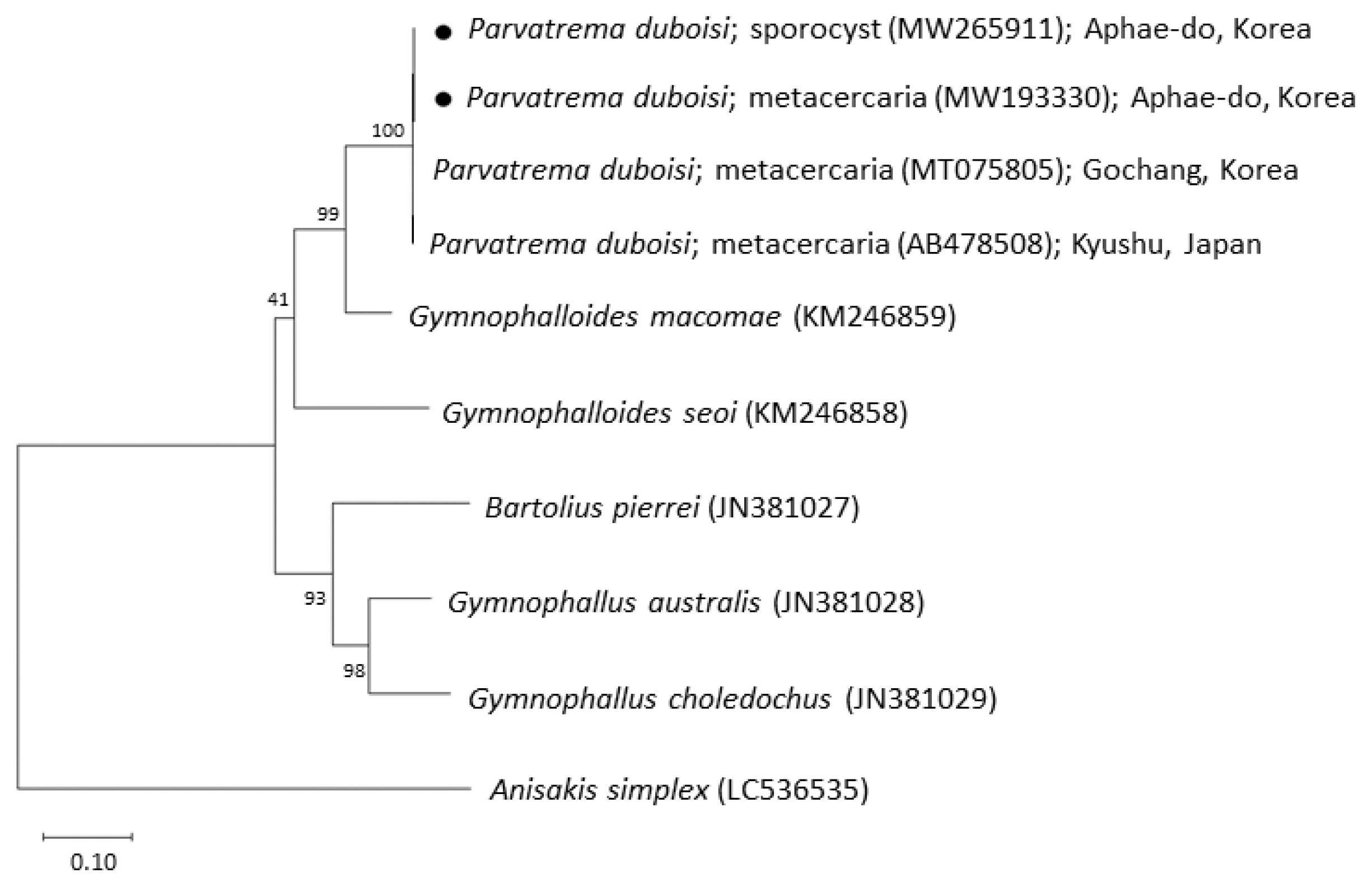
Table 1Sequence comparison of our samples with members of the family Gymnophallidae based on ITS region (ITS1–5.8S rDNA-ITS2) at metacercarial stage
Table 1
|
ITS rDNA |
|
Our samples (MW193330) |
|
Parvatrema duboisi (MT075805; Gochang, Korea) |
99.9 |
|
Parvatrema duboisi (AB478508; Kyushu, Japan) |
99.8 |
|
Gymnophalloides macomae (KM246859) |
85.6 |
|
Gymnophalloides seoi (JN381024) |
77.1 |
|
Gymnophallus australis (JN381028) |
74.6 |
|
Gymnophallus choledocus (JN381029) |
74.5 |
|
Bartolius pierrei (JN381027) |
72.4 |
References
- 1. Scholz T. Family Gymnophallidae Odhner 1905. In Gibson DI, Jones A, Bray RA eds, Keys to the Trematoda. 1:London, UK. Natural History Museum. 2002, pp 245-251.
- 2. Chang TH, Jung BK, Shin H, Hong S, Lee J, Kim DG, Patarwut L, Sohn WM, Chai JY. Morphological and molecular confirmation of Parvatrema duboisi metacercariae in the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum from Gochang-gun, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2020;58:87-91.
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2020.58.1.87
- 3. Chai JY, Choi MH, Yu JR, Lee SH.
Gymnophalloides seoi: a new human intestinal trematode. Trends Parasitol 2003;19:109-112.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1471-4922(02)00068-5
- 4. Shin EH, Park JH, Guk SM, Kim JL, Chai JY. Intestinal helminth infections in feral cats and a raccoon dog on Aphae Island, Shinan-gun, with a special note on Gymnophalloides seoi infection in cats. Korean J Parasitol 2009;47:189-191.
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2009.47.2.189
- 5. Ching HL. Four new species of gymnophallid digeneans from rice rats, willets, and molluscs in Florida. J Parasitol 1995;81:924-928.
https://doi.org/10.2307/3284042
- 6. Lee SH, Chai JY, Hong ST.
Gymnophalloides seoi n. sp. (Digenea: Gymnophallidae), the first report of human infection by a gymnophallid. J Parasitol 1993;79:677-680.
https://doi.org/10.2307/3283602
- 7. Yamaguti S. Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan. Part 25. Trematodes of birds IV. Jpn J Zool 1939;8:129-210. (in Japanese)..
- 8. Yu JR, Chai JY, Lee SH.
Parvatrema timondavidi (Digenea: Gymnophallidae) transmitted by a clam, Tapes philippinarum, in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1993;31:7-12.
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1993.31.1.7
- 9. Sohn WM, Na BK, Ryang YS, Ching HL, Lee SH.
Parvatrema chaii n. sp. (Digenea: Gymnophallidae) from mice experimentally infected with metacercariae collected from surf-clam, Mactra veneriformis
. Korean J Parasitol 2007;45:115-120.
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2007.45.2.115
- 10. Chung OS, Lee HJ, Sohn WM, Park YK, Chai JY, Seo M. Discovery of Parvatrema duboisi and Parvatrema homoeotecnum (Digenea: Gymnophallidae) from migratory birds in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2010;48:271-274.
https://doi:10.3347/kjp.2010.48.3.271
- 11. Chai JY, Han ET, Choi D, Seo M, Kim JL, Guk SM, Shin EH, Lee SH. A new gymnophallid trematode from the intestine of mice infected with metacercariae from the razor clam Sinonovacula constricta
. J Parasitol 2007;93:132-137.
https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-829R2.1
- 12. Sohn WM, Chai JY, Lee SH. Infection status of Tapes philippinarum collected from southern coastal areas of Korea with Parvatrema spp. (Digenea: Gymnophallidae) metacercariae. Korean J Parasitol 1996;34:273-277. (in Korean). https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1996.34.4.273
- 13. Sohn WM, Na BK, Cho SH, Lee WJ. Prevalence and density of digenetic trematode metacercariae in clams and oysters from western coastal regions of the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2017;55:399-408.
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2017.55.4.399
- 14. Lee SH, Chai JY, Lee HJ, Hong ST, Yu JR, Sohn WM, Kho WG, Choi MH, Lim YJ. High prevalence of Gymnophalloides seoi infection in a village on a southwestern island of the Republic of Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1994;51:281-285.
https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.1994.51.281
- 15. Yanagida T, Shirakashi S, Iwaki T, Ikushima N, Ogawa K. Gymnophallid digenean Parvatrema duboisi uses Manila clam as the first and second intermediate host. Parasitol Int 2009;58:308-310.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2009.05.006
- 16. Ching HL. Life cycles of Lacunovermis conspicuus n. gen., n. sp. and Meiogymnophallus multigemmulus n. gen., n. sp. (Gymnophallidae: Trematoda) from Macoma inconspicua and diving ducks from Vancouver, Canada. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 1965;32:53-63.
- 17. Yamaguti S. Synopsis of digenetic trematodes of vertebrates. I:Tokyo, Japan. Keigaku Publishing Co. 1971, pp 511-515.
- 18. Ching HL. Evaluation of characters of the digenean family Gymnophallidae Morozov. 1955. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 1995;52(suppl):78-83.
https://doi.org/10.1139/f95-511
- 19. Ching HL.
Paragymnophallus odhneri gen.n., sp. n. (Trematoda: Gymnophallidae) for Gymnophallus somateriae sensu Odhner (1900, 1905). Can J Zool 1973;51:807-810.
https://doi.org/10.1139/z73-120
- 20. Cremonte F, Gilardoni C, Pina S, Rodrigues P, Ituarte C. Revision of the family Gymnophallidae Odhner, 1905 (Digenea) based on morphological and molecular data. Parasitol Int 2015;64:202-210.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2014.12.003
- 21. Dollfus RP. Le Trématode des perles de nacre des moules de Provence. CR Acad Sci Paris 1923;176:1427-1429. (in French)..
- 22. Bartoli P. Note preliminaire sur l’anatomie et la biologie de Parvatrema timondavidi n. sp. (Trematoda: Digenea). CR Acad Sci Paris 1963;273:518-520. (in French)..
- 23. Bartoli P. Données novelles sur la morphologie et la biologie de Parvatrema timondavidi Bartoli 1963 (Trematoda: Digenea). Ann Parasitol (Paris) 1965;40:155-164. (in French)..
- 24. Bartoli P. Researches sur le Gymnophallidae F. N. Morozov, 1955 (Digenea), parasites d’oiseaux des côtes de Camargue: systématique, biologie et ecologie. Thèse. Université de Droit, d’Economie et des Sciences d’Aix-Marseille; 1974. 1-338.
- 25. Ogata T. On the morphology, ecology and life history of an agamodistome parasitic in a bivalve, Paphia (Ruditapes) philippinarum (Adames et Reeve). Sci Rep Tokyo Bunrika Daigaku 1944;7:1-24.
- 26. Endo T, Hoshina T. Redescription and identification of a gymnophallid trematode in a brackish water clam, Tapes (Ruditapes) philippinarum
. Jpn J Parasitol 1974;23:73-77.
- 27. Shimura S, Yoshinaga T, Wakabayashi H. Two species of marine metacercariae, Parvatrema duboisi (Gymnophallidae) and Proctoeces sp. (Fellodistomidae), in the clam Tapes philippinarum from Lake Hamana, Japan: morphology and level of infection. Fish Pathol (Japan) 1982;17:187-194. (in Japanese). https://doi.org/10.3147/jsfp.17.187
- 28. Gaevskaya AV. On the biology of Parvatrema duboisi Bartoli, 1963 (Trematoda: Gymnophallidae) in the Black Sea. Parazitologiia 1973;7:61-66. (in Russian)..
- 29. Özer A, Güneydag S. Seasonality and host-parasite interrelationship of Mytilus galloprovincialis parasites in Turkish Black Sea coasts. J Marine Biol Assoc UK 2015;95:1591-1599.
https://doi.org/10.1017/s0025315415000740
 , Taehee Chang1, Hyejoo Shin1, Seungwan Ryoo1, Sooji Hong1, Jeonggyu Lee1, Hyemi Song1, Jaeeun Cho1, Deok-Gyu Kim1, Hojong Jun2, Min-Jae Kim3, Eun Jeong Won4, Eun-Taek Han5
, Taehee Chang1, Hyejoo Shin1, Seungwan Ryoo1, Sooji Hong1, Jeonggyu Lee1, Hyemi Song1, Jaeeun Cho1, Deok-Gyu Kim1, Hojong Jun2, Min-Jae Kim3, Eun Jeong Won4, Eun-Taek Han5 , Eun-Hee Shin6,7, Jong-Yil Chai1,6,*
, Eun-Hee Shin6,7, Jong-Yil Chai1,6,*