Abstract
The DM9 domain is a protein unit of 60–75 amino acids that has been first detected in the fruit fly Drosophila as a repeated motif of unknown function. Recent research on proteins carrying DM9 domains in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae and the oyster Crassostrea gigas indicated an association with the uptake of microbial organisms. Likewise, in the trematode Fasciola gigantica DM9-1 showed intracellular relocalization following microbial, heat and drug stress. In the present research, we show that FgDM9-1 is a lectin with a novel mannose-binding site that has been recently described for the protein CGL1 of Crassostrea gigas. This property allowed FgDM9-1 to agglutinate gram-positive and -negative bacteria with appropriate cell surface glycosylation patterns. Furthermore, FgDM9-1 caused hemagglutination across all ABO blood group phenotypes. It is speculated that the parenchymal located FgDM9-1 has a role in cellular processes that involve the transport of mannose-carrying molecules in the parenchymal cells of the parasite.
-
Key words: Fasciola gigantica, DM9 domain, mannose-binding, agglutination
In previous work we have described
Fasciola gigantica DM9-1 (FgDM9-1) as a 16.8 kDa cytoplasmic protein which showed intracellular relocalization to vesicular structures following bacterial, drug and heat stress [
1]. This was similar to the behavior observed for
Anopheles gambiae PRS1 (AgPRS1) which relocated from the cytoplasm to vesicles upon infection with
Plasmodium [
2]. AgPRS1 was detected in salivary glands and midgut whereas FgDM9-1 was present in parenchymal cells. Both proteins carried a pair of DM9 domains that were described in protein family databases as domains of unknown function, e.g., IPR006616 (InterPro), SM00696 (Smart), DUF3421 (Pfam), and 128937 (CDD). Furthermore, recombinant FgDM9-1 showed a tendency to oligomerize and the protein was predicted to have a β-strand rich secondary structure. The same behavior was observed for
Opisthorchis viverrini DM9-1 a homologous (but not orthologous) protein with 2 DM9 domains that was detected in the tegumental layer [
3]. Circular dichroism analysis of OvDM9-1 supported a high β-strand content of DM9 proteins. Structure analysis in Phyre2 showed similarity to
Ascaris cytoplasmic motility protein (MFP2), a protein found in sperms that contains 4 DM9 domains [
4]. A biochemical activity could not be assigned, neither to MFP2 nor to PRS1, FgDM9-1, and OvDM9-1. Shortly afterwards
Crassostrea gigas lectin 1 (CGL1), a homologous 15.5 kDa protein with 2 DM9 domains, was described as a novel lectin with high mannose specificity [
5,
6]. CGL1 contained 2 mannose-binding sites that were unrelated to any previously described mannose-binding site. Each of the 2 DM9 domains contributes residues to each binding site and some of these residues show high conservation among proteins with DM9 domains.
This study investigated whether FgDM9-1 was capable to bind mannose as CGL1 and if this lectin activity extended to bacteria and human erythrocytes with mannosylated molecules on their surface. Concanavalin A (ConA), an extensively researched protein of the jack bean with comparable lectin properties [
7,
8] but a distinct mannose-binding site [
9] was used for comparison. The structural conservation of the mannose-binding sites between CGL1 and FgDM9-1 was theoretically analyzed to understand how residues can be substituted without disturbing binding activity.
The resolved tertiary structure of CGL1 [
5] (PDB: 5IDB) was used as a template to build a model of FgDM9-1 in SWISS-MODEL [
10]. The amino acid alignment created during the modelling process is shown in
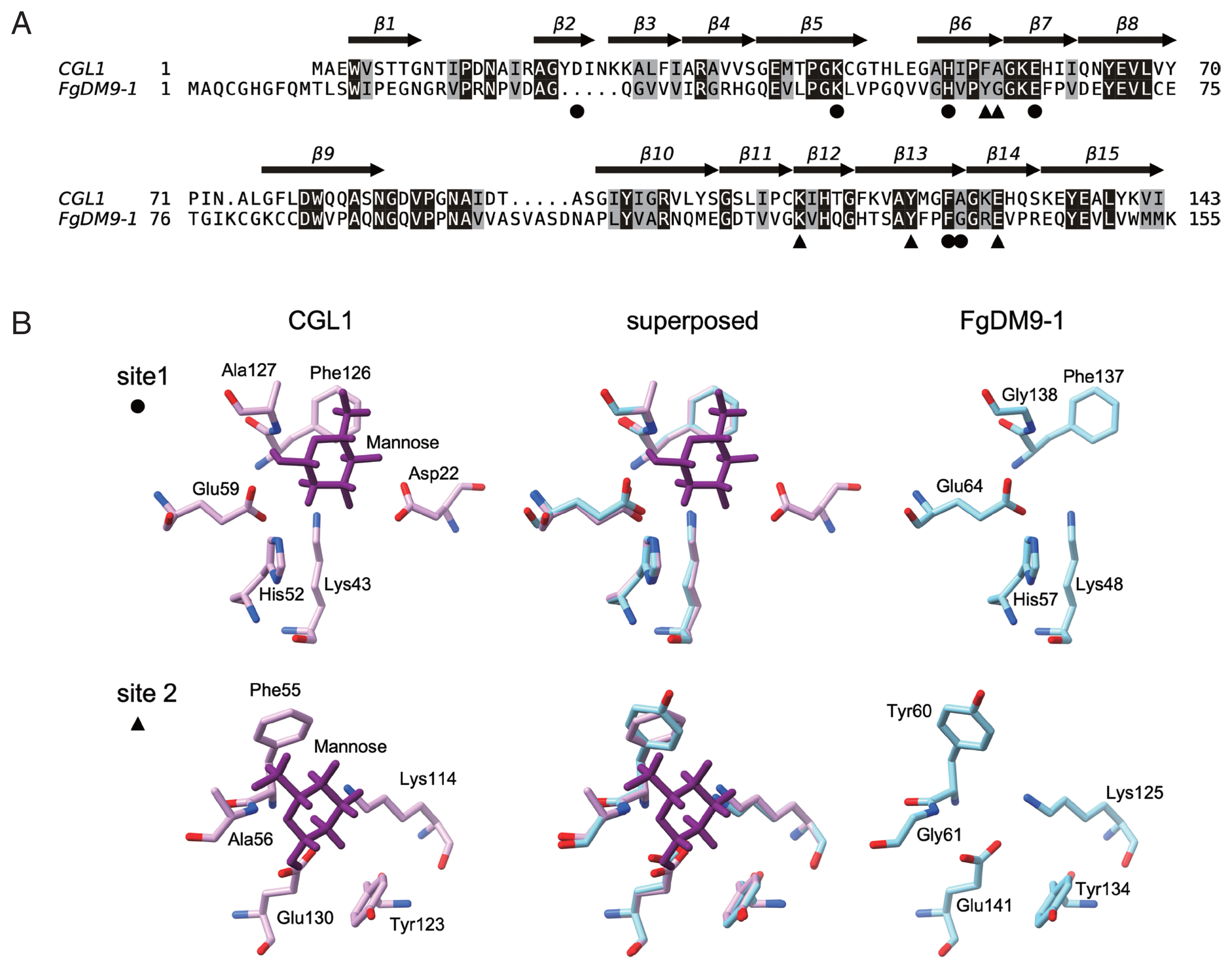
Fig. 1A. Sequence conservation between the 2 proteins is modest with 42 residues fully conserved resulting in an identity of 26.2% as calculated in EMBOSS aligncopypair [
11]. FgDM9-1 carries ten additional residues at the N-terminus and one additional residue at the C-terminus. Larger internal differences are 2 indels, a 5-residue deletion and a 5-residue insertion. The 2 mannose-binding sites identified in CGL1 [
5,
6] show high conservation in FgDM9-1 with the exception of an aspartic acid (Asp22) in the first binding site (
Fig. 1B). This residue is missing due to the 5-residue deletion in FgDM9-1 and while it seems to be essential for in vitro mannose-binding of CGL1 [
6] there is at present no proof that this is also the case in vivo. In any way, the second binding site of CGL1 contains only 5 residues lacking an equivalent aspartic acid. On the other hand, the 5-residue insertion carried by FgDM9-1 and other trematode DM9 proteins might provide a residue that contributes to mannose-binding in binding site 2. The 5 residues include an aspartic acid, and this residue is also present in
Anopheles gambiae PRS1 a homologous protein with 2 DM9 domains [
2]. In the model none of these 5 residues is close enough to interact with mannose in the second binding site. This might be a limitation of the automated calculation because there is no corresponding CGL1 sequence to model on. In addition to the lack of aspartic acid in binding site 1 FgDM9-1 carries a glycine in place of alanine (CGL1: DKHEFA, FgDM9-1: -KHEFG) and binding site 2 has 2 substitutions tyrosine for phenylalanine, glycine for alanine (CGL1: KYEFA, FgDM9-1: KYEYG). In both proteins histidine in binding site 1 is substituted by tyrosine in binding site 2. These substitutions are conservative because the involved amino acids are similar in their physicochemical properties and should support the binding of mannose. The always found lysine and glutamic acid in the binding sites are also highly conserved in the DM9 domains of other proteins suggesting that they are the most important residues in this novel mannose-binding site. Substitution of lysine in binding site 1 by alanine knocked out mannose-binding in CGL1 [
6].
The complete 468 nt open reading frame of the FgDM9-1 transcript (GenBank: KT865082) [
1] was amplified by PCR. The primers 5′-cat atg GCG CAA TGT GGT CAC G-3′ and 5′-ctc gag TCA TTT CTT CAT CCA CAC-3′ introduced terminal
Nde I and
Xho I restriction endonucleases sites (lower case) at start- and stop-codon (underlined), respectively. These sites were used to insert the DNA fragment into the expression vector pET21b(+). Recombinant FgDM9-1 without His-tag was expressed in
Escherichia coli BL-21(DE3) and purified from the soluble bacterial protein fraction by affinity chromatography on D-mannose agarose. Mannose in the eluate was depleted by filtration and washes on 10 kDa cutoff centrifugal filter devices. The concentrated protein solution was transferred to a microtube and kept at −20°C. The plasmid pQE30-FgDM9-1 created in a previous analysis was used to obtain recombinant FgDM9-1 with an N-terminal His-tag as described [
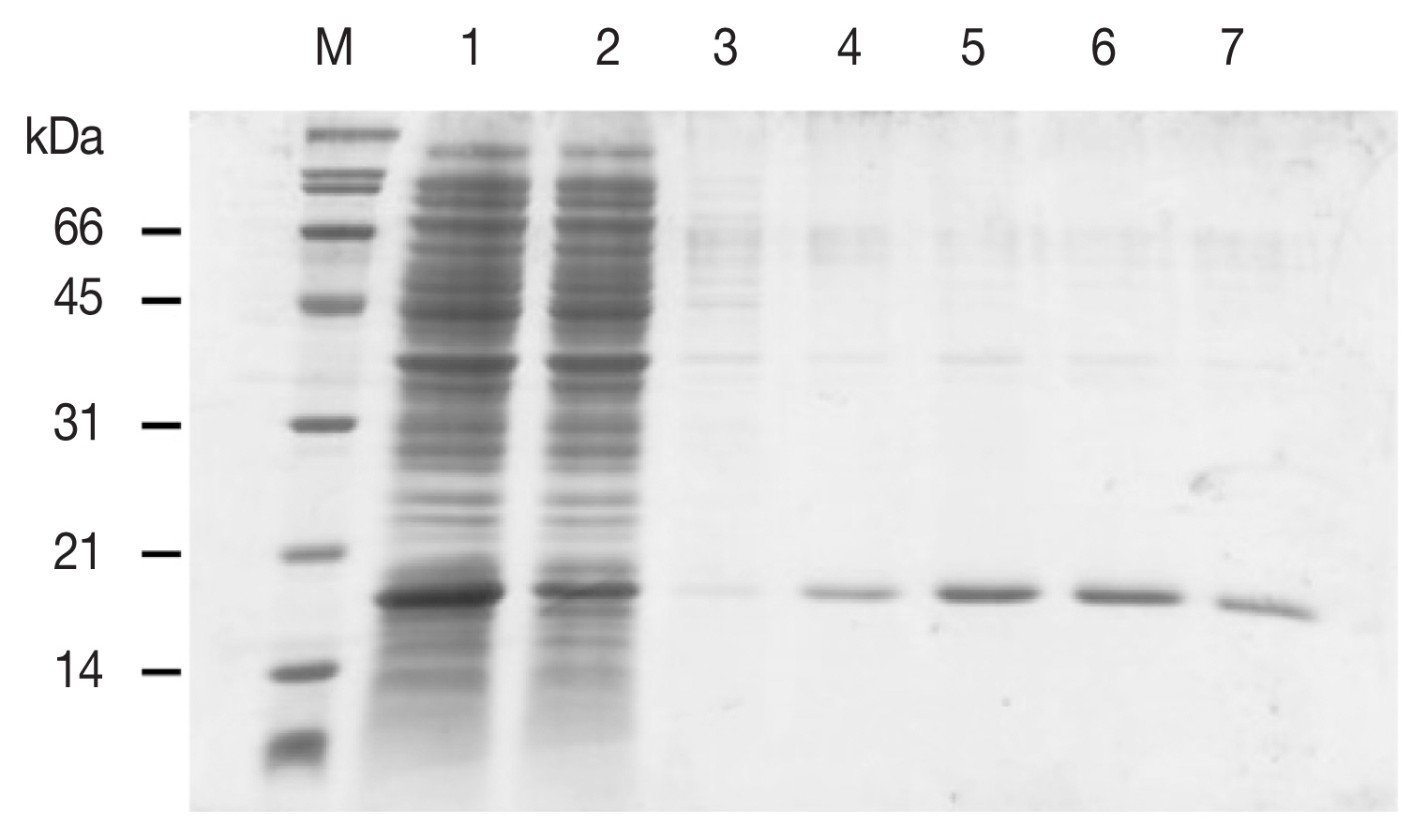
1]. The Bio-Rad Protein Assay was used to determine protein concentration. Only recombinant FgDM9-1 expressed without His-tag showed mannose-binding and migrated as a monomer at the expected 16.8 kDa molecular mass in SDS-PAGE (
Fig. 2). This result strongly supports the structure model of FgDM9-1 built on CGL1 with 2 conserved mannose-binding sites. It also suggests that aspartic acid as found in CGL1 binding site 1 is not essential for binding of mannose by FgDM9-1.
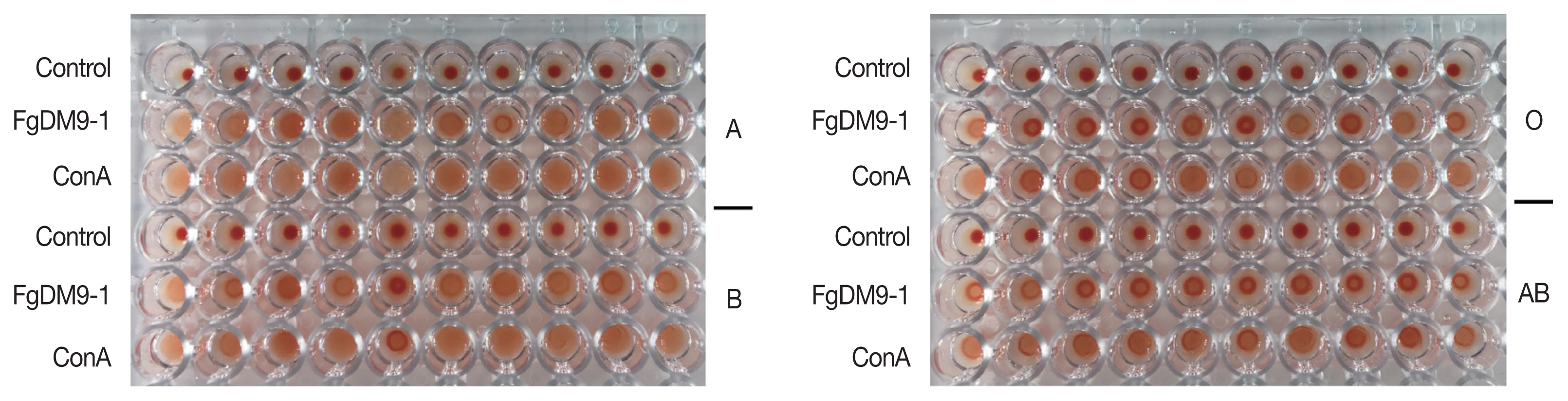
Forty EDTA red blood cell (RBC) samples classified by their ABO group specificity (10 each for A, B, AB, O) were obtained from Blood Bank Thammasat University Hospital and stored at 4°C until use. The protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethical Review Sub-Committee Board for Human Research Involving Sciences of Thammasat University (COE no. 007/2562). Hemagglutination activity of FgDM9-1 was assayed on a microtiter plate following Adamová and colleagues [
12]. RBC were packed by centrifugation, washed in PBS, packed again and resuspended in PBS to a final concentration of 1% [v/v]. A volume of 50 μl of FgDM9-1 [1 mg/ml] was pipetted into each well of a 96-well FASTEC U plate. ConA at the same concentration was used as a positive control and PBS was used as a negative control. In the next step 50 μl of 1% RBC were added to each well, mixed and incubated at room temperature for 45 min until the negative control had fully sedimented. Agglutination reactions were visually observed and graded as positive/negative. These experiments were done to evaluate whether FgDM9-1 was able to cross-link cells. Such activity is only possible if a single protein contains either multiple binding sites or if it oligomerizes to present more than one binding site. All samples regardless of blood group showed agglutination following incubation with either FgDM9-1 or ConA (
Fig. 3).
Twelve gram-positive and -negative bacterial strains (
Table 1) were kindly provided by Assistant Professor Dr. Potjanee Srimanote (Microbiology, Graduate Program in Biomedical Sciences, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Thammasat University). The protocol was reviewed and approved by the Biosafety Committee of Thammasat University (Ref no. 065/2562). All bacteria were grown in LB medium at 37°C, 250 rpm shaking until an OD
600 of 0.5. A volume of 50 μl of each bacterial suspension was pipetted into the wells of a 96-well FASTEC U plate. Then 50 μl of FgDM9-1 in TBS [1 mg/ml] were added and incubated at 37°C, 16 hr. ConA was used as a positive control at the same concentration. Agglutination reactions were visually observed and graded as positive/negative.
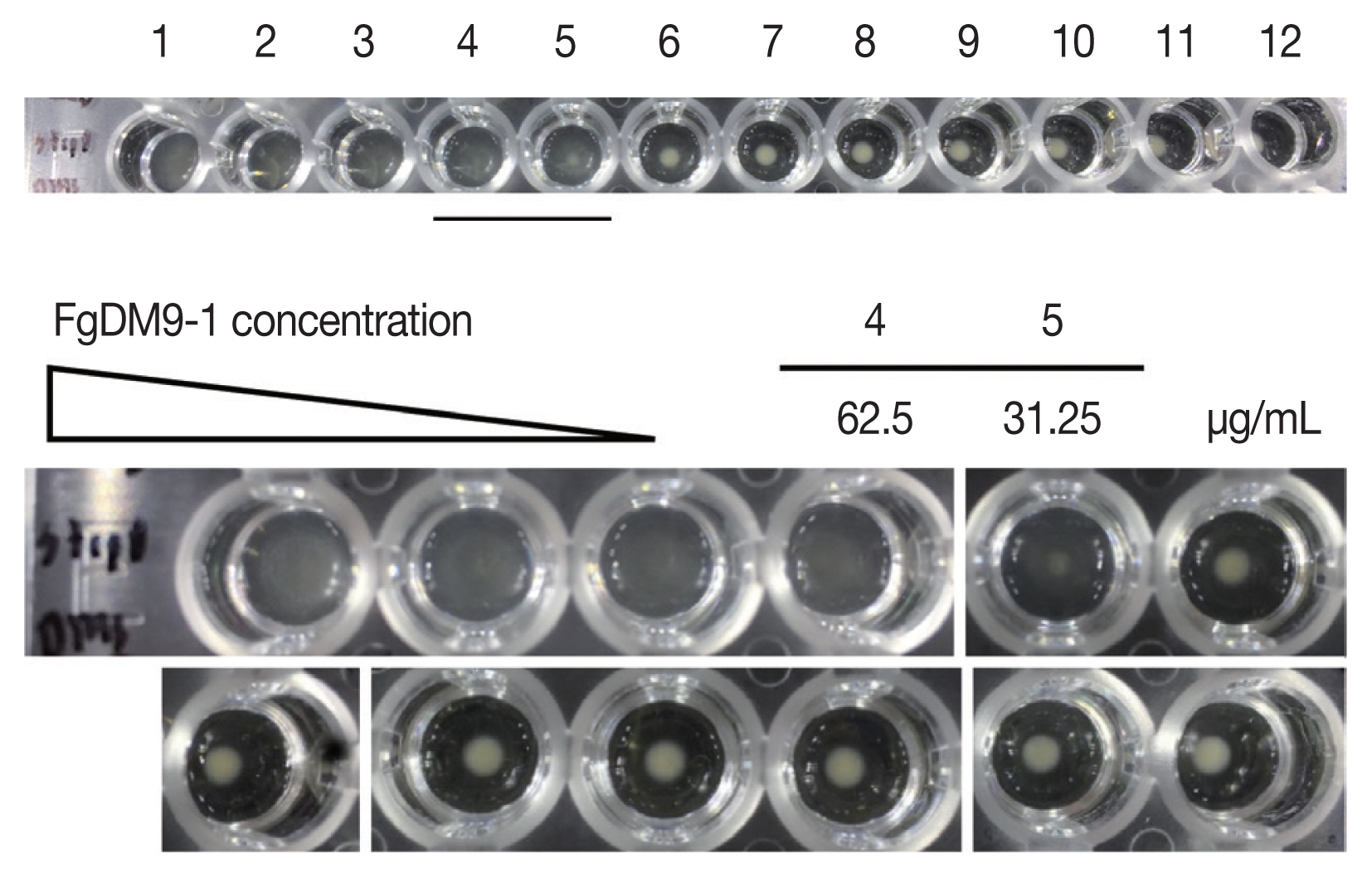
Streptococcus group A was used to find the minimum amount of FgDM9-1 that caused agglutination. FgDM9-1 protein solution was 2-fold diluted from 1 mg/ml to 4.88×10
−4 mg/ml and tested as above against 50 μl of bacterial suspension. All assays were performed 2 times with independently prepared FgDM9-1. Many but not all bacterial species carry mannose containing glycosylation on their surface. Six of the twelve tested bacterial strains were agglutinated by FgDM9-1 and ConA (
Table 1). Only a single species,
Serratia marcescens, was agglutinated by FgDM9-1 but not ConA. Five bacterial samples were neither agglutinated by FgDM9-1 nor ConA. The minimum concentration of FgDM9-1 that could fully agglutinate
Streptococcus group A was 62.5 μg/ml (
Fig. 4).
In conclusion, FgDM9-1 showed mannose-binding and lectin activity that facilitated agglutination of pro- and eukaryotic cells similar to ConA. The plant lectin ConA is a homotetrameric protein formed by 26.5 kDa subunits, each with one mannose/glucose-binding site [
9]. Monomeric FgDM9-1 contains 2 potential mannose-binding sites comparable to the homologous CGL1. The 2 studies concerning CGL1 in the oyster
Crassostrea gigas showed occupation of both binding sites by mannose in the crystallized CGL1 but found only the first site comprising 6 residues occupied by mannose in in vitro studies or upon isolation of the native protein [
5,
6]. The second site lacks an aspartic acid residue which was argued by the authors to stabilize mannose-binding through additional bonds. Substitution of residues in the first binding site of CGL1 (D22A, K43A, H52A) supported the importance of these residues in binding [
6]. Unfortunately, these mutant forms were not tested in presence of mannose in crystallization analysis to confirm the results in a situation that demonstrated binding of 2 mannose residues of the wild type sequence. Of course, a simple in vivo assay might not be able to mimic the acute intracellular situation in which the protein binds mannose. What are these situations? PRS1 of
Anopheles gambiae was found upregulated if infected with
Plasmodium and in blood feeding [
2,
13]. As mentioned in the introduction PRS1 also relocated to vesicles in salivary glands and midgut in infection. Likewise, FgDM9-1 when tested in insect cells reacted by relocalization to vesicles following cellular stress in form of heat, exposure to bacteria (
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and
Escherichia coli) or incubation with chloroquine [
1]. In
Crassostrea gigas CGL1 was abundant in hepatopancreas, mantle and hemocytes. In hemocytes challenged with bacteria relocalization of CGL1 from the cell membrane to the cytoplasm was observed [
6]. The authors speculated that proteins carrying DM9 domains provide an important defense mechanism against microbe invasion. This function is questionable for FgDM9-1 for 2 reasons; firstly
Fasciola gigantica should not encounter bacteria in host liver and bile ducts; secondly the protein was detected in the parenchyma, an internal tissue without direct host contact. The experimental observations might overstate a protective function when the basic function might be in general cellular transport of molecules with mannose residues. Further experiments would be necessary to identify these molecules in
Fasciola and other trematodes like
Opisthorchis.
Notes
-
We declare that we have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This study was financially supported by a grant through Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Thammasat University, contract no. 3/2561 and Thammasat University research fund, contract no. TUGR 2/46/2562.
Fig. 1Comparison of the amino acid sequences and mannose-binding sites of FgDM9-1 and CGL1. Panel A: Pairwise alignment of FgDM9-1 and CGL1 calculated during modeling of FgDM9-1 in SWISS-MODEL [
10]. TEXshade [
14] was used to prepare the graphics. Invariable residues are shaded in black and conserved residues are shaded in gray. The β-strand secondary structure of CGL1 is indicated by arrows and numbered from β1 to β15. The residues of CGL1 that were found to form 2 mannose-binding sites are indicated by black circle (●) and triangle (▲) symbols [
5,
6] Panel B: Structure comparison of the 2 mannose-binding sites of CGL1 and FgDM9-1. A model of FgDM9-1 using CGL1 (PDB: 5IDB) as template was calculated in SWISS-MODEL. Asp22 in binding site 1 of CGL1 is absent in FgDM9-1 and is not replaced by a different residue in the model. Ala127 in CGL1 is substituted by Gly138 in FgDM9-1. Phe55 and Ala156 in binding site 2 of CGL1 are substituted by Tyr60 and Gly61 in FgDM9-1. Binding site 2 of CGL1 comprises only 5 residues and lacks an equivalent to Asp22 in site 1. Glycine and tyrosine are by their physicochemical properties well suited as substitutions for alanine and phenylalanine in CGL1. Molecular graphics were performed in UCSF ChimeraX version 1.1.1 [
15].
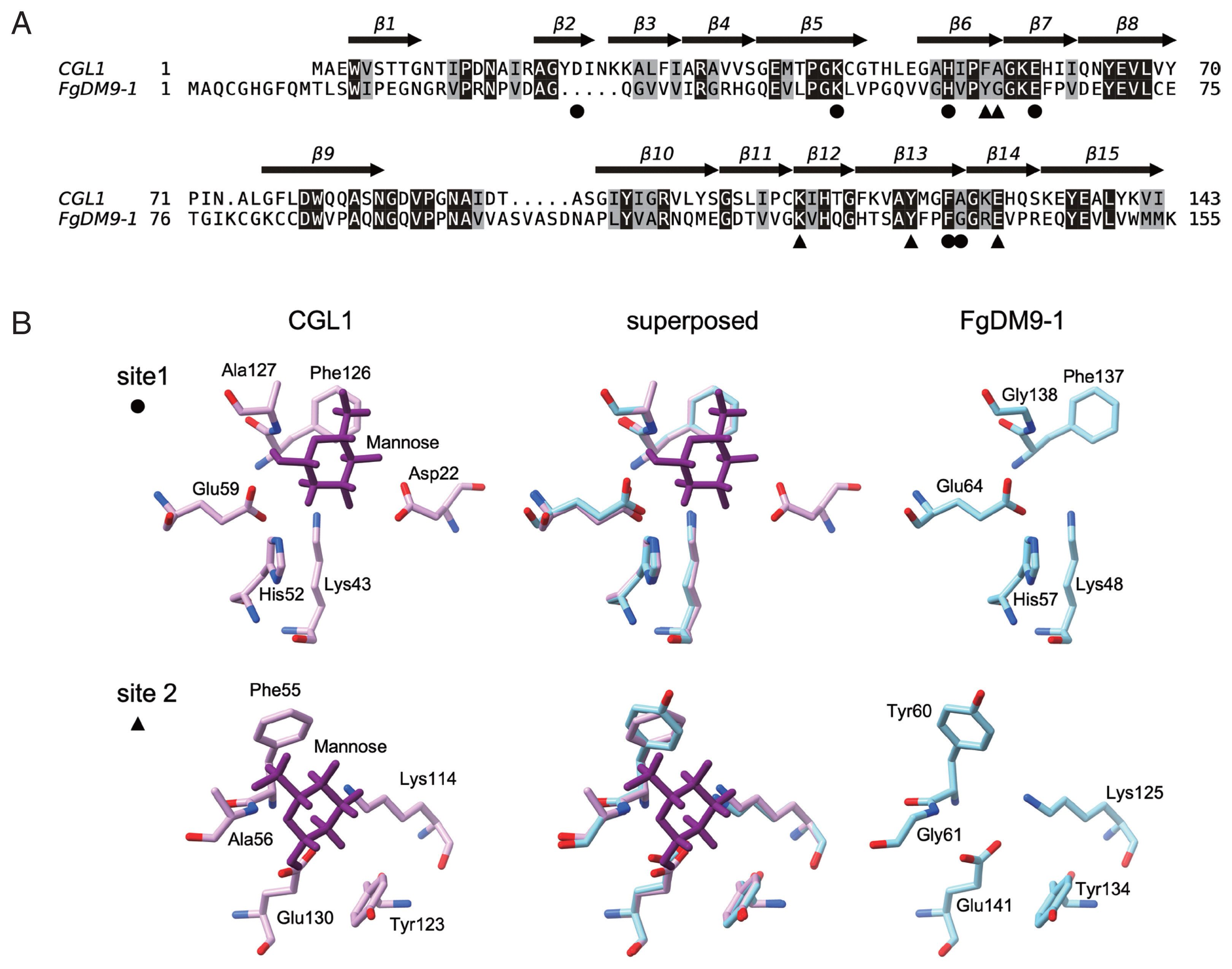
Fig. 2SDS-PAGE showing the purification of E. coli expressed soluble FgDM9-1 by mannose affinity chromatography. M: Broad range protein standard marker (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California USA). Lane 1: flow through, lanes 2–3: wash fractions, lanes 4–7: elution fractions. Recombinant FgDM9-1 migrates as a monomer at the expected molecular mass of 16.8 kDa.
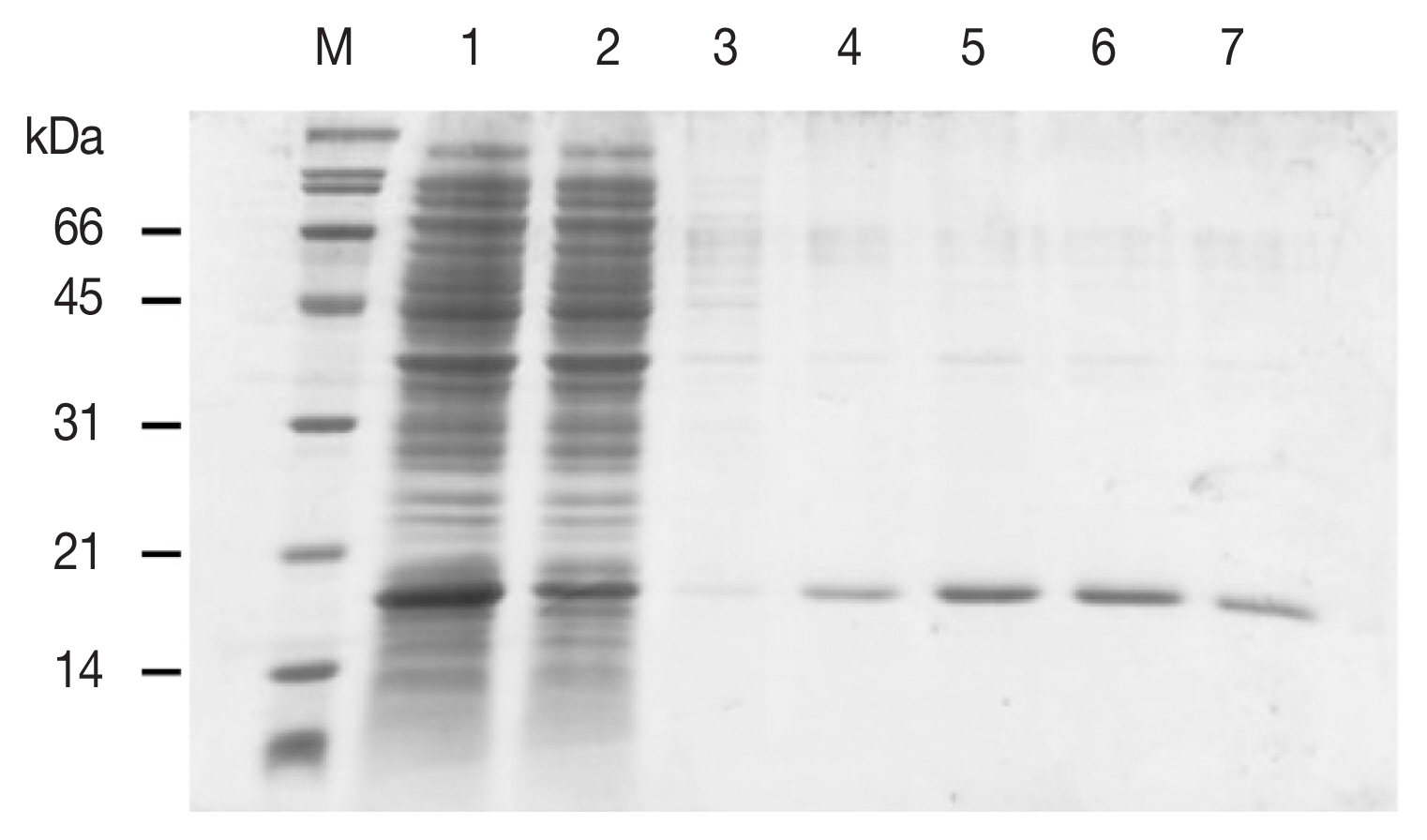
Fig. 3Results of hemagglutination assay classified by ABO blood groups. Ten samples each of human red blood cells for blood groups A, B, O, AB were tested for agglutination by FgDM9-1 and ConA at a final concentration of 0.5 mg/ml. FgDM9-1 showed clear effects for all samples but somewhat weaker than ConA, especially for blood group samples O and AB.
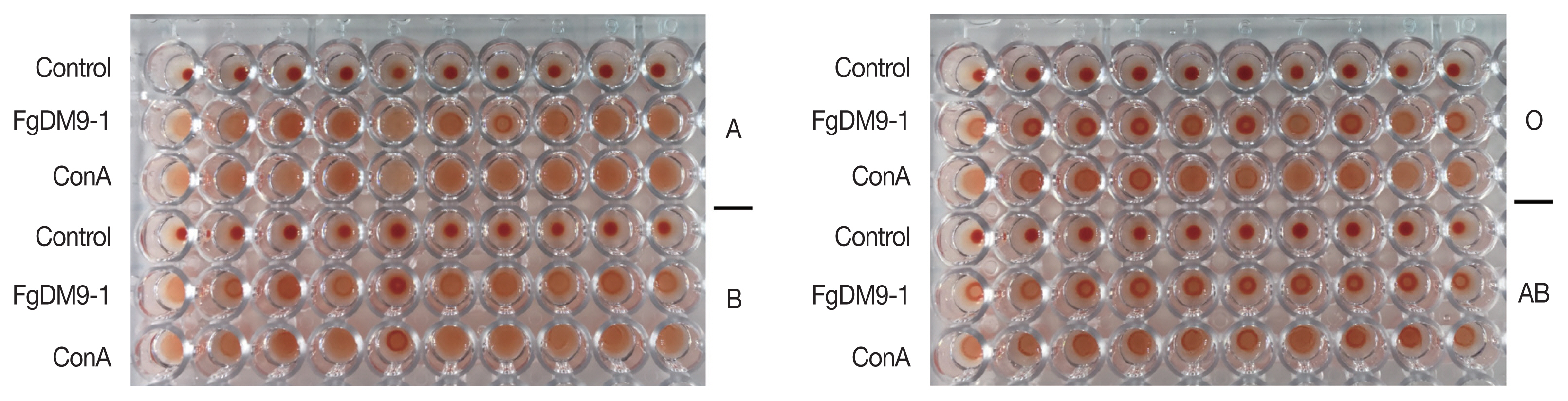
Fig. 4Results of FgDM9-1 titer in bacterial agglutination assay. The amount of FgDM9-1 necessary to agglutinate Streptococcus group A cells contained in 50 μl bacterial suspension at OD600 of 0.5 was tested by adding 50 μl of 2-fold dilutions of FgDM9-1. Wells 1–12 contained final concentrations of FgDM9-1 ranging from 500 μg to 0.49 μg/ml. Well 4 at 62.5 μg/ml FgDM9-1 still caused complete agglutination while 31.25 μg/ml FgDM9-1 caused incomplete aggregation in well 5.
Table 1
Table 1
|
Bacterial strain |
|
Agglutination |
|
ConA |
FgDM9-1 |
|
E. coli Top10 |
Gram-negative rod |
+ |
+ |
|
Shigella group D |
Gram-negative rod |
+ |
+ |
|
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) |
Gram-positive cocci |
+ |
+ |
|
Streptococcus group A |
Gram-positive cocci |
+ |
+ |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae
|
Gram-positive lancet-shaped cocci |
+ |
+ |
|
Vibrio cholerae VP03:k6 |
Gram-negative curved rods |
+ |
+ |
|
Serratia marcescens
|
Gram-negative rod |
− |
+ |
|
E. coli ETEC LT+ ST− |
Gram-negative rod |
− |
− |
|
E. coli AAEC TH |
Gram-negative rod |
− |
− |
|
Enterococcus spp. |
Gram-positive cocci |
− |
− |
|
Yersinia enterocolitica
|
Gram-negative coccobacillus |
− |
− |
References
- 1. Phadungsil W, Smooker PM, Vichasri-Grams S, Grams R. Characterization of a Fasciola gigantica protein carrying two DM9 domains reveals cellular relocalization property. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2016;205:6-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molbiopara.2016.02.008
- 2. Chertemps T, Mitri C, Perrot S, Sautereau J, Jacques JC, Thiery I, Bourgouin C, Rosinski-Chupin I. Anopheles gambiae PRS1 modulates Plasmodium development at both midgut and salivary gland steps. PLoS One 2010;5:e11538. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011538
- 3. Labbunruang N, Phadungsil W, Tesana S, Smooker PM, Grams R. Similarity of a 16.5kDa tegumental protein of the human liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini to nematode cytoplasmic motility protein. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2016;207:1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molbiopara.2016.04.002
- 4. Grant RP, Buttery SM, Ekman GC, Roberts TM, Stewart M. Structure of MFP2 and its function in enhancing MSP polymerization in Ascaris sperm amoeboid motility. J Mol Biol 2005;347:583-595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.01.054
- 5. Unno H, Matsuyama K, Tsuji Y, Goda S, Hiemori K, Tateno H, Hirabayashi J, Hatakeyama T. Identification, characterization, and X-ray crystallographic analysis of a novel type of mannose-specific lectin CGL1 from the pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Sci Rep 2016;6:29135. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29135
- 6. Jiang S, Wang L, Huang M, Jia Z, Weinert T, Warkentin E, Liu C, Song X, Zhang H, Witt J, Qiu L, Peng G, Song L. DM9 domain containing protein functions as a pattern recognition receptor with broad microbial recognition spectrum. Front Immunol 2017;8:1607. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01607
- 7. Sumner JB, Howell SF. Identification of Hemagglutinin of Jack Bean with Concanavalin A. J Bacteriol 1936;32:227-237. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.32.2.227-237.1936
- 8. Goldstein IJ, Hollerman CE, Smith EE. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. II. Inhibition studies on the interaction of concanavalin A with polysaccharides. Biochemistry 1965;4:876-883. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00881a013
- 9. Derewenda Z, Yariv J, Helliwell JR, Kalb AJ, Dodson EJ, Papiz MZ, Wan T, Campbell J. The structure of the saccharide-binding site of concanavalin A. EMBO J 1989;8:2189-2193. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08341.x
- 10. Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, de Beer TAP, Rempfer C, Bordoli L, Lepore R, Schwede T. SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 2018;46:296-303. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky427
- 11. Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A. EMBOSS: the European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet 2000;16:276-277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9525(00)02024-2
- 12. Adamová L, Malinovská L, Wimmerová M. New sensitive detection method for lectin hemagglutination using microscopy. Microsc Res Tech 2014;77:841-849. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.22407
- 13. Rosinski-Chupin I, Briolay J, Brouilly P, Perrot S, Gomez SM, Chertemps T, Roth CW, Keime C, Gandrillon O, Couble P, Brey PT. SAGE analysis of mosquito salivary gland transcriptomes during Plasmodium invasion. Cell Microbiol 2007;9:708-724. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00822.x
- 14. Beitz E. TEXshade: shading and labeling of multiple sequence alignments using LATEX2 epsilon. Bioinformatics 2000;16:135-139. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/16.2.135
- 15. Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Meng EC, Couch GS, Croll TI, Morris JH, Ferrin TE. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci 2021;30:70-82. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3943
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- The Calicophoron daubneyi genome provides new insight into mechanisms of feeding, eggshell synthesis and parasite-microbe interactions
Shauna M. Clancy, Mark Whitehead, Nicola A. M. Oliver, Kathryn M. Huson, Jake Kyle, Daniel Demartini, Allister Irvine, Fernanda Godoy Santos, Paul-Emile Kajugu, Robert E. B. Hanna, Sharon A. Huws, Russell M. Morphew, J. Herbert Waite, Sam Haldenby, Mark W
BMC Biology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - DM9CP-8 upon binding microbes activates MASPL-1-C3 axis to regulate the mRNA expressions of IL17s in oysters
Yinan Li, Jiejie Sun, Wenwen Yang, Yu Liu, Xingye Lian, Lingling Wang, Linsheng Song
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2025; 302: 140470. CrossRef - The regulation of CgDM9CP-7 for maintaining the homeostasis of hemolymph microbiota in oyster Crassostrea gigas
Shuyi Mu, Yinan Li, Shurong Li, Weishuai Shan, Qiuyan Guo, Zihan Wang, Wei Wu, Lingling Wang, Jiejie Sun, Linsheng Song
Comparative Immunology Reports.2025; 8: 200225. CrossRef - A novel intracellular signaling pathway elicited by DM9CP-6 regulates immune responses in oysters
Jiejie Sun, Yinan Li, Yu Liu, Lingling Wang, Linsheng Song
Cell Communication and Signaling.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A novel DM9-containing protein 7 involved in regulating the expression of CgMyD88 and CgIL-17 in oyster Crassostrea gigas
Yinan Li, Xingye Lian, Wenwen Yang, Jinyuan Leng, Jiejie Sun, Yu Liu, Siqi Fan, Lingling Wang, Linsheng Song
Developmental & Comparative Immunology.2024; 150: 105076. CrossRef - Mannose oligosaccharide recognition of CGL1, a mannose-specific lectin containing DM9 motifs from Crassostrea gigas, revealed by X-ray crystallographic analysis
Tomomitsu Hatakeyama, Kazuki Masuda, Mizuki Kudo, Koshi Tanaka, Ayaka Takeuchi, Hideaki Unno
The Journal of Biochemistry.2024; 175(1): 35. CrossRef - Carbohydrate-binding ability of a recombinant protein containing the DM9 motif from Drosophila melanogaster
Tomomitsu Hatakeyama, Fuki Kojima, Issei Ohkawachi, Hitomi Sawai, Hideaki Unno
The Journal of Biochemistry.2024; 175(6): 659. CrossRef -
CgDM9CP-5-Integrin-MAPK Pathway Regulates the Production of CgIL-17s and Cgdefensins in the Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea gigas
Yu Liu, Weilin Wang, Jiejie Sun, Yinan Li, Shasha Wu, Qing Li, Miren Dong, Lingling Wang, Linsheng Song
The Journal of Immunology.2023; 210(3): 245. CrossRef - Functional Diversity of Novel Lectins with Unique Structural Features in Marine Animals
Tomomitsu Hatakeyama, Hideaki Unno
Cells.2023; 12(14): 1814. CrossRef