Abstract
The present study aimed to survey the prevalence of chigger mites and Orientia tsutsugamushi (O. tsutsugamushi) infection in the northern regions of Gangwon-do, Korea. From early February to early June 2015, a total of 17,050 chiggers were collected from striped field mice, Apodemus agrarius, in Cheorwon-gun, Hwacheon-gun, Yanggu-gun, and Goseong-gun, which are well-known endemic areas of scrub typhus in Korea. The chiggers were analyzed using molecular genomic methods, as previously described. Among the 7,964 identified chiggers, the predominant species was Leptotrombidium pallidum (76.9%), followed by L. zetum (16.4%), L. orientale (4.3%), L. palpale (0.3%), L. tectum (0.2%), and Neotrombicula tamiyai (1.8%). The chigger index (CI) was highest in Hwacheon (115.58), followed by Cheorwon (97.02), Yanggu (76.88), and Goseong (54.68). Out of the 79 O. tsutsugamushi-positive chigger pools, 67 (84.8%) were identified as the Boryong strain, 10 (12.7%) as the Youngworl strain, and only 2 were the Jecheon strain. Based on the high infestation of chiggers in striped field rodents and the high rate of O. tsutsugamushi infection in chigger mites, Hwacheon-gun and Cheorwon-gun are presumed to be high-risk areas for scrub typhus. Furthermore, L. pallidum, a major vector of scrub typhus, and the dominant O. tsutsugamushi serotype, the Boryong strain, were found in the northern regions of Gangwon-do, Korea.
-
Key words: Orientia tsutsugamushi, chiggers, scrub typhus, strain, Korea
Introduction
Scrub typhus is caused by the obligate intracytosolic bacteria
Orientia tsutsugamushi, which is transferred to humans by the biting of the larvae of numerous species of trombiculid mites. Scrub typhus (tsutsugamushi illness) is found in Asia-Pacific countries such as Korea, Japan, China, Thailand, Taiwan, and India [
1–
3]. Scrub typhus is the most frequent acute febrile illness in Korea in the autumn, with the number of cases peaking between October and November [
4]. It occurs across Korea, particularly in the southern provinces of Jeolla-do, Gyeongsang-do, and Chungcheongnam-do [
5]. In Korea, it is one of the most frequent arthropod-borne infections.
More than 20 serotypes of
O. tsutsugamushi have been discovered based on antigenic features; the virulence of
O. tsutsugamushi depends on the serotype or strain, and the prevalence of serotypes varies by nation.
O. tsutsugamushi has 3 primary prototypes: Karp, Gilliam, and Kato serotypes [
6]. Several strains of
O. tsutsugamushi have been recorded in Korea, including the 3 important prototype strains Gilliam, Karp, and Kato, as well as strains (Boryong, Wonju, Jecheon, Pajoo, and Youngworl, Kanda, Oishi, OI011, Taguchi, and Shimokoshi) [
7–
9]. The Boryong strain is found in the southern and central parts of Korea, whereas the Gilliam, Karp, and Pajoo strains are mostly found in the central region [
10]. The epidemiological features of
O. tsutsugamushi strains are determined by the vector competence of chiggers in each region. There have been few investigations on chiggers and
O. tsutsugamushi infections in Gangwon-do, where scrub typhus is uncommon. The investigation of the
O. tsutsugamushi infection in Gangwon-do, Korea, which is near the Demilitarized Zone, is necessary.
We collected chigger mites from striped field mice, Apodemus agrarius, to explore O. tsutsugamushi infection in chigger mites, the vectors of scrub typhus in Gangwon-do, Korea.
Materials and Methods
Animals
The trapping of wild rodents was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Yonsei University Mirae Campus, Korea, and was approved by the committee (Approval No., YWC-151203). Standard procedures, as previously described [
11], were followed for the collection and transportation of specimens to minimize hazards from potentially infected rodents.
Wild rodents were captured in 4 locations (Cheorwon; 38° 26′ 92″, 127° 16′ 93″, Hwacheon; 38° 07′ 63″, 127° 52′ 12″, Yanggu; 38° 06′ 24″, 128° 16′ 89″, Cheorwon; 38° 26′ 92″, 127° 16′ 93″, and Goseong; 38° 29′ 27″, 128° 49′ 57″) in Gangwon-do, close to the Demilitarized Zone (
Supplementary Fig. S1). Wild rats were gathered from rice paddies, canals, hills, grasslands, reservoirs, and river banks.
Sherman live folding traps (7.7×9×23 cm; H.B. Sherman Traps, Tallahassee, FL, USA) with peanut butter biscuit bait were used to capture wild rats. Traps were placed 4–5 meters apart from 15: 00 to 18: 00 and removed at 07: 00 the next morning. Each trap was put in a safe container and delivered to the laboratory with the rat inside. The seized wild rats were carbon dioxide killed and identified using morphological keys: gender, weight, and body length.
Collection of chiggers
Chiggers were detached from the ears of wild rats collected using delicate forceps and a needle under a dissecting microscope. Chiggers put on a slide glass using polyvinyl alcohol mounting media (BioQuip Products, Rancho Dominguez, CA, USA). Chiggers were identified using morphological standard criteria after being viewed under a stereomicroscope [
12]. The number of chigger mites per rodent was used to compute the chigger index (CI).
One to 30 chiggers collected from each animal host were pooled and transferred to a reinforced homogenizing tube (Bertin Technology, Montigny-le-Bretonneux, France) containing 2.8 mm zirconium oxide beads (Bertin Technology) and 200 μl of sterile phosphate-buffered saline. The pooled chiggers were homogenized using a bead beater, Precellys 24 (Bertin Technology), with 2 cycles of 20 sec at 6,500 rpm. The genomic DNA was extracted from chiggers using the G-spin Genomic DNA Extraction Kit for Bacteria (iNtRON Biotechnology, Seongnam, Korea) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The extracted DNA was stored at −20°C until further use.
Detection of O. tsutsugamushi using nested PCR
Nested PCR was used to detect the 56-kDa type-specific antigen of O. tsutsugamushi using the Tsutsugamushi Detection Kit (TSUTSU, iNtRON) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Outer primer set: forward primer (5′-GCAATATTGCTAGTGCAATGTCTGC-3′) and reverse primer (5′-ATGCATGCATGRCGCTKCAATTTA-3′); inner primer set: forward primer (5′-ATAGGCCTATAAGTATWGCKGATCG-3′) and reverse primer (5′-CATCTAGAYGCACTATTAGGCAAA-3′). The first primer set was used for amplification, which included an initial denaturation at 94°C for 5 min, 40 cycles of 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 58°C for 30 sec, elongation at 72°C for 40 sec, and a final extension at 72°C for 5 min. Two μl of the first PCR product served as the template for the second round of PCR, which was carried out in 30 cycles under the same circumstances as the first. The PCR products were separated on a 1.5% agarose gel and visualized using a UV transilluminator.
DNA sequencing and phylogenetic analysis
A LaboPass gel and PCR clean-up kit (Cosmogenetech Inc., Seoul, Korea) were used to purify and sequence the PCR products. BLAST (
http:///ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blastn) identified the amplified sequence as a 56-kDa type-specific antigen (TSA) gene. The 56-kDa type-specific antigen (TSA) sequences of
O. tsutsugamushi were aligned using MUSCLE [
13] and the MEGA X program’s unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA). The phylogenetic analysis was carried out using the MEGA X program’s bootstrap and the maximum likelihood tree [
15]. MEGA 6.0 was used to determine the genetic distance, and the topologies were assessed using a bootstrap analysis with 1,000 iterations [
17].
Results
Collection of wild rodents by regions
Between February 2015 and early June 2015, a total of 186 wild rodents were captured in Cheorwon, Hwacheon, Cheorwon, Yanggu, and Goseong in northern Gangwon-do, Korea. The captured wild rodents belonged to 4 species (3 genera) of the Muridae family:
A. agrarius, A. peninsulae, Micromys minutus, and
Myodes regulus. Among these species,
A. agrarius was the most frequently captured, accounting for 90.8% (
n=169) of the total, followed by
Myodes regulus (4.8%,
n=9),
Micromys minutus (3.2%,
n=6), and
A. peninsulae (1.1%,
n=2) (
Table 1). The majority of wild rodents were captured in Hwacheon (
n=106, 57.0%), followed by Cheorwon (
n=43, 23.1%), Goseong (
n=19, 10.2%), and Yanggu (
n= 18, 9.7%) (
Table 1).
Among the wild rodents gathered in the research region, 17,050 chiggers were obtained from
A. agrarius. 150 (88.8%) of the 169
A. agrarius were infested with larval mites (
Table 2). Yanggu had the greatest infestation rate (100.0%, 17 of 17), while Cheorwon had the lowest (69.4%, 25 of 36). Hwacheon has the highest chigger index (CI) (115.58 CI), followed by Cheorwon (97.02 CI), Yanggu (76.88 CI), and Goseong (54.68 CI) (
Table 2).
Half of the detached chiggers were submitted for identification (
Table 3). The 7,964 chigger mites included 5
Leptotrombidium species and one
Neotrombicula species.
Leptotrombidium pallidum (L. pallidum) was the most common species (76.9%,
n=6,124), followed by
L. zetum (16.4%,
n=1,308),
Neotrombicula tamiyai (N. tamiyai) (1.8%,
n=150),
L. palpale (0.3%,
n=24), and
L. tectum (0.2%,
n=16)
L. pallidum was the most prevalent species in all research regions, with the largest geographical occurrence in Hwacheon (61.3%), Cheorwon (21.3%), Yanggu (8.8%), and Goseong (8.6%).
For the identification of
O. tsutsugamushi, 367 pools from 9,086 chiggers were submitted to nested PCR (
Table 4). The bacteria were found in 79 of the 367 chigger pools (0.9% minimum positive rate, 24.5% maximum positive rate). Cheorwon had the highest minimum positive rate of 1.6% (30 out of 73), followed by Yanggu (1.2%, 9 out of 28), Hwacheon (0.6%, 38 out of 242), and Goseong (0.4%, 2 out of 24).
In 79
O. tsutsugamushi-positive chigger pools, 3 strains of
O. tsutsugamushi were found. Boryong (84.8%, 67 of 79) was the most common
O. tsutsugamushi strain, followed by Youngworl (12.7%, 10 of 79) and Jecheon strains (2.5%, 2 of 79). Boryong strain filled 73.7% of the 38 pools in Hwacheon, with 28 pools, while Youngworl strain occupied 26.3%, with 10 pools (
Table 4). Boryeong strains were discovered in 8 of 9 pools in Yanggu, accounting for 88.9%, while Jecheon strains were detected in 11.1% of pools in Goseong. Boryong and Jecheon strains were each detected in Goseong. In Cheorwon, however, only the Boryeong strain was found. Boryong and Youngworl strains were found in the Hwacheon mountainous region, while only Boryong strains were found in the Cheorwon plains. Boryong and Jecheon strains were found in both Yanggu and Goseong, which were linked by mountain ranges (
Table 4).
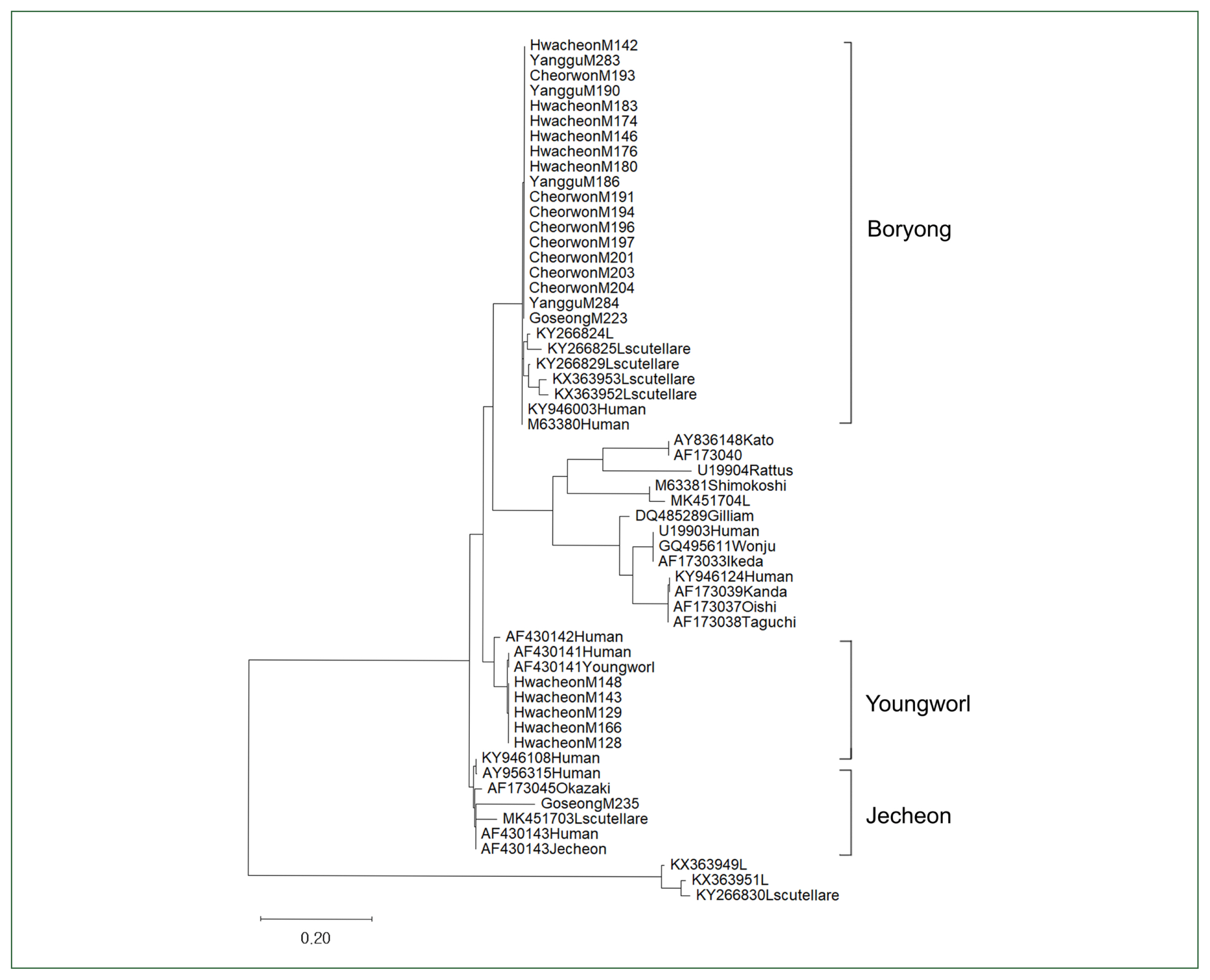
A phylogenetic study of
O. tsutsugamushi strains of chigger mites in northern Gangwon-do was undertaken, and it was categorized into 3 clusters, exhibiting Boryong, Jecheon, and Youngworl strains (
Fig. 1). Boryong strains isolated from chigger mites in the Hwacheon, Yanggu, and Cheorwon areas correlated with the reference Boryong strain (GenBank accession numbers: AM494475). The M235 Jecheon strain (OQ656415) obtained from Goseong chiggers was similar to the reference Jecheon strain (AF430143), and the Youngworl strains M166, M148, M143, M129, and M128 (OQ656409, OQ656410, OQ656413, and OQ656414) obtained from Hwacheon chiggers were similar to the reference Youngworl strain (AF430141).
Discussion
The chigger mite is one of the most medically significant outdoor mites in Korea, and it mediates scrub typhus, which occurs annually and presents a public health hazard [
1–
7]. Chigger mites,
L. pallidum and
L. scutellare, are recognized as the primary vectors of scrub typhus in Korea.
We researched the chigger mite from collected wild rodents and the O. tsutsugamushi infection of the chigger mites in Hwacheon, Cheorwon, Yanggu, and Goseong in the northern regions of Gangwon-do, Korea, where scrub is prevalent. Hwacheon has the highest population of wild rodents and chigger infestations among the 4 areas. Not only was the chigger infestation high in Cheorwon, but so was the detection rate of O. tsutsugamush chigger mites. These assume that Hwacheon and Cheorwon are scrub typhus hotspots. These findings show that chigger mite infestation and O. tustsugamushi infection might aid in estimating the risk of scrub typhus.
During the spring season, when there are few scrub typhus cases, there is evidence of
O. tsutsugamushi infection in chiggers. The most common chigger species was
L. pallidum (76.9%), followed by
L. zetum (16.4%),
L. orientale (4.3%),
N. tamiyai (1.8%),
L. palpale (0.3%), and
L. tectum (0.2%). The dominating species,
L. pallidum, was the most common in Hwacheon (61.3%), followed by Cheorwon (21.3%), Yanggu (8.8%), and Goseong (8.6%). These findings are consistent with prior research that found
L. pallidum to be the most common chigger mite in northern Gyeonggi-do [
18] and Gangwon-do [
19].
L. pallidum was followed by
L. orientale, L. scutellare, and
L. papale in Gyeonggi-do, and
L. palpale,
L. orientale, and
L. zetum in Gangwon-do [
18,
19]. In the current research, however,
L. scutellare was not found, unlike in Gyeonggi-do, and
L. zetum was the most prevalent after
L. pallidum, with
N. tamiyai and
L. tectum also found in Gangwon-do. These variations might be attributable to regional and seasonal changes.
In Gangwon-do, the average chigger index was 100.89 and peaked in the spring. These findings seem to corroborate with a previous finding [
20] that chigger indices spiked twice in the spring and fall. This might be explained by the fact that
L. pallidum achieves its height between September and November, nearly vanishes during the winter, and returns to its peak between March and June [
21]. This implies that
L. pallidum is the most major vector of
O. tsutsugamushi in Gangwon-do, northern Korea, in the spring, with other chiggers such as
L. zetum,
L. orientale,
N. tamiyai, L. tectum, and
L. palale also implicated [
21–
23].
The Boryong strain accounted for 84.8% of the total strains in the
O. tsutsugamushi genotyping study on chigger mites collected in northern regions of Gangwon-do, whereas Youngworl and Jecheon were minor strains. Boryong and Youngworl strains were dominant in the Hwacheon area, while Boryong and Jecheon strains were dominant in the Yanggu and Goseong regions. Only the Boryong strain was dominant in the Cheorwon area. Several strains of
O. tsutsugamushi have been documented in Korea, including the 3 prototype strains, Gilliam, Karp, and Kato, as well as 3 native strains (Boryong, Pajoo, and Youngworl). Boryong is the most prominent strain and has been documented in the central and southern parts of Korea; Gilliam, Karp, Kato, Pajoo, and Youngworl strains have also been identified in the central region [
10,
24–
26]. These results suggest that there is a correlation between the distribution of
O. tsutsugamushi strains, and the population density and vector competence of chigger mites.
The phylogenetic analysis of
O. tsutsugamushi strains in northern Gangwon-do was classified into three clusters: Boryong, Jecheon, and Youngworl were found to be similar to previous study results [
6].
According to a report by the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA;
https://is.kdca.go.kr), the incidence of scrub typhus was low in northern Gangwon-do in the spring. The current research found that the infection rate of
O. tsutsugamushi in chiggers was low in the spring, implying that the occurrence of scrub typhus in northern regions of Gangwon-do, was related to the rate of infection in chiggers in the spring.
Scrub typhus is most common in the southern and southwestern plains of Korea, particularly Jeonbuk (38.6%), Chungnam (32.7%), and Gyeongnam (9.8%) provinces [
8]. On the other hand, since the current study’s target area consists mostly of hilly areas in the country’s central and northeastern regions, the prevalence of typhus looks to be low. Scrub typhus has a high frequency in Korea in the fall, especially from October to November, and a low incidence in the spring [
26–
28], as seen in the current research. Extensive research on the
O. tsutsugamushi strains and their frequency is required in the future, particularly on the relationship between vectors and people.
In conclusion, Hwacheon and Cheorwon are high-risk areas for scrub typhus, with a high prevalence of chigger infestation on striped wild rats and a high rate of O. tsutsugamushi infection in chiggers. L. pallidum was the predominant chigger species, and various O. tsutsugamushi strains, including the dominant Boryong strain, Youngworl strain, and Jecheon strain, were identified in chiggers from the northern regions of Gangwon-do, Korea.
Notes
-
Author contributions
Conceptualization: Kim S
Formal analysis: Kim S, Lee IY, Sezim M
Investigation: Sezim M, Kim J, Seo JH
Project administration: Sezim M, Kim J, Seo JH
Resources: Kim S, Kim J
Writing – original draft: Lee IY, Jeon BY
Writing – review & editing: Lee IY, Yong TS, Jeon BY
-
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
We thank Namkyoung Kim and Jonguk Jeong for technical support. This study was supported by a grant from climate change vector surveillance programs of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA), and by a grant from Armed Forces Medical Research Institute, The Armed Forces Medical Command, Republic of Korea.
Fig. 1Phylogenetic tree constructed using the maximum likelihood method based on the 56-kDa type-specific antigen (TSA) of Orientia tsutsugamushi. The tree includes sequences from 45 chigger pools collected in northern Gangwon-do, Korea.

Table 1The collection results of wild rodents in northern regions of Gangwon-do from February to June 2015
Table 1
|
Locality |
Apodemus agrarius
|
Apodemus peninsulae
|
Micromys minutus
|
Myodes regulus
|
Total (%) |
|
Hwacheon |
97 |
2 |
2 |
5 |
106 (57.0) |
|
Cheorwon |
36 |
0 |
3 |
4 |
43 (23.1) |
|
Yanggu |
17 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
18 (9.7) |
|
Goseong |
19 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
19 (10.2) |
|
Total (%) |
169 (90.8) |
2 (1.1) |
6 (3.2) |
9 (4.8) |
186 (100.0) |
Table 2Chigger infestation status of Apodemus agrarius collected in northern regions of Gangwon-do from February to June 2015
Table 2
|
Locality |
No. of infested/no. of captured (%) |
No. of chiggers |
Chigger indices (CI)a
|
|
Hwacheon |
90/97 (92.8) |
11,211 |
115.58 |
|
Cheorwon |
25/36 (69.4) |
3,493 |
97.02 |
|
Yanggu |
17/17 (100.0) |
1,307 |
76.88 |
|
Goseong |
18/19 (94.7) |
1,039 |
54.68 |
|
Total (%) |
150,169 (88.8) |
17,050 |
100.89 |
Table 3Detection results of trombiculid mites in striped field mice, Apodemus agrarius, by the survey regions of Gangwon-do
Table 3
|
Locality |
Chigger species (%)a
|
Total (%) |
|
L. pallidum
|
L. orientale
|
L. palpale
|
L. tectum
|
L. zetum
|
N. tamiyai
|
|
Hwacheon |
3,756 |
276 |
24 |
16 |
1,144 |
66 |
5,282 (66.3) |
|
Cheorwon |
1,304 |
49 |
0 |
0 |
145 |
82 |
1,580 (19.8) |
|
Yanggu |
537 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
540 (6.8) |
|
Goseong |
527 |
16 |
0 |
0 |
19 |
0 |
562 (7.1) |
|
Total (%) |
6,124 (76.9) |
342 (4.3) |
24 (0.3) |
16 (0.2) |
1,308 (16.4) |
150 (1.8) |
7,964 (100) |
Table 4Results of detection and genotyping of Orientia tsutsugamushi in chiggers from northern regions of Gangwon-do
Table 4
|
Locality |
No. of tested chiggersa
|
No. of tested pools |
No. of positive pools |
O. tsutsugamushi strain |
Minimum positive rate (%; 95% CI) |
Maximum positive rate (%; 95% CI) |
|
Boryong |
Youngworl |
Jecheon |
|
Hwacheon |
5,929 |
242 |
38 |
28 |
10 |
0 |
0.64 (0.45–0.88) |
15.70 (11.36–20.91) |
|
Cheorwon |
1,913 |
73 |
30 |
30 |
0 |
0 |
1.57 (1.06–2.23) |
41.09 (29.71–53.23) |
|
Yanggu |
767 |
28 |
9 |
8 |
0 |
1 |
1.17 (0.54–2.22) |
32.14 (15.88–52.35) |
|
Goseong |
477 |
24 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0.42 (0.05–1.51) |
8.33 (1.03–26.99) |
|
Total (%) |
9,086 |
367 |
79 |
67 (84.8) |
10 (12.7) |
2 (2.5) |
0.87 (0.69–1.08) |
21.52 (17.43–26.09) |
References
- 1. Elliott I, Pearson I, Dahal P, Thomas NV, Roberts T, et al. Scrub typhus ecology: a systematic review of Orientia in vectors and hosts. Parasit Vectors 2019;12(1):513.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3751-x
- 2. Bhate R, Pansare N, Chaudhari Sp, Barbuddhe SB, Choudhary VK, et al. Prevalence and phylgenetic analysis of Orientia tsutsugamushi in rodents and mites from Central India. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2017;17(11):749-754.
https://doi.org/10.1089/vdz.2017.2159
- 3. Ha JH, Lee DH, Park JS, Cho OH, Kim DH, et al. Isolation and genetic characterization of Orientia tsutsugamushi from scrub typhus patients in Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea. J Bacteriol Virol 2016;46(4):275-282.
https://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2016.46.4.275
- 4. Roh JY, Song BG, Park WI, Shin EH, Park C, et al. Coincidence between geographical distribution of Leptotrombidium scutellare and scrub typhus incidence in South Korea. PLoS One 2014;9(12):e113193.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone0113193
- 5. Chung MH, Kang JS. History of tsutsugamushi disease in Korea. Infect Chemother 2019;51(2):196-209.
https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2019.51.2.196
- 6. Kelly DJ, Fuerst PA, Ching WM, Richards AL. Scrub typhus: the geographic distribution of phenotypic and genotypic variants Orientia tsutsugamushi
. Clin Infect Dis 2009;48(suppl):203-230.
https://doi.org/10.1086/596576
- 7. Shim SK, Shin YK, Choi EN, Han BG, Lee HK, et al. Analysis of cellular fatty acids in Orientia tsutsugamushi as taxonomic markers. Microbiol Immunol 2005;49(4):343-347.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2005.tb03738.x
- 8. Choi YJ, Lee IY, Song HJ, Kim J, Park HJ, et al. Geographical distribution of Orientia tsutsugamushi strains in chiggers from three provinces in Korea. Microbiol Immun 2018;62(9):547-553.
https://doi.org/10.1111/1348-0421.12639
- 9. Bahk YY, Ahn SK, Lee J, Kwon HW, Hong SJ, et al. Monitoring chigger mites for Orientia tsutsugamushi in field small mammals in Hwaseong-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea, 2019–2020. Korean J Parasitol 2021;59(3):319-324.
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2021.59.3.319
- 10. Shim SK, Choi EN, Yu KO, Park HJ, Kim CM, et al. Characterisation of Orientia tsutsugamushi genotypes from wild rodents and chigger mites in Korea. Clin Microbiol Infect 2009;15(suppl):311-312.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2008.02254.x
- 11. Mills JN, Corneli A, Young JC, Garrison LE, Khan AS, et al. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome-United States: updated recommendation for risk reduction. MMWR Recomm Rep 2002;51(RR-9):1-12.
- 12. Ree HI. Fauna and key to the chigger mites of Korea (Acarina: Trombiculidae and Leeuwenhoekiidae). Korea J Syst Zool 1990;6:57-70.
- 13. Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 2004;32(5):1792-1797.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
- 14. Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 2018;35(6):1547-1549.
https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
- 15. Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 1987;4(4):406-425.
https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
- 16. Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985;39(4):783-791.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
- 17. Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis Version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 2013;30(12):2725-2729.
https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
- 18. Lee IY, Kim HC, Lee YS, Seo JH, Lim JW, et al. Geographical distribution and relative abundance of vectors of scrub typhus in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parsitol 2009;47(4):381-386.
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2009.47.4.381
- 19. Lee IY, Lim JW, Seo JH, Kim HC, Lee KJ, et al. Geographical distribution and epidemiologic factors of chigger mites on Apodemus agrarius during autumn in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2021;59(5):473-479.
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2021.59.5.473
- 20. Kim SY, Gill B, Song BG, Chu H, Park WI, et al. Annual fluctuation in chigger mite populations and Orientia tsutsugamushi infections in scrub typhus endemic regions of South Korea. Osong Public Health Res Perpect 2019;10(6):351-358.
https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.6.05
- 21. Lee IY, Ree HI, Hong HK. Seasonal prevalence and geographical distribution of trombiculid mites (Acarina: Trombiculidae) in Korea. Korean J Zool 1993;36(3):408-415. (in Korean).
- 22. Ree HI, Chang WH, Kee SH, Lee IY, Jeon SH. Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi DNA in individual trombiculids using polymerase chain reaction in Korea. Med Entomol Zool 1997;48(3):197-209.
https://doi.org/10.7601/mez.48.197
- 23. Ree HI, Lee IY, Jeon SH, Yoshida Y. Geographical distribution of vectors and sero-strains of tsutsugamushi disease at mid-south inland of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1997;35(3):171-179.
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1997.35.3.171
- 24. Kim HC, Lee IY, Cheong ST, Richards AL, Gu SH, et al. Serosurveillance of scrub typhus in small mammals collected from military training sites near the DMZ, northern Gyeonggi-do, Korea and analysis of the relative abundance of chiggers from mammals examined. Korean J Parasitol 2010;48(3):237-243.
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2010.48.3.237
- 25. Shim SK, Shin YK, Choi EN, Han BG, Lee HK, et al. Analysis of cellular fatty acids in Orientia tsutsugamushi as taxonomic markers. Microbiol Immunol 2005;49(4):343-347.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2005.tb03738.x
- 26. Park SW, Lee CK, Kwak YG, Moon C, Kim BN, et al. Antigenic drift of Orientia tsutsugamushi in South Korea as identified by the sequence analysis of a 56-kDa protein-encoding gene. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2010;83(4):930-935.
https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0791
- 27. Noh MS, Lee YJ, Chu CS, Gwack J, Youn SK, et al. Are there spatial and temporal correlations in the incidence distribution of scrub typhus in Korea? Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2013;4(1):39-44.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.01.002
- 28. Chung MH, Kang JS. History of tsutsugamushi disease in Korea. Infect Chemother 2019;51(2):196-209.
https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2019.51.2.196
 , In Yong Lee2,†
, In Yong Lee2,† , Sezim Monoldorova1
, Sezim Monoldorova1 , Jiro Kim1,3
, Jiro Kim1,3 , Jang Hoon Seo4
, Jang Hoon Seo4 , Tai-Soon Yong2,*
, Tai-Soon Yong2,* , Bo Young Jeon1,*
, Bo Young Jeon1,*