Abstract
The taxonomy of Acanthamoeba spp., an amphizoic amoeba which causes granulomatous amoebic encephalitis and chronic amoebic keratitis, has been revised many times. The taxonomic validity of some species has yet to be assessed. In this paper, we analyzed the morphological characteristics, nuclear 18s rDNA and mitochondrial 16s rDNA sequences and the Mt DNA RFLP of the type strains of four Acanthamoeba species, which had been previously designated as A. divionensis, A. parasidionensis, A. mauritaniensis, and A. rhysodes. The four isolates revealed characteristic group II morphology. They exhibited 18S rDNA sequence differences of 0.2-1.1% with each other, but more than 2% difference from the other compared reference strains. Four isolates formed a different clade from that of A. castellanii Castellani and the other strains in morphological group II on the phylogenetic tree. In light of these results, A. paradivionensis, A. divionensis, and A. mauritaniensis should be regarded as synonyms for A. rhysodes.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba, taxonomy, 18s rDNA sequence analysis
INTRODUCTION
During the last few decades, the taxonomy of the genus
Acanthamoeba has been revised several times (
Marciano-Cabral and Cabral, 2003). Morphological characteristics, including the size of trophozoites and cysts, arm numbers of cysts, and the shape of the cyst wall, constituted the principal criteria by which the species of the genus have classically been identified (
Page, 1967,
1976;
Pussard and Pons, 1977). However, morphological characteristics alone have proven unreliable as taxonomic criteria, due to the high degree of observed variation within a clone (
Page, 1988;
Visvesvara, 1991). Several non-morphological methods have been applied to the taxonomy of the genus
Acanthamoeba. Alloenzyme profiles and mitochondrial DNA RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) have been reported to be suitable with regard to strain identification, differentiation, and characterization, rather than species identification, due to the high polymorphism observed between individual isolates (
Kong et al., 1995). Small subunit rDNA PCR-RFLP (riboprinting) and sequence analysis have been the most recently applied, and the promising methods for the identification of
Acanthamoeba species (
Gast et al., 1996;
Chung et al., 1998;
Stothard et al., 1998).
Some
Acanthamoeba species, which were assigned as a species based on their morphologic criteria alone, have been proposed to be, in actuality, invalid synonyms or junior synonyms, based on the data generated by new techniques which analyze the biochemical and molecular characteristics of the amoeba (
De Jonckheere, 1983;
Kim et al., 1996). De Joncheere (
1983) reported that
A. paradivionensis is considered to be an invalid synonym for
A. divionensis, as the former exhibits identical isoenzyme and total protein patterns with the latter. These two species originated from the same isolate, and
A. divionensis was differentiated from
A. paradivionensis on the basis of a difference in the arm numbers of the endocyst. Among Acanthamoeba species classed under morphological group III,
A. pustulosa is proposed to be synonym of
A. palestinensis, based on the isoenzyme and 18S rDNA RFLP patterns determined by Kim et al. (
1996). Therefore, it is necessary to reevaluate the taxonomic validity of species names which are assigned based on morphological criteria alone, via the application of novel identification techniques.
In the present paper, we evaluated the taxonomic validity of four Acanthamoeba isolates by comparing their morphological characteristics, nuclear 18s rDNA and mitochondrial 16s rDNA sequences, and by conducting Mt DNA RFLP. Ultimately, we propose three species, which were previously designated as A. divionensis, A. paradivionensis, and A. mauritaniensis, to be synonyms for A. rhysodes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Acanthamoeba
Four strains of Acanthamoeba, A. rhysodes Singh strain (ATCC#30973), A. divionensis AA2 strain (ATCC#50238), A. paradivionensis AA1 strain (ATCC#50251) and A. mauritaniensis 1652 strain (ATCC#50253), were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), and incubated in PYG media at 25℃. The size and number of arms of the cysts of four Acanthamoeba isolates were determined, in order to assign morphological grouping. The reference strain for Mt DNA RFLP, A. castellanii Castellani (ATCC#30011), was also purchased from the ATCC, and cultured in PYG media at 25℃.
Chromosomal DNA extraction and 18S rDNA amplification
The chromosomal DNA of
Acanthamoeba isolates was obtained by the methods described by Kong and Chung (
1996). In brief,
Acanthamoeba trophozoites (5 × 10
6) were washed with PBS, then boiled with 0.1 ml of 0.1 N NaOH for 3 min. Supernatants collected after 2 min of centrifugation at 800 g at room temperature were mixed with 0.2 ml of distilled water. Genomic DNA was then extracted with phenol and phenol/chloroform (1:1), and recovered by precipitation with cold absolute ethanol, in the presence of sodium acetate. The DNA was then used as a template for the PCR amplification of 18S rDNA. The primers, P3; 5'-CCGAATTCGTCGACAACCTGGTT GATCCTGCCAGT-3', and P4; 5'-GGATCCAAGCTTGATCCTTCTGCAGGTTCACCTAC-3', were designed to hybridize to highly conserved sequences at the extreme 5' (P3) and 3' (P4) termini of eukaryotic 18s rDNA (
Bhattacharya et al., 1995). The PCR products of the four isolates were electrophoresed on 2.5% agarose gel, with DNA size standards (Hind III digested λ phage DNA, Poscochem, Korea; Amplisize, Biorad, U.S.A.).
PCR products were sequenced after being cloned into pBSK+ (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) or PCR II (Invitrogen, San Diego, CA). The sequences of the four strains were compared pair-wise, then multi-aligned with those of 16 Acanthamoeba strains available in the GenBank database, using Clustal X. The phylogenetic tree was then constructed via the bootstrap method with the morphological group I species, A. astronyxis and A. tubiashi, used as an out-group. The intron sequence of A. griffini was omitted for this analysis.
Extraction of Mt DNA and RFLPs
We extracted
Acanthamoeba mtDNA via the method described by Yagita and Endo (
1990).
Acanthamoeba trophozoites, harvested at the end of the logarithmic growth phase, were washed in cold PBS. The amoebae were then lysed with fresh 1% sodium dodecyl sulfate solution in 0.2 N NaOH, after which, potassium acetate buffer was added, and the whole mixture was incubated for 30 min on ice. The mtDNA was extracted using phenol and phenol/chloroform (1:1), and recovered via precipitation with cold absolute ethanol in the presence of sodium acetate. We digested the mtDNA of the
Acanthamoeba isolates with two kinds of restriction enzymes,
EcoR I and
Cla I (Promega, USA), for 2 hr at 37℃ in a 20 µl reaction volume with the buffers specified for each restriction enzyme. The digested DNA was electrophoresed in 0.7% agarose gel at 4 V/cm for 1-2 hrs, then stained with ethidium bromide for 15 min. The mtDNA RFLP patterns were observed and photographed under an UV transilluminator.
The primers for the PCR, FP16; 5'-TTGTATAAACAATCGTTGGGTTTTATT-3', RP16; 5'-GTCCAGCAGCAGGTTCCCCTACCGCTA-3', are designed to hybridize to the highly conserved sequences at the extreme 5' (P3) and 3' (P4) termini of the mitochondrial ssu rDNA (
Lonergan and Gray, 1994). PCR was carried out as was described in the previous paper (
Yu et al., 1999). The PCR products were cloned into pBSK+ (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) or PCR II (Invitrogen, San Diego, CA). The sequencing of the PCR products was outsourced to Macrogene (Korea). The sequences of the 16s rDNA of four isolates were compared in a pair-wise manner.
RESULTS
Morphological examination
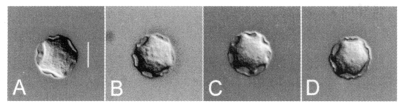
The four strains of
Acanthamoeba analyzed in this study exhibited cyst morphology characteristic of the
Acanthamoeba group II, as defined by the work of Pussard and Pons (
1977). All strains exhibited double-walled cyst morphology consisting of thick wrinkled ectocysts and polygonal or satellite endocysts (
Fig. 1). The cyst diameter and the number of arms are shown in
Table 1.
All four of the strains yielded PCR products which were approximately 2.3 kb in size, when amplified with specific primers for 18S rDNA. The nucleotide sequences of the 18s rDNA of all four strains were submitted to Genbank, and were allocated the following accession numbers: AF005998 for
A. rhysodes Singh, AF316545 for
A. divionensis AA2, AY148961 for
A. paradivionensis AA1, and AY148962 for
A. mauritaniensis 1652. We compared the 18S rDNA sequences of the four isolates with each other, as well as those of several reference strains stored in GenBank, and have presented the percentage differences of the sequences in
Table 2. The four isolates exhibited 0.2-1.1% of sequence difference with each other, but over 2% of difference from all other reference strains compared. As expected, AA2 and AA1 evidenced the closest measure of relatedness among the strains. Interestingly, the 1652 strain was determined to be genetically similar to the Singh strain, exhibiting a sequence difference of only 0.2%. The phylogenetic tree of the
Acanthamoeba 20 strains, based on analyses of their 18S rDNA sequences, is presented in
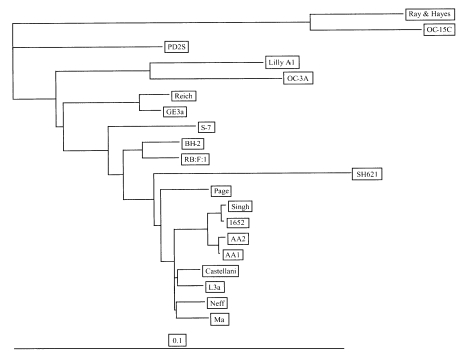
Fig. 2. Four isolates formed a different clade from
A. castellanii Castellani, as well as the other strains in morphological group II.
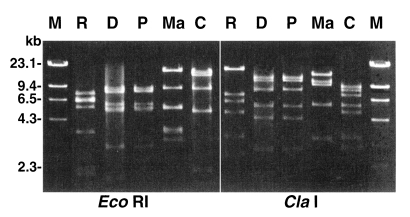
The Mt DNA RFLP of the four strains, as well as that of
A. castellanii Castellani (used as a reference strain) is presented in
Fig. 3. The RFLP pattern of
A. paradivionensis AA1 was almost identical to that of
A. divionensis AA2, with both restriction enzyme tested. The other strains exhibited very different Mt DNA RFLP patterns from each other.
Sequence dissimilarities in the 16S rDNA results from the four strains are shown in
Table 3. Percent sequence differences ranged from 0.8% between AA1 and AA2, to 2.9% between AA2 and 1652, or between AA1 and 1652. AA2 and AA1 were found to be the most closely related among the four strains, with a sequence difference of 0.8%.
DISCUSSION
Acanthamoeba investigators have long disagreed over the taxonomy of the genus Acanthamoeba. In the present paper, we evaluated the taxonomic validity of four species of Acanthamoeba, namely, A. divionensis, A. paradivionensis, A. mauritaniensis, and A. rhysodes, by analyses of nuclear 18s rDNA and mitochondrial 16s rDNA sequences analyses, as well as Mt DNA RFLP analysis. The four strains exhibited 0.2-1.1% 18S rDNA nucleotide dissimilarity, and 0.8-2.9% mitochondrial 16S rDNA nucleotide dissimilarity. AA1 and AA2, however, evidenced identical mitochondrial RFLP patterns. These results suggested that the AA1, AA2, and 1652 strains of Acanthamoeba, formerly designated A. paradivionensis, A. divionensis, and A. mauritaniensis, are actually synonyms for A. rhysodes.
Several common characteristics have been reported among the four strains analyzed in this study. They were isolated from soil, and proved to be either avirulent, or weakly virulent (
De Jonckheere, 1980). The Singh strain was isolated from English soil (
Singh, 1951), AA1 and AA2 were isolated from French soil (
Pussard and Pons, 1977), and 1652 was isolated from Moroccan soil (
Pussard and Pons, 1977). The AA1, AA2, and 1652 strains have proved incapable of growing at 40℃, and are almost completely avirulent in mice (
De Jonckheere, 1980). In the following experiment, De Jonckheere reported that
A. paradivionensis AA1 and
A. divionensis AA2, both of which exhibited identical isoenzymes profiles, were closely related to the
A. rhysodes R4c strain (
De Jonckheere, 1983). However, because in the case of the Singh strain, the
A. rhysodes type strain was not included in the experiment, he was unable to assign the species names AA1 and AA2.
Via the 18s rDNA PCR-RFLP analysis of 23
Acanthamoeba strains, Chung et al. (
1998) reported identical riboprints for AA1, AA2, and 1652, with the Singh strain, and suggested that
A. divionensis,
A. paradivionensis, and
A. mauritaniensis were synonyms for
A. rhysodes. The four strains were also closely related according to the phylogenetic tree, based on the PCR-RFLP of MtDNA 16s rDNA (
Yu et al., 1999).
Stothard et al. (
1998) placed
A. rhysodes Singh in the T4 sequence type of 18S rDNA, where
A. castellanii Castellani also belonged, and suggested that the various species in T4 might all be reclassified as
A. castellanii. However,
A. rhysodes Singh exhibited a 2.7% sequence dissimilarity with
A. castellanii Castellani (
Table 2). Although strains in the T4 sequence type are closely genetically related, and form a cluster which is distinct from the other strains in morphological group II, they would appear to constitute more of a species complex than a species, due to their diversity.
Gene sequences for nuclear 18S rRNA and mitochondrial 16S rRNA of AA1 and AA2 isolated from one strain (
Pussard and Pons, 1977), were not identical. Long periods of separated isolation may result in microchanges in the gene sequences of both isolates.
Although the differences in the mitochondrial 16S rDNA and nuclear 18S rDNA sequences of the four strains were not identical, the four isolates were determined by both analyses to be quite closely related. The higher degree of sequence differences with regard to mitochondrial 16s rDNA than were seen in the18s rDNA among the four strains may be attributable to the fact that organellar DNA evolves at a more rapid rate than does the nuclear genome (
Ferris et al., 1981).
References
- 1. Bhattacharya D, Helmchen T, Melkonian M. Molecular evolutionary analyses of nuclear-encoded small subunit ribosomal RNA identify and independent rhizopod lineage containing the euglyphina and the Chlorarachniophyta. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1995;42:65-69.
- 2. Chung DI, Yu HS, Hwang MY, Kim TH, Kim TO, Yun HC, Kong HH. Subgenus classification of Acanthamoeba by riboprinting. Korean J Parasitol 1998;36:69-80.
- 3. De Jonckheere JF. Growth characteristics, cytopathic effect in cell culture, and virulence in mice of 36 type strains belonging to 19 different Acanthamoeba spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 1980;39:681-685.
- 4. De Jonckheere JF. Isoenzyme and total protein analysis by agarose isoelectric focusing, and taxonomy of the genus Acanthamoeba. J Protozool 1983;30:701-706.
- 5. Ferris SD, Wilson AC, Brown WM. Evolutionary tree for apes and humans based on cleavage maps of mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1981;78:2432-2436.
- 6. Gast RJ, Ledee DR, Fuerst PA, Byers TJ. Subgenus systematics of Acanthamoeba: Four nuclear 18S rDNA sequence types. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1996;43:498-504.
- 7. Kim YH, Ock MS, Yun HC, Hwang MY, Yu HS, Kong HH, Chung DI. Close relatedness of Acanthamoeba pustulosa with Acanthamoeba palestinensis based on isoenzyme profiles and rDNA PCR-RFLP patterns. Korean J Parasitol 1996;34:259-266.
- 8. Kong HH, Park JH, Chung DI. Interstrain polymorphisms of isoenzyme profiles and mitochondrial DNA fingerprints among seven strains assigned to Acanthamoeba polyphaga. Korean J Parasitol 1995;33:331-340.
- 9. Lonergan KM, Gray MW. The ribosomal RNA gene region in Acanthamoeba castellanii mitochondrial DNA. A case of evolutionary transfer of introns between mitochondria and plastids? J Mol Biol 1994;239:476-499.
- 10. Marciano-Cabral F, Cabral G. Acanthamoeba spp. asagents of disease in humans. Clin Microbiol Rev 2003;16:273-307.
- 11. Page FC. Re-definition of the genus Acanthamoeba with descriptions of three species. J Protozool 1967;14:709-724.
- 12. Page FC. An illustrated key to freshwater and soil amoeba. 1976, Ambleside, England. Freshwater Biological Association. Freshwater Biological Association scientific publication no. 34.
- 13. Page FC. A new key to freshwater and soil gymnamoebae with instructions for culture. 1988, Ambleside, Cumbria. Freshwater Biological Association.
- 14. Pussard M, Pons R. Morphologie de la paroi kystique et taxonomie du genre Acanthamoeba (Protozoa, Amoebida). Protistologica 1977;13:557-598.
- 15. Singh BN. Nuclear division in nine species of small free-living amoebae and its bearing on the classification of the order Amoebida. Phil Trans Roy Soc London, Ser B 1952;236:405-461.
- 16. Stothard DR, Schroeder-Diedrich JM, Awwad MH, Gast RJ, Ledee DR, Rodriguez-Zaragoza S, Dean CL, Fuerst PA, Byers TJ. The evolutionary history of the genus Acanthamoeba and the identification of eight new 18SrRNA gene sequence types. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1998;45:45-54.
- 17. Visvesvara GS. Classification of Acanthamoeba. Rev Infect Dis 1991;13(suppl):S369-S372.
- 18. Yagita G, Endo T. Restriction enzyme analysis of mitochondrial DNA of Acanthamoeba strains in Japan. J Protozool 1990;37:570-575.
- 19. Yu HS, Hwang MY, Kim TO, Yun HC, Kim TH, Kong HH, Chung DI. Phylogenetic relationships among Acanthamoeba spp. based on PCR-RFLP analyses of mitochondrial small subunit rRNA gene. Korean J Parasitol 1999;37:181-188.
Fig. 1Micrographs of Acanthamoeba 4 strains analyzed in this study. A, A. rhysodes Singh; B, A. divionensis AA2; C, A. paradivionensis AA1; D, A. mauritaniensis 1652. Bar represents 10 µm.
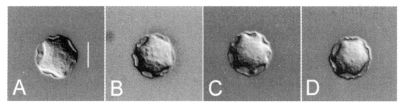
Fig. 2Phylogenetic tree of
Acanthamoeba 20 isolates based on 18S rDNA sequences. The scale bar represents an evolutionary distance equivalent to 1%. The species names of six reference strains are presented in
Table 2. The others are
A. castellanii Ma,
A. castellanii Neff,
A. lugdunensis L3a,
A. triangularis SH621,
A. stevensoni RB:F:1,
A. hatchetti BH-2,
A. griffini S-7,
A. pustulosa GE3a,
A. lenticulata PD2S, and
A. culbertsoni Lilly.

Fig. 3Agarose gel electrophoretic restriction fragment patterns for mitochondrial DNA from four Acanthamoeba strains. Lanes: R, A. rhysodes Singh; D, A. divionensis AA2; P, A. paradivionensis AA1; Ma, A. mauritaniensis 1652; C, A. castellanii Castellani; M, Hind III digested lambda DNA for molecular size standard.
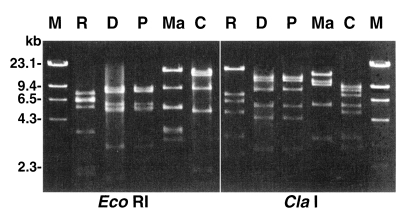
Table 1.Cyst diameter and the number of arms of the four strains of Acanthamoeba assessed in the present study
Table 1.
|
Species |
Cyst diameter (μm) |
Arm number |
|
A. rhysodes
|
12.3-22.0 (16.5) |
5-7 (5.5) |
|
A. divionensis
|
12.0-21.5 (16.5) |
4-7 (5.6) |
|
A. paradivionensis
|
12.5-22.3 (16.9) |
5-8 (6.5) |
|
A. mauritaniensis
|
10.3-19.8 (15.6) |
4-7 (5.6) |
Table 2.Percentage differences between the 18S rDNA sequence for A. rhysodes Singh, A. divionenesis AA2, A. paradivionensis AA1 and A. mauritaniensis 1652 strains, and other Acanthamoeba strains representing the three morphological groups
Table 2.
|
Species and strain |
Group |
Percent differencea)
|
|
Singh |
AA2 |
AA1 |
1652 |
|
A. astronyxis Ray & Hayes (AF019064)b)
|
I |
26.7 |
26.6 |
26.7 |
26.7 |
|
|
(2681:2242) |
(2681:2243) |
(2681:2243) |
(2681.2243) |
|
A. tubiashi OC-15C (AF019065) |
I |
23.1 |
23.4 |
23.3 |
23.1 |
|
|
(2516:2242) |
(2516:2243) |
(2516:2243) |
(2516:2243) |
|
A. castellanii Castellani (U07413) |
II |
2.7 |
2.8 |
2.7 |
2.7 |
|
|
(2243:2242) |
(2243:2243) |
(2243:2243) |
(2243:2243) |
|
A. polyphaga Page (AF019061) |
II |
2.9 |
3.3 |
3.1 |
2.8 |
|
|
(2252:2242) |
(2252:2243) |
(2252:2243) |
(2252:2243) |
|
A. palestinensis Reich (U07411) |
III |
8.5 |
8.6 |
8.4 |
8.6 |
|
|
(2242:2242) |
(2242:2243) |
(2242:2243) |
(2242:2243) |
|
A. healyi OC-3A (AF019070) |
III |
15.1 |
14.9 |
14.9 |
15.1 |
|
|
(2322:2242) |
(2322:2243) |
(2322:2243) |
(2322:2243) |
|
A. rhysodes Singh |
II |
- |
1.1 |
0.8 |
0.2 |
|
|
|
(2242:2243) |
(2242:2243) |
(2242:2243) |
|
A. divionensis AA2 |
II |
|
- |
0.2 |
0.9 |
|
|
|
|
(2243:2243) |
(2243:2243) |
|
A. paradivionensis AA1 |
II |
|
|
- |
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
(2243:2243) |
Table 3.Percentage differences between the 16S rDNA sequence of A. rhysodes singh, A. divionenesis AA2, A. paradivionensis AA1 and A. mauritaniensis 1652 strains
Table 3.
|
Strain |
Percent differencea)
|
|
AA2 |
AA1 |
1652 |
|
Singh |
2.5 |
2.5 |
2.1 |
|
(1526:1528) |
(1526:1531) |
(1526:1527) |
|
AA2 |
- |
0.8 |
2.9 |
|
|
(1528:1531) |
(1528:1527) |
|
AA1 |
|
- |
2.9 |
|
|
|
(1531:1527) |