Abstract
The tegumental ultrastructure of juvenile and adult Himasthla alincia (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) was observed by scanning electron microscopy. One-, 5- (juveniles) and 20-day-old worms (adults) were harvested from chicks experimentally fed metacercariae from a bivalve, Mactra veneriformis. The juvenile worms were elongated and curved ventrally. The head crown bore 31 collar spines, arranged in a single row. The lip of the oral sucker had 12 paired, and 3 single type I sensory papillae, and the ventral sucker had about 25 type II sensory papillae. The anterolateral surface between the two suckers was densely packed with tegumental spines with 4-7 pointed tips. The adult worms were more elongated and filamentous, and had severe transverse folds over the whole body surface. On the head crown and two suckers, type I and II sensory papillae were more densely distributed than in the juvenile worms. Retractile brush-like spines, with 8-10 digits, were seen on the anterolateral surface, whereas claw-shaped spines, with 2-5 digits, were sparsely distributed posteriorly to the ventral sucker. The cirrus characteristically protruded out, and was armed with small spines distally. The surface ultrastructure of H. alincia was shown to be unique among echinostomes, especially in the digitation of its tegumental spines, the distribution of sensory papillae and by severe folds of the tegument.
-
Key words: Himasthla alincia, Echinostomatidae, surface ultrastructure, tegument, collar spine, sensory papilla
INTRODUCTION
Species of
Himasthla (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) are intestinal trematodes found in birds, including gulls, herons and oystercatchers (
Yamaguti, 1958;
Lumsden, 1962), fish (
Stunkard, 1966) and man (
Vogel, 1933). Twenty-two species of
Himasthla have been reported globally (
Yamaguti, 1958;
Stunkard, 1960,
1966;
Didyk and Burt, 1997), but only
Himasthla muehlensi has been found to infect humans (
Vogel, 1933). The metacercariae of
Himasthla species have been found in various marine molluscs (
Stunkard, 1938,
1966;
Adams and Martin, 1963;
Cheng et al., 1966;
Loos-Frank, 1967). The adult flukes are morphologically characterized by their long, filamentous body, head crown with a single uninterrupted row of spines, and extensive vitellaria (
Yamaguti, 1958).
Himasthla alincia was first reported by Dietz (
1909) in Brazil, and has been reported in semipalmated sandpipers (
Calidris pusilla) in Massachusetts, U.S.A. (
Stunkard, 1960), lesser yellowlegs (
Tringa flavipes) in Louisiana, U.S.A. (
Lumsden, 1962) and in migrating greater yellowlegs (
T. melanoleuca) in Texas and New Mexico, U.S.A. (
Secord and Canaris, 1993). In Korea, the metacercariae of
H. alincia were first found in several species of bivalves, during a survey of a western coastal area (unpublished data). These bivalves were also found to be infected with a number of metacercariae of
Acanthoparyphium tyosenense (
Chai et al., 2001;
Han et al., 2003).
Studies of the surface ultrastructures of trematodes is often helpful for discovering their taxonomic significance, and have been carried out on;
Echinostoma revolutum (
Fried and Fujino, 1984),
Isthmiophora melis (
Smales and Blankespoor, 1984),
Echinostoma hortense (
Lee et al., 1986),
Echinochasmus japonicus (
Lee et al., 1987),
Mesorchis denticulatus (
Køie, 1987),
Echinostoma malayanum (
Tesana et al., 1987),
Echinostoma cinetorchis (
Lee et al., 1992),
Echinostoma paraensei (
Maldonado et al., 2001) and
Echinoparyphium recurvatum (
Sohn et al., 2002). The surface ultrastructure had been found to vary according to the echinostome species, especially in size, shape, number and distribution of collar and tegumental spines, sensory papillae, and differentiation patterns during their development. The morphology of
H. alincia adult flukes was studied by light microscopy (
Dietz, 1909;
Lumsden 1962), but no description is available on the surface topography of the juvenile or adult flukes of
Himasthla, including
H. alincia.
The present study was performed to obtain data on the surface ultrastructures of juvenile and adult flukes of H. alincia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Metacercariae of H. alincia were collected from the muscles of the marine bivalve, Mactra veneriformis, purchased from a market near Gyehwa-myeon, Buan-gun, Jeollabuk-do, using a dissecting microscope. A total of 1,200 metacercariae was divided into groups of 50 to 100, and fed to 14, 1-3 week-old hatchery-raised broiler chicks. The chicks were sacrificed on days 1, 5 and 20 post-infection, and their whole guts resected. The small intestine was opened along the mesenteric border in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4. After washing of the intestinal contents with PBS several times, juvenile and adult H. alincia flukes were recovered from the sediment using a dissecting microscope. The worms were washed with 0.2 M cacodylate buffer (pH 7.3) and fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde. They were dehydrated with a graded series of ethanol in distilled water, dried in a critical point dryer (CPD7501, VG Microtech, England), mounted on aluminum stubs and coated with gold using an ion sputtering coater (IB-3, Giko Engineering Co., Japan). The specimens were observed under scanning electron microscopy (ISI DS-130C, Akashi Co., Japan) at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV.
RESULTS
Juvenile flukes
The one-day-old juvenile worms of
H. alincia were minute, plump-shape and slightly curved ventrally (
Fig. 1). The anterior end of the worm was elongated and rounded, but the posterior part was attenuated. The anterior part, from the oral to the ventral suckers, was slightly curved ventrally. The head crown was surrounded by 31 retractable, horseshoe-shaped collar spines, which were embedded in cytoplasmic pockets (
Fig. 2). The spines were arranged in a single row, with no interruption at the dorsomedial line (
Fig. 3), and had end grouped spines (
Fig. 2). The oral sucker was situated subterminally at the anteroventral side of the body. The lip of the oral sucker was devoid of spines, and had 12 paired type I sensory papillae (= ciliated knob-like swellings) anteriorly, and 3 single undeveloped type I sensory papillae posteriorly. Three clumped type I sensory papillae were symmetrically distributed in the lateral portion of the oral sucker (
Fig. 4). The ventral sucker was dome-shaped at the median level of the body. On the lip of the ventral sucker there were 24-26 equidistant type II sensory papillae (= round swellings of the tegument) (
Fig. 5). The tegumental spines at the anterolateral and dorsal portions were longer than they were wide, and had 4-5 branches on the tip (
Fig. 6). At the posterior part of the ventral sucker, peg-like tegumental spines were densely arranged at the anterior of the posterior half of the body (
Fig. 1). The excretory pore was subterminal, and covered by a smooth tegument, with no characteristic structure (
Fig. 7).
The 5-day-old juvenile worms of
H. alincia were more elongated, eel-shaped and slightly curved ventrally (
Fig. 8). The oral and ventral suckers were closely to each other, as the posterior part of the worms develops more rapidly than the anterior section (
Fig. 8). Tegumental spines were distributed at the anterior half of the body, over one fourth of the body, with the posterior half devoid of spines. Numerous types I and II sensory papillae were densely distributed on the lip of the oral sucker, which were symmetrically dispersed on the ventral side (
Fig. 9). There were lateral corner spines, composed of 3 oral and 2 aboral spines to each side (
Figs. 9, 10), making a total of 10. The collar spines were partially covered by the tegument, with the distal end of the spines emerging from the tegument (
Fig. 10). On the lip of the ventral sucker, there were 24 to 26 type II sensory papillae, distributed in a single row. The surface of the ventral sucker showed peg-like spines and type I sensory papillae of the protruding area (
Fig. 12). Tegumental spines, with 6 to 7 branches, were developed in the anterolateral portion on the ventral side (
Fig, 11). The tegument, just posterior to the ventral sucker, showed a few sparsely distributed peg-like spines (
Fig. 13), and the tegument in the middle part of the body was transversely wrinkled, and covered with variable sized, small peg-like spines and type I sensory papillae (
Fig. 14). The tegument of the ventroposterior extremity was devoid of spines, transversely wrinkled, and showed porous cytoplasmic processes (
Fig. 15).
The 20-day-old adult
H. alincia worms were quite long, slender, and with a filamentous body (
Fig. 16), and their surface was transversely deeply wrinkled and covered with cobblestone-like cytoplasmic processes. The genital pore was located ventrally and distant from the anterior margin of the ventral sucker. The cirrus was protruded and armed with small spines in the distal half (
Fig. 17). The rim of the ventral sucker had a wrinkled border and numerous, randomly distributed, domed and small ciliated type I sensory papillae (
Fig. 18). The tegumental spines at the anterolateral body were retracted, mature and had 8-10 tips (
Fig. 19). On the vertical groove, between oral and ventral suckers, velvety teguments were observed (
Fig. 20). Immediately posterior to the ventral sucker, there were sparsely distributed, claw shaped tegumental spines, with 2-5 digits on the tip (
Fig. 21). The surface of the ventromedial region was covered by severe folds, with spade-shaped spines and type II sensory papillae (
Fig. 22). At the posterior part of the anterior half of the body, there were irregularly distributed type II sensory papillae on the surface (
Fig. 23). The tegument of the mid-ventral surface was flat, with severe transverse rows of folds (
Figs. 1,
24). The tegument of the posterior body was cobblestone-like, and had only traces of spines (
Fig. 25).
DISCUSSION
Studies on the surface ultrastructure of
Himasthla spp. have been undertaken with larval stages of two species including
Himasthla leptosoma (
Irwin et al., 1984) and
Himasthla secunda (
Chapman and Wilson, 1970). However, the surface ultrastructure of developmental stages of
Himasthla was first observed in the present study.
The minute, and slightly elongated form of H. alincia juvenile changes to a long, filamentous form in its adult stage. Despite these changes, the distance between the anterior end of the body and the ventral sucker remained relatively constant throughout the experimental period. Therefore, the increase of the body length was considered to result mainly from the growth in the posterior portion. The growth of the posterior body was considered to be due chiefly to the development of genital organs contained therein.
A longitudinal ventral depression, between the oral and ventral suckers, has been observed in
Echinostoma caproni (
Fried et al., 1990),
Echinostoma trivolvis (
Fried et al., 1990),
E. paraensei (
Maldonado et al., 2001) and
E. recurvatum (
Sohn et al., 2002). In the present study, such a depression was also found in
H. alincia. Tegumental spines are absent at the ventral depression in several echinostomes species, such as
E. japonicus (
Lee et al., 1987),
M. denticulatus (
Køie, 1987),
E. caproni (
Fried et al., 1990) and
E. trivolvis (
Fried et al., 1990). Whereas, spines have been found on the ventral depression in
E. revolutum (
Smales and Blankespoor, 1984),
E. cinetorchis (
Lee et al., 1992),
E. hortense (
Lee et al., 1986),
E. malayanum (
Tesana et al., 1987),
E. paraensei (
Maldonado et al., 2001) and
E. recurvatum (
Sohn et al., 2002). In the present study, no tegumental spines were observed on the ventral depression of
H. alincia.
During the larval growth and development stages, two types of sensory papillae were observed in the anterior region of the body of
Himasthla spp; in the metacercariae of
H. leptosoma (
Irwin et al., 1984) and the cercariae of
H. secunda (
Chapman and Wilson, 1970). In the excysted metacercariae of
H. leptosoma, type I and II sensory papillae were commonly observed on the tegumental surface. The type II sensory papillae were distributed in an obvious ring shape, with others posteriorly distant to the oral sucker (
Irwin et al., 1984). In the cercariae of
H. secunda, sensory papillae were observed on the surface, between the oral sucker and collar spines, and on both sides of the ventral surface, between the oral and ventral suckers (
Chapman and Wilson, 1970). In juvenile and adult
H. alincia, type I sensory papillae were also abundant around the oral and ventral suckers, in both single and clumped forms, with an increased density around the oral sucker, as the fluke matured. With regard to the surface ultrastructure of larval stages of
Himasthla species,
H. alincia was similar to other
Himasthla spp. in the distribution and types of sensory papillae. These findings are also thought to be a common feature of the surface ultrastructure of echinostome trematodes.
In
H. leptosoma, tegumental spines were present on the surface of excysted metacercariae from just behind the collar spines in the region of the ventral sucker (
Irwin et al., 1984). The most anterior tegumental spines were simple peg-like, and merged posteriorly into more palmate structures, with progressively more points. Spines on the tegument, close to the ventral sucker, reverted to simple peg-like forms (
Irwin et al., 1984). In the present study, the anterolateral surface, between the oral and ventral suckers, was densely packed with tegumental spines having 4-7 point tips in 1- and 5-day-old worms, and retractile brush-like spines, with 8-10 digits, in 20-day-old adults. On the posterior surface, peg-like spines were distributed in 1- and 5-day-old worms, but, as the worm matured, claw-shaped spines, with 2-5 digits, were sparsely distributed posteriorly to the ventral sucker, but no spines were seen at the extremity near the excretory pore of 20-day-old adults. At all stages in
H. alincia worms the dense distribution of spines was limited to the anterior of the middle surface near the ventral sucker level. Spines on the surface, posterior to the ventral sucker, also showed a reduced density and number of points. The distribution of tegumental spines may aid in the locomotion of the worms in the intervillous space of the definitive host intestines.
Under a light microscopy,
H. alincia closely resembles
Himasthla limnodromi (
Didyk and Burt, 1997). However, these two species can be distinguished by their adult and egg sizes, and in particular by whether their cirrus is armed or not. The morphology of the cirrus is important in the differentiation of species of
Himasthla;
H. alincia is armed with spines (
Lumsden, 1962) and
H. limnodromi has aspinous cirrus (
Didyk and Burt, 1997). In the present study, the cirrus of
H. alincia armed with spines was first observed using a scanning electron microscope, and the results support the light microscopic observations of Lumsden (
1962). This genital organ was also observed in
Echinostoma spp. such as
E. caproni (
Fried et al., 1990),
E. trivolvis (
Fried et al., 1990) and
E. paraensei (
Maldonado et al., 2001), which have no spines.
Conclusively, the surface ultrastructure of H. alincia is similar to that of other echinostomes, but unique in the number, and arrangement, of collar spines, shapes and distribution of tegumental spines, and the type and distribution of sensory papillae.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to Sung-Yil Choi and Jae-Lip Kim for their excellent technical assistance in the laboratory.
References
- 1. Adams JE, Martin WE. Life cycle of Himasthla rhigedana Dietz, 1909 (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). Trans Am Micro Soc 1963;82:1-6.
- 2. Chai JY, Han ET, Park YK, Guk SM, Lee SH. Acanthoparyphium tyosenense: the discovery of human infection and identification of its source. J Parasitol 2001;87:794-800.
- 3. Chapman HD, Wilson RA. The distribution and fine structure of the integumentary papillae of the cercaria of Himasthla secunda (Nicoll). Parasitology 1970;61:219-227.
- 4. Cheng TC, Shuster CN Jr, Anderson AH. A comparative study of the susceptibility and response of eight species of marine pelecypods to the trematode Himasthla quissetensis. Trans Am Micro Soc 1966;85:284-295.
- 5. Didyk AS, Burt MD. Himasthla limnodromi n. sp. (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) from the short-billed dowitcher, Limnodromus griseus (Aves: Scolopacidae). J Parasitol 1997;83:1124-1127.
- 6. Dietz E. Die Echinostomiden der Vogel. Zool Anz 1909;34:180-192.
- 7. Fried B, Fujino T. Scanning electron microscopy of Echinostoma revolutum (Trematoda) during development in the chick embryo and the domestic chick. Int J Parasitol 1984;14:75-81.
- 8. Fried B, Irwin SWB, Lorry SF. Scanning electron microscopy of Echinostoma trivolvis and E. caproni (Trematoda) adults from experimental infection in the golden hamster. J Nat Hist 1990;24:433-440.
- 9. Han ET, Kim JL, Chai JY. Recovery, growth, and development of Acanthoparyphium tyosenense (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) in experimental chicks. J Parasitol 2003;89:(in press).
- 10. Irwin SWB, Mckerr G, Judge BC, Moran I. Studies on metacercarial excystment in Himasthla leptosoma (Tramatoda: Echinostomatidae) and newly emerged metacercariae. Int J Parasitol 1984;14:415-421.
- 11. Køie M. Scanning electron microscopy of rediae, cercariae, metacercariae and adults of Mesorchis denticulatus (Rudolphi, 1802) (Trematoda, Echinostomatidae). Parasitol Res 1987;73:50-56.
- 12. Lee SH, Hong SJ, Chai JY, Hong ST, Seo BS. Tegumental ultrastructure of Echinostoma hortense observed by scanning electron microscopy. Korean J Parasitol 1986;24:63-70.
- 13. Lee SH, Jun HS, Sohn WM, Chai JY. Tegumental ultrastructure of juvenile and adult Echinostoma cinetorchis. Korean J Parasitol 1992;30:65-74.
- 14. Lee SH, Sohn WM, Hong ST, Seo BS. Scanning electron microscopical findings of Echinochasmus japonicus tegument. Korean J Parasitol 1987;25:51-58.
- 15. Loos-Frank B. Experimentelle untersuchungen uber bau, entwicklung und systematik der Himasthlinae (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) des Nordeseeraumes. Z Parasitenkd 1967;28:299-351.
- 16. Lumsden RD. Four echinostome trematodes from Louisiana birds including the description of a new species. Tulane studies in Zool 1962;9:301-308.
- 17. Maldonado A Jr, Loker ES, Morgan JA, Rey L, Lanfredi RM. Description of the adult worms of a new Brazilian isolate of Echinostoma paraensei (Plathyhelminthes: Digenea) from its natural vertebrate host Nectomys squamipes by light and scanning electron microscopy and molecular analysis. Parasitol Res 2001;87:840-848.
- 18. Secord ML, Canaris AG. The metazoan parasite community of migrating greater yellowlegs, Tringa melanoleuca, from the Rio Grande Valley, Texas and New Mexico. J Parasitol 1993;79:690-694.
- 19. Smales LR, Blankespoor HD. Echinostoma revolutum (Froelich, 1802) Looss, 1899 and Isthmiophora melis (Schrank, 1788) Luhe, 1809 (Echinostomatidae, Digenea): scanning electron microscopy of the tegumental surface. J Helminthol 1984;58:187-195.
- 20. Sohn WM, Woo HC, Hong SJ. Tegumental ultrastructures of Echinoparyphium recurvatum according to developmental stages. Korean J Parasitol 2002;40:67-73.
- 21. Stunkard HW. The morphology and life cycle of the trematode Himasthla quissetensis (Miller and Northup, 1926). Biol Bull 1938;131:145-164.
- 22. Stunkard HW. Further studies on the trematode genus Himasthla with descriptions of H. mcintoshi n. sp., H. piscicola n. sp., and stages in the life history of H. compacta n. sp. Biol Bull 1960;119:529-549.
- 23. Stunkard HW. The morphology and life history of the digenetic trematode, Himasthla littorinae sp. n. (Echinostomatidae). J Parasitol 1966;52:367-372.
- 24. Tesana S, Kanla P, Maleewong W, Kaewkes S. Scanning electron microscopy of adult Echinstoma malayanum. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 1987;18:233-240.
- 25. Vogel H. Himasthla muehlensi n sp., ein neuer menschlicher Trematode der Familie Echinostomidae. Zbl Bakt Parasitol I Abt Org 1933;127:385-391.
- 26. Yamaguti S. Systema helminthum. The digenetic trematodes of vertebrates. 1958, Vol. (Part I and II):New York and London. Interscience Publishers Inc..
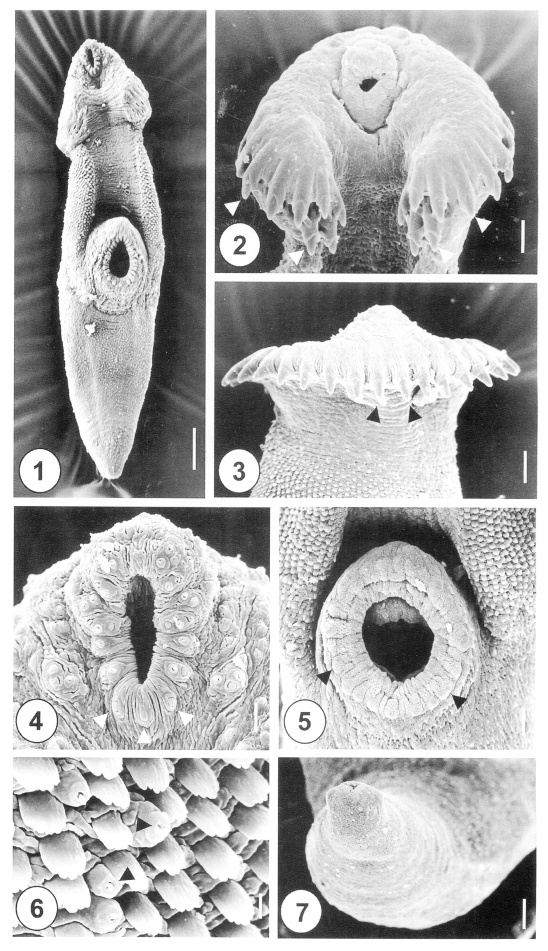
Figs. 1-7Scanning electron micrographs of 1-day-old juvenile Himasthla alincia. Fig. 1. Ventral view of a worm showing the tegumental spines covering three quarters of the whole body surface, with an oral sucker, head crown and ventral sucker. Bar = 28.6 µm. Fig. 2. Head crown with its oral sucker and collar spines (arrowheads). Bar = 0.8 µm. Fig. 3. Dorsal view of the head crown showing a single, uninterrupted row of spines (arrowheads). Bar = 9.5 µm. Fig. 4. Tegument around the oral sucker. Note the distribution of six pairs of type I sensory papillae on each side of the anterior part of the lip. On the posterior part of the lip, three single type I sensory papillae are seen (arrowheads). Three clumped, type I sensory papillae were symmetrically distributed posterolaterally to the oral sucker. Bar = 2.5 µm. Fig. 5. Ventral sucker showing type II sensory papillae on its lip (arrowheads). Bar = 5.8 µm. Fig. 6. Grouped type I sensory papillae (arrowheads) on the anterolateral surface to the ventral sucker. Bar = 0.8 µm. Fig. 7. Excretory pore showing no sensory papillae. Bar = 7.7 µm.

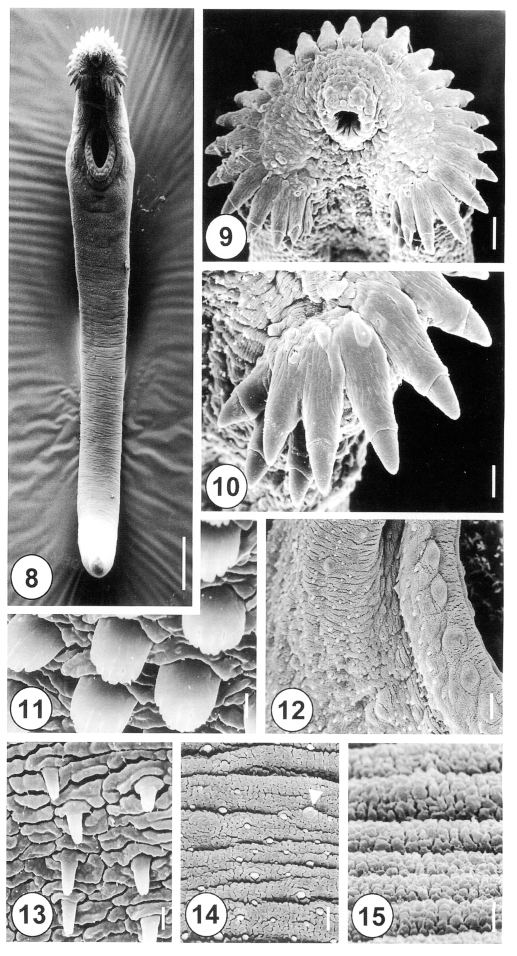
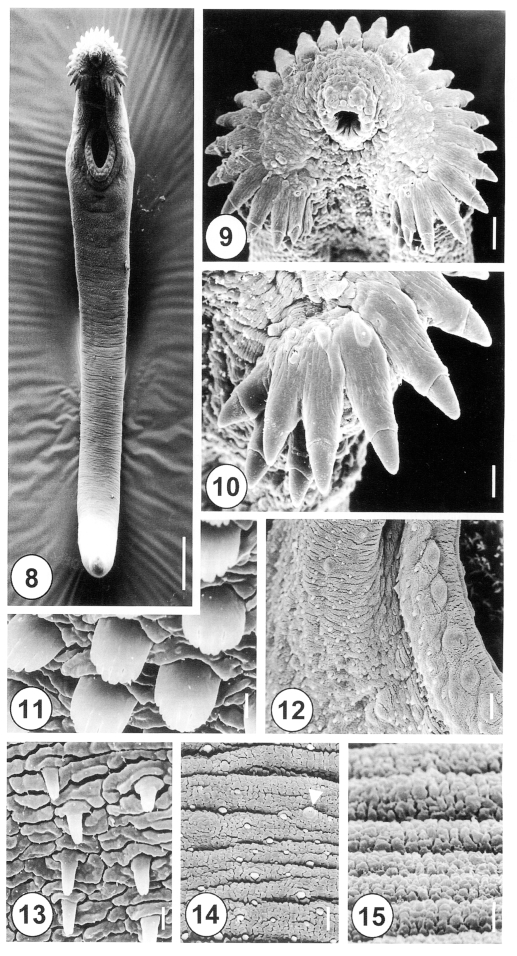
Figs. 8-15Scanning electron micrographs of 5-day-old juvenile Himasthla alincia. Fig. 8. Ventral view showing the tegumental spines covering the anterior half of the body. Note the elongated, eel-shaped, and slightly ventrally curved worm. Bar = 122.3 µm. Fig. 9. Oral sucker surrounded by collar spines. Note that the sensory papillae around the oral sucker are well developed. Bar = 11.7 µm. Fig. 10. Lateral end grouped spines of the head crown. Note the lateral end group spines with 3 oral and 2 aboral collar spines. Bar = 5.1 µm. Fig. 11. Tegument on the anterolateral body surface, showing each tegumental spine with 5-7 digits. Bar = 0.8 µm. Fig. 12. Ventral sucker with regular bumpy-shaped sensory papillae on the lip. Note the spined tegument in the raised ventral sucker areas. Bar = 4.8 µm. Fig. 13. Tegument of the ventral surface, posterior to the ventral sucker, showing peg-like spines. Bar = 0.8 µm. Fig. 14. Tegumental spines in the posterior half of the anterior body. Note the irregular distribution of peg-like spines and type I sensory papillae (arrowhead). Bar = 1.9 µm. Fig. 15. The tegument of the ventroposterior extremity is wrinkled and devoid of spines. Bar = 0.8 µm.
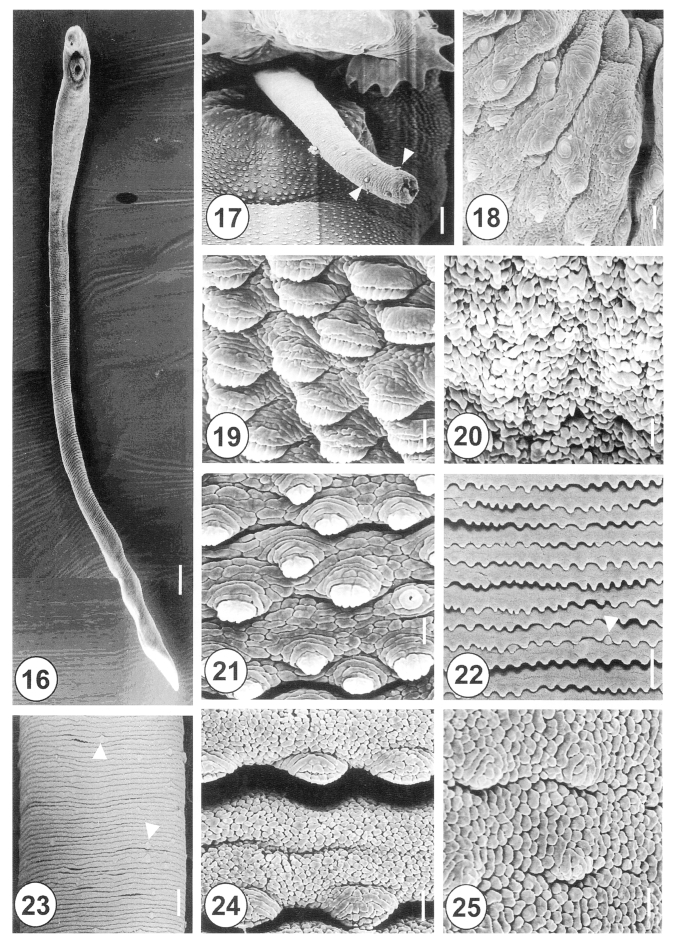
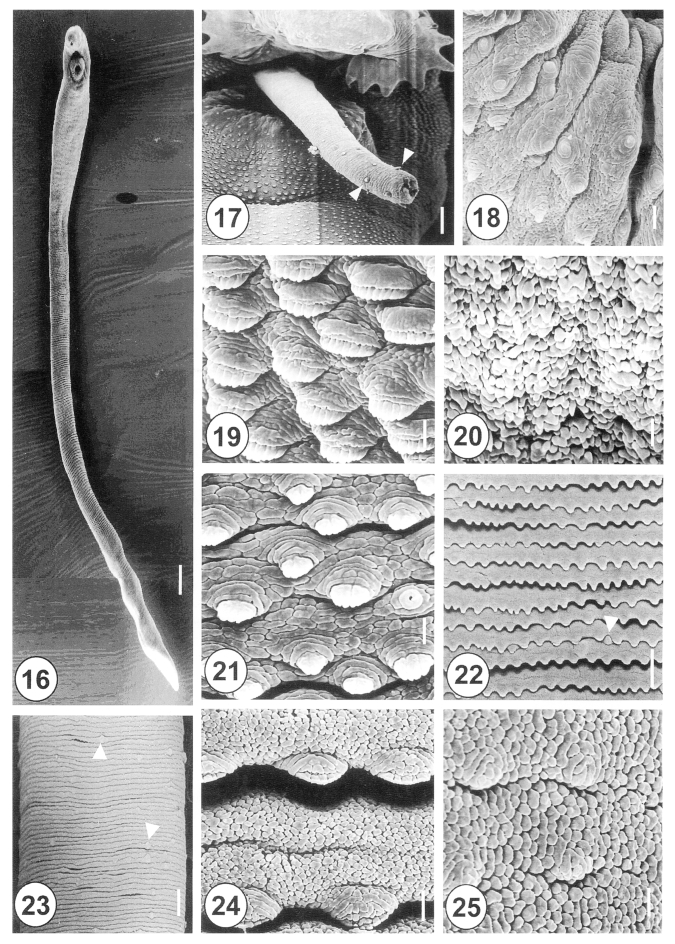
Figs. 16-25Scanning electron micrographs of 20-day-old adult Himasthla alincia. Fig. 16. Ventral view showing the long, elongated and filamentous body with wrinkling over the whole body surface. Bar = 147.7 µm. Fig. 17. The cirrus showing a few sparsely distributed spines (arrowheads) on its distal half. Bar = 12 µm. Fig. 18. Lip of the ventral sucker showing the wrinkled tegument and distribution of the type I sensory papillae. Bar = 2.5 µm. Fig. 19. Tegumental spines at the ventral surface, anterolateral to the ventral sucker. Note the tegumental spines are retracted and mature, with 8-10 digits each. Bar = 1.3 µm. Fig. 20. Ventral view of the vertical groove between the oral and ventral suckers. Note the tegument has a velvety appearance. Bar = 1.0 µm. Fig. 21. Tegument posterior to the ventral sucker, showing sparsely distributed, claw-shaped spines, with 2-5 digits on their tips. Bar = 1.3 µm. Fig. 22. The surface of the ventromedial region, showing row upon row of spade-shape spines and type II sensory papillae (arrowhead). Bar = 9.5 µm. Fig. 23. Surface of the posterior part of the anterior half of the body. Note the type II sensory papillae are irregularly distributed (arrowheads). Bar = 15.2 µm. Fig. 24. Tegument of the medial portion showing spade-shaped spines and transverse wrinkling. Bar = 1.3 µm. Fig. 25. Tegument of the posterior body showing a cobble-stone-like shape and traces of spines. Bar = 1.3 µm.