Abstract
An immunoelectron microscopy employing immunogold labeling method was performed to detect tissue origin of D1 fraction (D1A) among 5 antigenic protein fractions partially purified by DEAE-anion exchange chromatography from water-soluble crude antigen (PIWA) of adult Paragonimus iloktsuenensis. Immune reactions of adult worm tissues with rabbit serum immunoglobulin immunized with crude antigen (PI-Ig) and D1 antigen (D1-Ig), as well as rat serum immunoglobulin infected with P. iloktsuenensis were observed. D1A showed strong antigenicity in the intestinal epithelium of the worms during the early infection period of 2-4 weeks after infection. The vitellaria also showed stronger antigenicity than the other tissue sites in immune reaction of tissues against all immunoglobulins from 4 to 33 weeks after vitelline development. Therefore, it is suggested that D1A was mainly originated from the intestinal epithelial tissues before the development of vitelline gland of the parasites. Immuno-reactivity of two immunoglobulins (PI-Ig, D1-Ig) was significantly different in intestinal epithelial cytoplasmic protrusions (CP) and intestinal epithelial secretory granules (SG). In the experimental group with D1-Ig, gold particles were labeled significantly in CP than in SG when compared to the PI-Ig group. Thus, the major antigenic materials in D1 antigen having a strong antigenicity in the early infection period was considered to be originated from the intestinal epithelial tissue.
-
Key words: Paragonimus, tissue polypeptide antigen, chromatography, immunoelectron microscopy
Paragonimus iloktsuenensis is one of the two
Paragonimus spp. reported in Korea. The other
Paragonimus sp. is
P. westermani which causes human paragonimiasis.
P. iloktsuenensis has been infected to dogs and cats which are susceptible final hosts of
P. westermani (
Lee et al., 1989c); however, in nature, several species of small vertebrates including house rats, weasel and mink etc. become infected with this trematode, and the susceptible final host is known to be
Rattus spp. (house rats).
P. iloktsuenensis is similar to
P. westermani in many aspects including infection site, mode of infection (
Seo and Lee, 1973) and lung pathology (
Lee et al., 1989b) in the final host. They also have many common antigenic proteins with those of
P. westermani (
Lim et al., 1990).
P. iloktsuenensis shows a strong antigenicity in the intestine and vitellaria (
Kim and Lee, 1995) as in
P. westermani (
Sugiyama et al., 1987;
Kwon et al., 1991;
Rim et al., 1992;
Kong et al., 1992). Although the tissue origin of antigens of
P. westermani somewhat vary according to the investigators, the intestine and vitellaria were reported without exception as the tissue sites with strong antigenicity. The antigenicity of worm tegument was reported to vary in the intensity according to the antigenic materials and developmental stages of the worms. Kwon et al. (
1991) and Rim et al. (
1992) reported a strong tegumental antigenicity of
P. westermani. On the other hand, Lee et al. (
1989a) and Kong et al. (
1992) reported no antigenicity in tegumental tissue of
P. westermani. Recently, Jung and Lee (
1997) have reported that the first eluted fraction (D1) out of 5 antigenic protein fractions of
P. iloktsuenensis partially purified by DEAE-anion exchange chromatography showed strong immune reaction by ELISA test against rat serum infected with
P. iloktsuenensis and collected in the early stage of infection.
In the present experiment, we employed the immunogold labeling method in order to detect the tissue localization of D1 fraction eluted on DEAE-chromatography as compared with crude antigen which shows a strong antigenicity during the whole period of infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Parasites employed
Metacercariae of Paragonimus iloktsuenensis were separated from crabs (Sesarma dehaani) collected from Hadong, Gyeongnam, and 40-100 metacercariae were orally fed to each albino rat (Sprague-Dawley strain) weighing 150-200 g. Starting 2 weeks after infection, the worms were collected from the rat lungs in the interval of 1-2 weeks. Worm tissues for an immunoelectron microscopy were prepared with worms collected at week 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 14, 16, 29 and 33 after infection, and at least 2-3 worms were used in each week period.
Soluble antigens of P. iloktsuenensis
1. Whole worm crude extract of
P. iloktsuenensis (PIWA):
P. iloktsuenensis in several developmental stages were collected from the lungs of infected albino rats, and were washed twice with physiological saline and distilled water; and then lyophilized. The dried worms were homogenized with a small amount of 0.1% saline by means of Tsuji's method (
1975), and the homogenate was centrifuged at 20,000
g for 1 h at 4℃. The supernatant was lyophilized and dissolved in a small amount of 0.01M Tris-acetate buffer (pH 7.3) and used as the crude antigen (PIWA) (protein concentration, 13 mg/ml; determined by methods of
Lowry et al., 1951).
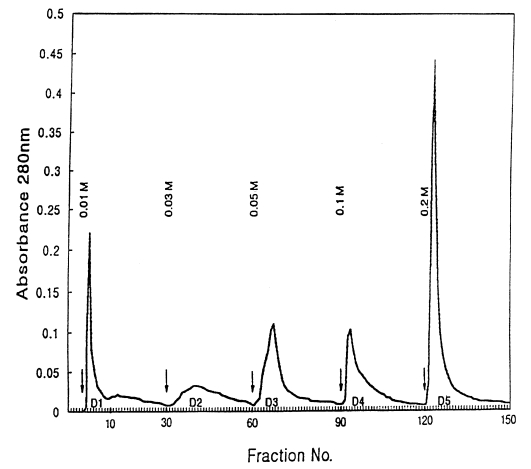
2. D1 antigen (D1A): The crude antigens (PIWA) were separated into 5 protein fractions using DEAE-anion exchange column chromatography as follows: The crude antigen equilibrated with 0.01M Tris-acetate buffer (pH 7.3) were applied to a column (10×15 cm) and put in DEAE-anion exchanger (DE52, Whatman, England) equilibrated with the same buffer. The crude antigens were eluted with Tris-acetate buffers (pH 7.3) containing 5 different molar concentrations of NaCl (0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 M), and the samples were eluted at the flow speed of 1 drop/3 sec. It took 4 min and 30 sec to collect 80 drops of eluents (about 7 ml) in a collecting tube. After collecting 30 tubes per buffer, the buffers used were exchanged. The A
280 was monitored with a spectrophotometer (model 200-20, Hitachi, Japan), and protein concentration curves according to the buffers were made (
Fig. 1). After pooling the eluents in the tubes showing high concentrations of protein in each buffer system, the samples were dialyzed with distilled water and lyophilized. Each sample was dissolved in a small amount of Tris buffer and used as D1-D5 antigens. The protein concentration of D1 antigen was 12 mg/ml.
3. SDS-PAGE: Each antigen of PIWA and D1A was electrophoresed on a 10% acrylamide gel (14×16 cm) at 15 mA/well (
Laemmli, 1970).
For an immunoelectron microscopy, tissue preparations of
P. iloktsuenensis were made by the method of Aikawa and Atkinson (
1990). Living worms collected from the lungs of albino rats were fixed in a mixing solution of 0.2% glutaraldehyde and 1% paraformaldehyde (pH 7.4) kept at 4-6℃ for 2-3 hrs. After washing and a process of dehydration, specimens were put in LR white resin solution and kept in a freezer (-20℃) for several hours or at room temperature (vacuum condition) for 48 hrs. Then, specimens were embedded in the gelatin capsules with resin solution at 40℃ for 5 days. Embedded worms were cut into thin sections (70Å) with a microtome. The tissue sections attached on a nickel grid (200 mesh) were used as tissue antigens.
The antibodies for immune reaction against P. iloktsuenensis tissue antigens were purified from sera of rabbits immunized with soluble crude antigen and D1 antigen (PI-Ig; D1-Ig). Rat serum immunoglobulin obtained from the albino rats experimentally infected with P. iloktsuenensis was also used in this experiment (PIR-Ig).
1. Rabbit anti-PIWA immunoglobulin (PI-Ig): One ml of a mixture with 0.5 ml of PIWA (2 mg/ml) and 0.5 ml of Freund's complete adjuvant (Sigma, F-5881) was once injected into subcutaneous tissue of the rabbits. A total of 7 subsequent injections with the same mixture as above were done in 1-week interval. The rabbit serum immunoglobulin was purified from sera of immunized rabbits using the ammonium sulfate sedimentation method. Immunoglobulin was dissolved in a small amount of 0.01M Tris-acetate buffer (pH 7.3) and used as the antibody (PI-Ig) against crude antigen (protein concentration; 23 mg/ml).
2. Rabbit ant-D1A immunoglobulin (D1-Ig): By injection with 1 ml of a mixture of 0.5 ml D1A (2 mg/ml) and 0.5 ml Freund's complete adjuvant into the rabbit, the immunoglobulin (D1-Ig) against D1A was made. D1-Ig (protein concentration, 24 mg/ml) was produced by the same method as PI-Ig.
3. Immunoglobulin of infected rats (PIR-Ig): Among the 4-16 weeks old albino rats after infection with P. iloktsuenensis, sera of the rats with more than 10 worms were collected. Serum immunoglobulin (PIR-Ig) was purified from rat sera (protein concentration, 17 mg/ml) by the ammonium sulfate sedimentation method as described before.
Immune reaction
1. Immune reaction of worm tissue antigen by immunogold labeling method
In order to observe the immune reaction of
P. iloktsuenensis tissues, a method of Aikawa and Atkinson (
1990) was applied: 0.1 M phosphate buffer (PGB, pH 7.2) containing 0.1% Tween 20 and 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) was used for washing grids, antibody dilution and conjugate dilution. Phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.2) without containing Tween 20 and BSA was used for washing after conjugate treatment. Each globulin was diluted 2,000 times and 1% protein A gold complex (10 nm, Sigma P1039) was used as conjugate. After conjugating for 1 hr, the tissues on the grids were fixed with phosphate buffer containing 1% glutaraldehyde. After washing with phosphate buffer and distilled water, the grids were post-stained with 6% uranyl acetate and Reynold lead, and observed under the electron microscope (JEM-100CXII, JEDL Co., Tokyo, Japan).
2. Immunoblotting of soluble antigens
EITB (enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot) was applied according to the method of Tsang et al. (
1983). Protein fraction bands of crude antigen (PIWA) and D1 antigen (D1A) on SDS-PAGE gel were transferred to the nitrocellulose paper, and immunoreactive protein bands on nitrocellulose were compared.
RESULTS
Worm tissue antigens of P. iloktsuenensis
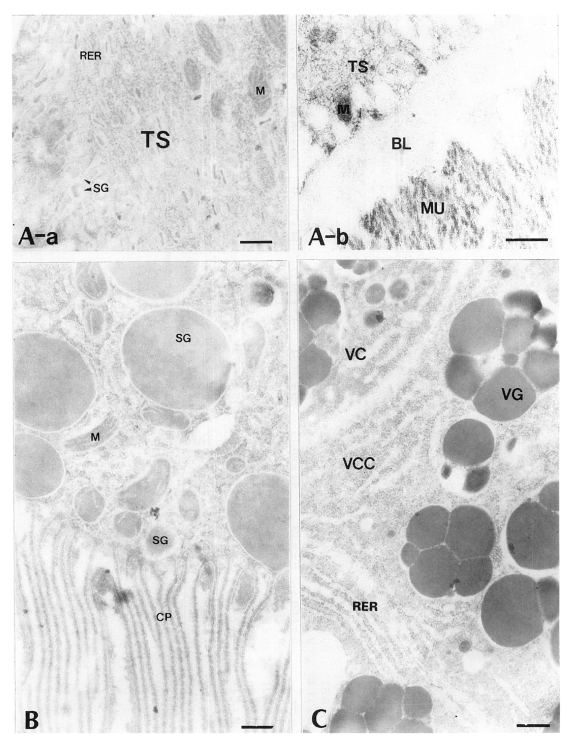
All of worm tissues of
P. iloktsuenensis showed no labeling of antigen-antibody binding gold particles in the immune reaction with control sera of normal rats (
Fig. 2A-C). In the experiment with PI-Ig, D1-Ig and PIR-Ig, the gold particles were labeled in all target tissues of the parasite with different particle densities. The overall antigenic intensity according to the target tissues was high in order of intestine, vitellaria and tegument of the parasite even though there were some differences of antigenic density among the individual worms collected even during the same infection period. In the tegument, gold particles were labeled in the tegumental syncytium (TS), cytoplasm of tegumental cells (TC) and basal layer (BL). Among these, TS showed less amount of the particles than the others. In the intestine, the gold particles were labeled mainly in the secretory granules (SG) and cytoplasmic protrusions (CP) of the intestinal epithelial cells. In the vitellaria, the gold particles were labeled mainly in the protoplasm between cleavages of cytoplasm (VCC) and vitelline globules (VG) in the vitelline cells (VC). The surface of the vitelline globules was labeled with less gold particles. Many gold particles were labeled strongly in the intestinal tissues, regardless of the worm maturity according to the infection period. Tegumental and intestinal tissues in the same worms showed more gold particles labeled in immune reaction with PI-Ig and D1-Ig than with PIR-Ig. On the contrary, immune reactions in vitellaria were observed more strongly in the experiment with PIR-Ig rather than with the other rabbit immoglobulins. The intensity of tissue antigenicity for each antibody was expressed by the average number of gold particles in
Table 1.
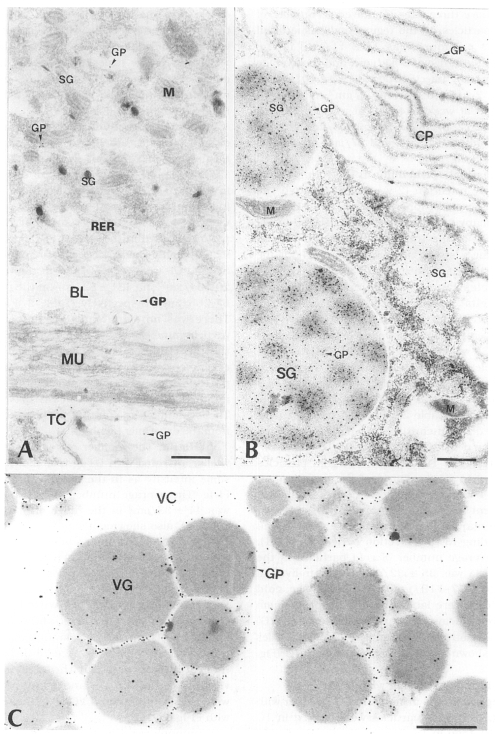
1. Immune reaction with PI-Ig
Tegument: In the immune reaction with PI-Ig and the tegumental tissues, more gold particles were shown generally in TC and BL of the same worm than in TS, but rarely some worms were labeled with the same intensity in the above three sites. The average number of gold particles on the tegumental tissue of all worms examined was 11 ± 11/µm
2 in the individual range of 3-41/µm
2, and the average numbers by infection periods were 10/µm
2 at week 2 after infection, 7/µm
2 at week 3, 10/µm
2 at week 4, 4/µm
2 at week 8, 13/µm
2 at week 12, 5/µm
2 at week 14, 9/µm
2 at week 16, 4/µm
2 at week 29 and 27/µm
2 at week 33 (
Table 1,
Fig. 3A).
Intestinal epithelium: In the young worms of early infection (2-week old) through the adult worms of long-term infection (33-week old), many gold particles were observed in SG and CP of the intestinal epithelial tissue, showing a strong antigenicity throughout the experiment. The average number of gold particles labeled in the entire intestinal epithelial tissue was 80 ± 61/µm
2 in the individual range of 35-199/µm
2 (
Table 1), and the average number of particles in sum of SG and CP was 141 ± 118/µm
2. The average particle numbers in SG and CP were 219 ± 120/µm
2 in the range of 67-470/µm
2 and 64 ± 39/µm
2 in the range of 14-133/µm
2, respectively (
Table 2). The gold particles were labeled significantly more in SG with high electron density than CP (p < 0.001) (
Fig. 3B).
Vitellaria: The numbers of gold particles labeled in the vitellaria of the worms older than 4 weeks after infection were somewhat different among individual worm tissues, but no remarkable differences were observed according to the infection periods (p > 0.1). The average number of gold particles in the vitellaria was 35 ± 32/µm
2 in the individual range of 7-119/µm
2 (
Table 1). The gold particles were labeled mainly in protoplasm between cleavages of vitelline globules (VG) and a relatively few numbers of gold particles were shown in the cytoplasm around VG (
Fig. 3C).
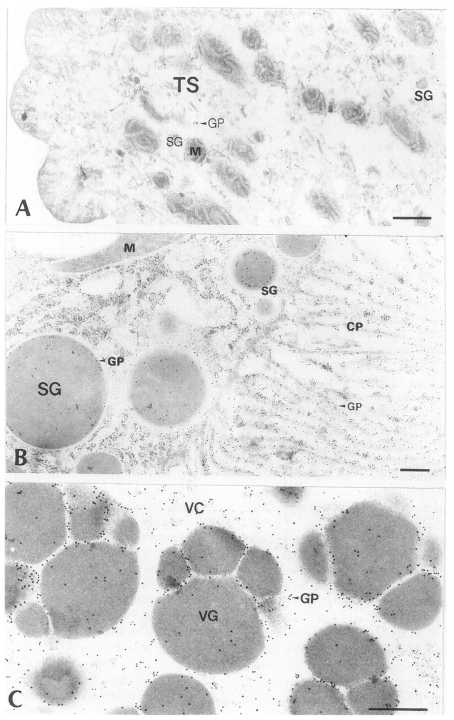
2. Immune reaction with D1-Ig
Tegument: As in the immune reaction with PI-Ig, more gold particles were labeled in TC and BL than in TS. As a whole, the number of gold particles in the tegument was fewer than in the intestinal epithelium and vitellaria. The average number of gold particles was 19 ± 19/µm
2 in the range of 3-61/µm
2 (
Table 1), showing relatively more gold particles were observed in the tegument treated with D1-Ig than those in the reaction with PI-Ig, but there was no significant difference between them (p > 0.1). As in the experiment with PI-Ig, the differences of particle numbers were observed more in the individual worms rather than in the infection periods (
Fig. 4A).
Intestinal epithelium: The average number of gold particles labeled in whole intestinal tissue was 63 ± 42/µm
2 in the range of 32-117/µm
2 (
Table 1), and significant differences in the particle density were also shown in the individual worms as in the immune reaction with PI-Ig. The average number of gold particles shown in the sum of SG and CP was 92 ± 78/µm
2. The average particle numbers in SG and CP were 53 ± 50/µm
2 in the range of 20-164/µm
2 and 131 ± 82/µm
2 in the range of 67-265/µm
2, respectively (
Table 2,
Fig. 4B). There was no significant difference of the particle numbers in the sum of SG and CP of the intestinal tissue with the sum in the experiment with PI-Ig (p > 0.1), but the average particle numbers of CP were significantly much higher than those of SG (p < 0.05). These results were contrary to those obtained from the experiment with PI-Ig.
Vitellaria: The number of gold particles in vitellaria treated with D1-Ig was shown in the same intensity as in the tissue reaction with PI-Ig. The average number of gold particles was 44 ± 33/µm
2 in the range of 8-137/µm
2 (
Table 1), also showing a significant difference in the particle numbers according to the individual worms as shown in the above results. Although there were some worms that showed relatively more gold particles than those in the experiments with PI-Ig, no significant difference was shown in the immune reactions of two immunoglobulins (p > 0.1). The gold particles were labeled mainly in protoplasm between the cleavages of vitelline globules (VG), and many particles were also labeled around VG as in the reaction with PI-Ig (
Fig. 4C).
3. Immune reaction with PIR-Ig
Tegument: In the experiments with PIR-Ig, the gold particles were labeled more in TC and BL than in TS as in the immune reactions with PI-Ig and D1-Ig. The average number of gold particles was 11 ± 25/µm
2 in the range of 2-93/µm
2 (
Table 1). No significant difference in the antigenic intensity was shown as compared with tissue reactions with immune rabbit antibodies. The gold particles were rarely observed in TS of the worms which showed a little amount of particles in TC and BL. The tegument of 29-week old worms was labeled with a few numbers of gold particles, whereas in the tegument of 33-week old worms relatively more gold particles were labeled. The difference of antigenic intensity was greater among the individual worms rather than in the degree of worm maturity (
Fig. 5A).
Intestinal epithelium: The average number of gold particles was 55 ± 43/µm
2 in the range of 38-142/µm
2, and the number in sum of SG and CP was 67 ± 72/µm
2. The average numbers in SG and CP were 33 ± 39/µm
2 in the range of 7-111/µm
2 and 102 ± 81/µm
2 in the range of 54-287/µm
2, respectively. The greater numbers of gold particles were labeled in CP than in SG, which had a similar pattern to the response with D1-Ig. The differences in the antigenic intensity were also observed in the individual worms as before (
Fig. 5B).
Vitellaria: The average number of gold particles was 89 ± 57/µm
2 in the range of 43-285/βµm
2, showing significantly more number of gold particles than in the immune reaction with PI-Ig and D1-Ig (p < 0.001). Gold particles were labeled mainly in protoplasm between cleavages of vitelline globules (VG), but showed up in less numbers in cytoplasm of the cells around the VG (
Fig. 5C).
SDS-PAGE and EITB
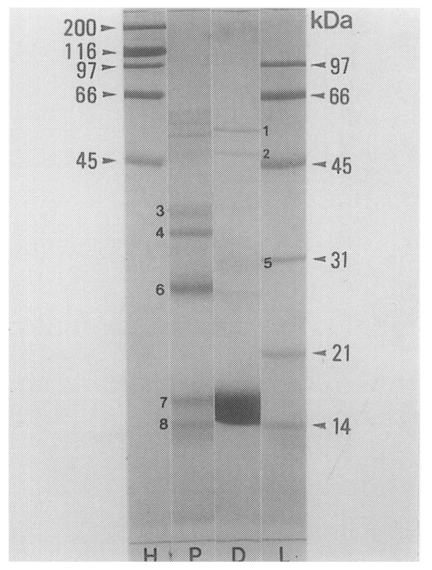
PIWA and D1A showed more than 25 and 20 protein bands, respectively, with molecular weights of 10-100 kDa on SDS-PAGE. The protein bands of the two antigens generally had the same molecular weights with each other, but there were different protein concentrations in some degree. Protein bands with the molecular weights of 15-18 kDa, 28 kDa and 35-38 kDa showed significantly stronger staining densities in D1A than in PIWA, and the bands of 30-32 kDa, 50 kDa and 56 kDa also showed relatively stronger staining densities in D1 antigen (
Fig. 6).
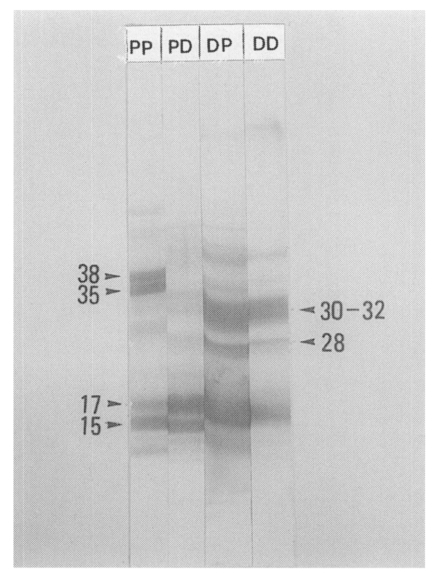
The antibody binding patterns on EITB of PIWA and D1A are shown in
Fig. 7. In general, the bands with high concentrations on SDS-PAGE were strongly reacted with antibodies on EITB with a few exceptions. Protein bands of 35-38 kDa in PIWA were bound strongly with PI-Ig, and the bands of 15-18 kDa were bound strongly with D1-Ig. In immune response of D1 antigen and D1-Ig, strong antibody bindings were observed with 15-18 kDa, 28 kDa and 30-32 kDa, and also these protein bands were strongly reacted with PI-Ig.
DISCUSSION
It is well known that
P. iloktsuenensis shows almost the same mode of infection (
Seo and Lee, 1973) and pathology (
Lee et al., 1989b) in the final host as those of
P. westermani, and shows cross immune reaction with common antigenic proteins (
Lim et al., 1990). In this study, the protein bands of 15-18 kDa in PIWA and D1A were strongly bound with their antibodies, but the bands of D1A did not show stronger antigenicity than the protein bands of PIWA. An explanation may be that D1A was only a fraction of crude antigen (PIWA) which included broad range of antigenic materials.
The intestinal tissue and vitellaria which contain strong antigenic materials in
P. iloktsuenensis (
Kim and Lee, 1995) were reported to be also strongly antigenic in
P. westermani (
Sugiyama et al., 1987;
Kwon et al., 1991;
Rim et al., 1992;
Nam, 1994). In general, the antigenicities in the tissues of
P. iloktsuenensis and
P. westermani were similar in the case of soluble antigen, but significantly different according to the techniques used (
Lee et al., 1989a;
Kwon et al., 1991;
Rim et al., 1992;
Kong et al., 1992) even in the same specis. Kong et al. (
1992) reported that a strong antigenicity was shown in the intestine, intestinal luminal materials and egg, but not present in the tegument and testis in the immune reaction with
P. westermani worm tissues and sera against water-soluble worm extract antigens separated with disk-PAGE. Lee et al. (
1989a) observed similar results as in the report of Kong et al. (
1992). On the contrary, Kwon et al. (
1991) and Rim et al. (
1992) reported that the tegumental tissues of
P. westermani had a much strong antigenicity than the intestinal tissues in the 4-week old young worms. However, the tegument of 33-week old worms showed relatively strong antigenicity in this study. The overall antigenicity of tegument was much lower than that of intestinal tissue or vitellaria. Moreover, tegumental tissue antigenicity in the reaction with PIR-Ig was much weaker than with PI-Ig and D1-Ig. Therefore, tegumental tissue antigen's affect on D1 antigen production may be marginal.
In the immune reactions with PI-Ig and D1-Ig, antigenic substances in the intestinal tissues of the worms were mainly from SG and CP, and reactivities of both organells were significantly different in the number of gold particles labeled (p < 0.001). However, it could not be proven how antigens from SG and/or CP affect the intestinal tissue antigenicity.
Having a high antigenicity, the vitellaria can also be thought to influence antigenic intensity of soluble antigen, since large parts of mature worms are occupied by the vitellaria. Kwon et al. (
1991) and Rim et al. (
1992) also reported a strong antigenicity of the vitellaria in
P. westermani. The vitellaria of
P. iloktsuenensis showed stronger reaction in PIR-Ig than in PI-Ig and D1-Ig in this study. It is certain that vitellaria of the worm is one of the tissues with strong antigenicity. However, the vitellaria of
P. iloktsuenensis seems not to affect the antigenic material up to 2 weeks after infection, since the development of the vitellaria is usually completed at 4-5 weeks in final host (
Seo and Lee, 1973), differently from the intestinal tissue which develops within 2 weeks after infection (
Fujino and Ishii, 1990).
In conclusion, the major antigenic substances of D1 antigen having a strong antigenicity at the early infection stage of P. iloktsuenensis were considered to be originated from intestinal tissues containing abundant cytoplasmic protrusion components of intestinal epithelium.
Notes
-
This study was supported by a grant from Soonchunhyang University research fund (1999).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Authors thank Sun-hwa Lee in Department of Parasitology and Jeong-hyeon Lee in Department of Electron Microscopy, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University for their technical assistance.
References
- 1. Aikawa M, Atkinson CT. In Baker JR, Muller R eds, Immunoelectron microscopy of parasites. Advances in Parasitology. 1990, Vol 29:Academic Press; pp 151-214.
- 2. Fujino T, Ishii Y. Paragonimus ohirai juveniles: ultrastructural cytochemical and autoradiographic studies on the development of the gastrodermal epithelium. Jpn J Parasitol 1990;39:186-197.
- 3. Jung KS, Lee OR. Antigenicity of protein fractions in adult worms of Paragonimus iloktsuenensis. J Soonchunhyang Med Coll 1997;3:181-193.
- 4. Kim HS, Lee OR. Ultrastructural antigenic localization in Paragonimus iloktsuenensis during developmental stage by immunogold labeling method. Korean J Parasitol 1995;33:365-376.
- 5. Kong Y, Park CY, Kang SY, Cho SY. Tissue origin of soluble component proteins in saline extract of adult Paragonimus westermani. Korean J Parasitol 1992;30:91-100.
- 6. Kwon OS, Lee JS, Rim HJ, Kim SJ. Antigenic localities in the tissues of the young adult worm of Paragonimus westermani using immunogold labeling method. Korean J Parasitol 1991;29:31-41.
- 7. Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970;227:681-685.
- 8. Lee SH, Sung SH, Chai JY. Immunohistochemical study on the antigenicity of body compartments of Paragonimus westermani. Korean J Parasitol 1989a;27:109-117.
- 9. Lee SH, Kim SY, Han YC, et al. Effect of praziquantel treatment on pulmonary lesions of rats infected with Paragonimus iloktsuenensis. Korean J Parasitol 1989b;27:119-130.
- 10. Lee SH, Koo KH, Chai JY, Hong ST, Sohn WM. Experimental infection of Paragonimus iloktsuenensis to albino rats, dogs and cats. Korean J Parasitol 1989c;27:197-202.
- 11. Lim BK, Lee OR, Nam HS. ELISA of rat sera infected with Paragonimus iloktsuenensis. Korean J Parasitol 1990;28:207-212.
- 12. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Fan AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurements with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 1951;193:265-275.
- 13. Nam HS. Ultrastructural localization of antigenic sites in Paragonimus iloktsuenensis. J Soonchunhyang Univ 1994;17:1427-1441.
- 14. Rim HJ, Kim SJ, Sun IJ, Lee JS. Antigenic localities in the tissues of Paragonimus westermani by developmental stages using immunogold labeling method. Korean J Parasitol 1992;30:1-14.
- 15. Seo BS, Lee WJ. Studies on the lungfluke, Paragonimus iloktsuenensis III. Migration, development and egg-production in albino rats. Seoul J Med 1973;14:131-141.
- 16. Sugiyama H, Sugimoto M, Akasaka K, Horiuchi T, Tomimura T, Kozaki S. Characterization and localization of Paragonimus westermani antigen stimulating antibody formation in both the infected cat and rat. J Parasitol 1987;73:363-367.
- 17. Tsang VC, Peralta JM, Simons AR. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques(EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol 1983;92:377-391.
- 18. Tsuji M. Comparative studies on the antigenic structure of several helminths by immunoelectrophoresis. Jpn J Parasitol 1975;24:227-236.
Fig. 1Elution profile of water-soluble crude extract of adult Paragonimus iloktsuenensis (PIWA) on DEAE-anion exchange chromatography. Five protein fractions (D1-D5) are indicated by arrows. Elution buffer: 0.01 M Tris-acetate buffer containing 0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 M-NaCl, pH 7.3; column: 10×1.5 cm; flow rate: 1 drop/3 sec, 80 drops/tube.
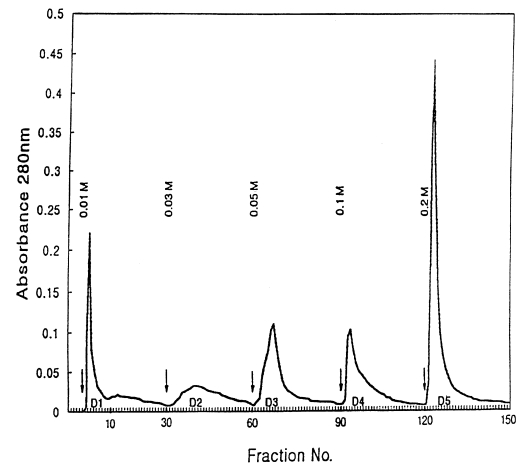
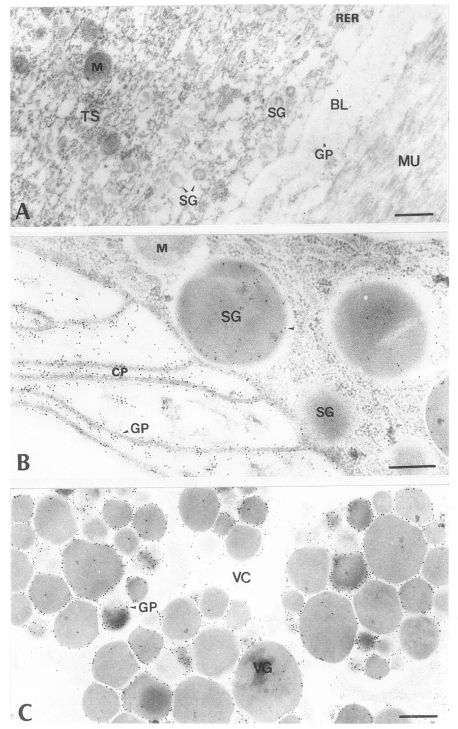
Fig. 2Electron-micrographs of worm tissues of Paragonimus iloktsuenensis reacted with control sera of normal rats. No labeling of gold particles was observed. A, tegument, ⓐ 6-week old worm (×30,000), ⓑ 8-week old worm (×39,000); B, intestinal epithelium, 6-week old worm (×30,000); C, vitelline gland, 6-week old worm (×30,000), Bar=3 µm. TS: tegumental syncytium, RER: rough endoplasmic reticulum, BL: basal lamina, M: mitochondria, MU: muscle, SG: secretory granule, CP: cytoplasmic protrusion, VC: vitelline cell, VCC: cytoplasm of vitelline cell, VG: vitelline globule.
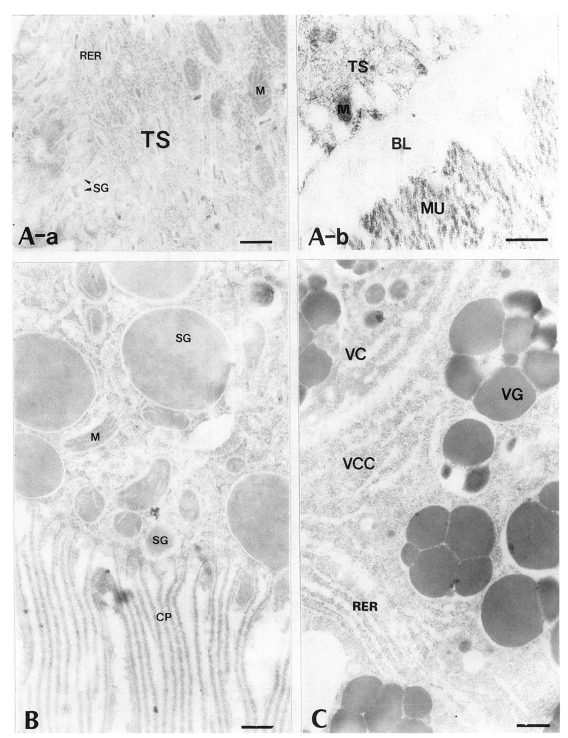
Fig. 3Electron-micrographs of worm tissues of
Paragonimus iloktsuenensis reacted with rabbit anti-PIWA immunoglobulin (PI-Ig). A, A few gold particles were labeled in the tegument, but were shown in TC and BL of the 8-week old worm (×39,000); B, Many gold particles were observed in SG and CP in the intestinal epithelium of 2-week old worm (×39,000); C, The gold particles were labeled mainly in protoplasm between cleavages of vitelline globules (VG) of 33-week old worm (×60,000), Bar=3 µm. TC: tegumental cell, GP: gold particle. Other abbreviations are same as in
Fig. 2.
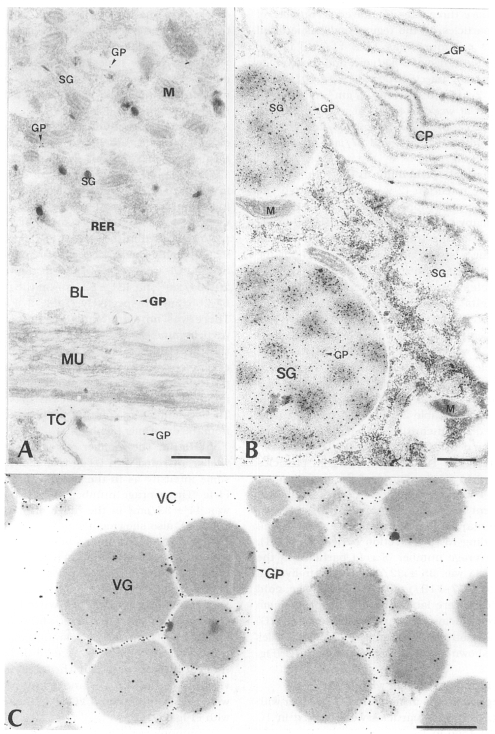
Fig. 4Electron-micrographs of worm tissues of
Paragonimus iloktsuenensis reacted with rabbit anti-D1A immunoglobulin (D1-Ig) A, A few gold particles were labeled in the tegument as in
Fig. 3A, but were shown in TC of 12-week old worm (×39,000); B, The average particle numbers in CP were significantly much higher than those of SG in the intestinal epithelium of 3-week old worm (×30,000). These results were contrary to those obtained from the experiment with PI-Ig; C, The gold particles were labeled mainly in protoplasm between the cleavages of VG of 33-week old worm (×60,000), Bar=3 µm. The abbreviations are same as in
Figs. 2 and
3.
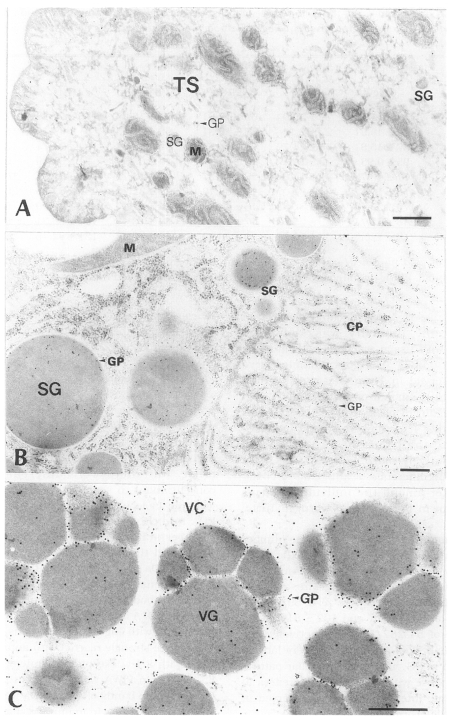
Fig. 5Electron-micrographs of worm tissues of
Paragonimus iloktsuenensis reacted with immunoglobulin of infected rats (PIR-Ig). A, A few particles were labeled more in BL than in TS of 12-week old worm (×39,000); B, The greater numbers of the particles were labeled in CP than in SG of the intestinal epithelium of 2-week old worm (×48,000); C, The gold particles were labeled mainly in protoplasm between cleavages of VG of 33-week old worm (×39,000), Bar=3 µm. The abbreviations are same as in
Figs. 2 and
3.
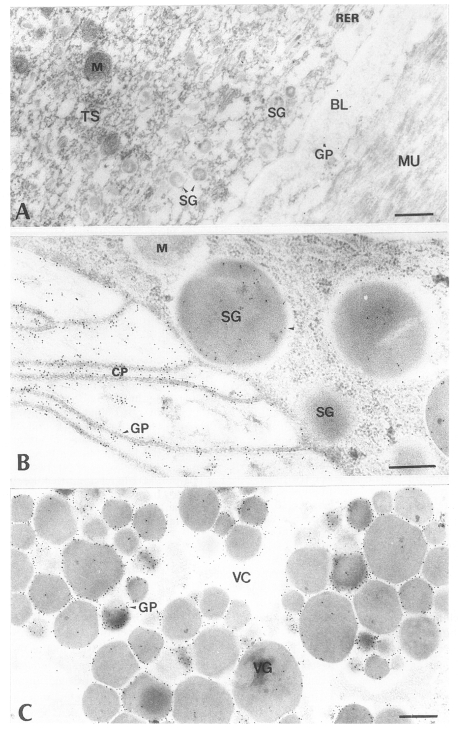
Fig. 6SDS-PAGE analysis of PIWA and D1A. More than 25 protein bands with molecular weights of 10-100 kDa on SDS-PAGE were recognized in both of PIWA and D1A; but, the bands with the molecular weights of 15-18 kDa, 28 kDa and 35-38 kDa showed significantly stronger densities in D1A than in PIWA. Molecular weights (kDa) of standard protein markers (arrow heads) and main bands of PIWA and D1A are indicated by numbers: 1 = 56 kDa, 2 = 50 kDa, 3 = 38 kDa 4 = 35 kDa 5 = 30-32 kDa, 6 = 28 kDa, 7 = 17 kDa, 8 = 15 kDa. H: high markers, L: low markers, P: PIWA, D: D1A.
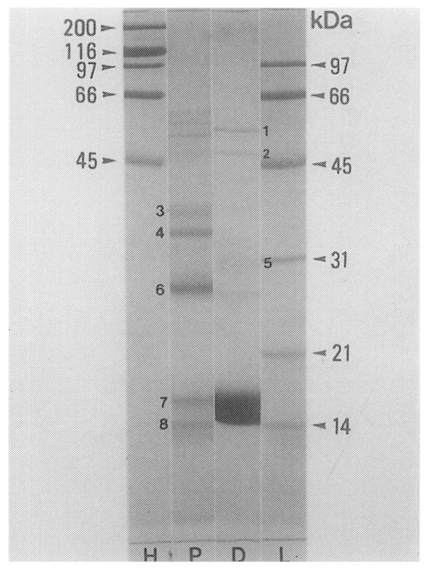
Fig. 7Immunoblot analysis of PIWA and D1A against PI-Ig and D1-Ig. Protein bands of 35-38 kDa in PIWA were bound strongly with PI-Ig, and the bands of 15-18 kDa were bound strongly with D1-Ig. Molecular weights (kDa) are indicated by the arrow heads. PP: binding band of PIWA and PI-Ig on a nitrocellulose sheet. PD: binding band of PIWA and D1-Ig on a nitrocellulose sheet. DD: binding band of D1A and D1-Ig on a nitrocellulose sheet. DP: binding band of D1A and PI-Ig on a nitrocellulose sheet.
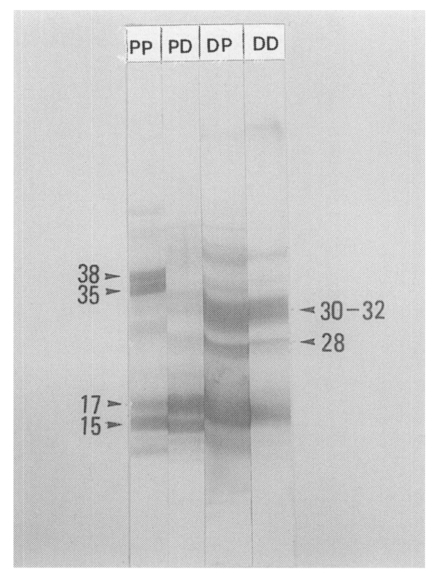
Table 1.The mean number of the gold particles labeled on the tissues of
Paragonimus iloktsuenensis according to weeks after infection
a)
Table 1.
|
Weeks after infection |
Tegument
|
Intestinal epithelium
|
Vitelline gland
|
|
PI-Ig |
D1-Ig |
PIR-Ig |
PI-Ig |
D1-Ig |
PIR-Ig |
PI-Ig |
D1-Ig |
PIR-Ig |
|
2 |
10 ± 3.17 |
15 ± 6.53 |
4 ± 2.16 |
86 ± 70.41 |
51 ± 23.87 |
50 ± 27.71 |
— |
— |
— |
|
3 |
7 ± 5.52 |
26 ± 12.58 |
2 ± 1.83 |
48 ± 27.23 |
38 ± 28.85 |
71 ± 53.58 |
— |
— |
— |
|
4 |
10 ± 11.49 |
3 ± 1.99 |
3 ± 2.21 |
64 ± 23.84 |
78 ± 34.41 |
45 ± 25.61 |
28 ± 25.61 |
32 ± 14.76 |
285 ± 85.86 |
|
6 |
— |
3 ± 1.66 |
6 ± 6.13 |
44 ± 20.15 |
55 ± 35.94 |
43 ± 39.27 |
14 ± 10.70 |
30 ± 28.01 |
85 ± 27.07 |
|
8 |
4 ± 1.72 |
22 ± 27.55 |
6 ± 2.88 |
107 ± 66.90 |
44 ± 51.00 |
37 ± 21.71 |
24 ± 6.71 |
30 ± 11.07 |
50 ± 19.25 |
|
12 |
13 ± 5.21 |
16 ± 8.25 |
5 ± 2.78 |
125 ± 102.51 |
— |
— |
46 ± 29.33 |
49 ± 16.57 |
134 ± 25.61 |
|
14 |
5 ± 3.86 |
29 ± 16.92 |
9 ± 3.02 |
136 ± 77.54 |
117 ± 39.44 |
102 ± 79.26 |
36 ± 7.49 |
46 ± 9.19 |
101 ± 24.89 |
|
16 |
9 ± 4.11 |
14 ± 5.01 |
4 ± 2.72 |
79 ± 38.34 |
45 ± 16.79 |
38 ± 26.39 |
16 ± 4.80 |
22 ± 4.39 |
87 ± 12.53 |
|
29 |
4 ± 1.80 |
11 ± 3.56 |
5 ± 3.73 |
— |
— |
— |
20 ± 6.00 |
30 ± 7.13 |
65 ± 17.34 |
|
33 |
27 ± 19.04 |
47 ± 31.17 |
34 ± 47.56 |
155 ± 70.22 |
111 ± 68.56 |
142 ± 66.0 |
96 ± 47.10 |
119 ± 33.79 |
125 ± 35.92 |
|
Mean |
11 ± 11.09 |
19 ± 19.44 |
11 ± 25.03 |
80 ± 61.28 |
63 ± 42.52 |
55 ± 43.07 |
35 ± 32.92 |
44 ± 33.10 |
89 ± 47.45 |
Table 2.The mean number of the gold particles labeled on the secretory granules (SG) and cytoplasmic protrusion (CP) in intestinal epithelial cells of
Paragonimus iloktsuenensis according to weeks after infection
a)
Table 2.
|
Weeks after infection |
SG
|
CP
|
|
PI-Ig |
D1-Ig |
PIR-Ig |
PI-Ig |
D1-Ig |
PIR-Ig |
|
2 |
242 ± 116.75 |
72 ± 35.04 |
60 ± 17.61 |
78 ± 18.65 |
155 ± 97.43 |
171 ± 59.47 |
|
3 |
88 ± 40.31 |
22 ± 8.12 |
38 ± 19.31 |
63 ± 34.73 |
81 ± 39.10 |
165 ± 55.29 |
|
4 |
137 ± 45.81 |
56 ± 24.79 |
75 ± 44.33 |
93 ± 50.64 |
194 ± 71.71 |
125 ± 39.02 |
|
6 |
95 ± 9.93 |
33 ± 18.29 |
12 ± 6.04 |
14 ± 3.44 |
91 ± 60.39 |
57 ± 22.12 |
|
8 |
67 ± 66.70 |
45 ± 11.89 |
29 ± 22.37 |
42 ± 13.79 |
67 ± 21.97 |
101 ± 37.98 |
|
14 |
470 ± 109.72 |
164 ± 81.05 |
111 ± 52.13 |
127 ± 32.72 |
265 ± 82.36 |
287 ± 70.27 |
|
16 |
179 ± 37.45 |
20 ± 8.13 |
15 ± 9.47 |
24 ± 4.99 |
67 ± 12.29 |
54 ± 20.07 |
|
33 |
246 ± 55.71 |
35 ± 23.22 |
7 ± 3.88 |
62 ± 13.45 |
151 ± 56.31 |
54 ± 17.45 |
|
Mean |
219 ± 120.70 |
53 ± 50.75 |
33 ± 39.16 |
64 ± 39.47 |
131 ± 82.45 |
102 ± 81.22 |