Abstract
Three cases of human infection by Trichinella spiralis were first confirmed by detecting encysted larvae in the biopsied muscle in December 1997, in Korea. The patients were one 35- and two 39-year-old males residing in Kochang-gun, Kyongsangnam-do. They had a common past history of eating raw liver, spleen, blood and muscle of a badger, Meles meles melanogenys, and complained of high fever, facial and periorbital edema, and myalgia. Hematologic and biochemical examinations revealed leukocytosis and eosinophilia, and highly elevated levels of GOT, GPT, LDH and CPK. In the gastrocnemius muscle of a patient, roundly coiled nematode larvae were detected. The larvae measured 0.775-1.050 (av. 0.908) mm in length, and 0.026-0.042 (av. 0.035) mm in maximum width. The specific IgG antibody levels in three patients' sera were significantly higher when compared with those of normal controls. The patients were treated with flubendazole and albendazole for 15-30 days, and discharged at 13-34 days post-admission. From the above findings, it was confirmed that T. spiralis is present in Korea, and the badger plays a role of as the natural host.
-
Key words: epidemiology, Trichinella spiralis, Korea, human, badger
Trichinosis is one of the most widespread helminthic zoonoses. Unlike other parasite infections, it has been the main public health problem in advanced countries where there is a great amount of meat consumption such as European countries and USA. This nematode infection has been reported in all of the continents except Australia (
Despommier, 1998). Due to the widespread of trichinosis in many Asian countries including China and Japan (
Yamaguti, 1989;
Miyazaki, 1991), it has been suspected to be prevalent in Korea for a long time. However, trichinosis had not been reported in Korea until 1997. In December 1997, the first human infection with
Trichinella spiralis was confirmed by detecting encysted larvae in the biopsied muscle.
A 35- and two 39-year-old men residing in Kochang-up were admitted to Seokyong Hospital in Kochang-gun, Kyongsangnam-do on December 4, 1997. They chiefly complained of high fever, facial and periorbital edema, and myalgia, and had a common past history of eating raw liver, spleen, blood and muscle of a badger, Meles meles melanogenys. They mentioned that the severe symptoms such as abdominal pain, watery diarrhea, high fever, chill, headache, facial and periorbital edema, general pain, and myalgia, appeared 3-14 days after eating a badger.
Hematologic examinations performed at 26, 30, 33 and 35 days after infection revealed eosinophilia (2-19%, 7-16% and 0-6% in each patients) and leukocytosis (18,000, 26,550 and 12,500/mm
3 in average). Biochemical examinations showed highly elevated levels of GOT, GPT, LDH (lactic dehydrogenase) and CPK (creatine phosphokinase) (
Table 1,
2). Becuase the symptoms and the laboratory findings were highly suggestive of trichinosis, muscle biopsy was performed to verify it. The biopsied muscles were examined by the pressure method using two slide glasses. Roundly coiled nematode larvae were detected in the gastrocnemius muscle of a patient at 34 days after eating raw badger flesh (
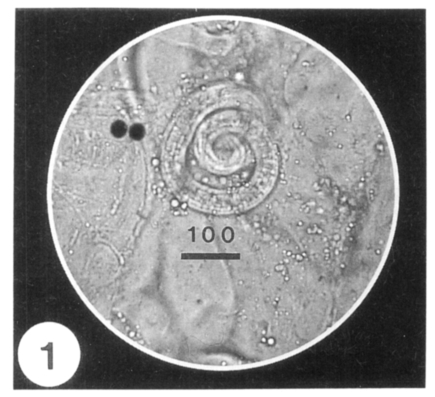
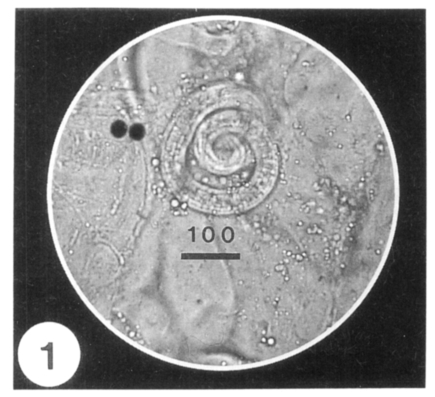
Fig. 1). Larvae were measured to be 0.775-1.050 (0.908 in average) mm in length, and 0.026-0.042 (0.035 in average) mm in the maximum width. In sectioned specimen of the biopsied muscle, the worm cyst was surrounded by numerous inflammatory cells and a nurse cell-larva complex was observed (
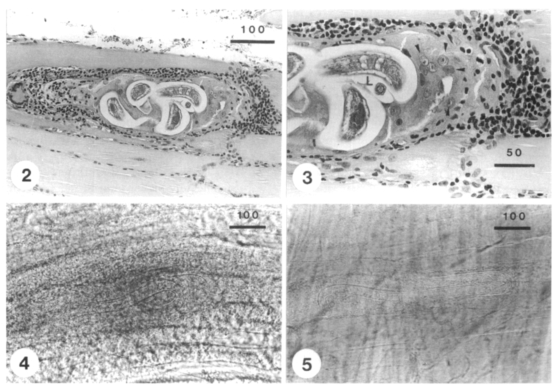
Figs. 2, 3).
The muscle biopsied at 34 days after eating raw badger was artificially digested with pepsin-HCl solution to investigate the intensity of infection. A total of 212 larvae per gram of muscle was recovered. The recovered larvae were given orally to a ICR mouse. At 50 days after experimental infection, a large number of larval
T. spiralis was harvested from the mouse. However, after treatment with flubendazole for 7 days and with albendazole for 3 days, the larvae in biopsied muscle were uncoiled (
Figs. 4, 5), and they did not infect four mice and a hamster experimentally
To alleviate symptoms, antibiotics and steroids were administered. Praziquantel, flubendazole and albendazole were also given orally to eradicate helminths. All patients were discharged at 13-34 days post-admission because most of symptoms disappeared. We measured the specific IgG antibody levels in three patients' sera sampled at 32 days after infection. The absorbances were measured by ELISA. As a normal control, the sera from four adults were used. The values were significantly higher when compared with those of normal controls (
Table 3).
By the present study, it was confirmed for the first time that
T. spiralis is distributed in Korea. This nematode infection has been found in humans and various mammals in many Asian countries such as Far East USSR, China, Japan, Tailand, Indonesia, Vietnam and Laos (
Yamaguti, 1989). The presence of
T. spiralis in Korea has been suspected for a long time; however, this nematode infection has not been reported before the present study.
The prevalence of human trichinosis in endemic countries cannot be estimated because there are no recent systematic surveys. However, sporadic outbreaks are still common in Spain, France, Italy, Yugoslavia, USA and Canada, and it recently occurred in China, Japan, and the Middle East (
MacLean et al., 1989;
Olaison and it Ljungstrom, 1992;
Pozio et al., 1993;
Dworkin et al., 1996). Especially, it is noteworthy that the recent incidence of human trichinosis in China (about 10,000 cases annually) is the highest in the world (
Markell et al., 1999). The present study showed that an outbreak of trichinosis occurred in a nearby country of China.
Until recently,
T. spiralis was the only human infecting species in the genus
Trichinella. However, four other distinct species, i.e.
T. pseudospiralis,
T. britovi,
T. nativa and
T. nelsoni, have been recognized (
Pozio et al., 1992). They can be distinguished from
T. spiralis by the inability to form cysts, pathogenicity and regional medical importance. While
T. spiralis is the most important species among these parasites in most part of the world due to the widespread distribution and higher pathogenicity,
T. pseudospiralis does not form the worm cyst and is infectious to avian hosts. The remaining three species are of more regional importance (
Markell et al., 1999). On the basis of the aforementioned characteristics, the nematode parasite isolated in this study was identified as
T. spiralis.
Trichinosis is definitely diagnosed by the detection of larvae in the biopsied muscle. However, prior to diagnosis, past histories, manifesting symptoms and laboratory findings provide helpful information in making a decision before conducting a muscle biopsy (
Despommier, 1998). Because the patients in this study showed symptoms and laboratory findings suggesting the trichinosis, and had a common past history of eating raw badger, muscle biopsy was undertaken for definite diagnosis.
A laboratory finging that is always associated with
T. spiralis infection is eosinophilia in the blood examination (
Gould, 1970). In severely infected cases, eosinophils may be as high as 80-95%. Overall, the total WBC count is slightly elevated. In patients moderately or severely infected with this nematode, muscle enzymes such as CPK and LDH are released into the circulating blood and their presence in the serum can be another clue to the diagnosis of trichinosis (
Murrell and Bruschi, 1994;
Capo and Despommier, 1996). In the present study, although eosinophilia was not so high, other laboratory findings such as leukocytosis and elevated enzyme levels were similar to those of previous reports.
ELISA can detect antibodies in some patients as early as 12 days after infection (
Ljungstrom, 1983). In the present study, the specific IgG antibody levels were measured in three patients' sera sampled at 32 days after infection by the ELISA. The antibody levels were significantly higher than those of normal controls. Two out of three patients, who were larva negative in biopsied muscles, were serologically confirmed to be infected with
T. spiralis.
It has been known that thiabendazole and mebendazole are useful for treatment against trichinosis (
Miyazaki, 1991). Albendazole may be effective, but its role is not yet established (
Markell et al., 1999). On the other hand, during an outbreak of
T. pseudospiralis in Thailand, treatment with albendazole for 2 weeks was found to be effective, but administration of thiabendazole and mebendazole was ineffective (
Jongwutiwes et al., 1998). The present cases were ultimately treated by flubendazole and albendazole from the 6th day after admission for 15-30 days. After treatment for 10 days, the larvae were uncoiled, and they did not show the infectivity in experimental animals. They were probably damaged by the antihelminthics, and lost their coilings and infectivities.
Notes
-
This work was supported by a research grant for basic medical sciences, Ministry of Education (1996-1998), Republic of Korea.
References
- 1. Capo V, Despommier DD. Clinical aspects of infection with Trichinella spp. Clin Microbiol Rev 1996;1. 47-54.
- 2. Despommier DD. In Cox FEG, Kreier JP, Wakelin D eds, Trichinella and Toxocara. Parasitology (Vol 5) of Topley & Wilson's Microbiology and Microbial Infections. 1998, 9th ed. London, UK. Arnold. pp 597-602.
- 3. Dworkin MS, Gamble HR, Zarlenga DS, Tennican PO. Outbreak of trichinellosis associated with eating cougar jerky. J Infect Dis 1996;174:663-666.
- 4. Gould SE. In Gould SE, Thomas CC eds, Clinical pathology: diagnostic laboratory procedures, Trichinosis in man and animals. 1970, Illinois, USA. Springfield. pp 191-221.
- 5. Jongwutiwes S, Chantachum N, Kraivichian P, et al. First outbreak of human trichinellosis caused by Trichinella pseudospiralis. Clin Infect Dis 1998;26:111-115.
- 6. Ljungstrom I. In Campbell WC ed, Immunodiagnosis in man, Trichinella and trichinosis. 1983, New York, USA. Plenum Press. pp 403-424.
- 7. MacLean JD, Viallet J, Law C, Staudt M. Trichinosis in the Canadian Arctic: report of five outbreaks and a new clinical syndrome. J Infect Dis 1989;160:513-520.
- 8. Markell EK, John DT, Krotoski WA. Markell and Voge's Medical Parasitology. 1999, 8th ed. Philadelphia, USA. W.B. Saunders. pp 340-345.
- 9. Miyazaki I. Helminthic Zoonoses. 1991, Tokyo, Japan. International Medical Foundation of Japan. pp 452-459.
- 10. Murrell D, Bruschi F. In Tsien Sun ed, Clinical trichinellosis. Progress in Clinical Parasitology. 1994, Boca Raton. CRC Press. pp 117-150.
- 11. Olaison L, Ljungstrom I. An outbreak of trichinosis in Lebanon. Trans Roy Soc Trop Med Hyg 1992;86:658-660.
- 12. Pozio E, La Rosa G, Murrell KD, Lichtenfels JR. Taxonomic revisions of the genus Trichinella. J Parasitol 1992;78:654-659.
- 13. Pozio E, Varese P, Morales MA, Croppo GP, Pelliccia D, Bruschi F. Comparison of human trichinellosis caused by Trichinella spiralis and by Trichinella britovi. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1993;48:568-575.
- 14. Yamaguti T. Trichinella and trichinelliasis in Japan. 1989, Tokyo, Japan. NKD.
Fig. 1A coiled Trichinella spiralis larva in the biopsied gastrocnemius muscle of a patient at 34 days after eating raw badger.
Figs. 2-5
Larvae of Trichinella spiralis detected from muscle biopsy of the patient.
Fig. 2. A sectioned larva in the worm cyst of muscle biopsied at 34 days after infection (H-E stained). Fig. 3. Enlarged view of Fig. 2, showing the intense inflammatory response around the nurse cells (arrow heads)-larva (L) complex (H-E stained). Figs. 4 & 5. Two larvae in press preparation of muscle biopsyed at 41 days after eating raw badger (at 10 days after treatment with flubendazole and albendazole). The larvae detected at the same day were uncoiled and did not show the infectivity in mice and a hamster. The bar represents µm in length.
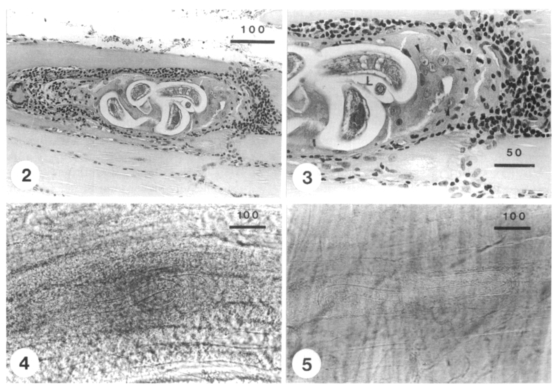
Table 1.Results of the biochemical examination on GOT
a) and GPT
b)
Table 1.
|
Days from eating row badger to examination |
Patient A
|
Patient B
|
Patient C
|
|
GOT |
GPT |
GOT |
GPT |
GOT |
GPT |
|
22 |
31 |
56 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
26 |
52 |
47 |
194 |
111 |
62 |
65 |
|
30 |
80 |
92 |
419 |
322 |
134 |
208 |
|
33 |
81 |
124 |
611 |
637 |
183 |
334 |
|
35 |
87 |
113 |
420 |
561 |
72 |
221 |
|
41 |
155 |
332 |
122 |
275 |
- |
- |
|
49 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
49 |
145 |
|
59 |
- |
- |
23 |
31 |
- |
- |
Table 2.
Table 2.
|
Days from eating row badger to examination |
Patient A
|
Patient B
|
Patient C
|
|
LDH |
CPK |
LDH |
CPK |
LDH |
CPK |
|
26 |
54 |
28 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
30 |
803 |
560 |
1121 |
1208 |
805 |
934 |
|
33 |
609 |
702 |
1421 |
760 |
821 |
670 |
|
41 |
897 |
382 |
830 |
334 |
- |
- |
|
49 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
503 |
202 |
|
59 |
- |
- |
348 |
210 |
- |
- |
Table 3.Specific IgG antibody levels in sera of three patients sampled at 32 days after infection
Table 3.
|
|
Antibody levelsa)
|
|
Patient |
A |
1.064 ± 0.068 |
|
B |
1.111 ± 0.024 |
|
C |
1.584 ± 0.039 |
|
|
Controlb)
|
I |
0.107 ± 0.016 |
|
II |
0.118 ± 0.021 |
|
III |
0.132 ± 0.023 |
|
IV |
0.091 ± 0.019 |
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- From wildlife to humans: The global distribution of Trichinella species and genotypes in wildlife and wildlife-associated human trichinellosis
Cody J. Malone, Antti Oksanen, Samson Mukaratirwa, Rajnish Sharma, Emily Jenkins
International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife.2024; 24: 100934. CrossRef - Human parasitic infections of the class Adenophorea: global epidemiology, pathogenesis, prevention and control
Jitrawadee Intirach, Chang Shu, Xin Lv, Suzhen Gao, Nataya Sutthanont, Tao Chen, Zhiyue Lv
Infectious Diseases of Poverty.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Wild Mesocarnivores as Reservoirs of Endoparasites Causing Important Zoonoses and Emerging Bridging Infections across Europe
Fabrizia Veronesi, Georgiana Deak, Anastasia Diakou
Pathogens.2023; 12(2): 178. CrossRef - Wildmeat consumption and zoonotic spillover: contextualising disease emergence and policy responses
Charlotte Milbank, Bhaskar Vira
The Lancet Planetary Health.2022; 6(5): e439. CrossRef - Prevalence of meat-transmitted Taenia and Trichinella parasites in the Far East countries
Yi Liu, Zijian Dong, Jianda Pang, Mingyuan Liu, Xuemin Jin
Parasitology Research.2021; 120(12): 4145. CrossRef - Proteomic analysis of the response of Trichinella spiralis muscle larvae to exogenous nitric oxide
Xiaoli Wang, Liang Li, Xing Wei, Yuanyuan Wang, Hui Zhang, Ao Shi, Tao Liu, Xiaodi Yang, Qiang Fang, Linsheng Song
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0198205. CrossRef - Meat sources of infection for outbreaks of human trichinellosis
Ali Rostami, H. Ray Gamble, Jean Dupouy-Camet, Hooshang Khazan, Fabrizio Bruschi
Food Microbiology.2017; 64: 65. CrossRef - Prevalence of Trichinella spp. antibodies in wild boars (Sus scrofa) and domestic pigs in Korea
H.J. Kim, W.S. Jeong, E.M. Kim, S.G. Yeo, D.J. An, H. Yoon, E.J. Kim, C.K. Park
Veterinární medicína.2015; 60(4): 181. CrossRef - Prevalence of Antibodies toToxoplasma gondiiin South Korean Wild Boar (Sus scrofa coreanus)
Wooseog Jeong, Hachung Yoon, Yong Kwan Kim, Oun-kyong Moon, Do-Soon Kim, Dong-Jun An
Journal of Wildlife Diseases.2014; 50(4): 902. CrossRef - Chemotherapeutic drugs for common parasitic diseases in Korea
Sun Huh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2013; 56(6): 513. CrossRef - Clinical Update on Parasitic Diseases
Min Seo
Korean Journal of Medicine.2013; 85(5): 469. CrossRef - Trichinosis Caused by Ingestion of Raw Soft-Shelled Turtle Meat in Korea
Sang-Rok Lee, Sang-Hoon Yoo, Hyun-Seon Kim, Seung-Ha Lee, Min Seo
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2013; 51(2): 219. CrossRef - An Outbreak of Trichinellosis with Detection ofTrichinellaLarvae in Leftover Wild Boar Meat
Gayeon Kim, Min-Ho Choi, Jae-Hwan Kim, Yu Min Kang, Hee Jung Jeon, Younghee Jung, Myung Jin Lee, Myoung-don Oh
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2011; 26(12): 1630. CrossRef - The Fifth Outbreak of Trichinosis in Korea
Ji-Young Rhee, Sung-Tae Hong, Hye-Jung Lee, Min Seo, Suk-Bae Kim
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2011; 49(4): 405. CrossRef - Pathogenesis of restricted movements in trichinellosis: An experimental study
Dalia S. Ashour, Reda H. Elbakary
Experimental Parasitology.2011; 128(4): 414. CrossRef - The epidemiology of human trichinellosis in China during 2004–2009
J. Cui, Z.Q. Wang, B.L. Xu
Acta Tropica.2011; 118(1): 1. CrossRef - Recent Advances in the Use of Anthelmintics for Treating Nematode Infections
Jong-Yil Chai
Infection and Chemotherapy.2011; 43(1): 26. CrossRef - Changing Patterns of Human Parasitic Infection in Korea
Myoung-Hee Ahn
Hanyang Medical Reviews.2010; 30(3): 149. CrossRef - Human Trichinosis after Consumption of Soft-Shelled Turtles, Taiwan
Yi-Chun Lo, Chien-Ching Hung, Ching-Shih Lai, Zhiliang Wu, Isao Nagano, Takuya Maeda, Yuzo Takahashi, Chan-Hsien Chiu, Donald Dah-Shyong Jiang
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2009; 15(12): 2056. CrossRef - Fifty Years of the Korean Society for Parasitology
Seung-Yull Cho
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2009; 47(Suppl): S7. CrossRef - Review of Zoonotic Parasites in Medical and Veterinary Fields in the Republic of Korea
Heejeong Youn
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2009; 47(Suppl): S133. CrossRef - Trends in parasitic diseases in the Republic of Korea
Eun-Hee Shin, Sang-Mee Guk, Hyo-Jin Kim, Soon-Hyung Lee, Jong-Yil Chai
Trends in Parasitology.2008; 24(3): 143. CrossRef - Food-borne parasitic zoonosis: Distribution of trichinosis in Thailand
Natthawut Kaewpitoon, Soraya Jatesadapattaya Kaewpitoon, Prasit Pengsaa
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2008; 14(22): 3471. CrossRef - Tissue Invading Helminthic Diseases
Yoon Kong
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2007; 50(11): 967. CrossRef - World distribution of Trichinella spp. infections in animals and humans
Edoardo Pozio
Veterinary Parasitology.2007; 149(1-2): 3. CrossRef - Emerging Parasitic Diseases in Korea
Jong-Yil Chai
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2007; 50(11): 946. CrossRef - Food-Borne Parasitic Diseases
Han-Jong Rim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2007; 50(11): 984. CrossRef - Trichinosis: Epidemiology in Thailand
Natthawut Kaewpitoon
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2006; 12(40): 6440. CrossRef - Food-borne Parasitic Diseases
Jong-Yil Chai
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2004; 47(6): 496. CrossRef - Molecular identification of Korean Trichinella isolates
Woon-Mok Sohn, Sun Huh, Dong-Il Chung, Edoardo Pozio
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2003; 41(2): 125. CrossRef - PCR-RFLP patterns of four isolates of Trichinella for rDNA ITS1 region
Hye Soo Kwon, Myung Sook Chung, Kyoung Hwan Joo
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2001; 39(1): 43. CrossRef - Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Trichinella spiralis antibodies and the surveillance of selected pig breeding farms in the Republic of Korea
Sung-Hwan Wee, Chung-Gil Lee, Hoo-Don Joo, Yung-Bai Kang
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2001; 39(3): 261. CrossRef