Abstract
To determine the pathogenicity of Acanthamoeba spp. isolated in Korea and to develop a isoenzymatic maker, the mortality rate of infected mice, in vitro cytotoxicity against target cells and isoenzyme band patterns were observed. Five isolates of Acanthamoeba spp. (YM-2, YM-3, YM-4, YM-5, and YM-7) were used in this study as well as three reference Acanthamoeba spp. (A. culbertsoni, A. hatchetti, and A. royreba). According to the mortality rate of infected mice, Korean isolates could be categorized into three groups: high virulent (YM-4), low virulent (YM-2, YM-5, YM-7) and the nonpathogenic group (YM-3). In addition, the virulence of Acanthamoeba spp. was enhanced by brain passage in mice. In the cytotoxicity assay against chinese hamster ovary cells, especially, the cytotoxicity of brain-passaged amoebae was relatively higher than the long-term cultivated ones. The zymodeme patterns of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), malate dehydrogenase (MDH), hexokinase (HK), glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT) and malic enzyme (ME) of Acanthamoeba spp. were different among each isolate, and also between long-term cultured amoebae and brain passaged ones. In spites of the polymorphic zymodemes, a slow band of G6PD and HK, and an intermediate band of MDH were only observed in pathogenic Acanthamoeba spp., which should be used as isoenzymatic makers.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba sp., Korean isolate, pathogenicity, virulence, isoenzyme, cytotoxicity
INTRODUCTION
Acanthamoeba species that exist in atmosphere, fresh water, sewages, cooling towers, and swimming pools are known as the causative protozoa of the glanulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE) and keratitis (Fowler and Carter, 1965;
Hwang et al., 1976;
Stehr-Green et al., 1989;
Srikanth and Berk, 1993;
Vesaluoma et al., 1995;
Mathers et al, 1996). Most of the strains isolated from the environment are not pathogenic to the experimental animals and to humans. However, recently,
Acanthamoeba spp. were isolated from contact lens containers and a few amoebic keratitis cases were reported in Korea (
Kim et al., 1995).
In order to differentiate the pathogenicity of
Acanthamoeba spp., an experimental meningoencephalitis was demonstrated by intranasal or intracaecal inoculation into various animals (
Culbertson et al., 1966). When the temperature tolerance of the free-living pathogenic amoebae was compared to that of the nonpathogenic amoebae, the pathogenic amoebae showed a higher temperature tolerance (
Griffin, 1972). In addition, pathogenic
Acanthamoeba spp. showed an induced agglutination in the presence of lectin (
Kim et al., 1980). Cytotoxicity test using tissue cell lines, such as Vero cell, chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell, rat neuroblastoma cell, and HeLa cell, was used for the pathogenicity determination of
Acanthamoeba sp. (
Marciano-Cabral et al., 1982;
Lee et al., 1986). When using CHO cells as target cells, high virulent
Acanthamoeba spp. showed a higher cytotoxicity than low virulent amoebae, which was revealed by the crystal violet staining method (
Shin et al, 1992).
Sargeaunt and Williams (
1979) verified isoenzyme (phosphoglucomutase, glucose phosphate isomerase, etc.) patterns that are important tools in differentiating the pathogenicity of
Entamoeba histolytica. When cultured with
Escherichia coli for a short period of time,
E. histolytica showed an increasing virulence, but Mirelman et al. (
1984) reported that the bacterial association did not cause any change in the electrophoretic isoenzyme patterns of
E. histolytica.
In this study, in order to differentiate the pathogenic Acanthamoeba spp. from the nonpathogenic ones and to develop a isoenzymatic maker, the pathogenicity of Acanthamoeba spp. including the Korean isolates was demonstrated by observing the mortality rate of the infected mice, the degree of cytotoxicity levels against CHO cells and the comparison of band patterns of five isoenzymes. In addition, the virulence of brain-passaged amoebae was compared to that of amoebae cultured for a longer period of time by three above categories.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Amoebae
The amoebae were axenically cultured and maintained at 37℃ in CGV medium (
Willaert, 1976) in plastic culture flasks. Five Korean isolates of
Acanthamoeba spp. and three reference
Acanthamoeba strains used in the present study are listed in
Table 1.
Live trophozoites were washed twice with 0.85% saline solution, centrifuged and suspended in the equal volume of enzyme stabilizer (1 mM dithiothreithol, 1 mM ε-aminocaproic acid, 1 mM ethylene diaminotetraacetic acid). Then, the amoebae were subjected to 3 to 4 cycles of freezing and thawing by the method of Moura et al. (
1992). The lysate was prepared by centrifugation at 24,000
g at 4℃ for 30 min, and stored at -70℃ until use. The protein concentration of the lysate was determined by the method of Bradford (
1976).
Mice used for the experimental infection were outbred ICR mice each weighing 15 to 18 g. Trophozoites of Acanthamoeba spp. were harvested, washed twice with saline and suspended in saline (1 × 105 trophozoites per 5 µl saline). Suspended trophozoites were inoculated intranasally into mice under anesthesia that was induced by intraperitoneal injection of secobarbital, 0.06 mg per gram of mouse body weight. The death of mice was observed after day 30 post-inoculation (PI). Autopsy was performed immediately after the death, and pieces of the forebrain tissue were placed into the culture medium for amoebae. In order to compare the virulence between long-term cultured (subcultured since the primary isolation) and brain-passaged amoebae (subcultured from the brain tissue of infected mice), the isolating amoebae were also cultured for subsequent infection.
In vitro cytotoxicity
The chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells were used as target cells. The CHO cells were cultured and maintained in a Eagle's minimal essential medium (Gibco BRL, NY, USA) in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37℃ and harvested by treatment of trypsin-EDTA solution (Gibco BRL). After the cells were suspended in 0.4% trypan blue, the number of viable cell was counted using the hemocytometer.
The non-radioactive cytotoxicity assay (Promega, WI, USA) was used to determine the cytopathic effect of live trophozoites of Acanthamoeba and their lysates. The target cells (1 × 104) and various concentrations of lysates were added to each well of 96-well round-bottomed plates. The plates were spun at 250 g for 4 min and incubated at 37℃ in a 5% CO2 incubator for 4 hr. After centrifugation, 50 µl of supernatant fluid was harvested from each well, transferred to the fresh 96-well microtiter plates containing equal volume of substrate mixture and incubated at the room temperatute for 30 min. The absorbance of red colored formazan, which was developed by lactic dehydrogenase released from the dead target cells, was read at 490 nm by ELISA reader (Dynatech MR 5000, USA). The percent of cytotoxicity was calculated by using the following equation;
Observation of isoenzyme band patterns
The lysates were subjected to thin-layer starch-gel electrophoresis as previously described by Soliman et al. (
1982) with some modifications. A constant 75 mA of power was supplied to each gel for 4 hr. Chemicals used for the assay include glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT), malate dehydrogenase (MDH), malic enzyme (ME), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), and hexokinase (HK). Preparation of buffers, coenzymes, substrates, and other staining procedures are listed in
Table 2.
RESULTS
Pathogenicity in mice
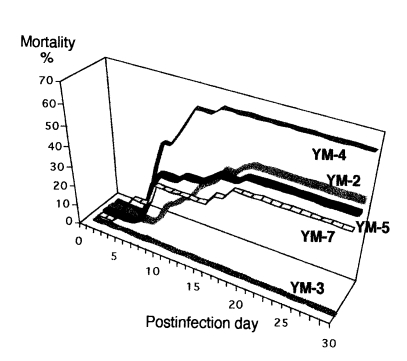
Mice inoculated intranasally with amoeba began to die after day 4 PI, but no death was observed from mice inoculated with
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-3. The mortality rate varied among different strains or isolates of
Acanthamoeba, but the majority of mice died from day 6 to day 15 PI (
Table 3). The mortality rate was the highest in mice infected with
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 (
Fig. 1). Although some of the infected mice survived, the amoebae were detected from the brains of mice after sacrifice. The virulence between the long-term cultured and second brain-passaged amoeba (especially
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4, YM-5, and
A. hatchetti) revealed a significant difference in intensification. Mice inoculated with brain-passaged amoebae died earlier than mice with long-term cultured amoebae. Especially,
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 produced a low mortality rate (2.8 %) in mice inoculated with the long-term cultured amoeba, but they induced a higher mortality rate (65.5 %) when they went through the brain passages twice.
Acanthamoeba culbertsoni,
A. hatchetti,
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-2, and YM-5 also exhibited the enhanced virulence (P<0.001). According to the above results, the Korean isolates and reference
Acanthamoeba spp. can be divided into three groups based on the mortality rate of infected mice: highly virulent (
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4,
A. culbertsoni and
A. hatchetti), low virulent (
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-2, YM-5, YM-7 and
A. royreba), and the non-pathogenic groups (
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-3).
Cytotoxicity of the Korean isolates of
Acanthamoeba spp. did not agree with the level of pathogenicity demonstrated by the mortality rate of the infected mice (
Table 4.). Nevertheless, the cytotoxicity of the nonpathogenic YM-3 was relatively low when compared to that of the pathogenic Korean isolates,
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 or YM-7; in addition, the cytotoxicity of the brain-passaged amoeba was relatively higher than that of the long-term cultivated ones.
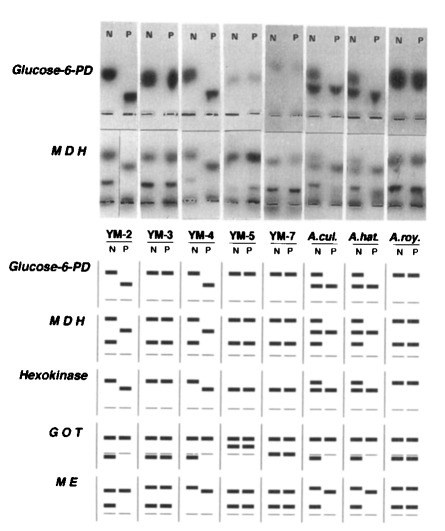
Three migrating bands (slow, intermediate, and fast) of different electrophoretic mobility in each isoenzyme were observed (
Table 5). All strains or isolates of
Acanthamoeba spp. exhibited multiple forms of each isoenzyme patterns. But the isoenzyme band patterns were correlated with the pathogenicity or virulence, which was demonstrated by the mortality of the infected mice in this experiment. In case of G6PD, all pathogenic isolates or strains showed a slow band with the same mobility. And, all pathogenic or virulent isolates or strains revealed an intermediate band in migrating pattern of MDH, but did not show a slow band in HK. The isoenzyme band patterns of brain-passaged amoeba was distinctly different from those of long-term cultivated ones (
Fig 2) On the other hand, the isoenzyme band patterns of brain-passaged
Acanthamoeba spp. changed to those of long-term cultured ones several months later; five and ten months later in case of
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-2 and
A. culbertsoni, respectively (
Table 6). This period was not related to the virulence degree of amoeba.
DISCUSSION
For the determination of the pathogenicity, several studies have been conducted using the morphological, biochemical, immunological, and genetical tools (
Kim et al, 1984). In this study, the Korean isolates and the reference strains of
Acanthamoeba spp. were differentiated based on the mortality of the mice intranasally inoculated with amoebae. Also, the possible use of electrophoretic analysis for separating pathogenic strains was exploited in the present paper. Four out of five Korean isolates were proven to be virulent, and the remaining isolate,
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-3, was nonpathogenic to mice.
The degree of amoeba virulence is not constant, but changes with respect to the duration of culture time which also depends on other factors. Lee et al. (
1983) compared the difference of virulence between axenically maintained strains of
Naegleria fowleri and those obtained by a serial brain passage in mice. They demonstrated that the virulence of amoeba was enhanced through the brain passage in mice. In this study, in order to elucidate the virulence of brain-passaged amoebae, the inoculation and isolation of amoebae into/from mice were examined monthly. The virulence of Korean isolates which showed the low mortality rate of mice could be enhanced by brain passage. These present results verify a general rule that the actual virulence of pathogenic strains of
Acanthamoeba can be restored by the intranasal infection in mice, although this is not the case for the nonpathogenic strains.
To differentiate the pathogenic strains from the nonpathogenic
Acanthamoeba, enzymatic experiments which include trypsin, esterase, phosphatase, phospholipase, peroxidase, and other hydrolase treatments have been proven to be important (
Kim et al., 1988;
Mazur and Hadas, 1994). Mazur and Hadas (
1994) indicated that the increased levels of peroxidase and proteinase activities thoroughly correlated with the increasing virulence of
Acanthamoeba. It would be of important value if the isoenzyme electrophoretic patterns could separate the pathogens from the nonpathogens. In the present study, three (G6PD, MDH and HK) out of the five systems were demonstrated to be useful for differentiation of the pathogenic strains.
It was very interesting that isoenzyme band patterns of brain-passaged amoebae were clearly different from those of the long-term cultivated amoebae. It was also verified that isoenzyme patterns of the brain passaged amoeba returned to those of long-term cultured ones several months later. The functional significance of this difference is not clear. The correlation between the pathogenicity of amoeba and its isoenzyme patterns is not elucidated at the present time.
On the other hand, in vitro cytotoxicity assay measuring LDH release from the target cells was used for the pathogenicity differentiation of Korean isolates of
Acanthamoeba spp. in this experiment. The cytotoxic effect of Korean isolates was not related with the amoeba pathogenicity. But the degree of cytotoxicity of brain-passaged amoebae was relatively higher than that of long-term cultivated amoebae. By the
51Cr release assay, Lee et al. (
1986) observed the cytotoxicity differences between the pathogenic and nonpathogenic amoeba in culture systems using CHO cells as target cells. And it was reported that the lysate of
A. culbertsoni was proven to be cytotoxic to CHO cells (
Shin et al., 1993). Further work needs to be performed to set up the standard tool for the pathogenicity determination of
Acanthamoeba spp.
Finally, the present study showed that the Korean isolates of Acanthamoeba spp. could be determined as virulent (YM-2. YM-4, YM-5 and YM-7) and nonpathogenic (YM-3) strains. The virulence of long-term cultured Acanthamoeba spp. including Korean isolates was enhanced by the mouse brain passage. And it was observed that isoenzyme band patterns of brain-passaged amoebae returned to those of long-term cultured ones several months later. In addition, the slow band of G6PD and HK, and the intermediate band of MDH could be very helpful markers to differentiate the pathogenicity of Acanthamoeba spp.
Notes
-
This study was supported by the Research Grant of the Faculty Research Project, Yonsei University, 1997.
References
- 1. Bradford M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 1976;72:248-254.
- 2. Culbertson CG, Ensminger PW, Overton WM. Hartmanella (Acanthamoeba). Experimental chronic granulomatous brain infections produced by new isolates of low virulence. Am J Clin Pathol 1966;46:305-314.
- 3. Griffin JL. Temperature tolerance of pathogenic and nonpathogenic free-living amoebas. Science 1972;178:869-870.
- 4. Hwang HK, Yun DJ, Im KI, Soh CT. Experimental study on the pathogenicity of free-living amoeba. Yonsei J Med Sci 1976;9:182-194.
- 5. Kim CK, Im KI, Choi HJ, Soh CT. Agglutinability of free-living amoebae with phytoagglutinin in consideration with their pathogenicity. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1980;11:14-19.
- 6. Kim JJ, Kim MK, Park IW, Lee HB. Acanthamoeba keratitis in contact lens wearer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 1995;36:2042-2047.
- 7. Kim YJ, Kim JJ, Min DY, Soh CT. Correlation of isoenzyme patterns and the pathogenicity of free-living amoebae collected in Korea. Yonsei J Med Sci 1984;17:329-340.
- 8. Kim YK, Kim TU, Joung IS, Im KI. A comparative study on hydrolase activities in Acanthamoeba culbertsoni and A. royreba. Korean J Parasitol 1988;26:95-106.
- 9. Lee DK, Lee KT, Im KI. Changes in the pathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri by serial brain passage in mice. Korean J Parasitol 1983;21:234-240.
- 10. Lee YW, Kim TU, Joung IS, Chung PR, Lee KT. An experimental study on the cytotoxicity of free-living amoebae. Yonsei J Med Sci 1986;19:358-369.
- 11. Marciano-Cabral FM, Patterson M, John DT, Bradley SG. Cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri and Naegleria gruberi for established mammalian cell cultures. J Parasitol 1982;68:1110-1116.
- 12. Mathers WD, Sutphin JE, Folberg R, Meier PA, Wenzol RP, Elgin RG. Outbreak of keratitis presumed to be caused by Acanthamoeba. Am J Ophthalmol 1996;121:129-142.
- 13. Mazur T, Hadas E. The effect of the passages of Acanthamoeba strains through mice tissues on their virulence and its biochemical markers. Parasitol Res 1994;80:431-434.
- 14. Mirelman D, Bracha R, Sargeaunt PG. Entamoeba histolytica: Virulence enhancement of isoenzyme-stable parasites. Exp Parasitol 1984;57:172-177.
- 15. Moura H, Wallace S, Visvesvara G. Acanthamoeba healyi N. sp. and the isoenzyme and immunoblot profiles of Acanthamoeba spp., Group 1 and 3. J Protozool 1992;39:573-583.
- 16. Sargeaunt PG, Williams JE. Electrophoretic isoenzyme patterns of the pathogenic and non-pathogenic intestinal amoebae of man. Trans Roy Soc Trop Med Hyg 1979;73:225-227.
- 17. Shin HJ, La MS, Im Ki. Cytotoxicity of Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 (Korean isolate). Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1993;24:31-38.
- 18. Soliman MA, Ackers JP, Catterall RD. Isoenzyme characterization of Trichomonas vaginalis. Br J Venerol Dis 1982;58:250-256.
- 19. Srikanth S, Berk SG. Stimulatory effect of cooling tower biocides on amoebae. Appl Environ Microbiol 1993;59:3245-3249.
- 20. Stehr-Green JK, Bailey TM, Visvesvara GS. The epidemiology of Acanthamoeba keratitis in the United States. Am J Ophthalmol 1989;107:331-336.
- 21. Vesaluoma M, Kalso S, Jokipii L, Warhurst D, Ponka A, Tervo T. Microbiological quality in finnish public swimming pools and whirlpools with special reference to free living amoeba: a risk factor for contact lens wearers. Br J Ophthalmol 1995;79:178-181.
- 22. Willaert E. Etude immunotaxonomique des genres Naegleria et Acanthamoeba (Protozoa; Amoebida). Acta Zool Pathol (Antwerp) 1976;65:1-239.
Fig. 1The mortality of mice infected intranasally with Korean isolates of Acanthamoeba sp. YM-2, YM-3, YM-4, YM-5, and YM-7.

Fig. 2Photographic and diagrammatic representation of isozyme zymodemes of Korean isolates and reference strains of Acanthamoeba spp. YM-2, YM-3, YM-4, YM-5, and YM-7 represent Korean isolates of Acanthamaeba spp. A. cul, Acanthamoeba culbertsoni; A. hat, A. hatchetti; A. roy, A. royreba; Glucose-6-PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; MDH, malate dehydrogenase; HK, Hexokinase; GOT, glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase; ME, malic enzyme; N, non-passaged amoeba; P, passaged amoeba.

Table 1.
Acanthamoeba spp. used in this study
Table 1.
|
Species |
Strain |
Isolated
|
|
from |
in |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. |
YM-2 |
water puddle |
1975 |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. |
YM-3 |
reservoir |
1975 |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. |
YM-4 |
fish gill |
1975 |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. |
YM-5 |
sewage |
1993 |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. |
YM-7 |
corneal washing |
1994 |
|
Acanthamoeba culbertsoni
|
|
human |
1976 |
|
Acanthamoeba hatchetti
|
|
brackish water |
1977 |
|
Acanthamoeba royreba
|
|
cell culture |
1977 |
Table 2.Staining reagent buffers used for visualizing isoenzymes
Table 2.
|
Enzyme |
Buffer |
Coenzyme |
Substrate |
Linking enzyme |
Dye |
Other Reagent |
Agar (2.0%) |
|
GOTa)
|
0.2M Tris-HCl |
P5Pb)
|
α-Ketoglutarate |
|
FBBc) 50 mg |
— |
— |
|
(EC 2.1.1.1)d)
|
PH 8.0, 25 ml |
2.5 mg |
50 mg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
α-Aspartic acid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75 mg |
|
|
|
|
|
MDHe)
|
0.2M Tris-HCl |
NADf)
|
Sol. Ag), 5 ml |
— |
NBTh) (1%)1 ml |
— |
5 ml |
|
(EC 1.1.1.37) |
PH 8.0, 8 ml |
(1%) 1 ml |
|
|
PMSi) (1%)0.5 ml |
|
|
|
MEj)
|
0.2M Tris-HCl |
NADPk)
|
Sol. A, 5 ml |
一 |
NBT (1%)1 ml |
MgCl2
|
5 ml |
|
(EC 1.1.1.40) |
PH 8.0, 8 ml |
(1%) 1 ml |
|
|
PMS (1%)0.5 ml |
(1%) 1 ml |
|
|
G6PDl)
|
0.2M Tris-HCl |
NADP |
G6Pm) 20 mg |
— |
NBT (1%)1 ml |
EDTA |
5 ml |
|
(EC 1.1.1.49) |
PH 8.0, 10 ml |
(1%) 1 ml |
|
|
PMS (1%)0.5 ml |
25 mg |
|
|
HKn)
|
0.2M Tris-HCl |
NADP |
Glucose 40 mg |
G6PD |
NBT (1%)1 ml |
MgCl2
|
5 ml |
|
(EC 2.7.1.1) |
PH 8.0, 10 ml |
(1%) 0.5 ml |
ATP 15 mg |
50IU, 20 μg |
PMS (1%)0.5 ml |
(1%) 1 ml |
|
Table 3.Mortality of the mice infected intranasally with Acanthamoeba spp.
Table 3.
|
Amoeba Strains |
Brain passage |
No. of mice |
Number of dead mice in each post-inoculation day
|
Total |
Mortality (%) |
|
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
|
YM-2 |
Na)
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
5.7 |
|
1stb)
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
46.4 |
|
2ndc)
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
47.4 |
|
YM-3 |
N |
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
1st |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
2nd |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
YM-4 |
N |
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2.9 |
|
1st |
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
21.2 |
|
2nd |
29 |
|
3 |
5 |
4 |
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
65.5 |
|
YM-5 |
N |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
1st |
25 |
|
1 |
|
4 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
28 |
|
2nd |
32 |
|
|
1 |
3 |
4 |
2 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
43.8 |
|
YM-7 |
N |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
11.5 |
|
1st |
30 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
2 |
7 |
23.3 |
|
2nd |
18 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
38.9 |
|
A. culbertsoni
|
N |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
3.3 |
|
1st |
29 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
1 |
9 |
31 |
|
2nd |
30 |
|
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
4 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
2 |
18 |
60 |
|
A. hatchetti
|
N |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
5 |
|
1st |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
10 |
|
2nd |
20 |
|
|
1 |
3 |
7 |
|
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
75 |
|
A. royreba
|
N |
21 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
9.5 |
|
1st |
18 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
16.7 |
Table 4.Cytotoxicity (%) of Acanthamoeba spp. against the chinese hamster ovary cells
Table 4.
|
Amoebae |
Non-passage group
|
Brain-passage group
|
|
2.0a)
|
1.0 |
0.5 |
0.25 |
2.0 |
1.0 |
0.5 |
0.25 |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-3 |
56.4 |
40.4 |
31.9 |
21.3 |
66.7 |
36.9 |
29.8 |
21.7 |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-2 |
22.3 |
14.9 |
12.7 |
4.2 |
99.9 |
48.4 |
32.3 |
19.7 |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 |
59.6 |
25.5 |
19.1 |
9.6 |
94.0 |
54.4 |
32.7 |
30.9 |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-5 |
50.0 |
23.4 |
17.0 |
14.9 |
62.7 |
23.4 |
21.2 |
12.2 |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-7 |
48.9 |
24.5 |
13.8 |
13.8 |
82.5 |
38.8 |
23.1 |
18.9 |
|
Acanthamoeba culbertsoni
|
31.9 |
12.7 |
14.9 |
13.8 |
44.3 |
21.3 |
19.9 |
26.4 |
|
Acanthamoeba hatchetti
|
35.1 |
15.9 |
11.7 |
11.7 |
93.4 |
47.4 |
36.8 |
26.4 |
|
Acanthamoeba royreba
|
47.9 |
35.1 |
31.9 |
37.2 |
72.4 |
41.5 |
36.7 |
27.3 |
Table 5.Rate of flow values of fraction of Acanthamoeba spp. separated electrophoretically
Table 5.
|
Bands of fraction |
Isoenzymes
|
|
G6PDa)
|
MDHb)
|
HKc)
|
GOTd)
|
MEe)
|
|
Slow |
0.14 |
0.10 |
0.34 |
-0.02 |
0.10 |
|
Intermediate |
0.24 |
0.20 |
0.42 |
0.08 |
0.36 |
|
Fast |
|
0.28 |
|
0.16 |
0.40 |
Table 6.Changes of isoenzyme band patterns of Acanthamoeba spp. subcultured several months after brain passage
Table 6.
|
Amoebae |
Culture duration after brain passage (months) |
Changes of band pattern |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-2 |
5 |
Yes |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-3 |
13 |
No |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 |
15 |
No |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. YM-5 |
11 |
No |
|
Acanthamoeba culbertsoni
|
10 |
Yes |
|
Acanthamoeba hatchetti
|
15 |
No |
|
Acanthamoeba royreba
|
27 |
No |