Abstract
This prospective study was aimed to detect acute and chronic ocular toxoplasmosis by comparison of anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM and IgG antibody levels and IgG avidity test. One hundred and seventeen patients with ocular toxoplasmosis (OT) who referred to the Farabi Eye Hospital, Tehran, Iran were included in this study. Of the patients, 77 cases were positive for anti-T. gondii IgG, and 8 cases were positive for anti-T. gondii IgM. IgG avidity test revealed 11, 4, and 102 cases were low, intermediate, and high, respectively, and 6.8% and 9.4% of cases were positive for IgM and IgG avidity tests, respectively (P=0.632). Agreement (Kappa value) between paired tests IgG-IgM, IgG-IgG avidity, and IgM-IgG avidity was 0.080, 0.099, and 0.721, respectively (P<0.05). This study showed that conventional serologic tests (IgM and IgG levels) and IgG avidity correlate well each other and can be used to differentiate recent infections from old OT. It seems that reactivated old infections rather than recently acquired infections are majority of Iranian OT patients.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, IgG, IgM, IgG avidity, ocular toxoplasmosis
INTRODUCTION
Toxoplasma gondii an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite with global distribution is a major cause of retinochoroiditis and uveitis [
1]. Ocular toxoplasmosis (OT) involves typically the posterior pole of eye but can have a range of clinical manifestations depending on the exact location of the involved area and level of inflammation [
2,
3]. Early reduction in visual acuity can occur if the lesion is in the posterior pole of eye, and visual acuity may drop to a very low level when macula is involved [
4,
5]. OT has been considered as a neglected disease by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) USA, 2014 [
6]. The prevalence of the disease is variable in different countries and is estimated from 0.3 to 1% in Europe and North America [
7–
9]. A study in UK revealed that the risk of developing of this disease is 18 in 100,000 individuals [
8]. This number may rise to 382 in 100,000 in West Africa [
10]. The prevalence of OT is very high in Brazil and ranges from 2% to 25% in adolescents and adults [
7,
11–
14].
OT can be present either as the reactivation of latent congenital infection or newly acquired infection [
15,
16]. The prevalence of OT was 21.3% in individuals of age 13 years or older and was 0.9% in 1–8 year old children [
12]. This finding suggests that, most of the OT cases in this population were caused by postnatal rather than congenital acquisition of infection [
17].
The clinical ophthalmological findings should be confirmed by positive anti-
toxoplasma antibodies to provide sufficient information on which to base a diagnosis. In most cases, the OT can be clinically diagnose, but some para-clinical methods could help to diagnosis of congenital and acquired ocular toxoplasmosis [
18]. Also, the diagnosis of acute and chronic OT is crucially important for designing prevention programs and also for therapeutic strategies [
19].
Serological analyses for specific anti-
Toxoplasma antibodies including IgG, IgM, and IgA have been used for this purpose, but recently the reliability of this methods has been debated [
19]. IgG avidity test is a quantitative serological test. A low IgG avidity index is not specific for recently acquired OT but a high IgG avidity index can reject the recently acquired infection [
3]. The IgG avidity test is based on the immovability antigen and antibody attachment. The IgG antibodies bind weakly to the antigen during initially stage but over weeks or months IgG antibody response be mature and the avidity increases progressively. The aim of this study was to evaluate the IgG avidity test for diagnosis of recently acquired OT and reactivated old infection and its potential correlation with other serological methods.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subject and samples
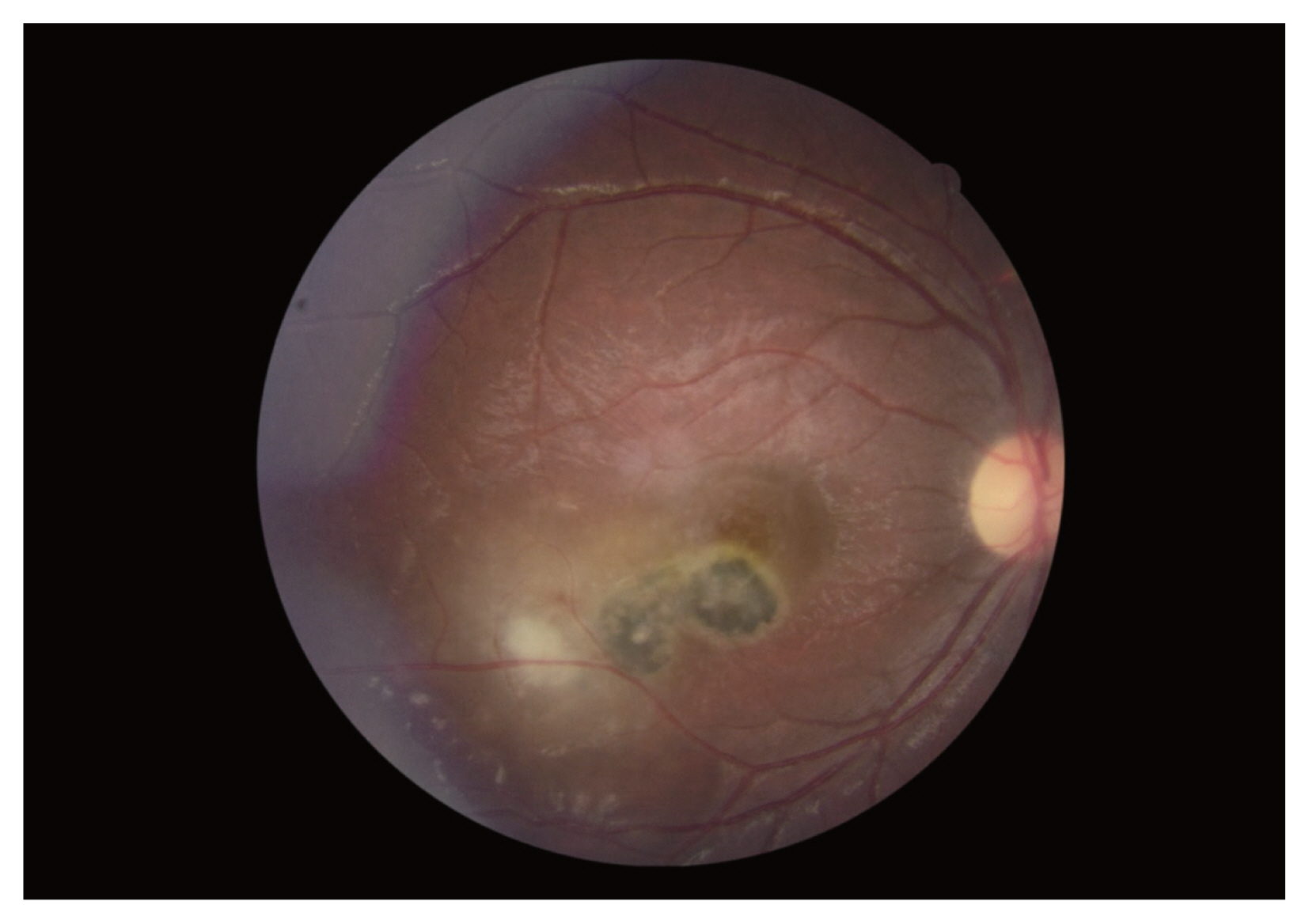
One hundred and seventeen patients with clinical diagnosis of ocular toxoplasmosis were included in this study. Diagnosis of OT was made by ophthalmologists in Farabi Eye Hospital, a comprehensive center of ophthalmology in Iran, during 2015–2016. Characteristic ocular findings of focal yellowish white or gray retinal patches with fuzzy borders, some degree of overlying vitritis and presence of pigmented scars, were characteristics of ocular toxoplasmic retinochoroiditis (
Fig. 1). In the cases without pigmented retinal scars at the time of presentation, the diagnosis of ocular toxoplasmosis would be made during the follow-up period, if the aforementioned active retinal patch evolved into a scar with some dark pigmentation and sharp borders observed.
Following obtaining informed consent, 5 ml of peripheral blood was collected, and centrifuged at 2,500 rpm in 5 min and serums were separated in a new tube and stored in -20°C for serologic studies.
Anti-Toxoplasma IgM and IgG
Anti-Toxoplasma IgM and IgG antibodies were analyzed by VIDAS TOXO IgG and IgM Kit (bioMérieux, Marcy-l’Etoile, France). The assay combined an enzyme immunoassay method by immune-capture with a final fluorescent detection (ELFA). According to the kit manufactures, the solid phase receptacle (SPR) served as the solid phase as well as the pipetting device for the assay. Reagents for the assay were ready to use and pre-dispensed in the sealed reagent strips. All of the assay steps were performed automatically by the instrument. The anti-Toxoplasma IgM and IgG were specifically detected by inactivated Toxoplasma antigen (RH Sabin strain), which was itself detected by an alkaline phosphatase- labeled murine monoclonal anti-Toxoplasma antibody (anti P30). During the final detection step, the substrate (4-methyl-umbellif eryl phosphate) is cycled in and out of the SPR. The conjugate enzyme catalyzed the hydrolysis of this substrate into a fluorescent product (4-methyl umbelliferone), the fluorescence of which is measured at 450 nm. The intensity of the fluorescence is proportional to the concentration of the antibodies in the sample. At the end of the assay, an index was automatically calculated by the instrument compared to the standard quantities stored in machine memory. During the procedure, between all steps, unbounded compounds were eliminated by washing. The test results were interpreted as follows: for IgM,<0.55 IU/ml: negative, 0.55≤ to <0.65 IU/ml: equivocal, ≥0.65 IU/ml: positive; for IgG,<4 IU/ml: negative, between 4≤ to <8: intermediate, and ≥8: positive.
Toxoplasma IgG avidity
Measurement of Toxoplasma IgG avidity test was performed and interpreted according to the manufacturers, instructions (VIDAS Toxo-IgG avidity; bioMérieux) using the fully automated VIDAS machine. The test strips were contained 6 M urea to remove the low-avidity IgG antibodies from their binding sites and only antibodies with high avidity remained bound to the solid phase. The ratio between the quantity of high-avidity antibodies (test strip) and the quantity of total antibodies (reference strip) provides an index which indicates the avidity of the antibody in the tested sample. The avidity index allows specimen classification as low (avidity index, 0.2 indicating an acute infection), borderline (avidity index, 0.20–0.25) or high (avidity index, 0.25) avidity. A high-avidity index excludes primary infection within the previous 16 weeks.
Ethical consideration
The study was approved by Ethical Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Ethical Committee of Farabi Eye Hospital, Iran (no. 23/96–28, Dec 2014).
Data analysis
Data were analyzed by using SPSS-22 software (Chicago, Illinois, USA). Fisher exact test used for less than 5 numbers of frequencies, Pearson chi- square test for more than 5 numbers of frequency and Kappa test is used for the comparison between 2 tests.
RESULTS
One hundred and seventeen patients who met the diagnostic criteria (as described in Subject and samples) were included in this study. Of these patients, 29 (24.7%) cases were up to 10 years old, 41 (35.0%) cases were 11–20 years old, 29 (24.8%) cases 21–30 years old, 14 (12.0%) cases were 31–40 years old, 3 (2.6%) cases were 41–50 years old, and 1 (0.9%) cases were more than 50 years old. Anti-
Toxoplasma IgG test result was positive, intermediate and negative in 77, 6, and 34 cases, respectively. Association between anti-
Toxoplasma IgG seropositivity and demographic/epidemiologic descriptor are shown in
Table 1.
Anti-
Toxoplasma IgM was positive in 8 and negative in 109 cases. Anti-
Toxoplasma IgM seropositivity was not significantly associated with sex, living area, contact with the cat, using the raw/undercooked meat and age (
Table 2). IgG avidity was low, intermediate and high in 11, 4, and 102 cases, respectively (
Table 3). As demonstrated in
Table 3, 6.8% and 9.4% of cases were positive for IgM and IgG avidity tests, respectively (
P = 0.632).
Table 4 shows the distribution of IgM, IgG and IgG avidity results in 117 patients. As it is evident, there was a significant association between results of IgM test and IgG avidity test (
P =0.006), but no significant association was found between results of IgM test and IgG test (
P =0.632).
Kappa coefficient was used to examine agreement between different test results (
Table 5). The Kappa value for IgG-IgM, IgG-IgG avidity and IgM-IgG avidity agreements were 0.080, 0.099, and 0.721, respectively. The best agreement was seen between results of IgM test and IgG avidity test (kappa=0.721,
P =0.000).
DISCUSSION
Clinical examination is the standard diagnostic method for OT [
8], but in some cases, atypical clinical features or lack of sufficient response to conventional treatments, make supporting para- clinical methods valuable in confirming the disease [
20]. Serological tests, mainly anti-
Toxoplasma IgM and IgG levels, are the basis of serodiagnosis and differentiation between the acute and chronic/reactivated forms of OT [
20,
21]. In the present study further clarify characteristics of serological tests (anti-
Toxoplasma IgM, IgG, and IgG avidity) in patients with OT was investigated. The results of the current study indicated that 85 (72.6%) cases out of 117 were positive for at least one type of anti-
Toxoplasma antibody (IgM and/or IgG) and 32 (27.4%) cases were negative for these antibodies, so it seems that negative serologic evidence cannot be used to reliably rule out the diagnosis of OT.
In this study, most of patients with IgG/IgM seropositivity were less than 40 years old, which is consistent with the report of Suresh et al. [
22] and Dodds et al. [
23]. According to many published studies, patients with positive IgM and/or low IgG avidity are considered as acutely acquired cases (usually defined as acquisition of infection in recent 6 months) and patients with negative IgM and positive IgG are considered as chronic/reactivated cases, respectively [
24]. In this study, 17 cases (14.5%) were positive for IgM and/or IgG low avidity and 69 cases (59.0%) were IgM-negative and IgG positive. Moreover, 102 cases (87.2%) had high IgG avidity. All of these suggest that, in our population reactivation of chronic infection is responsible for the majority of clinical OT cases. This is similar to the results by Jones et al. [
25] who reported that 11.7% of their patients in the United States have recently acquired infection and 88.3% were IgG positive/IgM negative, which showed they had chronic ocular toxoplasmosis. They did not use IgG avidity testing in their study.
T. gondii IgG avidity test is an alternative technique for serological diagnosis of the recently acquired toxoplasmosis. Although the diagnosis of recently acquired ocular toxoplasmosis cannot be based on the low IgG avidity index, but primary toxoplasmosis developed during the recent 5 months is excluded by a high IgG avidity index [
22]. In immunocompetent patients,
Toxoplasma IgG avidity test is helpful to distinguish between reactivation of old infection and recent infection [
26]. In a case-control study in Iran, Rahbari et al. [
27], indicated that IgG avidity test could distinguish the acute and chronic stage of toxoplasmosis in humans.
Suresh et al. [
22] used
Toxoplasma IgG avidity test in OT and found that 3.8% of patients were positive for both IgG and IgM antibodies and only 0.8% of their patients had low IgG avidity, which is comparable to our results. Both positive IgM titer and IgG low avidity are acceptable for differentiation of recently acquired infection and old infection in OT. In current study, based on serological results, 17 patients (14.5%) were diagnosed to have recent and/or active ocular toxoplasmosis infection (positive for both IgM and/or IgG low avidity). Several published reports indicated that serological tests are insensitive to diagnosis acute OT but only for local antibody production and are limited in diagnosis of OT from blood samples [
5].
Most of the patients in current work were less than 40 years old and only 4 patients (3.4%) were more than 41 years old. Clinically active OT is typically a disease of young adults. Similarly, Atmaca et al. [
28] reported an age range of 14 to 50 years (mean 23.0±1.4 years) for the patients with active OT lesions. The exact reason of this age distribution is not fully understood. One hypothesis can be that as it is shown in our study, the majority of cases with clinically active OT are due to reactivation of infections which have been acquired in earlier life (possibly congenital toxoplasmosis). Why this infection remains latent in some patients but reactivates in others is not clear. However, it seems plausible to presume those factors (e.g. genetic factors) that predispose that special subset of patients to infection reactivation, usually show their effect before the fifth decade of life; if a patient is going to present clinically reactivated OT, he or she will do so prior to fifth decade of life [
28].
This study showed that conventional serologic tests (IgM and IgG levels) and IgG avidity seem to correlate well with each other and can be used to differentiate between recently acquired infection and old infection in OT. Moreover, it seems that reactivated old infection rather than recently acquired infection is responsible for OT in majority of Iranian patients. A prospective cohort would be needed to identify truly incident cases of new or reactivated lesions.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None of the authors have any proprietary interests or conflicts of interest related to this submission.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to express their deep thanks to all staffs of toxoplasmosis laboratory in Tehran Medical University for help in the study. This project is supported by Tehran University of Medical Science (grant no. 29998-160-03-94).
Fig. 1This fundus photograph of the right eye shows a typical macular hyperpigmented toxoplasmic scar adjacent to an active white retinochoroiditis patch, inflammation of nearby vessels and overlying vitreous haziness.
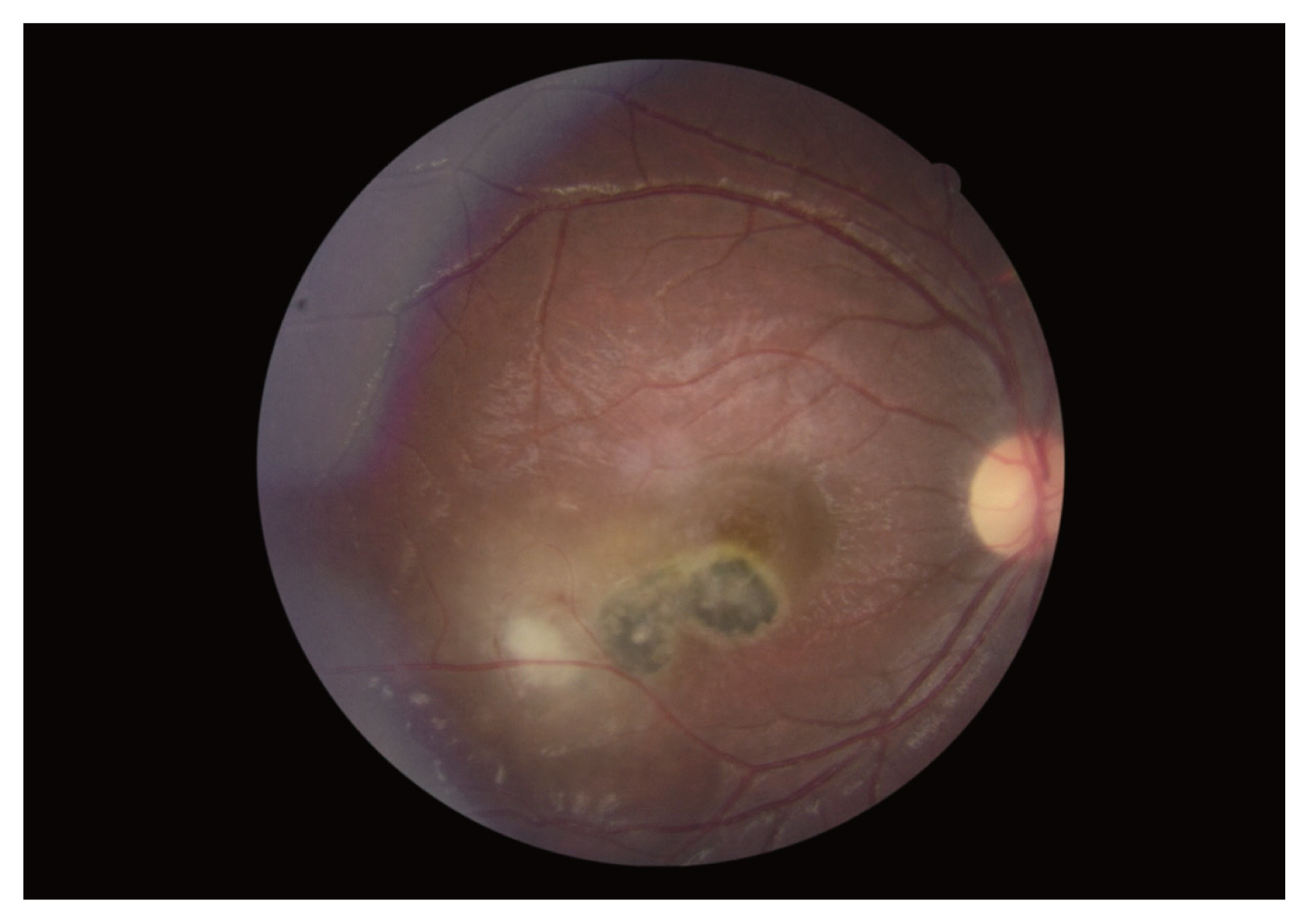
Table 1Association of anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgG levels in patients with ocular toxoplasmosis and demographic/epidemiologic descriptors
Table 1
|
Variable |
IgG |
P-value |
|
|
No. positive (%) |
No. intermediate (%) |
No. negative (%) |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
|
|
Male |
44 (67.6) |
1 (1.5) |
20 (30.7) |
0.171 |
|
Female |
33 (63.4) |
5 (9.6) |
14 (26.9) |
|
|
|
Living area |
|
|
|
|
|
Urban |
24 (40.0) |
5 (8.3) |
31 (51.6) |
0.000 |
|
Rural |
53 (92.9) |
1 (1.7) |
3 (5.2) |
|
|
|
Contact to cat |
|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
38 (92.6) |
1 (2.4) |
2 (4.8) |
0.000 |
|
No |
39 (51.3) |
5 (6.5) |
32 (42.1) |
|
|
|
Eating raw/undercooked meat |
|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
13 (92.8) |
0 (0.0) |
1 (7.1) |
0.081 |
|
No |
64 (62.1) |
6 (5.8) |
33 (32.0) |
|
|
|
Age |
|
|
|
|
|
0–10 |
14 (48.2) |
3 (10.3) |
12 (41.3) |
0.002 |
|
11–20 |
29 (70.7) |
2 (4.8) |
10 (24.3) |
|
|
21–30 |
25 (86.2) |
0 (0.0) |
4 (13.7) |
|
|
31–40 |
9 (31.0) |
1 (3.4) |
4 (13.7) |
|
|
41–50 |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
3 (100.0) |
|
|
>50 |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
1 (100.0) |
|
Table 2Association of anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM levels in patients with ocular toxoplasmosis and demographic/epidemiologic descriptors
Table 2
|
Variable |
IgM |
P-value |
|
|
No. positive (%) |
No. negative (%) |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
|
Male |
4 (6.1) |
61 (93.8) |
1.000 |
|
Female |
4 (7.6) |
48 (92.3) |
|
|
|
Living area |
|
|
|
|
Urban |
6 (10.0) |
54 (90.0) |
0.273 |
|
Rural |
2 (3.5) |
55 (96.4) |
|
|
|
Contact to cat |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
4 (9.7) |
37 (90.2) |
0.448 |
|
No |
4 (5.2) |
72 (94.7) |
|
|
|
Eating raw/undercooked meat |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
1 (7.1) |
13 (92.8) |
1.000 |
|
No |
7 (6.7) |
96 (93.2) |
|
|
|
Age |
|
|
|
|
0–10 |
2 (6.8) |
27 (93.1) |
0.420 |
|
11–20 |
5 (12.1) |
36 (87.8) |
|
|
21- 30 |
1 (3.4) |
28 (96.5) |
|
|
31–40 |
0 (0.0) |
14 (100.0) |
|
|
41–50 |
0 (0.0) |
3 (100.0) |
|
|
>50 |
0 (0.0) |
1 (100.0) |
|
Table 3Results of serological tests for IgG, IgM, and IgG avidity in 117 patients with ocular toxoplasmosis
Table 3
|
IgG |
IgM |
IgG avidity |
|
|
|
|
|
No. positive |
No. intermediate |
No. negative |
No. positive |
No. negative |
Low |
Intermediate |
High |
|
No. of cases (%) |
77 (65.8) |
6 (5.1) |
34 (29.1) |
8 (6.8) |
109 (93.2) |
11 (9.4) |
4 (3.4) |
102 (87.2) |
Table 4Distribution of test results on IgM and IgG antibodies and IgG avidity in 117 patients
Table 4
|
Comparison |
IgM |
P-value*
|
|
|
No. positive (%) |
No. negative (%) |
|
Results of avidity |
2 (25.0) |
9 (8.3) |
0.006 |
|
Low |
2 (25.0) |
2 (1.8) |
|
|
Intermediate |
4 (50.0) |
98 (89.9) |
|
|
High |
|
|
|
|
|
Results of IgG |
7 (87.5) |
70 (64.2) |
0.632 |
|
Positive |
0 (0.0) |
6 (5.5) |
|
|
Intermediate |
1 (12.5) |
33 (30.3) |
|
|
Negative |
|
|
|
Table 5Agreement between tests, expressed as kappa coefficient
Table 5
|
Test pair |
Kappa value |
Asymptomatic standard error |
Approx. T |
Approx. sig |
|
IgG- IgM |
0.080 |
0.033 |
2.029 |
0.042 |
|
IgG- IgG avidity |
0.099 |
0.028 |
2.649 |
0.008 |
|
IgM- IgG avidity |
0.721 |
0.095 |
8.869 |
0.000 |
References
- 1. Novais EA, Commodaro AG, Santos F, Muccioli C, Maia A, Nascimento A, Moeller CTA, Rizzo LV, Grigg ME, Belfort R Jr. Patients with diffuse uveitis and inactive toxoplasmic retinitis lesions test PCR positive for Toxoplasma gondii in their vitreous and blood. Br J Ophthalmol 2014;98:937-940.
- 2. Ali-Heydari S, Keshavarz H, Shojaee S, Mohebali M. Diagnosis of antigenic markers of acute toxoplasmosis by IgG avidity immunoblotting. Parasite 2013;20:18.
- 3. Laboudi M, Sadak A. Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasmosis: the effect of measurement of IgG avidity in pregnant women in Rabat in Morocco. Acta Trop 2017;172:139-142.
- 4. Hill D, Dubey JP.
Toxoplasma gondii: transmission, diagnosis and prevention. Clin Microbiol Infect 2002;8:634-640.
- 5. Montoya JG. Laboratory diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis 2002;185(Suppl):73-82.
- 6. Jones JL, Parise ME, Fiore AE. Neglected parasitic infections in the United States: toxoplasmosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2014;90:794-799.
- 7. Gilbert RE, Freeman K, Lago EG, Bahia-Oliveira LM, Tan HK, Wallon M, Buffolano W, Stanford MR, Petersen E. Ocular sequelae of congenital toxoplasmosis in Brazil compared with Europe. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2008;2:e277.
- 8. Holland GN. Ocular toxoplasmosis: a global reassessment. Part I: epidemiology and course of disease. Am J Ophthalmol 2003;136:973-988.
- 9. Petersen E, Kijlstrab A, Stanford M. Epidemiology of ocular toxoplasmosis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 2012;20:68-75.
- 10. Ronday MJ, Stilma JS, Barbe RF, McElroy WJ, Luyendijk L, Kolk AH, Bakker M, Kijlstra A, Rothova A. Aetiology of uveitis in Sierra Leone, west Africa. Br J Ophthalmol 1996;80:956-961.
- 11. Khan A, Jordan C, Muccioli C, Vallochi AL, Rizzo LV, Belfort R Jr, Vitor RW, Silveira C, Sibley LD. Genetic divergence of Toxoplasma gondii strains associated with ocular toxoplasmosis, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis 2006;12:942-949.
- 12. Glasner PD, Silveira C, Kruszon-Moran D, Martins MC, Burnier M, Silveira S, Camargo ME, Nussenblatt RB, Kaslow RA, Belfort R. An Unusually High Prevalence of ocular toxoplasmosis in southern Brazil. Am J Ophthalmol 1992;114:136-144.
- 13. Vallochi AL1, Muccioli C, Martins MC, Silveira C, Belfort R Jr, Rizzo LV. The genotype of Toxoplasma gondii strains causing ocular toxoplasmosis in humans in Brazil. Am J Ophthalmol 2005;139:350-351.
- 14. Silveira C1, Belfort R Jr, Muccioli C, Abreu MT, Martins MC, Victora C, Nussenblatt RB, Holland GN. A follow-up study of Toxoplasma gondii infection in southern Brazil. Am J Ophthalmol 2001;131:351-354.
- 15. Arantes TE, Silveira C, Holland GN, Muccioli C, Yu F, Jones JL, Goldhardt R, Lewis KG, Belfort R Jr. Ocular involvement following postnatally acquired Toxoplasma gondii infection in southern Brazil: a 28-year experience. Am J Ophthalmol 2015;159:1002-1012.
- 16. Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG, Maldonado Y, Montoya JG. Acute Toxoplasma gondii infection among family members in the United States. Emerg Infect Dis 2013;19:1981-1984.
- 17. Grigg ME, Dubey JP, Nussenblatt RB. Ocular toxoplasmosis: lessons from Brazil. Am J Ophthalmol 2015;159:999-1001.
- 18. Farhadi A, Haniloo A, Fazaeli A, Moradian S, Farhadi M. PCR-based diagnosis of toxoplasma parasite in ocular infections having clinical indications of toxoplasmosis. Iran J Parasitol 2017;12:56-62.
- 19. Jones JL, Bonetti V, Holland GN, Press C, Sanislo SR, Khurana RN, Montoya JG. Ocular toxoplasmosis in the United States: recent and remote infections. Clin Infect Dis 2015;60:271-273.
- 20. Maenz M, Schlüter D, Liesenfeld O, Schares G, Gross U, Pleyer U. Ocular toxoplasmosis past, present and new aspects of an old disease. Prog Retin Eye Res 2014;39:77-106.
- 21. Ongkosuwito JV, Bosch-Driessen EH, Kijlstra A, Rothova A. Serologic evaluation of patients with primary and recurrent ocular toxoplasmosis for evidence of recent infection. Am J Ophthalmol 1999;128:407-412.
- 22. Suresh S, Nor-Masniwati S, Nor-Idahriani MN, Wan-Hazabbah WH, Zeehaida M, Zunaina E. Serological IgG avidity test for ocular toxoplasmosis. Clin Ophthalmol 2012;6:147-150.
- 23. Dodds EM. Toxoplasmosis ocular. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol 2003;78:531-541.
- 24. Silveira C, Vallochi AL, Rodrigues da Silva U, Muccioli C, Holland GN, Nussenblatt RB, Belfort R, Rizzo LV.
Toxoplasma gondii in the peripheral blood of patients with acute and chronic toxoplasmosis. Br J Ophthalmol 2011;95:396-400.
- 25. Jones JL, Kruszon-Moran D, Sanders-Lewis K, Wilson M.
Toxoplasma gondii infection in the United States, 1999 2004, decline from the prior decade. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2007;77:405-410.
- 26. Paul M. Immunoglobulin G avidity in diagnosis of toxoplasmic lymphadenopathy and ocular toxoplasmosis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 1999;6:514-518.
- 27. Rahbari AH, Keshavarz H, Shojaee S, Mohebali M, Rezaeian M. IgG avidity ELISA test for diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis in humans. Korean J Parasitol 2012;50:99-102.
- 28. Atmaca LS, Simsek T, Batioglu F. Clinical features and prognosis in ocular toxoplasmosis. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2004;48:386-391.