Abstract
Pneumocystis carinii is the most important opportunistic pathogen of humans in the world. Pneumocystis carinii is experimentally detected in the lungs of rats, mice, rabbits, and monkeys, however, the organisms from different mammals are identical in microscopic morphology. The present study tried to find out more mammalian hosts of P. carinii and also to differentiate the organisms from different mammals by karyotyping. Rats, mice, hamsters, rabbits, cats, and dogs were successfully infected by P. carinii, but guinea pigs and pigs were not. Karyotype of P. carinii from rabbits showed similar size range of chromosomes with that of the prototype, but in different pattern. The patterns from cats and dogs were also different from that of rats. The present study confirms that cats and dogs are infected by P. carinii and at least total three karyotype strains of P. carinii are proven in Korea.
-
Key words: Pneumocystis carinii, rat, dog, cat, rabbit, karyotype
INTRODUCTION
Pneumocystis carinii is a pathogenic protist which causes opportunistic pneumonia in immunocompromised hosts. It can infect not only humans but also other mammals. The organisms from different animals are morphologically identical, therefore, it is impossible to differentiate the organisms from different species of hosts by microscopical findings. The hosts which are known to be infected by
P. carinii except for human are rats, mice, guinea pigs, hamsters, ferrets, rabbits and monkeys (
Matsumoto et al., 1987;
Walzer et al., 1989;
Bauer et al., 1993). Other animals were not proved yet as its host. Hong et al. (
1992a) recorded that they failed to verify the organism from guinea pigs, hamsters, rabbits, cats, dogs, and pigs. However, the mammals still have the possibility of
P. carinii infection because immunosuppression in that study was insufficient.
Since many species of mammals are infected by P. carinii, it is necessary to determine whether P. carinii from different species of mammals are genetically same or not. The present study has two objectives. The first one is to verify whether cats and dogs are infected by P. carinii. The other is to observe how many karyotype strains are found from different mammals in Korea. Eight different mammals were immunosuppressed by steroid injection and the isolates of P. carinii were purified and analyzed by molecular karyotyping.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Immunosuppression of mammals for P. carinii infection
The rats, mice, hamsters, guinea pigs, rabbits, cats, dogs, and pigs were weekly injected with methylprednisolone 10 mg/kg for 5 to 10 weeks (
Table 1). They were fed with commercial diet and tap water. After the experiment, their lungs were smeared on glass slides by impression. The slides were stained in Diff-Quik solution (Fisher Scientific, USA) and were microscopically observed under immersion oil lens magnification.
The lungs were dissected after ether anesthesia and chopped into pieces as small as possible. The chopped materials were homogenized in a blender (Stomacher, Seaward Medical, UK). The procedures for purification and gel blocks were same as described previously (
Hong et al., 1992b). The gel blocks were stored in 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) at 4℃ until use.
Pneumocystis carinii nuclei of 109 were prepared in one block of low melting point agarose. Each block was loaded into the trough in 1% agarose gels, and the electrophoresis was run. The conditions for gel electrophoresis by CHEF and FIGE were individually modified. The gels were stained in ethidium bromide solution and observed through UV-illumination.
RESULTS
Infection of P. carinii in different mammals
The rats, mice, hamsters, rabbits, cats and dogs were proven of
P. carinii infection in their lungs (
Fig. 1). The mammals used in this study were summarized in
Table 1. The infected mammals showed big differences between the intensity of infection. However, no cystic forms were confirmed on the lung smears of guinea pigs and pigs.
Two karyotype patterns of
P. carinii were found from rats (
Fig. 2). One was 16 bands from 275 to 695 bp, and the other is 15 bands from 275 to 695 bp. The two patterns were not determined by strains of rats but by the source of the rats. The rat colony in different vendors showed different karyotype patterns. Density of the organisms in mice was too low to identify the karyotype pattern. The karyotype of
P. carinii from rabbits was found different from that of rats (
Figs. 2,
3). Total 14 chromosomal bands were recognized between 300 and 700 bp. The karyotypes from cats and dogs were too faint to exactly identify the band patterns but the largest chromosomal band from cats measured 730 bp, which was the first band of
P. carinii over 700 bp (
Figs. 2,
3). However exact size estimation of individual band was difficult.
DISCUSSION
The present study succeeded to demonstrate that rabbits, cats and dogs are infected by
P. carinii. Both trophic forms and cystic forms of
P. carinii were found on the impression smears of the three animals (
Fig. 1). Of course they were quite same in microscopic features with those from rats. The present success suggests that previous unsuccessful findings with dogs and cats (
Farrow et al., 1972;
Hong et al., 1992a) may be due to improper immunosuppression. The present data also strongly suggest that almost all kind of mammals may be the host of
P. carinii.
Although the organisms from cats and dogs are morphologically identical, the organisms were not same with those from rats in the karyotype pattern. The taxonomical confusion of
P. carinii had long been a hot topic, but the molecular karyotype shows that the organisms which we handle as
P. carinii are a complex of genetically variant protists (
Hong et al., 1990;
Lundgren et al., 1990;
Cushion et al., 1993;
Stringer et al., 1997).
It is evident that
P. carinii hominis which infect humans are genetically different from those infecting rats (
Sinclair et al., 1991;
Stringer et al., 1993;
Pariset et al., 1997). Some organisms transmitted among Americans were found not including the repeat sequence which is common in all chromosomes of the prototype
P. carinii carinii from rats (
Stringer et al., 1993), and this fact must be very important. Since the human isolate from Koreans was insufficient, karyotype of human
P. carinii has not been observed yet. The karyotype pattern is a future topic of great interest, because the basic karyotype pattern of rat
P. carinii is very similar over the world.
Infection of P. carinii has been noticed in many species of mammals. Among them, the rat is the host of prototype organism which is used as a standard experimental model for this research, because most of the organisms are obtained in vivo from rats. This is one of rare protists which can not be supplied by in vitro cultivation. Cultivation of P. carinii is still unsuccessful by too many knotty requirements which are unclarified. All of its researches should supply the organisms from rats.
Though the guinea pig is a known host of
P. carinii, we failed to find infected guinea pigs in this study and also in the previous trial (
Hong et al., 1992a). The same was in pigs. Goats and foals were reportedly unsuccessful (
McConnel et al., 1971;
Shively et al., 1973). Reasons of this failure may be that the animals were exposed to many kinds of saprophytous microorganisms and they died by acute infections after immunosuppression or other complications much earlier than development of pneumocystosis.
The karyotype of
P. carinii from cats showed different pattern from that of rat
P. carinii. The largest band of cat
P. carinii was 730 bp and this is the largest band ever recorded. Although the karyotypes from rabbits and dogs were not clear enough for definite analysis, we found at least 3 different patterns of
P. carinii karyotype from rats or cats in Korea (
Hong et al., 1990,
1992b). Of course additional karyotypes may be added by further studies on
P. carinii from cats, dogs, and humans. In this context, karyotyping and gene mapping is one of useful methods to probe a specific strain or to differentiate mixed strains.
In conclusion, this study proved the dogs and cats can be hosts of P. carinii. More specification is necessary for different nomenclature of subspecies. Also three karyotype strains of P. carinii are confirmed among mammals in Korea.
Notes
-
This study was supported by the grant from the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF 941-0700-024-1), 1994.
References
- 1. Bauer NL, Paulsrud JR, Bartlett MS, Smith JW, Wilde CE III. Pneumocystis carinii organisms obtained from rats, ferrets, and mice are antigenically different. Infect Immun 1993;61:1315-1319.
- 2. Cushion MT, Zhang J, Kaselis M, Giuntoli Dm Stringer SL, Stringer JR. Evidence for two genetic variants of Pneumocystis carinii coinfecting laboratory rats. J Clin Microbiol 1993;31:1217-1223.
- 3. Farrow BRH, Watson ADJ, Hartley WJ. Pneumocystis pneumonia in the dog. J Comp Pathol 1972;82:447-453.
- 4. Hong ST, Lee M, Seo M, Choo DH, Moon HR, Lee SH. Immunoblotting analysis for serum antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii by growth and infection status of rats. Korean J Parasitol 1995;33:187-194.
- 5. Hong ST, Park KH, Lee SH. Susceptibility of various animals to Pneumocystis carinii infection. Korean J Parasitol 1992a;30:277-281.
- 6. Hong ST, Ryu JS, Chai JY, Lee SH. Transmission modes of Pneumocystis carinii among rats observed by karyotype analysis. Korean J Parasitol 1992b;30:283-288.
- 7. Hong ST, Steele PE, Cushion MT, Walzer PD, Stringer SL, Stringer JR. Pneumocystis carinii karyotypes. J Clin Microbiol 1990;28:1785-1795.
- 8. Lundgren B, Cotton R, Lundgren JD, Edman JC, Kovacs JA. Identification of Pneumocystis carinii chromosomes and mapping of five genes. Infect Immun 1990;58:1705-1710.
- 9. Matsumoto Y, Yamada M, Tegoshi T, et al. Pneumocystis infection in macaque monkeys Macaca fuscata fuscata and Macaca fascicularis. Parasitol Res 1987;73:324-327.
- 10. McConnel EE, Basson PA, Pienaar JC. Pneumocystosis in a domestic goat. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 1971;38:117-126. (cited from Walzer et al., 1989).
- 11. Pariset C, Rabodonirina M, Carlotti A, Piens M-A, Vandenesch F. Genetic diversity among Pneumocystis carinii hominis isolates from HIV-infected patients and other immuno-suppressed patients in France. J Euk Microbiol 1997;44:18s.
- 12. Shively JN, Dellers RW, Buergelt CD, et al. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in two foals. J Am Vet Med Assoc 1973;162:648-652.
- 13. Sinclair K, Wakefield AE, Banerji S, Hopkin JM. Pneumocystis carinii derived from rat and human hosts are genetically distinct. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1991;45:183-184.
- 14. Stringer JR, Stringer SL, Zhang J, Baughman R, Smulian AG, Cushion MT. Molecular genetic distinction of Pneumocystis carinii from rats and humans. J Euk Microbiol 1993;40:733-741.
- 15. Stringer JR, Wakefield A, Cushion MT, Dei-Cas E. Pneumocystis taxonomy and nomenclature: an update. J Euk Microbiol 1997;44:5s-6s.
- 16. Vasquez J, Smulian AG, Linke M, Cushion MT. Antigenic differences associated with genetically distinct Pneumocystis carinii from rats. Infect Immun 1996;64:290-297.
- 17. Walzer PD, Kim CK, Cushion MT. In Walzer P.D, Genta R eds, Pneumocystis carinii from Parasitic Infections in the Compromised Host. 1989, New York and Basel. Marcel Dekker, Inc.; pp 83-178.
- 18. Weinberg GA, Durant PJ. Genetic diversity of Pneumocystis carinii derived from infected rats, mice, ferrets, and cell cultures. J Euk Microbiol 1994;41:223-228.
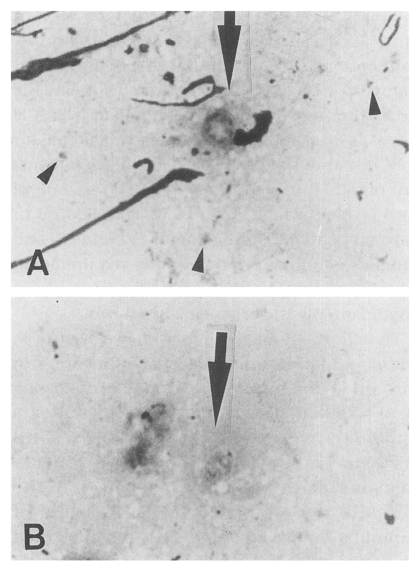
Fig. 1
Pneumocystis carinii discovered from the lungs of an infected cat, Diff-Quik stained, original magnification ×1,500. A. One octanucleate cystic form (arrow) and a few trophic forms (arrow heads) are shown. B. One developing cystic form (arrow) began to divide the nucleus (arrow).
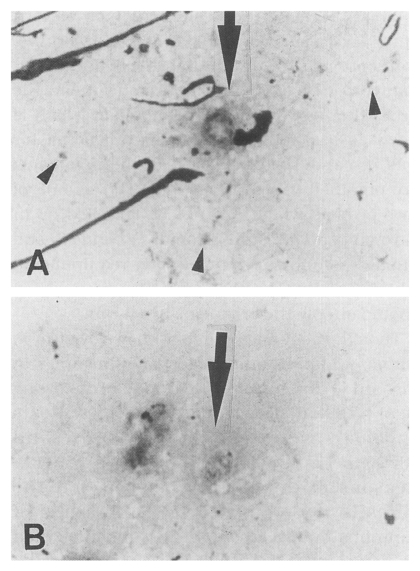
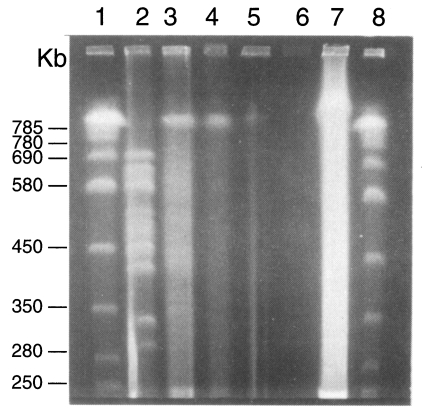
Fig. 2Karyotype patterns of Pneumocystis carinii from rats, cats, dogs and rabbits in a 1% agarose CHEF gel in 0.5× TBE buffer. Running conditions were 50 sec initial and 200 sec final, 1:1 A/B ratio, and 6 V/cm for 40 hr. Lane 1, size marker of Saccharomyces cerevisiae AB 972; 2, W37, P. carinii from Wistar rats, 3, C2-3 P. carinii from cats; 4, D2-2 P. carinii from dogs; 5-7, P. carinii from rabbits; 8, same size marker of lane 1.
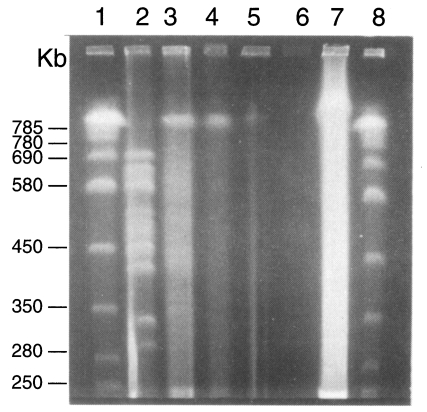
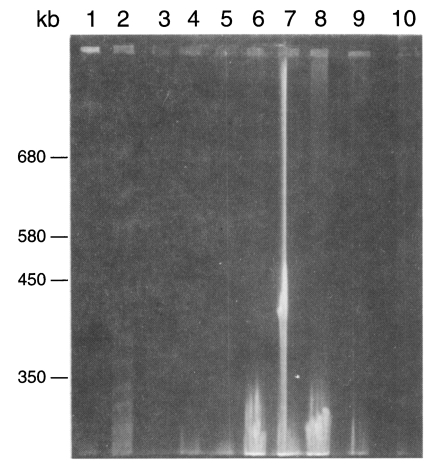
Fig. 3Karyotype patterns of Pneumocystis carinii from different animals in a 1% agarose gel of FIGE. Running parameters were 50 sec forward and 25 sec backwards, and 105 V for 120 hr. 1, size marker from Saccharomyces cerevisiae AB 972; 2, W26 P. carinii from wistar rats; 3, C2-3 P. carinii from cats; 4-6, D2-1, D2-2, D4 P. carinii from dogs; 7-9, Rb2, Rb9, Rb6-1 P. carinii from rabbits; 10, size marker from S. cerevisiae AB 972.
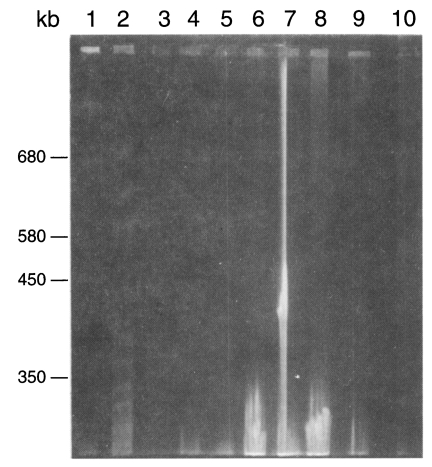
Table 1.Status of Pneumocystis carinii infection in different animals
Table 1.
|
Animals |
No. of exam |
No. of infected |
Infection rate (%) |
Mean No. of cysts |
|
Rats |
|
|
|
|
|
(Wistar) |
59 |
57 |
96.6 |
NDa)
|
|
(Sprague-Dawley) |
57 |
57 |
100 |
ND |
|
(Fisher) |
26 |
26 |
100 |
ND |
|
Subtotal |
142 |
140 |
98.6 |
ND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mice |
29 |
10 |
34.5 |
16.3 |
|
Hamsters |
21 |
2 |
9.5 |
0.8 |
|
Guinea pigs |
13 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Rabbits |
14 |
9 |
64.3 |
12.0 |
|
Cats |
10 |
5 |
50.0 |
65.0 |
|
Dogs |
10 |
8 |
80.0 |
7.4 |
|
Pigs |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- Axenic Long-Term Cultivation of Pneumocystis jirovecii
Diana Riebold, Marie Mahnkopf, Kristina Wicht, Cristina Zubiria-Barrera, Jan Heise, Marcus Frank, Daniel Misch, Torsten Bauer, Hartmut Stocker, Hortense Slevogt
Journal of Fungi.2023; 9(9): 903. CrossRef - Respiratory Diseases in Guinea Pigs, Chinchillas and Degus
María Ardiaca García, Andrés Montesinos Barceló, Cristina Bonvehí Nadeu, Vladimír Jekl
Veterinary Clinics of North America: Exotic Animal Practice.2021; 24(2): 419. CrossRef - Molecular detection ofPneumocystisin the lungs of cats
Patrizia Danesi, Michela Corrò, Christian Falcaro, Antonio Carminato, Tommaso Furlanello, Monia Cocchi, Mark B Krockenberger, Wieland Meyer, Gioia Capelli, Richard Malik
Medical Mycology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Pneumocystis: from a doubtful unique entity to a group of highly diversified fungal species
Magali Chabé, Cécile-Marie Aliouat-Denis, Laurence Delhaes, El Moukhtar Aliouat, Eric Viscogliosi, Eduardo Dei-Cas
FEMS Yeast Research.2011; 11(1): 2. CrossRef - Analysis of Internal Transcribed Spacer 1 Sequences of Pneumocystis jiroveci from Clinical Specimens
Jae-Seok Kim, Yong-Kyun Kim, Ji Young Park, Eun Kyung Mo, Han Sung Kim, Wonkeun Song, Hyoun Chan Cho, Kyu Man Lee
Chonnam Medical Journal.2008; 44(2): 82. CrossRef - Pneumocystis species, co-evolution and pathogenic power
Cécile-Marie Aliouat-Denis, Magali Chabé, Christine Demanche, El Moukhtar Aliouat, Eric Viscogliosi, Jacques Guillot, Laurence Delhaes, Eduardo Dei-Cas
Infection, Genetics and Evolution.2008; 8(5): 708. CrossRef - Pneumocystis
James R. Stringer
International Journal of Medical Microbiology.2002; 292(5-6): 391. CrossRef - Genetic heterogeneity of Pneumocystis carinii from rats of several regions and strains
Byung-Suk Chung, Yun-Kyu Pars, Sun Huh, Jae-Ran Yu, Jin Kim, Xiaohua Shi, Sang Rock Cho, Soon-Hyung Lee, Sung-Tae Hong
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2000; 38(3): 151. CrossRef